Types of epithelial cells
There are several types of epithelial tissue:
- Single layer
. It can be divided into several more: flat, edged, cylindrical and cubic; - Multilayer
. This type includes flat keratinized or non-keratinized, glandular, transitional and, quite rarely, cubic and cylindrical.
Doctors and various laboratories most often use the term “squamous epithelium”. Using an analysis of the quantitative content of epithelial tissue in a smear or urine, the doctor can draw appropriate conclusions about the patient’s health and give the necessary recommendations for treatment. There are certain standards; in a healthy person, the content of squamous epithelium is within certain permitted values. A significant increase in indicators indicates a progressive course of the inflammatory process, which means that prompt therapeutic intervention is required.
Normal amount of epithelium in the smear
To conduct a general clinical examination, material is taken from three zones
: from the outside of the cervix, from the urethra and cervical canal.
The purpose of this study is to identify and prevent inflammatory processes in the organs of the woman’s reproductive system. Indications for taking material are the following symptoms:
- suspicious, specific discharge;
- painful cramps in the lower abdomen not associated with menstruation;
- change in the color of the external genitalia;
- severe itching of the genitals.
A smear of the vaginal secretion flora must be taken from all women planning pregnancy in the near future, pregnant women and taking antibacterial drugs, antitumor agents and corticosteroids for a long time, as they reduce the protective functions of the immune system.
To obtain more objective results, it is necessary to exclude the use of any drugs used vaginally for 3 days, and to exclude sexual intercourse for 24 hours, otherwise the epithelium in the smear may be significantly overestimated.
The norm for women of epithelial cells in a smear on different days may differ, depending on the menstrual cycle.
Detection of a higher than normal number of cells in a smear may indicate a possible pathological process of an inflammatory nature (vaginitis, cervicitis, urethritis). While its insignificant amount indicates insufficient production of the necessary sex hormones.
Table for visual interpretation of analyses.
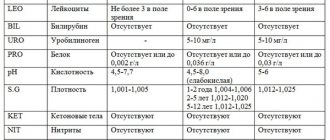
| Indicators | V | C | U |
| Epithelium is flat | From 5 to 10 | From 5 to 10 | From 5 to 10 |
| Leukocytes | 0 to 10 | From 0 to 30 | 0 to 5 |
| Gonococci | — | — | — |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | — | — | — |
| Key cells | — | — | — |
| Yeast-like fungi | — | — | — |
| Slime | Moderate content | Moderate content |
The pregnancy period is associated with hormonal changes that increase the risk of developing various pathological processes in the vagina. During this period, an analysis of the microflora in the birth canal is required at least three times throughout the pregnancy. If there are complaints and other indications, additional research is carried out.
Complexes with this research
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure RUB 16,590 Composition
Female check-up No. 2 Preventive examination of the urogenital tract RUB 5,140 Composition
Pregnancy planning. Cervical screening and STIs RUB 3,450 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 11,430 RUR
- Women's reproductive health RUR 2,780
- Women's safety RUR 1,640
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 6,310 RUR
Normal amount of epithelium in urine
Even completely healthy people have squamous epithelium in their urine. The norm for women is slightly higher than for men, but, regardless of gender, the normal number of cells is calculated in the units.
The same indicator of the number of squamous epithelial cells in urine may indicate the healthy condition of a woman and developing prostatitis or urethritis in a man.
In a person who does not have any diseases, up to 10 units
.
Exceeding this norm indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the genitourinary system. Significant excesses of indicators can be detected in the following diseases:
- cystitis;
- prostatitis;
- urethritis;
- nephrosis;
- acute nephritis.
To determine the number of cells, a general analysis is taken, in which several parameters of urine are studied at once, which include the following: leukocytes, erythrocytes, casts, bacteria, protein, glucose. However, it is not advisable to conduct a study only for the presence of epithelium in the urine, since the indicator is rather weak and does not always completely indicate the presence of the disease. Therefore, the analysis is carried out comprehensively, with the study of various characteristics.
Reference values for general urine analysis.
| Color | Yellow-straw |
| Smell | Unsharp |
| Transparency | Transparent, not cloudy |
| Reaction | pH 4 to 7 |
| Protein | Maximum 0.033g/l |
| Density | From 1012 to 1022 g/l |
| Glucose | Maximum 0.8 mmol/l |
| Ketone bodies | — |
| Hemoglobin | — |
| Leukocytes | Until 6 |
| Red blood cells | Until 3 |
| Epithelium | Within 10 |
| Cylinders | Single |
| Mushrooms | — |
| Bacteria | — |
| salt | — |
Smear degree of purity (for flora)
Description A smear of purity (for flora) is the easiest way to detect some pathogens that cause diseases such as thrush, vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, etc.
Indications for taking a smear for flora are:
- the presence of vaginal discharge, indicating a possible inflammatory process;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning or itching in the vagina;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- pregnancy planning;
- preventive examination, etc.
Preparing for a smear test
1-2 days before taking a smear, sexual intercourse and douching are not recommended, and the use of lubricants, suppositories, tablets and creams is excluded. A smear should not be taken during menstruation, as menstrual flow distorts the laboratory picture. 2-3 hours before going to the gynecologist you should not urinate. Genital hygiene is not carried out on the day of the visit to the gynecologist, and the day before - only with warm water without using soap.
It is advisable to take a smear in the first days after menstruation or before the start of a new cycle.
Decoding smears for flora
The results of a laboratory smear test for flora may indicate the following data:
White blood cells in a gynecological smear are present only in small quantities. The norms for their content in the vagina and urethra are no more than 10 in the field of view, and no more than 30 in the cervical canal. An increase in the number of leukocytes in a smear indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
During pregnancy, the leukocyte count in the smear increases slightly. Their number can reach 20-30 in the field of view.
Squamous epithelium is the cells lining the surface of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervical canal. Their normal amount depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Normally, squamous epithelium should be detected in a smear in the amount of 5-10 cells. If no epithelium is found at all, this may indicate atrophy of the epithelial layer, while an increase in the number of squamous epithelial cells may indicate inflammation.
Mucus - found in moderate quantities in a gynecological smear and is normal, since it is produced by the glands of the cervical canal and vagina.
Lactobacilli (Doderlein bacilli) - normally these bacilli are present in large quantities in the vaginal microflora. A decrease in their number indicates bacterial vaginosis.
Yeast - in small quantities, is part of the normal microflora of the vagina, but its increase (over 104 CFU/ml), especially against the background of characteristic itching in the vagina and curdled discharge, is a sign of thrush.
“Key” cells are squamous epithelial cells covered with bacteria - gardnerella. The presence of a large number of them in the smear indicates gardnerellosis.
Leptothrix is an anaerobic gram-negative bacteria found in mixed sexually transmitted infections such as candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis or trichomoniasis and chlamydia. Detection of these bacteria in a gynecological flora smear requires the appointment of a more serious examination than a simple smear.
Mobiluncus is also an anaerobic microorganism found in women with candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis.
Trichomonas is the simplest single-celled microorganism that causes inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area.
Gonococci (diplococci) are the causative agents of gonorrhea. Normally they are not detected in a smear.
Escherichia coli is normally present in the smear only in small quantities. The content of a large amount of E. coli in the smear indicates bacterial vaginosis, violation of personal hygiene rules and contamination of the smear with feces.
Cocci (streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci) are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. They are part of the normal flora in small quantities, while an increase in their number indicates the presence of infection.
The letter values indicate the areas from which the swabs were taken. So the letter “U” stands for the urethra, “V” for the vagina, and “C” for the cervix.
Indicators of a normal smear in women
| Normal in the vagina (V) | Normal in the cervix (C) | Normal in the urethra (U) | What if it's not normal? | |
| Leukocytes | 0 – 10 in field of view | 0 - 30 in field of view | 0 - 5 in view | An increase in leukocytes indicates the presence of inflammation |
| Epithelium (squamous epithelium) | moderately | moderately | moderately | A large amount of epithelium may indicate inflammation. The absence of epithelium in the smear is also not good and may indicate a lack of the female sex hormone estrogen. |
| Slime | moderately | moderately | Moderate or absent | A large amount of mucus indicates inflammation. |
| Gram-positive rods (gr.+), Doderlein rods, lactobacilli | A large number of | none | none | A large number of these sticks in the vagina indicates good immunity. You are not in danger of inflammation. A decrease in the number of these rods or their absence indicates a disturbance in the composition of the vaginal microflora and inflammation. |
| Gram-negative rods (gr.-), anaerobic rods | none | none | none | The appearance of these sticks indicates dysbacteriosis and possible inflammation. |
| Gonococci (“gn”, Neisseria gonorrhoeae) | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Detection of gonococci indicates gonorrhea. |
| Trichomonas (Trichomonas vaginalis) | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | The detection of Trichomonas indicates trichomoniasis. |
| Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | The detection of chlamydia indicates chlamydia. |
| Key cells or atypical cells | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | The presence of key cells indicates inflammation (bacterial vaginosis). |
| Yeast fungi, or yeast, or candida (candida) | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | The presence of yeast fungi indicates candidiasis (thrush). |
Based on all of the above indicators, the degree of vaginal cleanliness is determined, which reflects the state of its microflora as a whole. In gynecology, it is customary to distinguish four degrees of vaginal cleanliness:
- 1. Typical for healthy women. The vaginal microflora is optimal. This degree is extremely rare.
- 2. There are minor deviations in the microflora. The most common degree of cleanliness among healthy women.
- 3. Deviations from the norm are detected in the smear (increase in the number of fungi, growth of opportunistic bacteria). This degree indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
- 4. A significant deviation from the norm is determined in the smear, which indicates the presence of bacterial vaginosis and other sexually transmitted infections.
Analysis of a smear for flora is only a preliminary step in the diagnosis of diseases, therefore, if abnormalities are detected in it, the doctor may prescribe you a repeat test, which will include bacteriological culture and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. Diagnostics using the PCR method may also be required, which can detect hidden infections of the genital tract.
Therapeutic procedures
The most commonly diagnosed disease of the female reproductive system is vaginitis.
. It is caused by various fungi, bacteria, parasites, and a decrease in natural hormonal support. Its treatment is carried out using antibacterial therapy, antifungal agents, depending on the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process.
Failure to go to the clinic in a timely manner can aggravate the problem, because as the infection progresses, it rises higher and affects the uterus.
Urethritis is one of the most common diseases of the genitourinary system. The cause of inflammation can be chlamydia, herpes, cytomegalovirus.
It is unacceptable to use any medications without medical supervision.
Treatment is most often carried out with the help of antibacterial drugs if the pathogen is infectious in nature. Non-infectious urethritis is treated with special substances that relieve irritation of the mucous membranes. After restoration of the normal amount of epithelium and other indicators, the patient’s condition stabilizes.