Ekaterina Smolnikova
Practicing endocrinologist (10 years of experience). He has extensive experience working in private and public clinics in Russia.
Ask a Question
Last updated August 22, 2021 at 3:20 pm
Often, a blood test shows that the leukocytes in the blood are elevated. The reasons for women are very diverse - from banal acute respiratory infections to serious diseases. What elevated white blood cells indicate should be understood in each individual case. For this purpose, additional laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out.
What are leukocytes?
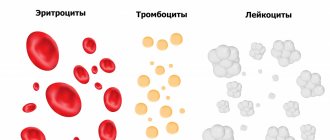
Leukocytes are white blood cells. They protect the body by absorbing pathogenic microbes. They were first discovered by scientists I. Mechnikov and P. Ehrlich, who in 1908 received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. Scientists have developed a theory of immune defense and described different types of leukocytes.
Leukocytes can penetrate the cell wall and engulf foreign microorganisms. This process is called phagocytosis, and the leukocytes involved in it are called phagocytes. To maintain immunity, white cells are constantly synthesized in the bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes.
How long do white calves live?
Their lifespan is 10-12 days.
Where are leukocytes destroyed?
If too many pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the cells, the phagocytes grow in size and are destroyed.
The result of destruction is a local inflammatory reaction, expressed in redness and swelling of the tissue. An even larger number of white cells join the site of inflammation, they die, destroying foreign cells. Purulent discharge is nothing more than dead leukocytes.
Leukocytes are diverse in their appearance and functions. Some of them provoke phagocytosis, others synthesize antibodies. Based on this feature, white cells are divided into two large groups:
- Granular: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
- Non-granular: lymphocytes, monocytes.
Increased levels of various white cells are found in various diseases. For example, the number of eosinophils increases with allergies and parasitic infections. An increase in lymphocytes indicates the presence of a viral infection.
Therefore, a blood test examines the leukocyte formula, that is, the balance of different types of leukocytes. If a so-called shift to the right is detected, then they speak of an increase in the number of young leukocytes; with a shift to the left, mature “old” cells predominate in the blood.
Norm of leukocytes in the blood (table)
The norm of leukocytes in the blood of adults and children differs. In children, the number of white cells is always higher and changes with age. White blood cells also increase slightly in pregnant women, especially in the third trimester, and this is considered normal and does not require treatment.
Article on the topic:
LDH in a biochemical blood test - what is it?
The content of leukocytes by age is presented in the table:
| Patient category | Norma (10 9 l) |
| Children up to 5 days | 8-29 |
| Children 5-8 days | 8-14 |
| Child under 1 year | 5-12 |
| Child 1-6 years old | 4-12 |
| Child 6-12 years old | 4-11 |
| Men | 4-9 |
| Women | 4-9 |
| Pregnant | 7-11 |
What does high content mean? This pathology is called leukocytosis. If the white cells in the blood are much lower than expected, then we are talking about leukopenia.
Standard indicators: general information
The normal white blood cell count may vary from person to person. Moreover, the main criterion for difference is the age of the subject. So, in children this figure will be higher than in adults. Due to the fact that the norm is estimated in units per liter of blood, diet, body condition and time of day should also be taken into account. So, in the afternoon, after eating, after any stress, physical or mental, the concentration of the indicator will be increased. Gender has virtually no effect on the number of leukocytes. The amendment needs to be made only for a pregnant woman and a woman after 50 years, when due to hormonal changes the concentration of the indicator changes.
For a healthy person, the leukocyte composition of the blood looks like this:
- 55% – neutrophils: 45-72% – segmented neutrophils, 1-6% – band neutrophils;
- 19-37% – lymphocytes;
- 3-11% – monocytes;
- 0.5-5.0% – eosinophils;
- 0.5-1% – basophils.
In a blood test, these data are taken into account in relation to the content of the total number of immune cells.
On the Internet you can find a variety of white blood cell standards that differ greatly from each other. In reality, everything is much simpler - the range from 4 to 9 * 109 is accepted as the norm, with slight adjustments for gender, pregnancy, and age. Children have their own norms, this is due to the passage of a long period of growth and development from newborns to puberty.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
When is promotion normal?
Leukocytosis can be physiological. White cell levels fluctuate several times a day, which may be due to the following factors:
- A hearty lunch.
- Exercise stress.
- Visiting the sauna or being in the sun.
For these reasons, the blood test is performed on an empty stomach after rest.
The level of leukocytes is also affected by:
- Smoking.
- Sports activities. In athletes, the number of these cells always fluctuates.
- Prolonged stress.
- Eating large amounts of red meat. The body perceives the components of meat dishes as foreign and reacts to this by releasing white cells.
- Pregnancy after 6 months. This is due to the increased load on a woman’s body.
- Use of medications.
- Last days before menstruation.
- The first days after vaccinations. This is due to the entry of a small number of microbes into the blood.
As for leukopenia, the physiological reasons are:
- stress;
- taking antibiotics;
- following a strict diet.
How is a blood test for leukocytes performed?
A standard blood test is ordered to measure white blood cell levels. Blood is drawn in the morning.
Before the study you cannot:
- Exercise.
- Be nervous.
- Eat food.
- Take medications.
If a deviation from the norm is detected in the blood, the analysis should be repeated after 5-7 days. With a physiological increase, everything will return to normal. Maintaining an elevated level indicates pathological conditions.
Treatment for leukocytosis
There is no symptomatic treatment for leukocytosis. To normalize the level of white blood cells, it is necessary to combat the underlying pathology that caused leukocytosis. With minor leukocytosis during the period of recovery from an infectious disease, no medical intervention is needed. However, even a moderate increase in leukocytes in the blood that persists for a long time requires consultation with a specialist to determine the cause.
Antibacterial, antiviral, and anthelmintic drugs are used to treat diseases accompanied by leukocytosis. If the high level of leukocytes is due to rheumatological pathology, drugs that suppress the inflammatory process (glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants) are used. Allergic reactions are effectively treated with antihistamines and corticosteroids.
If the cause of leukocytosis is malignant hematological diseases, a long course of chemotherapy is required, and in some cases, allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Suppurative processes (phlegmons, abscesses) are subject to surgical intervention, which involves dissection of soft tissue, washing and draining of the lesion. Endocarditis may require valve surgery or replacement.
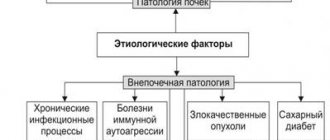
Causes of pathological increase in leukocyte levels
Pathological leukocytosis can be true and redistributive.
In the first case, the synthesis and release of leukocytes from the bone marrow increases. In the second case, the cells that are on the surface of the vessels enter the blood, but their production is not increased.
The causes of true leukocytosis are leukemia and other oncological diseases, as well as the first period of radiation sickness.
Important! In chronic leukemia, the number of white cells increases tenfold. However, in the acute period, on the contrary, the number of leukocytes is much lower than normal.
Causes of redistributive leukocytosis:
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza, sore throat). After recovery, leukocytes remain above normal for another 10 days, then the level gradually decreases.
- Inflammatory processes caused by bacterial infections (otitis media, pharyngitis, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, gynecological problems, etc.).
- Infected wounds, internal inflammation (appendicitis, boil, peritonitis).
- Heart attack.
- Severe burns or frostbite.
- Significant blood loss.
- Autoimmune diseases: lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Chemical poisoning.
- Rubella, mumps, chickenpox, hepatitis.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Kidney failure.
- Diffuse mastopathy.
- Allergy.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- HIV AIDS.
- Condition after removal of the spleen.
Article on the topic:
What is ACTH hormone? Normal blood levels in women and interpretation of tests
With purulent inflammation, the level of leukocytes is significantly increased; a slight increase indicates a chronic inflammatory process when the body is fighting infection. Leukemia and other oncological diseases are characterized by a multiple increase (up to 300 units).
Also, against the background of a general increase in leukocytes, an increase in the number of lymphocytes may be observed. This happens when:
- Asthma.
- Tuberculosis.
- Whooping cough.
- Lymphocytic leukemia.
- Drug use.
An increase in the level of neutrophils is usually associated with purulent processes and indicates the following pathologies:
- Peritonitis.
- Internal purulent inflammation.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Intoxication.
- Suppression of bone marrow activity.
Important! A large number indicates deadly pathologies and requires a thorough examination and urgent medical care.
Leukocytosis in women
In addition to an increase in white blood cells in the blood, women often have a large number of these cells in the smear. Normally, they should not be more than 15 units. Otherwise, we can talk about STIs (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, herpes, trichomoniasis, etc.).
Leukocytosis in the urine means diseases of the urinary organs (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urolithiasis).
Causes of leukocytosis
Infections
The most common cause of leukocytosis is considered to be various infections (bacterial, viral, parasitic). Since the main function of all leukocytes is to maintain anti-infective immunity, the presence of a foreign pathogen in the body is accompanied by a reactive increase in white blood cells in the blood. Moreover, a certain type of microorganism causes various types of leukocytosis.
- Bacterial infections
. During bacterial infections, the content of neutrophils and monocytes in the blood increases, which destroy pathogens through phagocytosis and an “oxygen explosion.” In localized infections (angina, pyelonephritis, bronchitis), leukocytosis is usually insignificant. Severe purulent processes (abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis) and generalized infections (sepsis, endocarditis) are characterized by high leukocytosis, and sometimes a leukemoid reaction occurs. A distinctive feature of leukocytosis, the cause of which was a bacterial infection, is a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, i.e. the appearance in the blood of “young”, immature forms of neutrophils (metamyelocytes, promyelocytes). In acute processes, leukocytosis increases sharply and reaches a maximum on days 1-2 of the disease, then gradually decreases and returns to normal. In chronic bacterial infections, the white blood cell count may be at or slightly above the upper limit of normal. - Viral infections
(flu, measles, mononucleosis). They cause an increase in lymphocytes in the blood, which have the ability to trigger the apoptosis mechanism in viral cells and produce specific antibodies (immunoglobulins) against them. Lymphocytosis is most often moderate and can persist for a long time (weeks, months, years), especially with persistent viral infections (cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus). - Helminthic infestations.
Infection with helminths (roundworms, pinworms, hookworms) is considered one of the most common causes of eosinophilic leukocytosis. Eosinophils contain in their granules eosinophilic cationic protein, which disrupts metabolic processes in the body of helminths. Eosinophilia occurs approximately on the 5th day of illness, grows rapidly and reaches very high values by 35-40 days, and then begins to slowly (over several weeks) decrease to normal numbers.
Systemic diseases
Leukocytosis is often caused by chronic systemic inflammatory processes. The exact pathogenetic mechanisms of the increase in leukocytes in these pathologies are still unknown. It is assumed that mediators and cytokines produced during rheumatic inflammation stimulate the production of leukocytes in the bone marrow. This mainly concerns the following rheumatic diseases:
- Joint diseases
: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis. - Diffuse connective tissue diseases
: systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleroderma. - Systemic vasculitis:
nonspecific aortoarteritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, giant cell arteritis.
In arthritis and diffuse connective tissue diseases, leukocytosis is usually moderate. In systemic vasculitis with necrotizing inflammation in the vascular wall, leukocytosis can reach high numbers.
Symptoms of elevated white blood cell levels
A slight increase in cell levels is almost not felt by a person and is detected during a blood test.
If there are a lot of white cells, the patient feels the following symptoms:
- Temperature increase.
- Weakness.
- Increased fatigue.
- Pain in joints, muscles.
- Sweating.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Poor appetite.
In addition, inflammation and pain may occur in the affected area (for example, pain in the throat or stomach).
Reasons for decreased leukocyte levels
Why does a decrease in leukocytes occur? Pathological leukopenia is said to occur when the level of white cells remains below 4 for a long time. This is usually associated with diseases such as:
- Acute leukemia.
- Bone marrow aplasia.
- Anemia.
- Metastatic tumor.
- Thyroid pathology.
- Anaphylaxis.
- Typhoid fever.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Diabetes.
Symptoms of decline
Some symptoms of leukopenia are similar to those of leukocytosis:
- Temperature.
- Prostration.
- Increased heart rate.
- Chills.
This condition usually means a decrease in immunity, which is fraught with infection. Therefore, leukopenia requires careful examination and treatment.
Other reasons
- Massive tissue breakdown
: myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, pancreatic necrosis, extensive burns. - Toxic effects on the bone marrow
: poisoning with lead, organic hydrocarbon compounds, ionizing radiation. - Endocrine disorders
: chronic adrenal insufficiency, autoimmune polyglandular syndromes, congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. - Primary immunodeficiencies
: Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Jobe syndrome (hyper-IgE syndrome). - Malignant neoplasms
: small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, colon adenocarcinoma. - Lung diseases
: pulmonary eosinophilia (eosinophilic pneumonia), Langerhans cell histiocytosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. - Dermatological diseases
: eczema, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, scabies. - Condition after removal of the spleen (splenectomy)
: as a component of post-splenectomy syndrome.
How to detect?
Treatment for leukocytosis depends on the underlying cause. To do this, a number of additional examinations are carried out:
- Biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
- Tests for STIs.
- Enzyme immunoassay blood test to detect autoimmune diseases and allergies.
- Blood test for parasites.
- Ultrasound.
- X-ray.
- If leukemia is suspected, a spinal cord puncture is performed.
Article on the topic:
What is DHEA-S hormone? Tests and normal values in women
Diagnostics
Leukocytosis is detected during a clinical blood test. Since there are many reasons for an increase in white blood cell levels, you should first consult a general practitioner. The doctor collects a detailed medical history, conducts a physical examination of the patient, including measuring body temperature, examining the skin and mucous membranes, etc. Based on the data obtained, in order to confirm the disease that caused leukocytosis, the following studies are prescribed:
- Blood tests
. Markers of inflammation are determined in the blood - high ESR and CRP, autoantibodies (rheumatoid factor, ACCP, antibodies to the cytoplasm of neutrophils). The leukocyte formula (percentage of leukocyte forms) must be calculated. A blood smear is examined for the presence of toxic granularity of neutrophils, atypical mononuclear cells, and Botkin-Gumprecht shadows. If a septic condition is suspected, presepsin is measured. - Pathogen detection
. To identify the infectious pathogen as the cause of leukocytosis, bacterial culture of blood, sputum, and urine is performed. The enzyme immunoassay method detects antibodies (class and immunoglobulins) to bacteria, viruses, helminths, and their DNA is detected using the polymerase chain reaction. - Allergy diagnostics
. In order to confirm the allergic nature of the disease, the level of immunoglobulin E (IgE) is measured using the ELISA method. To identify the causative allergen, basophil tests and various allergological tests are performed - skin (scarification, patch, prick tests), provocative (nasal, inhalation, conjunctival). - Radiography
. In case of pneumonia, chest x-rays show infiltrates in the lungs, foci of darkening; x-rays of joints in patients with arthritis show narrowing of the joint space, osteoporosis, and bone erosion. With osteomyelitis, x-rays of bones reveal thickening of the periosteum and sequestration foci (areas of bone necrosis). - Ultrasound
. With pyelonephritis, an ultrasound examination of the kidney reveals an increase in the size of the kidneys, expansion and thickening of the pyelocaliceal system. Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly. Echocardiography may show vegetations on the valves and effusion into the pericardial cavity. - Histological studies
. If leukemia is suspected, a trephine biopsy or sternal puncture is performed, the material of which reveals hyperplasia of the granulocytic lineage and a large number of blast cells. To diagnose lymphomas, an aspiration biopsy of an enlarged lymph node is performed; the biopsy specimen reveals lymphocytic hypercellularity, collagen proliferation, and Berezovsky-Sternberg giant cells.
The leukocyte formula allows you to determine the percentage of different types of leukocytes
Treatment of elevated white blood cells in women
If the increase in white blood cells is caused by bacterial or viral infections, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics or antiviral drugs. For severe allergic reactions, corticosteroid therapy is prescribed. In some cases (appendicitis, peritonitis) urgent surgical intervention is required.
If leukemia or another cancer is confirmed, the question arises of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
How to bring leukocytes back to normal?
When the increase in white cell count is associated with physiological conditions, no special treatment is required. Therapy consists of eliminating provoking factors. In particular, the following rules should be observed:
- Get more rest and sleep.
- Establish proper nutrition.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day to speed up the removal of toxins from the body.
- Minimize spicy and salty foods in the menu.
- Take vitamins and minerals to strengthen your immune system.
- Take walks in the fresh air every day.
The patient's diet should contain foods rich in B vitamins, especially B12. These are meat, dairy, seafood.
Folic acid also reduces leukocytosis. It is found in foods such as legumes, greens, vegetables, fruits. Copper has a positive effect on the level of leukocytes. To compensate for the deficiency of this element, it is recommended to consume more fish, seafood, liver, and buckwheat porridge.
Folk remedies for elevated leukocytes
It is also possible to reduce leukocytosis using folk remedies. Since the increase in these cells is associated primarily with inflammatory processes, agents are used that reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
The following recipes will help you cope with the problem:
- A mixture of birch leaves, lingonberries and strawberries. A tablespoon of raw material is steamed with boiling water, cooled and taken ½ cup before meals.
- Linden blossom decoction. A spoonful of herbs is poured with water and placed in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then cool and filter. Drink as tea during the day.
- Horsetail decoction. A spoonful of raw materials is brewed with hot water and left for at least 8 hours. Drink 1 tbsp. before meals.
- Alcohol infusion of propolis. It has powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Dissolve 20 drops of tincture in water and drink. Can be consumed up to 3 times a day.
Leukocytes perform one of the main functions - they protect the human body from bacteria and viruses. An increase in their level indicates health problems. To bring white cells back to normal, it is necessary to detect and treat the disease that caused the imbalance.