Diastase is an alpha-amylase enzyme that is excreted in the urine. This enzyme is produced in the pancreas.
A urine test for diastase is carried out primarily if inflammation of the pancreas is suspected - pancreatitis. A sharp increase in the level of this enzyme in the urine most often indicates an acute or chronic stage of pancreatic disease.
Also, an increase in the value of diastase in the urine may indicate an inflammatory process occurring in the peritoneum, for example, peritonitis. But the decrease in the indicator, especially in men, can be associated with prostatitis.
The main task of the enzyme is to break down carbohydrates and starch. They break down into simple sugars. Part of the juice produced by the pancreas passes into the intestinal tract and is actively involved in the digestion process.
To determine alpha-amylase, a laboratory test of urine is performed.
Taking a sample for analysis
Urine collection is done in the morning, on an empty stomach. Before collecting the material, you need to perform genital hygiene.
The first few drops of urine go down the toilet, the rest into a sterile container. It is important to send the container with the collected urine to the laboratory within two hours, since alpha-amylase is quickly destroyed.
If the doctor has diagnosed or suspects acute pancreatitis, then a diastasis test is prescribed in the form of monitoring. That is, the patient donates urine throughout the day, every three hours. It is important to donate urine in this way because the level of diastase can vary over time.
Urine analysis for diastase is a method for more in-depth diagnosis of inflammation of the pancreas.
There are some factors that can lead to distortion of laboratory test results. For example, if a person took certain medications the day before: antibiotics (tetracycline), hormones, anticoagulants, diuretics, narcotics. The day before the test you should not drink alcoholic beverages. Pregnancy may also affect the results.
Indications for diastase analysis
A child may be prescribed this type of examination if he is bothered by abdominal pain.
But this is not the only reason why you need to collect urine and have it analyzed for amylase:
- Suspicion of pancreatitis;
- Damage to the parotid glands;
- The presence of acute viral infections;
- Presence of pancreatic diseases;
- Suspicion of diabetes (mellitus or non-diabetes).
In all these cases, the amylase level in combination with other indicators makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, confirm or exclude the presence of certain diseases.
The essence of the method
The study is carried out in laboratory conditions using reagents and a photometer. An iodine solution with the test material already added is dripped into a starch solution preheated to 37 degrees Celsius. Then dilution is done in test tubes.
Using a photometer, the color intensity in each cuvette is measured. The more intense the coloring, the higher the level of diastase in the urine. If a blue color is observed in the test tube, then there is no amylase in this sample or there is very little of it.
What is α-amylase
This is an enzyme that breaks down and helps digest complex carbohydrates - glycogen and starch ("amylon" translated from Greek - starch). It is produced mainly by the exocrine glands - salivary and pancreatic, a small amount is produced by the glands of the ovaries, fallopian tubes and lungs. The bulk of this enzyme is contained precisely in digestive juices: in saliva and pancreatic secretions. But a small concentration is also present in the blood serum, since the cells of any organs and tissues are constantly renewed.
The blood contains two fractions of α-amylase:
- pancreatic (P-fraction) – 40% of total amylase;
- salivary (S – type) - 60%.
However, the study of individual amylase fractions is rarely carried out, only for special indications. Most often, it is enough to determine total amylase. In combination with clinical symptoms, its increase confirms the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
This is the most common indication for this test. Amylase in this case will be increased precisely due to the pancreatic fraction. Its molecule is small and is well filtered through the renal tubules, so if its content in the blood increases, it will also be increased in the urine (alpha amylase in the urine is usually called diastase).
Normal values
The task of a laboratory test of urine for diastase is to determine the quantitative volume of the enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates in a certain period of time. A normal indicator for an adult is considered to be no more than 120 U/L, but not less than 20. In children, the indicators are much lower - from 10 U/L to 64 U/L. The average normal level is close to 50.
With pancreatitis, the level of the enzyme can increase tens of times, and, for example, with severe toxicosis in pregnant women, on the contrary, the level decreases. It is worth noting that each laboratory can refer to its own normal values for the indicator. This may depend on the reagents used or if different units of measurement are used.
Calcium standards in urine analysis in a child: reasons for deviations and rules for preparing for the study
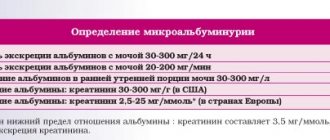
Testing urine for calcium (Ca) can reveal abnormalities in metabolism. Therefore, such tests are often prescribed by pediatricians. If the calcium content in a child’s urine is increased or decreased, the diet is adjusted and vitamins are prescribed.
The level of calcium in urine differs in children of different ages. A growing body needs to maintain a sufficient amount of this macronutrient so that the skeleton is formed in accordance with age standards. Determining its content in urine allows you to detect hidden diseases in time and take measures to eliminate them.
When is a urine calcium test ordered?
Ca is absorbed in the small intestine. It travels with the blood to all organs. The parathyroid gland releases it from bone tissue if the macronutrient is not supplied with food and the body experiences a need for it. The undigested macronutrient is excreted in urine or feces. An important indicator is the daily excretion of calcium in urine.
As the child develops, his skeleton also grows: the length and thickness of the bones increase. At this time, it is necessary to maintain a balance between the excretion and intake of macronutrients. A lack of calcium leads to brittle bones and increases the likelihood of fractures. Determination of calcium in urine allows you to maintain its content at the required level.
1% Ca is found outside the bones. This element is involved:
- in stabilizing pressure;
- in blood clotting processes;
- in the functioning of the brain;
- in the transmission of impulses from the brain to muscle tissue.
A urine calcium test reveals how much of the element is excreted from the body through the kidneys. The study helps determine:
- how the macronutrient is absorbed through the intestines;
- is there enough of it in food;
- how the element is absorbed by the body;
- whether it causes the formation of kidney stones;
- why it is washed out of bones;
- How does the parathyroid gland work?
During the examination, the doctor decides to send the child for a urine test. Timely diagnosis of hypocalciuria makes it possible to prevent disorders in the formation of the skeleton and other pathologies. A decrease in the amount of Ca in a child’s urine indicates a metabolic disorder, which leads to:
- to muscle spasms;
- tingling sensation in the fingers;
- pain in the abdominal cavity.
Not only a lack of an element is dangerous, but also an excess. When Ca levels exceed a person, a person develops:
- fatigue;
- general weakness;
- thirst;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain);
- frequent urge to urinate.
Blood and urine tests help determine the amount of Ca. To determine the exact level of calcium in the blood, material is taken from a vein. To correctly determine its content in urine, it is preferable to take daily biomaterial. Since all processes in the body occur with a certain cyclicity, and their activity changes, the data from one study may not reflect the real amount of Ca.
When a referral for research is given:
- The reason for the analysis may be diseases of the thyroid gland, problems with the parathyroid gland.
- Observe the excretion of calcium in the urine during the period of taking vitamins or calcium-containing drugs. The study allows you to control the amount of macronutrients and the effectiveness of treatment.
- Determination of the amount of Ca is necessary in case of digestive disorders.
- A urine calcium test is regularly taken by people suffering from kidney failure and patients who have undergone a kidney transplant.
- Patients with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and neuralgic diseases need control over the excretion of calcium from the body.
- Patients who experience pain in the back or side complain that blood appears in the urine (hematuria). In such a situation, urine examination helps in accurate diagnosis.
Minor deviations in calcium levels from the norm do not appear outwardly. If the normal value is significantly exceeded, a person experiences general weakness, pressure drops, and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract can be identified. If you ignore the signs of the disease, it can develop into a more severe form, in which kidney stones form.
Deviations from the norm and their causes
The level of calcium in a child's urine shows its content in the blood and the amount processed by the kidneys. Deviations from the normal indicator, both in the direction of excess and in the direction of decrease, can lead to problems in the body.
Diseases in which diastasis is increased
Diabetes in humans leads to a significant increase in the level of this enzyme in urine, and sugar is also found in the urine. Normally it should be absent altogether.
A high level is observed in renal failure, but in this case, high concentrations of urea and creatinine are also detected in the urine.
If in the analysis only diastasis is increased, in some cases it exceeds the normal value by 200 times or more, then we can talk about a chronic form of pancreatitis. A high level of the indicator in pancreatitis remains in the urine for a relatively short time, then it tends to normal values.
Diastasis in urine increases, but only slightly, during the inflammatory process of the salivary glands.
Amylase levels also increase when:
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- appendicitis;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- oncology;
- peritonitis;
- taking adrenaline;
- intestinal obstruction.
Therefore, when high analysis results are obtained, a more in-depth and comprehensive examination is necessary to determine the pathology.
Causes of increased and decreased urine diastasis
An increase in alpha-amylase is preceded by inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most common reason for determining an increase in this enzyme is pancreatic disease.
The gland takes an active part in the digestion of food, namely proteins, fats and carbohydrates. When food enters the body, the gland begins to produce active substances that pass through the duct to the duodenum. When interacting with food, pancreatic enzymes promote the digestion and absorption of nutrients entering the body.
With the development of various problems, such as obstructive diseases (stones in the bladder, in the genitourinary system, sand, compression of the duct by surrounding organs), when food enters, enzymes cannot leave the pancreas, because of this their activation occurs prematurely, thus the substances of the gland digest its tissues.
In this case, the organ itself enlarges, tissue dies and infection occurs.
Excessive enzyme retention can cause symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
The more a person eats foods that cause active production of trypsin, amylase, insulin and lipase, the faster signs of intoxication develop and inflammatory reactions develop in the pancreas.
As a result, there is an increased secretion of alpha-amylase and its excretion in the urine. You can also identify other diseases when the level of this enzyme increases:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- acute appendicitis;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- mumps;
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
With the development of the already necrotic stage of pancreatitis, which is called pancreatic necrosis, a decrease in the level of diastase occurs. A decrease is also observed in the following diseases and conditions of the body:
- Pancreatic necrosis.
- Pancreatic atrophy.
- Pregnancy.
- Liver failure.
- Abdominal injuries.
Increased diastase occurs in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Features of deciphering a general urine test in children
A general urine test evaluates the functioning of the urinary, cardiovascular systems, kidneys, and liver. The indicators that determine are the same for adults and children. The difference lies in the quantitative changes.
- The color of urine indicates the concentration ability of the kidneys and the state of water-salt balance. In a healthy person of any age, it should be straw-yellow. In the morning it is different, since urine becomes more concentrated overnight (more substances are formed, less liquid). When drinking less water per day or increased sweating, urine undergoes temporary physiological changes and a color deviation to amber appears.
- Transparency of urine: normally, the liquid should be free of impurities, sediment, cloudiness, and foam. When examined in the light, complete transparency is revealed. Cloudiness is detected when the urinary system is disrupted.
- The smell of urine is specific, not putrid. For children, it is typical for it to change after eating various foods, since the filtration capacity of the kidneys is not developed.
- Specific gravity (density). This physical indicator evaluates the filtration function of the kidney glomeruli; the more substances (protein, glucose) are released through the organ, the darker the urine and the higher the specific gravity. The density of urine depends on the food consumed: from protein - it increases, from a large amount of vegetables - it decreases.
- Acid-base state. Depends on the ratio of acids and alkalis that are released from the blood into the kidneys and bladder. The alkaline index is typical for newborns; it increases with age.
- Protein cannot be detected in a healthy person of any age. The appearance of protein is observed during pathological processes in the body.
- Glucose in the urine is usually absent in a healthy person of any age; it appears when there is a metabolic disorder. It is determined in the urine if there is an excess of carbohydrate in the blood. The appearance of glucose is observed in diabetes and kidney disorders.
- The epithelium in urine is the cells that line the urinary tract. Present in small amounts in healthy people of all ages. If the reading is elevated, the doctor will look for inflammation of the urinary system. Most often it occurs with inflammation of the bladder and urethra.
- Casts are structures that form inside the kidney tubules. A urine test of a healthy child does not reveal them. Their appearance is allowed only for newborns. If casts are detected, this indicates renal failure.
- Leukocytes are cells of the immune system; they serve to destroy foreign microorganisms. Therefore, if they appear numerously, the therapist will suspect an infection caused by microbes. Their number depends on the age of the child.
- Red blood cells are cells of the intravascular fluid that carry protein - hemoglobin. Their number for a normal urine test is limited. If the number of red blood cells has increased, it means that damage has occurred to the mucous membrane of the urinary system. The number of normal red blood cells is the same for all ages.
- Bacteria and fungi are absent in healthy people. Their appearance occurs due to improper collection of excretory fluid or long transportation. Microbes in the analysis are detected in pyelonephritis in children.
- Salts appear in healthy people with a typical diet (consumption of pickles, table salt in the diet). In infants, when complementary foods are introduced or breastfeeding, it is found to be normal. Many crystals are found only in the presence of urolithiasis.
- Mucus is formed after inflammatory diseases of the urinary system; it is absent in healthy people.
- Bilirubin, urobilinogen absent, is a sign of liver disease.
- Ketone bodies are a component of fat and carbohydrate metabolism; they are absent in healthy people and appear only in young children after a long carbohydrate-free diet.
To evaluate the interpretation of a general urine test, contact a therapist. Diseases pass with an increase in several indicators, for example, leukocytes, red blood cells and casts increase after the onset of urolithiasis.
Research results
Interpretation of the results must be carried out taking into account the fact that each laboratory has its own standard indicators. Therefore, when interpreting, it is necessary to take into account the general well-being of the person and the complaints presented by him.
However, the analysis results sometimes turn out to be incorrect due to the influence of various factors. The test results may be distorted if the patient violated the rules for collecting urine. Taking certain substances and medications leads to incorrect results. Factors that negatively affect the bottom line:
- antibiotics of the tetracycline group;
- drugs containing adrenaline;
- narcotic analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs;
- gold-based preparations.
Antibiotics of the tetracycline group
Diastase indicators may also be unreliable if the patient was taking blood thinners, hormonal contraceptives, or diuretics.
An incorrect diagnosis based on urine diastase analysis occurs if the urine was collected in an unclean container. False readings may be due to contamination of the obtained biological material. In addition, the result is unreliable when the person taking the test had a cold or infectious disease accompanied by a cough.
To exclude an incorrect diagnosis when receiving test results different from the norm, it is recommended to conduct a repeat analysis. A diagnosis made on the basis of these indicators should be confirmed only after a thorough examination.
Before collecting tests, the patient is required to consult a doctor; this will help avoid controversial issues and conflicts when obtaining the result. All symptoms of the body must be reported to the doctor in advance; do not remain silent about hereditary diseases or allergic reactions, seasonal colds.