One of the most obvious symptoms of inflammation is temperature with prostatitis in men. This is a common urological disease, and like any inflammatory process, this condition is accompanied by a reaction of the body in the form of hyperthermia. As a rule, infection penetrates the prostate gland in three ways:
- 1. Ascending from a sick woman during sexual intercourse.
- 2. Descending route with infected urine from the kidneys (with pyelonephritis, acute respiratory infections, influenza, diseases of the teeth and tonsils, pneumonia, etc.
- 3. Horizontal route with lymph flow from the intestines.
It is well known that a huge number of bacteria live in our intestines and help us live - about 1000 phylotypes, about 2 kilograms by weight. With intestinal dysbiosis, the intestinal walls become passable for pathogenic bacteria. In popular words - leaky gut. In addition to etiological and predisposing factors, there are also provoking factors.
Can there be a temperature with prostatitis, symptoms and consequences
Provoking factors include:
- Poor nutrition
- hypothermia;
- physical inactivity; passive lifestyle
- lack of sleep, chronic stressful situations;
- problems with stool;
- prolonged sexual abstinence or excessive sexual activity;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the body and foci of infection;
- venereal and urological diseases (urethritis, gonorrhea).
Many men are interested in whether there can be a temperature during the development of prostatitis? The development of the inflammatory process is caused by the proliferation of microorganisms that secrete toxins. The man’s body responds to the infection with an increase in temperature, chills, difficulty urinating, decreased urine pressure, pain in the sacrum, in the perineum and prostate gland, testicles and scrotum, penis, and bladder may occur.
Sources
- Biebel MG., Pate WR., Chai TC. Transurethral resection of prostatic abscess. // Can J Urol - 2021 - Vol28 - N2 - p.10638-10642; PMID:33872565
- Romero Pérez P. // Arch Esp Urol - 2021 - Vol74 - N3 - p.276-286; PMID:33818423
- Sigle A., Suarez-Ibarrola R., Pudimat M., Michaelis J., Jilg CA., Miernik A., Grabbert MT., Schultze-Seemann W., Gratzke C., Schlager D. Safety and side effects of transperineal prostate biopsy without antibiotic prophylaxis. // Urol Oncol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33736977
- Banza MI., Kasanga TK., Mukakala AK., N'dwala YTB., Ngoie CN., Cabala VPK., Shutsha NT., Lire LI., Unen EW., Kapessa ND. [Acute prostatitis associated with noncancerous prostate at the Lubumbashi University Clinics: epidemioclinical and therapeutic features]. // Pan Afr Med J - 2021 - Vol37 - NNULL - p.290; PMID:33654514
- Shakur A., Hames K., O'Shea A., Harisinghani MG. Prostatitis: imaging appearances and diagnostic considerations. // Clin Radiol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33632522
- El-Ghar MA., Farg H., Sharaf DE., El-Diasty T. CT and MRI in Urinary Tract Infections: A Spectrum of Different Imaging Findings. // Medicina (Kaunas) - 2021 - Vol57 - N1 - p.; PMID:33401464
- Wooster ME., Huang G., Sanders JW., Peacock JE. Prostatic abscess: clinical features, management, and outcomes of a “Stealth” infection: retrospective case series and review of the literature. // Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis - 2021 - Vol99 - N4 - p.115285; PMID:33360491
- Cicerello E., Mangano MS., Cova G., Zordani A. Urological emergency activities during COVID-19 pandemic: Our experience. // Arch Ital Urol Androl - 2021 - Vol92 - N4 - p.; PMID:33348953
- Morote J., Schwartzman I., Borque A., Esteban LM., Celma A., Roche S., de Torres IM., Mast R., Semidey ME., Regis L., Santamaría A., Planas J., Trilla E. Prediction of clinically significant prostate cancer after negative prostate biopsy: The current value of microscopic findings. // Urol Oncol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33160846
- Cannarella R., Calogero AE., Condorelli RA., Aversa A., La Vignera S. Systemic effects of the hormonal treatment of male hypogonadism with preliminary indications for the management of COVID-19 patients. // Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab - 2021 - Vol11 - NNULL - p.2042018820966438; PMID:33133492
Why is prostatitis dangerous?
The consequences caused by prostatitis depend on the age at which treatment is started and the stage of the disease. The acute form of bacterial prostatitis in advanced cases can cause various complications:
- chronic or acute cystitis;
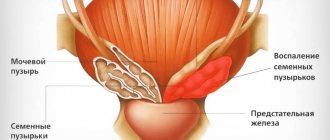
- vesiculitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- epididymo-orchitis and other inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system;
- transition from acute to chronic prostatitis;
- problems with urination, the appearance of stones in the prostate gland;
- sclerosis, fibrosis, prostate adenoma;
- renal failure, impaired renal function;
- formation of stones in the bladder, kidneys or urethra;
- impotence, erection problems;
- ejaculation disorder;
- infertility and decreased libido;
- prostate cancer.
Problems with potency, disturbances in the genitourinary system and sexual dysfunction can cause the development of psychological disorders and complications in family life. Constant stress leads to neuroses that significantly worsen the quality of life.
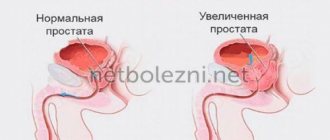
Features of the organ
The prostate is a gland, the secretion of which, together with other components, forms sperm. The health of the organ determines the reproductive capabilities of a man. In addition, smooth muscle cells form a valve that prevents urine from entering the urethra during an erection.
The gland is connected to the reproductive and urinary systems, so the pathology of the organ significantly affects a man’s health. The most common signs of prostatitis are problems with urination and ejaculation. The chronic course of the disease affects the general well-being of the patient; it is dangerous for the development of apathy, depression, and increased fatigue.
There are acute and chronic forms. The conditions differ in symptoms, but both require qualified therapy and medication support.
Why does temperature occur with prostatitis?
Like any inflammatory process, bacterial prostatitis can be accompanied by hyperthermia. Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, the indicator remains in the range of 37–38 °C. A higher temperature is a symptom of an associated pathology. It can be:
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections;
- malignant neoplasm;
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- autoimmune diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- other infections.
With chronic prostatitis, the temperature can be either elevated or decreased. When the temperature is low, the patient experiences sweating, weakness, drowsiness, apathy, tremors and tachycardia, which can last for years in the absence of complex therapy.
In addition, the following symptoms may occur:
- drip of urine;
- painful ejaculation;
- pain in the groin;
- erectile disfunction.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by a sudden increase in temperature, which can also be accompanied by severe pain in the groin area, radiating to the perineum and rectum. In addition to specific signs of inflammation of the prostate gland, against the background of high temperature, which occurs with prostatitis, performance decreases, weakness, headache, dizziness occur, as well as irritability and loss of appetite. The genitals and perineum may be painful and a burning sensation may be felt.
Fever is just a symptom and eliminating it will not lead to healing. It is important to understand why hyperthermia occurred and, with the help of a doctor, begin the correct treatment. An antipyretic drug is not able to eliminate the underlying disease, since temperature is not its cause, but a consequence.
Self-medication carries significant risks. For example, the cause of an increase in temperature may be renal failure, and not inflammation of the prostate gland. And if the correct diagnosis is not made in time, you can cause harm to the body.
Regardless of what the temperature is with prostatitis, constant use of painkillers and antipyretics erases the clinical picture of the disease, contributing to its transition to a chronic form, the appearance of urinary incontinence, impotence and constant pain. If a high temperature occurs due to prostatitis, any medications should be taken only after consulting a doctor. Most often, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen) or rectal suppositories are prescribed.
Signs of different types of prostatitis
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- spicy;
- chronic prostatitis.
Characteristic symptoms of acute prostatitis:
- fever, sudden increase in body temperature (up to 40 degrees);
- severe headaches, weakness, fatigue, irritability;
- pain in the groin, back, when urinating, frequent urges;
- changes in the quality of urine (becomes more cloudy, viscous, mixed with blood), unusual discharge from the urethral canal occurs.
If you do not seek medical help in time, acute prostatitis can cause complications:
- abscess in the body of the prostate;
- vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles);
- colliculitis (inflammation of the seminal tubercle);
- the occurrence of scars and adhesions in the gland and spermatic cord;
- stagnant processes in the tissues of the prostate gland;
- pyelonephritis, cystitis;
- infertility;
- oncology.
A feature of the chronic form is the blurring of clinical manifestations and symptoms of prostatitis. The manifestations are similar to the acute form, but are sluggish in nature. The causes of the pathology are usually abacterial prostatitis, prostatosis (stagnation of blood in the vessels).
Antipyretic drugs
It is believed that before the thermometer reaches 38.1 °C, it is not worth lowering the temperature, so as not to interfere with the body’s fight against the infectious pathogen. At higher values, antipyretic drugs are recommended.
ORDER
Depending on the main active ingredient included in the antipyretic, these medications can be divided into 4 groups.
- Preparations containing paracetamol. They are highly effective, but have a bad effect on the liver and excretory system. It is not recommended for prostatitis.
- Medicines containing ibuprofen. According to doctors, they are the safest of all drugs in this pharmaceutical group. They have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Dyspeptic side effects are possible.
- Preparations containing acetylsalicylic acid. Negatively affects the stomach, respiratory, cardiovascular and excretory systems.
- Preparations containing metamizole sodium (tempalgin, analgin, etc.). Antipyretic ability is low, use is not recommended.
Absolutely all antipyretic drugs have contraindications, so their use must be agreed with the attending physician, who will accurately determine whether it is worth lowering the temperature.
Is it worth lowering the temperature yourself?
If the temperature is about 37 degrees, then you shouldn’t bring it down yourself. Doctors speak the same way about a temperature of 38 degrees. After all, temperature is an indicator that the body is trying on its own to fight harmful bacteria that cause various diseases (including the infectious form of prostatitis).
When the temperature rises above 38 degrees, there is no need to ignore your condition. It is already necessary to take specific measures to reduce the temperature, regardless of what exactly caused this condition.
Folk remedies
Bacteria and viruses that enter the body send a signal to the immune system to produce pyrogens, which affect the hypothalamus and cause an increase in body temperature. The adrenal glands and thyroid gland produce hormones that stimulate metabolism and cause contraction of small muscles and capillary spasm. The body feels chills, the temperature rises, and the body fights the infection.
There are three stages of fever:
- more heat is generated than is given off; this is hyperthermia
- heat transfer is balanced with its production; this is Normothermia
- heat transfer outpaces production, the temperature decreases. This is hypothermia
Reliable and time-tested folk methods of combating fever with chronic prostatitis.
- Rubbing and cold compress applied to the forehead.
- Drinking liquid in large quantities, as a result of which sweating increases, and when sweat evaporates, the body cools.
- Herbal decoctions (linden, chamomile, coltsfoot, rosehip, etc.).
- Honey dissolved in warm water.
- Berries (strawberries, raspberries, cranberries, currants).
How to bring down the temperature?
The most drastic way that doctors advise in order to bring down a body temperature that has risen above 38 degrees is to rule out its cause, namely, carry out antibacterial therapy. You need to start taking certain antibiotics, most often these are broad-spectrum medications. They will be able to influence the pathogenic bacteria that cause the described symptom.
Important! An increase in body temperature to 40 degrees with prostatitis indicates that the chronic phase of the disease has passed into the acute stage. Immediate treatment is required.
But it is important to understand that if you have prostatitis and fever (as with any other disease), antibiotics should be selected together with your doctor. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and possibly take certain tests. Only after this will the doctor be competent to prescribe antibiotics of a certain spectrum to the patient.
Also, to reduce body temperature, you can use special medications (antipyretics), such as: Ibuprofen, TheraFlu, Coldrex, Fervex, paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), etc.
Wet towels placed on the forehead, neck, back and other parts of the body will help reduce the temperature a little.
Medical help, when to seek help?
If a fever occurs, there is a reason to seek qualified medical help. Self-medication and ignoring the symptoms of prostate inflammation in men (pain, discomfort, etc.) can cause serious complications: cystitis, pyelonephritis, vesiculitis, prostate adenoma or malignant neoplasms.
Fever with prostatitis is a question that the attending physician will answer. In order not to start the disease, you need to make an appointment with a urologist or andrologist and undergo an initial examination, including a rectal examination, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and prostate gland, and bacteriological culture of prostate secretions. Drug therapy eliminates congestion, normalizes the secretion of the prostate gland and blood circulation in the genitourinary system.
Prevention of acute inflammation of the prostate
Prevention of any disease can be primary or secondary. Primary involves preventing disease in a healthy person, secondary is aimed at eliminating relapses of existing diseases. Basic preventive measures:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely elimination of foci of infection;
- absence of promiscuity;
- complete balanced nutrition;
- regular physical activity;
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns;
- limiting the intake of alcoholic beverages;
- no hypothermia;
- strengthening immunity.
- Healthy lifestyle and nutritious nutrition
At the moment, the effectiveness of folk remedies for the prevention of prostatitis has not been proven. Any herbal preparations can be taken only after consulting a doctor.
"SMART-PROST" - a physiotherapeutic device for the prevention of prostatitis
The physiotherapeutic device “SMART-PROST” is an effective means for the treatment of chronic prostatitis of various etiologies and concomitant diseases of the prostate gland. Thanks to magnetic, infrared and thermal effects, microcirculation in the prostate gland and surrounding organs improves, the regeneration process is stimulated, muscle sphincters are strengthened and congestion in the prostate is reduced.
The maximum result is achieved with the combined use of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents, α1-adrenergic receptor blockers, immunomodulators and other drugs.
Clinical effect:
- increase in average and maximum urination rate;
- reduction in the volume of residual urine in the bladder;
- a significant reduction in the symptoms of the disease (reduction of pain and dysuric manifestations);
- decrease in the number of leukocytes in the secretion of the prostate gland.
There are certain indications for the use of the SMART-PROST physiotherapeutic device. These include urethroprostatitis, prostatovesiculitis, chronic prostatitis of various etiologies and disorders of copulative function. The device is not used for acute prostatitis, cancer of the rectum, as well as for exacerbation of chronic prostatitis in the phase of increasing symptoms of the disease, active tuberculosis or suspected prostate tuberculosis. Get acquainted with the SMART-PROST device.
“SMART-PROST” is an affordable and effective device for the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system. Timely administration of physiotherapy in combination with medications guarantees quick results and a significant improvement in health.