Compatibility of Furosemide and alcohol
? If a patient undergoes furosemide therapy and simultaneously drinks alcoholic beverages, the following effects occur in the body:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure, which can cause vascular collapse and death of the patient;
- inflammatory conditions of the kidneys, which lead to the release of red blood cells in urine in large and small quantities;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system, which together with alcohol leads to confusion, delirium, hallucinations, the patient often experiences delirium tremens;
- water-electrolyte metabolism is disrupted, a person’s amount of water in the body sharply decreases, which leads to dehydration and a decrease in many microelements in the blood and tissues;
- Allergic reactions often occur, which can be observed not only on the skin and mucous membranes, but also systemically throughout the body; this is dangerous for human life.
The drug has a large number of side effects, especially if used incorrectly. With additional consumption of any doses of alcohol, the negative effects intensify. Therefore, simultaneous use with alcohol is prohibited.
What you need to know when taking the drug: possible adverse reactions
Furosemide must be taken with great caution as it has many side effects, the most common of which are:
- hearing and vision impairments;
- anemia;
- arrhythmia, tachycardia;
- migraine, dizziness, confusion;
- paresthesia;
- feeling tired;
- failure in water-salt metabolism;
- urticaria, redness of the skin, dermatitis, arteritis;
- blood clots in the urine, nephritis, sexual dysfunction (impotence).
A considerable number of people use Furosemide to eliminate alcohol intoxication. But at the same time as the toxic substances of alcohol, the diuretic removes useful and necessary substances from the body.
Brief characteristics of the drug
This is a medicine that has a diuretic effect. It is produced in the form of tablets or solution for intravenous administration.
The drug contains the active substance of the same name, which affects the body as follows:
- increased release of sodium ions, which removes water from the body through the kidneys;
- changes in the distribution of intrarenal blood flow;
- increased production of kidney mediators;
- excretion together with urine of calcium, magnesium, potassium, and other microelements;
- lowering blood pressure by reducing the amount of fluid in the body.
The drug is metabolized by the liver, excreted through the kidneys and bile.
Indications for use:
- severe swelling, for example, in case of dysfunction of the heart, liver, kidneys;
- edema of the lungs, brain;
- eclampsia;
- a strong increase in blood pressure, hypertensive crises;
- increased amount of calcium in the body.
The dosage of the drug is selected for each patient, depending on the amount of excess fluid and the condition of the internal organs.
Side effects:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure, which can lead to vascular collapse;
- heart rhythm disturbances, increased heart rate;
- pain, muscle cramps, headache, dizziness, numbness of the limbs;
- depression, apathy, sleep disturbance, confusion;
- dysfunction of the eyes, inner ear;
- dyspeptic reactions, dry mouth and thirst, loss of appetite, inflammation of the liver and pancreas;
- impaired potency, urinary retention due to inflammation and enlargement of the prostate gland, inflammation of the kidneys, excretion of red blood cells in the urine;
- increased excretion of potassium, chlorine, sodium, calcium, magnesium from the body, which leads to their deficiency and brittle bones;
- systemic, local allergic reactions;
- inflammation of the venous endothelium.
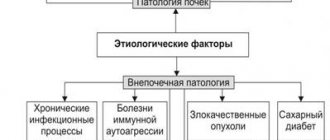
Contraindications for use:
- serious pathologies of the urinary system, anuria;
- inflammation, liver failure;
- coma of various origins;
- inflammatory diseases of the joints associated with a violation of the microelement composition of blood and tissues;
- serious diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- metabolic disorders, electrolytes;
- pancreatitis.
During pregnancy, the drug is used, but in rare cases, only for vital signs.
https://myweak.ru/alkogolizm/lekarstva/furosemid-sovmestimost.html
Features of the use of Furosemide
Furosemide (Lasix) is a diuretic drug. The medicine blocks the reabsorption (reabsorption) of sodium and chloride ions in the kidney tubules. And due to the increased excretion of sodium, a secondary increase in the excretion of water from the body occurs. This is how the diuretic effect of the drug develops.
Due to increased diuresis, the volume of circulating blood decreases (due to the liquid part of the plasma). Thus, the load on the blood vessels is reduced, which means that blood pressure will also decrease.
Based on this, Furosemide is prescribed for the following indications:
- Edema in congestive heart failure;
- Edema in chronic renal failure;
- Edema in nephrotic syndrome;
- Edema due to liver diseases;
- Arterial hypertension.
Use of the drug for alcoholism
If a person is dependent on alcohol (alcoholism), alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis are formed. The function of the urinary system and mineral metabolism are disrupted, and central nervous system pathologies occur.
The instructions for use of the medicine indicate that it is prohibited for use in these conditions. A serious disorder does not form immediately, but gradually, as the concentration of ethanol and medication in the blood increases.
The liver and kidneys gradually fail. The functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system is disrupted. Systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock, often occur.
Consequences of drinking alcohol
If a person, despite the doctor’s prohibition, drinks alcohol and the drug together, the following consequences arise:
- general health worsens, blood pressure decreases, and convulsions occur;
- the heart begins to work harder to normalize blood circulation, which is why arrhythmia and tachycardia occur;
- mental disorder, apathy and depression, with chronic alcoholism delirium tremens appears;
- if the concentration of ethanol together with the drug is high, the patient loses consciousness and may fall into a coma.
A doctor can eliminate the consequences of joint use of substances only in a medical facility.
Diuretics for hangover
In case of alcohol intoxication, experts advise drinking more fluids. In this way, the body can quickly get rid of alcohol decomposition products. Diuretics (diuretics) speed up the detoxification process during a hangover.
Diuretics are quite strong drugs that can both cure and negatively affect the patient’s condition. Therefore, the decision to use them in anti-hangover therapy should be balanced.
Among the contraindications to medications in this group:
- liver and kidney diseases;
- problems with water-electrolyte balance and urine flow;
- digitalis intoxication (poisoning with cardiac glycosides).
Diuretics should be taken with caution by persons suffering from hypotension, diabetes mellitus and diarrhea. In case of pancreatitis and myocardial infarction, you should definitely consult a specialist. Only an experienced doctor is able to objectively assess the clinical picture and prescribe adequate therapy.
Furosemide and beer
If the drug is taken immediately after drinking beer or another drink containing alcohol, there is a high probability of developing irreversible consequences:
- the occurrence of side effects;
- increased effect of tablets, which threatens overdose.
In case of overdose, death occurs. The side effects of the drug are dangerous for the cardiac system and liver.
Combination with ethanol can lead to:
- Heart attack.
- Stroke.
- Cirrhosis.
- Breaking my heart.
The medicine is prohibited for athletes, as it is classified as doping.
Furosemide for hangover
Many people the morning after a feast are faced with a problem such as swelling. A variety of methods are used, in particular Furosemide tablets. In fact, you shouldn't take this medicine if you have a hangover, and here's why.
The fact is that excessive alcohol consumption causes severe dehydration. In this case, the remaining water in the body is redistributed in a special way. Fluid moves into the intercellular space, which leads to the appearance of edema.
If you drink Furosemide during a hangover, your already dehydrated body will lose even more fluid . This will lead to the symptoms of a hangover intensifying, causing malaise, nausea, headache, rapid heartbeat, etc.
To eliminate a hangover, on the contrary, you need to drink a lot of Borjomi-type mineral water, which will help restore the water-salt balance in the body. As soon as the water-salt balance is restored, the person’s condition will improve and the swelling will disappear.
Valeria Grigorova, doctor, medical columnist
5, total, today
( 68 votes, average: 4.37 out of 5)
Panadol tablets
Proposol spray: instructions for use, features of use during pregnancy
Related Posts
Organs affected by the toxin
The combined use of pharmacological agents and alcohol has a toxic effect on the internal organs and environments of the body. Alcohol, entering into a chemical reaction with a medicine, leads to poisoning, disrupts physiological processes, enhances or weakens the healing properties of drugs.
The liver suffers more than other organs. She gets hit twice. Many medications have a side effect - hepatotoxicity, destroy cells, and disrupt the physiology of the organ. In the liver, alcohol breaks down to ethanal, a substance 20-30 times more toxic than ethanol, which causes the death of hepatocytes.
Dangerous groups of drugs for the organ in combination with alcohol:
- anti-inflammatory;
- hormonal;
- antibacterial;
- antifungal;
- glucose control agents for diabetes mellitus;
- anti-tuberculosis;
- cytostatics (chemotherapy drugs);
- tranquilizers (anti-epileptic, psychotropic).
In second place among the internal organs exposed to the harmful effects of alcohol together with medications are the heart and vascular system. Strong drinks during drug therapy constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure. The simultaneous intake of alcohol and chemical substances leads to failure of the myocardium and increases the risk of developing an attack of angina pectoris and a heart attack.
A mixture of ethanol and pharmaceuticals disrupts the quality of the blood and reduces clotting. This is dangerous due to internal bleeding and strokes.
Rules for taking medications and alcohol
Drinking alcohol during treatment minimizes the clinical effect of therapy and creates a risk of developing complications of the disease.
If this cannot be avoided, follow the rules of behavior that will reduce the occurrence of negative consequences:
- Do not drink strong drinks (vodka, cognac, whiskey), choose dry wine (100-150 ml), beer (no more than 300 ml). Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach.
- The interval between taking the medicine and alcohol should be at least 2 hours.
- To reduce the toxic effect, take medications that protect the liver (hepatoprotectors), pancreas (pancreatin), and stomach (antacids ─ Rennie, Almagel).
If a person takes antiviral medications for colds, anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol in moderation does not pose a threat to the body.
Alcoholic drinks during treatment are strictly contraindicated in cases of liver cirrhosis, severe infectious diseases, and during a course of chemotherapy.
Medicines, alcohol and chronic diseases
If a person has chronic diseases, simultaneous use of alcohol and medications is potentially dangerous for the functioning of vital organs. Since patients systematically take prescribed medications, the influence of alcohol can lead to negative consequences.
People with chronic heart disease (angina pectoris, heart defects) develop arrhythmias of varying severity. Heart attacks with severe pain syndrome develop, which is not relieved by Nitroglycerin, and the risk of developing myocardial infarction increases significantly.
In case of chronic liver diseases (viral hepatitis, hepatosis), alcohol during treatment can become a trigger in the development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (cancer).
Drinking alcohol during cirrhosis leads to the following consequences:
- bleeding into the abdominal cavity;
- liver decomposition, infection, peritonitis;
- hepatic coma;
- death.
If a person is on long-term treatment with sedatives, psychotropic drugs, tranquilizers, he is contraindicated in drinking alcohol. This leads to severe depression and the appearance of obsessive states (hallucinations, phobias). Suicidal feelings develop. Such a patient needs constant monitoring and assistance from a psychiatrist.
Consequences of drinking alcohol and Furosemide
The described tandem leads to serious consequences, in some cases even death. Negative consequences from different body systems:
- Concurrent use of alcohol and medication has a negative effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, in such cases, a person experiences nausea, vomiting, a dry mouth, and a constant desire to drink. With an inflamed pancreas, an exacerbation of the pathology occurs.
- After absorption of the two components into the blood plasma, they simultaneously cause an intense diuretic effect. The result is a sharp decrease in fluid, leaching of minerals and salts that are necessary for the proper functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Subsequently, blood pressure decreases, blood circulation is impaired, which provokes arrhythmia, tachycardia and other diseases that can lead to cardiac arrest.
- The combination has a negative effect on the central nervous system - lowering blood pressure, dizziness, headaches, weakness in the body, limb cramps, depression.
- A large load is placed on the urinary system. As a result, kidney failure and, in some cases, complete organ failure may occur. This condition occurs so quickly that doctors are powerless.
The most dangerous combinations and consequences
The combination of alcohol and chemical-based drugs can lead to serious disorders in the body, and in some cases to fatal consequences.
List of medications and their side effects in combination with alcohol:
| Name of group, drug | Negative results of interaction |
| Neuroleptics (tranquilizers, anticonvulsants, hypnotics) | Severe intoxication, up to cerebral coma |
| CNS stimulants (Theophedrine, Ephedrine, Caffeine) | Rapid increase in blood pressure, hypertensive crisis |
| Antihypertensives (Captofrin, Enalapril, Enap-N), diuretics (Indapamide, Furosemide) | Sudden drop in pressure, collapse |
| Analgesics, anti-inflammatory | Increased toxic substances in the blood, general poisoning of the body |
| Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) | Acute gastritis, perforation of gastric ulcer and 12-PC |
| Paracetamol | Toxic liver damage |
| Hypoglycemic (Glibenclamide, Glipizide, Metformin, Phenformin), insulin | A sharp decrease in blood sugar levels, hypoglycemic coma |