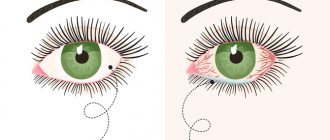
Household injuries account for the majority of all traumatic eye injuries. One of the common situations is when an aerosol containing alcohol is accidentally sprayed into the eye. What problems can eye contact with this substance cause? How to act in case of an alcohol burn? Find out about this from the article.
Alcohol is present in many liquids found in the home. It is found in medicines, household chemicals, cosmetics, and alcoholic beverages. If you handle any of these objects carelessly, there is a risk of getting a chemical burn. Alcohol negatively affects the delicate tissues of the eyeball. It destroys both outer membranes and intracellular structures. The negative effects of alcohol can persist long after injury, which is often accompanied by delayed consequences, including blindness. To minimize this risk, you need to know about emergency measures for alcohol burns.
What to do if alcohol gets into your eye?
Symptoms
A person who has received a burn to the mucous membrane of the eye experiences traumatic and painful shock. Alcohol usually absorbs moisture inside the eye, dissolves the protein, and acts as a poison when it penetrates the blood. The degree of exposure to alcohol-containing substances also depends on the duration of their effect on the organs of vision. Characteristic signs of a chemical burn of the eyes with alcohol:
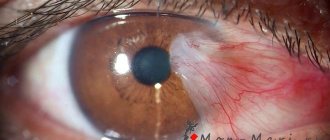
- redness of the mucous membrane and skin around the visual organ;
- acute pain lasting a long period of time;
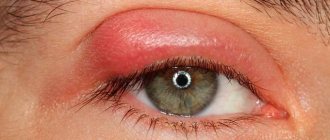
- swelling, puffiness;
- severe lacrimation;
- formation of a white film on the eyes;
- photophobia;
- decreased quality of vision;
- discomfort;
- high eye pressure.
Often, it is not possible to improve vision with medication alone; this may require surgery.
Dangerous consequences
Depending on the symptoms and possible consequences, the following areas of damage are distinguished: the area around the eyes and the skin of the eyelids, the cornea along with the conjunctiva, the eyeball, and the adnexa. In addition, there are 4 stages, depending on the duration and degree of exposure. If medical alcohol or ammonia gets into the eye, then the pathological processes go through the following stages:
- Elementary. It lasts no more than two days. During this period, the patient feels discomfort, his cornea begins to swell, and tissue death occurs.
- Second stage. It lasts from two days to several weeks, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. In addition to corneal edema, severe trophic disorders occur that can cause irreparable damage to health.
- Third stage. It takes another 2-3 months. Hypoxia and trophic processes begin due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues of the organ of vision, and the vessels of the cornea grow.
- The final stage. It can take up to several years. During this period, tissue scarring occurs, during which the body produces collagen in large quantities.
Return to contents
First aid
If there is an eye burn with alcohol. At the initial stage, it is necessary to take urgent measures to provide the victim with the necessary assistance, otherwise his vision may subsequently be subject to serious impairment, even complete loss. If vodka, alcohol or other alcohol-containing substances get into your eye, you must quickly follow these recommendations: immediately rinse your eye with plenty of cold water to remove as many harmful substances from the mucous membrane as possible. If you have potassium permanganate on hand, you can rinse with a solution of this substance.
Do not rub your eyes too much, even if they itch and hurt. After this, apply eye drops, for example, Visine, to relieve the patient of redness and irritation. It is recommended to apply an antibacterial ointment, 1% tetracycline, behind the eyelid. The patient should be given a pain reliever. It is advisable to darken the room, since the patient often experiences severe photophobia after injury. Next, you should consult an ophthalmologist for advice.
Treatment for burns
Drug therapy usually begins with preventive measures to avoid infection. For this, the patient is prescribed antiseptic drops and eye ointments with antibiotics (4 times a day). With the help of autologous blood with the inclusion of antibiotics, intoxication is neutralized. This is done by injection under the conjunctiva of the eye. Preventive measures against scarring include applying eye ointment and using special contact lenses (inserts).
Corneal regeneration is carried out using drops of “Taufon” (4%) or “Balarpan” (0.01%), 4 times a day. Octovegin ointment, Solcoseryl gel or sea buckthorn oil are also recommended. To prevent the development of iridocyclitis, 1% Atropine and Diclofenac ointment is prescribed. High eye pressure is treated with Timolol drops (0.25 to 0.5 percent). If necessary, surgical treatment is prescribed using the following procedures: scleroplasty, layered keratoplasty for therapeutic purposes or to eliminate a post-burn sore.
Red eyes after drinking alcohol
Redness of the white of the eye is another sign of the negative effects of alcohol. It manifests itself in hangover syndrome. Once in the body, ethyl alcohol leads to a sharp decrease in red blood cells. Their deficiency causes a drop in hemoglobin levels and the formation of clots in the blood. Because of this, little oxygen reaches the eye tissues, and hypoxia develops. It is accompanied not only by redness of the sclera, but also by other symptoms:
- eyelids twitch;
- blurred vision;
- diplopia;
- loss of visual acuity.
These signs go away after some time. A person needs to get a good night's sleep and remove alcohol breakdown products from the body. After this, vision is restored and the redness in the eyes disappears. However, systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages can cause more serious consequences.
The vessels of the eye and brain are responsible for supplying the cells of the eyeballs with oxygen. Their narrowing, which occurs during a hangover, leads to increased intracranial pressure.
Because of this, the retinal vessels burst. They are very thin and their damage is immediately reflected in their appearance - they turn red.
This is accompanied by itching, burning, and a sensation of a foreign body in the eyes. In this case, not only the head hurts, which is what people usually face after some holiday, but also the eyeballs and brow ridges. If these symptoms become chronic, vision declines.
Symptoms of eye burns with alcohol
The degree of damage caused by alcohol or vodka depends on the duration of exposure to the caustic substance. The main symptomatic manifestations of a chemical burn are:
- severe pain syndrome, which is long-term in nature;
- formation of swelling at the burn site;
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the visual apparatus;
- intense secretion of tear secretion;
- photophobia;
- formation of a white veil;
- decreased quality of vision;
- pressure surges inside the cavity of the visual organs;
- redness in the affected area.
Additional symptoms may appear, which will be provoked by the chronic course of pathologies of the visual apparatus.
First aid
If your eyes are burned with caustic alcohol, you must follow the basic steps for first aid:
- Eliminate the effect of liquid on the organ of vision as much as possible. Complete removal of fluid from the eyes can be achieved by rinsing. It is better to carry out manipulations using purified water.
- Anesthetize the area of contact with the caustic substance.
- Call an ambulance or take the victim to a medical facility.
- It is forbidden to rub the affected eye or apply mechanical force to it.
- Lay the patient down and wait in a calm environment for medical services.
After an ophthalmological examination, the doctor removes all foreign particles from the organs of vision.
The doctor performs additional rinsing by injecting saline solution. To eliminate additional infection and more active regeneration, drug therapy is prescribed. Treatment may include both drops and preparations in ointment form.
Treatment of chemical burns to the eye
The entire process of treating a chemical burn can include both conservative and surgical methods. The main thing is to preserve vision. Patients with severe burns need to be hospitalized immediately. In case of damage to degrees I and II, it is advisable to consult a doctor after providing first aid and follow all recommendations at home.
Stages of treatment for chemical eye damage:
- Removing the irritant. The most important step in emergency care for chemical burns is copious rinsing. If possible, the eye should be anesthetized before rinsing. Local anesthesia reduces pain and blepharospasm. It is advisable to use a sterile buffer solution (normal saline or Ringer's solution).
- Control of the inflammatory process. At the time of damage, inflammatory mediators are released, which provoke necrosis. This process inhibits re-epithelialization and increases the risk of ulcers and corneal perforation. You can interrupt the inflammation with the help of local steroids; citrate or ascorbic acid is additionally prescribed. To inhibit collagenosis and prevent ulcers, 10% or 20% Acetylcysteine is sometimes used.
- Acceleration of regeneration. Full epithelization begins only after the irritant is removed from the eye. Chemical damage causes a temporary increase in tear production and a decrease in future tear production, so it is important to use moisturizers for healing. Ascorbic acid helps restore collagen structure and accelerate corneal regeneration. In some cases, wearing therapeutic bandage lenses is recommended.
Since chemical burns to the eyes are accompanied by severe pain, the victim is prescribed powerful anesthetics. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs that prevent the formation of adhesions are used. Treatment of burns usually begins with tetanus vaccination.
Glucocorticosteroids
If severe inflammation develops during a burn, doctors prescribe glucocorticosteroids:
- Dicaine. Eye drops with leocaine and sodium chloride have a local anesthetic effect, relieve pain and prepare the cavity before surgery. The dosage is determined by the degree of burn.
- Ciprofloxacin. The ophthalmic drug is available in the form of drops or ointment, but in case of a burn, the use of a solution is recommended. Ciprofloxacin has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The drug is instilled every 15 minutes for the first 6 hours, then every half hour the next day. On days 3-14, the interval is increased to 4 hours. Ciprofloxacin is only allowed in patients over 1 year of age.
- Atropine. For chemical burns to the eyes, this remedy helps reduce pain and prevent adhesions. The active ingredient is atropine sulfate. The drug is instilled three times a day, 1-2 drops.
- Diacarb. The drug in tablet form is prescribed for increased intraocular pressure. The effectiveness of Diacarb is due to the content of acetazolamide, magnesium stearate, povidone, croscarmellose sodium and other substances. Usually prescribed one tablet 3-4 times a day. Diacarb is contraindicated in diabetes mellitus, acute liver and kidney failure, uremia, hyponatremia, metabolic acidosis, hypokalemia, in the first trimester of pregnancy and during lactation. The drug is prescribed to patients over 3 years of age.
- Prednisolone. This glucocorticosteroid is taken only with the permission of a doctor. Usually prescribed one tablet per day. Prednisolone is contraindicated for fungal infections.
Although chemical burns require emergency treatment, the prognosis is often good. If the damage did not affect the deep structures of the eye, and the appropriate measures were carried out in a timely and correct manner, the preservation of vision will be ensured. In some cases, even immediate help does not prevent the formation of an eyesore. Even after successful treatment, scars may remain and affect the quality of vision.
Relieving pain from eye burns
A serious chemical burn does not occur without prolonged and severe pain. At the initial stage, oral analgesics are most often used. The spam of the ciliary muscle can be weakened with the help of cycloplegic drugs.
Prevention of secondary infection
If the burn has severely damaged the corneal epithelium, the risk of infection increases. At the initial stage of therapy, antibiotics are prescribed for prophylaxis. Minor, deep corneal injuries can be treated with cyanoacrylate eye glue.
Monitoring intraocular pressure
If elevated pressure levels are observed during a burn, blockers of the production of intraocular fluid are prescribed. Such drugs are indicated both at the initial stage of treatment and during late rehabilitation therapy. When elevated intraocular pressure persists even with the use of antihypertensive agents, surgical intervention (penetrating antiglaucoma or surgery with shunt or valve devices) is required.
Medicines
Due to the ingress of caustic liquid, hyperemia and infiltration are observed in the affected area. Drug therapy can reduce the severity of symptoms and accelerate the regeneration of tissue structures. Groups of drugs prescribed:
- Antibiotics in the form of drops. To eliminate possible infection, drugs with a bacteriostatic effect are prescribed.
- Anesthetics. Pain relief occurs with instillation of medications based on lidocaine or novocaine.
- Antiseptic medicines. Ointments are prescribed to prevent scars, on the basis of which an overlay is made for the damaged organ of vision.
- Regenerants and reparants. This group of drugs is prescribed to accelerate the regeneration of tissue structures of the organ of vision.
To speed up recovery, it is possible to use traditional medicine methods, but only after consulting an ophthalmologist.
What happens and what to do if alcohol gets into your eye? First aid for adults and children
Chemical burn of the eyeball - this diagnosis sounds so frightening and distant .
It seems that only people in certain professions whose activities involve hazardous chemicals can get such an injury.
But, in fact, most injuries occur everyday life - during meals, medical procedures, cleaning , etc.
What to do if alcohol gets into your eye ? How to help yourself at home ? Is it possible to do without medical help? Read our article.
Is traditional medicine effective in the fight against alcohol burns to the eyes?
When carrying out treatment at home, it would not be superfluous to resort to traditional medicine recipes, thanks to which it will be possible to speed up the healing process and restore damaged tissues of the organ of vision.
Speaking about effective folk remedies recommended for use in cases of eye burns with alcohol-containing solutions, we should immediately highlight a decoction of chamomile or calendula, which is used to wash inflamed eyelids and mucous membranes. Sea buckthorn oil, which has anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and analgesic properties, has proven itself to be excellent in combating the consequences of alcohol burns to the eyes.
Symptoms
The degree of destructive effect of an alcohol-containing substance depends on its quantity, concentration and duration of stay on the surface of the eyeball.
The following clinical picture is typical for an alcohol burn of the eye:
- sharp, cutting pain;
- redness of the white of the eyeball, protruded capillaries;
- swelling of the eyelids, swelling;
- photophobia, tearfulness when changing lighting;
- decreased visual acuity, myopia;
- high intraocular pressure;
- white veil over the eye.
How to provide first aid at home?
This is an extremely dangerous situation in which it is important to navigate in time and provide first aid.
How to help an adult?
The following instructions will help you provide first aid to the victim or yourself if you are faced with a problem alone.
- Call an ambulance . A chemical burn to the eye is a serious injury. If you are unable to provide first aid to yourself and then go to the hospital yourself, call an ambulance. Remember - the sooner you receive qualified help, the higher the chance of maintaining eye health.
- Rinse eyes with plenty of water . To do this, you can use an enema or a large syringe without a needle. Direct a stream of warm water from the outer edge of the eye to the tear duct, being careful not to touch the eyelid with your hands. Water should flow freely down your face and into a sink or basin. Rinsing must be carried out for quite a long time - from 15 to 25 minutes. In the absence of the above devices, you can use a sterile bandage or gauze soaked in water or saline solution.
- After rinsing the eye, keep yourself or the victim at rest. Take a horizontal position and wait for paramedics to arrive.
Alcohol has a detrimental effect on the cornea and, if treatment is delayed, you can partially or completely lose your vision.
How to help a child?
Many adults panic when it comes to helping a child. The baby cries, screams, rubs his eyes with his fists and it seems that there is simply no time to find a solution.
The instructions for providing first aid are exactly the same as in the case of injury to adults - it is necessary to act despite the spasm and acute pain.
To alleviate the child’s suffering before the arrival of medical workers, it is permissible to give him a painkiller.
Surgical treatment of eye burns and possible complications
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical treatment of the consequences of the burn is performed. Depending on the complications, a variety of techniques are used.
Surgical treatment for an eye burn may include:
- partial removal of areas of necrosis of the conjunctiva or corneal surface;
- temporary covering with amniotic membrane;
- transplantation of limbal cells or cultured corneal epithelial cells;
- removal of the fusion of the conjunctiva of the eyelids with the eyeball (symblepharon).
To speed up rehabilitation, penetrating or partial keratoplasty and keratoprosthesis are used. If a cataract occurs, it is extracted.
Primary complications of a chemical burn include conjunctivitis, corneal erosion, swelling or clouding, acute increase in intraocular pressure, and melting of the cornea. Secondary complications are usually more varied.
Possible consequences of a chemical burn to the eye:
- glaucoma;
- cataract;
- scarring of the conjunctiva;
- corneal ulcers;
- thinning and tearing of the cornea;
- destruction of the corneal surface;
- opacification and vascularization;
- subatrophy of the eye.
The main measure to prevent burns is to follow safety precautions when working with household chemicals and in production where chemicals are used. It is important to exercise caution and wear safety glasses.
- October 15, 2018
- Ophthalmology
- Oksana Skripchenko
Boric acid is an effective remedy for various diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms. In medical practice, ready-made alcohol solutions are most often used. But they are not suitable for particularly sensitive organs such as the eyes. For such cases, it is better to use aqueous solutions. They are not sold in pharmacies, so you need to know how to dilute boric acid to wash your eyes yourself. The effectiveness of therapy depends on how accurately the proportion is observed.
What consequences might there be?
Alcohol burns to the eye are classified in several areas of damage: eyelid skin, cornea, conjunctiva, eyeball, adnexa.
There are four stages of burn :
- Initial stage . It lasts for one or two days. During this period, the patient feels acute discomfort in the eye and suffers from tearing. It is at this stage that tissue death occurs.
- Second stage. Duration from two days to several weeks (depending on the individual characteristics of the body). The cornea swells, severe trophic disorders occur, which can cause irreparable damage to vision.
- Third stage. Takes another 4 – 16 weeks. Hypoxia begins. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues of the eyeball, trophic processes begin, and the vessels of the cornea grow.
- Fourth, final stage. It may take several years. The mucous membranes become scarred due to excessive production of collagen by the body.
- Decreased visual acuity. Initially, this may be due to epithelial damage, swelling or cloudiness caused by lacrimation. It is worth considering that vision may not deteriorate immediately - some consequences of burns become apparent only after a while. Most often, myopia caused by an injury of this kind is irreversible.
- Increased intraocular pressure. Caused by deformation and shortening of collagen in the trabecular apparatus. In the future, it can provoke inflammatory processes in the anterior part of the eye.
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva . This disease is possible even with a mild alcohol burn. It causes severe discomfort and makes the eyes more sensitive to light.
- Corneal perforation . A rather rare phenomenon that occurs only in severe chemical burns, when the ability for natural tissue regeneration is significantly reduced.
- Scarring of the eyelid/conjunctival surface. Leads to serious problems, complications and inflammation, especially if the scar prevents the proper closure of the palpebral fissure (closure of the eyelids).
Features of burns with acids and alkalis
Eye burns from sulfuric acid are not as dangerous as from alkali. This is due to the fact that a film of coagulated protein forms on the eye when the irritant reacts with the mucous membrane. The film does not allow acid to penetrate deep into the eye, protecting the eye from deep damage. However, coagulation does not protect against complications if a concentrate of nitric and hydrofluoric acids gets into the eyes. An acid burn is characterized by severe pain, and sometimes even painful shock.
It is noteworthy that when the eye is damaged by alcohol, a person experiences severe pain, but minimal damage is noted. However, alcohol can absorb moisture from the lubricating fluid and the eyeball, penetrating deep into and damaging the cornea and lens. If washed in a timely manner, there will be no consequences for vision.
The most dangerous are alkali burns. In this case, there is severe dehydration and cell destruction. Alkalies provoke the decomposition of protein structures, wet necrosis develops, and when the irritant gets into the intraocular fluid, the deep structures of the eye are affected. Alkali can reach the corneal stroma and trabecular meshwork. As a result, the cornea becomes cloudy and intraocular pressure increases.
Common symptoms of a chemical burn
- Deterioration of vision. The initial decrease in visual acuity is caused by epithelial defects, increased lacrimation, clouding and discomfort. Even with moderate to severe burns, vision may be preserved if the corneal clouding is minor, but severe deterioration will occur over time.
- Fragments of the irritant in the arches of the outer shell. Residues of foreign matter are visible when plaster and other solid irritants enter the eye. The fragments must be removed immediately, otherwise they will continue to release toxins and worsen the damage. Only after cleansing the eye does the natural recovery process begin. Carbide and lime are the most dangerous because they dissolve in the tear and cause severe damage. If these substances come into contact, do not delay cleansing.
- Increased intraocular pressure. A sharp increase in pressure occurs due to deformation and contraction of collagen fibers in the anterior part of the eyeball. Subsequently, the increase is associated with inflammation.
- Inflammatory process in the conjunctiva. Even with mild damage, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane is noted. Sometimes when a burn occurs, the color of the conjunctiva changes (brown when damaged by chromic acid, yellowish when exposed to nitric acid).
- Perilimbal ischemia. Based on the degree of blanching, one can make a prediction about the restoration of the cornea, because limbal sprout cells restore the epithelium. Severe ischemia indicates an unfavorable course of the process.
- Cloudiness. If the cornea is transparent, a zero degree of damage is determined, and if the cornea is completely clouded, the fifth degree is determined. Complete stromal opacification makes it impossible to examine the anterior chamber of the eye.
- Defects of the corneal epithelium. Damage to the cornea can be expressed as diffuse punctate keratitis or complete absence of the epithelium. In the latter case, the defect is poorly stained with fluorescein and may not be diagnosed. If the epithelial defect is not visible during the initial examination, prompt re-examination is recommended.
- Corneal perforation. The symptom appears a few days after a severe eye burn, when the cornea's ability to regenerate decreases.
- Inflammation in the anterior region. The reaction may affect single cells or have a pronounced fibrinoid form. Inflammation is more pronounced when alkali gets into the eye, since these substances can penetrate deep into the structures.
- Scarring or other damage to the conjunctiva and eyelids. The symptom may be a problem if scarring prevents the palpebral fissure from closing.
Symptoms of disorders
An eye burn with alcohol is quite dangerous, especially if the necessary therapy is ignored, but signs of dysfunction may sometimes not appear immediately.
Symptoms of chemical injury:
- Acute pain syndrome for a long time.
- The membrane of the eye and eyelids swell.
- Redness of tissues and mucous membranes.
- Severe lacrimation, itching.
- Photophobia, tissue sensitivity.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Formation of a whitish film on the cornea.
- The appearance of high intraocular pressure.
3-4 days after the chemical enters the eyeball, most of the symptoms disappear, but the main problem does not go away. The pathological process will continue, so immediate treatment is required. This will help prevent complications and return visual acuity to normal.
What medications are used to treat burn injuries to the eye with an alcohol solution?
After emergency assistance is provided, the victim is taken to the hospital. There he is washed with saline solutions, after which the ophthalmologist draws up a scheme for further therapy. As a rule, treatment of eye burns with alcohol is carried out using medications in the form of drops and ointments. I bring to your attention a standard treatment regimen for burn injury with an alcohol solution:
- To prevent infection from getting into the eye, antiseptic drops are installed 3-4 times a day, and ointments that contain an antibiotic are also applied.
- To stimulate regeneration of the cornea, drops of Taufon (4%) or Balarpan (0.01%) are instilled about 4 times a day. In parallel with this, Solcoseryl or Octovegin ointment (20%) is used twice a day.
- One of the consequences of an eye burn with alcohol can be iridocyclitis. To prevent this, intramuscular injections of Atropine (1%) and Diclofenac are administered.
- If IOP is increased, the damaged organ of vision is instilled with Timolol drops (0.25-0.5%).
- In order to prevent scarring of the affected mucous membrane of the eye, the victim may be prescribed to wear special contact lenses.
Emergency measures
Lotions, vodka, and perfumes can cause severe alcohol burns to the eye. This is a dangerous situation in which most of the damage occurs on the cornea.
Immediate measures can prevent complications:
- First, you should immediately rinse your eye with plenty of clean, cold water.
- Keep the victim calm and place him in a horizontal position.
- Do not delay and contact an ophthalmologist.
- Do not rub your eyelids under any circumstances, even if itching or burning occurs.
When vodka gets into the eye, ethyl destroys the cornea; if treatment is delayed, you can partially lose vision.
If you see double after drinking alcohol
Diplopia, a condition in which a person sees double, is the most common symptom of intoxication. Anyone who drinks alcoholic beverages has encountered it. This causes vision to deteriorate temporarily. Diplopia can also persist in a state of so-called hangover. It usually goes away after the body has fully recovered.
Alcohol primarily affects the center of the brain. Because of this, the performance of all eye structures decreases.
The eye muscles work slowly, the visual axes shift. In this case, the ocular muscles of the left and right eyes function inconsistently. One of them may see worse than the other. A person receives two different pictures that cannot be combined into one image. This symptom occurs only when drinking alcohol in large quantities. A glass of light wine does not cause double vision.
What to do if alcohol gets into your eye, drug therapy
Due to the ingress of esters, the recovery course is hampered by a high rate of hyperemia and infiltration of the conjunctiva and cornea.
Treatment with medications will help prevent photophobia, lacrimation, relieve swelling and pain:
- It is necessary to prevent infection of the injured organ; to do this, instill eye drops with the antibiotic "Levomycetin", "Gentamicin", "Albucid".
- If alcohol gets into the eye, then Novocaine or Lidocaine drops are used to reduce pain symptoms after a burn.
- To prevent the formation of scar tissue between the conjunctiva of the eyelids and the eyeball, a special pad with antiseptic ointments and insert lenses are used, but this procedure is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
- What to do if an alcohol-containing drug gets into your eye? Taufon 4% drops stimulate accelerated regeneration of damaged corneal tissue. Effective “Balarpan” drops are also used for this.
- To heal burned areas after alcohol gets into the eyes, they also use Solcoseryl gel and Actovegin 20% ointment.
- An eye burn with alcohol can provoke the development of iridocyclitis - inflammation of the iris and ciliary body of the apple, which can be prevented by Atropine or Diclofenac drops.
Sometimes it is effective to use eyelid massage, as well as a course of physical therapy, simultaneously with medications and alternative medicine recipes, but only starting from the second stage of healing.
When an eye burn occurs with alcohol, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist about what to do. Based on the severity of the injury, he will select adequate therapy. In extreme cases, surgery is recommended to prevent complete loss of vision.
If alcohol gets into your eye, this can be a difficult, dangerous situation, which is accompanied not only by physical injuries, but also by psychological trauma. This is important to consider during the rehabilitation process.
Healing procedures
For a chemical burn to the eye, first aid involves a set of certain actions. It must be provided on an emergency basis. It’s good if there is a person nearby with a medical education or basic knowledge in this area. But even an ordinary person can help.
First aid
So, what to do for chemical eye burns? There are several stages of emergency assistance:
First, it is urgent to rinse the affected eye (no later than 30 minutes after contact with the chemical). To do this, use a physiological solution of sodium chloride 0.9% (table salt) or a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). They have antiseptic properties.
If nothing is available, rinse the eyes with plain water from the inner corner of the eye to the outer corner to avoid chemicals getting into the healthy eye. If there are solid particles of the chemical (lime) in the eye, they should be removed with a dry cotton swab before rinsing.
- When it is known exactly what substance caused the burns, it can be neutralized. In case of an alkaline burn, the eyes should be rinsed with water and vinegar or 2% boric acid. A few drops per 500 ml of water is enough. If the burn is caused by acid, you need to treat your eyes with a weak soda solution.
- To avoid infection, antiseptic eye drops are dripped into the eye. A solution of furatsilin or sodium sulfacil is suitable for this purpose.
- local anesthesia for the purpose of carrying out manipulations to remove aggressive substances (Lidocaine);
- antitetanus serum;
antibiotics to prevent infection (drops containing ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin eye ointment);
- cycloplegic drugs that reduce pain and prevent scarring (atropine sulfate solution);
- tear fluid substitutes (Lakrisin);
- drugs that reduce intraocular pressure (Timolol, acetazolamide solution);
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) are prescribed when inflammation occurs.
After all these manipulations, you should cover the affected area with a clean bandage, give the patient a sedative and send him to the hospital, where appropriate treatment will be carried out.
It depends on the severity of damage to the eyeball and the presence of concomitant conditions (inflammation, pain shock and others).
Further therapy
Medical centers offer these procedures to treat eyes damaged by chemicals. First of all, medications are used. Among them:
Additionally, citrates (citric acid salts) or ascorbic acid are prescribed, which improve calcium metabolism in the affected area.
If extensive damage to the eyeball is observed (with burns of 3 or 4 degrees of severity, when defective conditions occur), then surgical intervention may be required:
- tarsography (suturing the skin of the eyelids during healing);
- tissue transplantation;
- autotransplantation;
- keratoplasty (to remove scars);
- prompt correction of the consequences of burns (glaucoma, cataracts).
In some conditions (subatrophy - slow death of the damaged eye), keratoprosthesis may be required - replacing the cloudy cornea with an artificial optical device.
Eye burns of chemical origin are common. Most often they are caused by acids and alkalis that enter the eye due to carelessness or failure to follow safety rules when in contact with aggressive chemicals. Such burns should be treated by a qualified physician.
>