Consequences of meningitis in adults
According to the nature of the pathological change in the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, meningitis is divided into:
- Purulent meningitis. Like any inflammatory process, meningitis can be accompanied by the formation of pus - this form of the disease is called purulent. A typical case is the meningococcal variety of the disease.
- Serous meningitis. Serous meningitis is much easier, in which no pronounced inflammatory products appear in the cerebrospinal fluid, and it remains transparent. More often, this type of meningitis is caused by viruses, but it can also be caused by some bacteria (tuberculosis bacillus, leptospira), and fungi. A striking example of serous meningitis is the meningeal form of tick-borne encephalitis.
Reference! During the period of exacerbation, meningitis poses a huge danger to men, women and children. If treatment of the disease was not started on time, then the pathological process may spread.
In the first case, an adult may develop as a consequence of meningitis:
- cerebral edema – characterized by sharp fluctuations in blood pressure, impaired consciousness, tachycardia and shortness of breath;
- infectious-toxic shock - occurs due to poisoning of the body with decay products of bacteria that cause meningitis. There is a high probability of falling into a coma and death two to three hours after the onset of the active phase of the complication.
In both options, if emergency resuscitation is not provided.
Complications of mild meningitis in adults may include the following:
- frequent and monotonous headaches;
- memory impairment and decreased mental functions;
- spontaneous and causeless convulsions.
The consequences of severe meningitis in adults are more serious. Men and women are likely to experience the following pathological conditions:
- epileptic seizures;
- disturbances in the motor, mental and speech functions of the body, depending on which part of the brain was affected as a result of the infection;
- paralysis of certain parts of the body;
- hormonal disorders that can lead to metabolic disorders and brain activity;
- blurred vision and deafness (complete or partial);
- dropsy of the brain.
Attention! Meningitis poses a particular danger to women during pregnancy. During this period, the expectant mother’s immunity decreases, which increases the risk of contracting any infection. In certain cases of meningitis, there is a negative effect on the fetus, which can lead to a slowdown in its development.
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture is rightfully considered the most effective method for diagnosing the disease. Cerebrospinal fluid examination reveals mildly elevated protein levels, normal glucose concentrations, and lymphocytosis.
In the first two days after infection of the body, cytosis is predominantly neutral. That is why it is worth repeating the study after 8-12 hours to monitor whether a lymphocytic shift has appeared or not. As a rule, the glucose concentration in viral meningitis is normal. Its decrease indicates tuberculous or fungal meningitis, as well as a non-infectious disease.
Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid also suggests isolation of the virus from it. However, this method is rather auxiliary, since it does not allow obtaining an extensive clinical picture of the disease. This is due to the fact that the virus is present in the cerebrospinal fluid in small quantities. Moreover, the disease can be caused by a variety of viruses, and they need to be cultured differently. To isolate the virus, you need to obtain at least two milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid, and then immediately send the material to the laboratory.
The virus can be isolated not only from cerebrospinal fluid, but also from other sources. For example, adenoviruses and enteroviruses can be detected in a patient’s stool, cytomegalovirus in urine, enteroviruses and arboviruses in blood, and mumps virus and enteroviruses in nasopharyngeal washings. However, it must be taken into account that the presence of enteroviruses in stool may not indicate viral meningitis, but a recent infectious disease.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
After suffering from meningitis, the doctor individually selects a rehabilitation scheme for each patient, depending on many factors. The course of recovery and the duration of this period depend on the extent of inflammation, the age of the patient and impaired body functions.
Rehabilitation after meningitis in adults and children using physiotherapeutic procedures is a prerequisite for a complete recovery. This is due to the fact that the disease rarely occurs in a mild form, in which residual effects are not observed. Meningitis is difficult for children.
- Symptoms and signs of meningitis in a teenager
Physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed only by the attending physician, depending on the severity of the pathology, the nature of the course, and the age of the patient. The presence of contraindications is also taken into account. Often during the rehabilitation period the following are prescribed:
- Electrosleep. The therapeutic effect is achieved through exposure to currents supplied by a special apparatus in pulse mode. At the same time, increased production of serotonin begins. This hormone has a beneficial effect on the body and also has a calming effect on the nervous system. The course of treatment ranges from 10 to 15 procedures, which are carried out every two days.
- Electrophoresis using drugs. During the procedure, the patient's body is exposed to galvanic currents of a programmed frequency. At the same time, medications are added to the device, which, when sprayed, penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, reaching the source of the inflammatory process.
- Pine baths. The concentrate is diluted in a proportion of 50 mg per 1 liter of water. Needles have been used in folk medicine for a long time, but even today doctors recommend using it because it has a calming effect. The procedure should be carried out every two days, no more than 15 times.
Each method of physiotherapy has a number of contraindications. That is why you should consult a doctor who will determine the need to use physical therapy methods after meningitis and determine the duration of therapy.
What is serous meningitis and how to protect yourself from it
Author:
gastroenterologist Anton Smirnov
2 minutes
2019
Alarming reports from Samara, where an outbreak of serous meningitis continues, raised many questions about this disease. Let's understand what serous meningitis is and what its causes and symptoms are.
What causes serous meningitis?
Serous meningitis is an acute inflammatory process in the soft membrane of the brain. It can be caused by viruses (in approximately 80% of cases), as well as bacteria and fungi. Most often, the causative agents of viral serous meningitis are enteroviruses, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, adenoviruses, influenza viruses, polio, measles and some others. The disease affects children much more often than adults .
What symptoms are characteristic of serous meningitis?
This disease is characterized by an “acute onset”: a rise in temperature to 400C, severe headaches, signs of intoxication of the body - pain in muscles and joints, weakness, nausea, vomiting. Headaches are constant and debilitating, worsening with head movements, bright light, sharp sounds or noise.
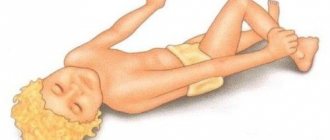
One of the typical symptoms of meningitis is excessive tension (rigidity) of the posterior cervical muscles. As a result , it becomes difficult or impossible for the patient to tilt his head forward so that his chin touches his chest . In addition, a typical sign of serous meningitis is the characteristic position of the patient: on the side with the limbs pressed to the body and the head thrown back (the so-called “cooper’s dog position” ).
In this case, meningitis is often accompanied by signs of ARVI: cough, sore throat, rhinitis. Strabismus and difficulty swallowing may occur.
How can you become infected with serous meningitis?
The version that you can catch meningitis while walking around without a hat in cold weather is nothing more than a myth. The source of infection is patients and virus carriers. The incubation period ranges from two to ten days. The route of infection can be almost any: airborne, contact (through objects), water (through reservoirs, swimming pools).
What to do if you suspect meningitis?
If you suspect meningitis, you should immediately call an ambulance and hospitalize the patient. Since serous meningitis is most often caused by viruses, the use of antibiotics in these situations is not advisable. However, in some cases they are prescribed before the final diagnosis is made. In the future, viral meningitis is treated with antiviral drugs, and also prescribed drugs that cause dehydration (to reduce intracranial pressure), painkillers, anticonvulsants, antispasmodics, isotonic solutions to reduce intoxication.
Is it possible to avoid infection?
- Of course, by following certain safety measures, the likelihood of contracting meningitis can be reduced.
- During outbreaks of serous meningitis, you should not attend public events or crowded places, and it is also undesirable to swim in open water.
- You should always drink only specially purified or boiled water.
- It is necessary to constantly observe the rules of personal hygiene, thoroughly wash your hands with detergents after using the toilet and immediately before eating.
- You should always wash fruits and vegetables before eating, and if possible, pour boiling water over berries and fruits.
- Avoid contact with pigeons, stray animals, and especially rodents, since they are considered the main carriers of viruses.
How to cure and not cause harm
The most correct decision is immediate hospitalization as soon as the first signs of infection appear. In the hospital, the patient’s temperature must be brought down with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If there are signs of bacterial meningitis, an antibiotic is prescribed. If your child gets meningitis, you need to make every effort to completely eliminate this disease so that you don’t have to return to it in the future.
Immediate hospitalization is a mandatory measure as soon as the first signs of infection appear
An anticonvulsant drug is used only when the patient has severe seizures, and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out with dexamethasone. To completely cure this disease, it is necessary to undergo proper rehabilitation after meningitis, because it is a full recovery after meningitis that will prevent the likelihood of getting it again.
Rehabilitation after meningitis in children
In children, recovery from meningitis is quite difficult. During the rehabilitation period, it is important to follow the recommendations of specialists. For 6 months, parents should ensure that the child is not exposed to direct sunlight for a long time and does not overheat.
Rehabilitation after meningitis in children should take place in camphor conditions; sudden climate changes, which are stressful for the body, should be avoided. After an illness, it is important to limit physical activity and the intensity of sports. As one of the measures to prevent re-infection, children are immunized. However, vaccination does not guarantee complete protection against the disease, as there are many forms of the disease.
Diet
The rehabilitation period after meningitis in children and adults also involves following a specially designed diet. The basis is considered to be fractional meals. Patients should eat at least 5 times a day. All foods should contain a variety of minerals, vitamins and nutrients, which helps strengthen the immune system.
The diet may include the following components:
- Lean boiled meat. Children are given pureed poultry, rabbit or veal.
- Steamed vegetables and fruits.
- Boiled fish.
- Lightly dried bread.
- Chicken eggs, soft-boiled or omelettes.
- Dairy products.
- Compotes, infusions, decoctions, juices, tea, low-fat broths.
You can also eat porridge from various cereals. During the rehabilitation period, you should not eat fried, spicy or too sour foods. Patients may be prescribed vitamin complexes as additional therapy.
Lack of treatment and non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period of meningitis in children and adults causes the development of serious diseases. Most often these are impaired hearing quality, mental retardation, blindness, strabismus and various mental disorders.
Meningitis is a fairly serious and dangerous disease that occurs regardless of age and gender. Like any disease, pathology is easier to prevent than to treat. Experts recommend paying close attention to your health, dressing appropriately for the weather, not getting too cold, carrying out hardening procedures and taking vitamin complexes in the autumn and spring.
- The first signs and symptoms of meningitis
Mild meningitis is easily treatable, but the recovery period can take quite a long time. At this time, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since complete recovery can only be achieved with an integrated approach to treatment.
Effective recovery after meningitis at the Yusupov Hospital
Treatment and rehabilitation after meningitis is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital. At the first signs of this disease, emergency hospitalization is necessary, which will reduce the likelihood of complications and speed up recovery from meningitis. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital receive patients with signs of meningitis, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Qualified psychologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide psycho-emotional rehabilitation after meningitis, which helps patients return to work life and normalize sleep. The daily work of the medical team at the Yusupov Hospital makes it possible to improve the quality of life of even seriously ill patients who were abandoned in other clinics.
Rehabilitation after meningitis allows patients to return to active life without unpleasant symptoms and complications. If you have signs of meningitis or need rehabilitation after an illness, make an appointment with neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital by phone or by filling out the feedback form on the website.
Purulent meningitis: symptoms
The duration of the incubation period for primary purulent meningitis is, on average, from two to five days. The disease has an abrupt onset. Patients experience increased body temperature, which can reach 40°C, intense and worsening headache, severe chills, nausea and repeated vomiting. The appearance of delirium, psychomotor agitation, confusion, and convulsive syndrome may occur.
Purulent meningitis in adults and children is accompanied by specific symptoms (Brudzinsky, Kernig, Guillain, stiff neck), which occur at an early stage of the disease and intensify after 2-3 days. Patients exhibit severe hyperesthesia and decreased abdominal reflexes, while deep reflexes are increased. In some cases, a diffuse hemorrhagic rash appears.
With purulent meningitis, patients experience double vision, strabismus, drooping of the upper eyelid, and anisocoria, which is associated with damage to the oculomotor nerves.
In more rare cases, there is damage to the trigeminal nerve, the development of neuritis of the facial nerve, dysfunction of the vestibulocochlear (progressive development of hearing loss) and optic nerve (decreased visual acuity, loss of visual fields).
If the inflammatory process spreads to brain tissue, patients develop meningoencephalitis.