Cytological examination of smears from the cervix allows one to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence or absence of signs of pathological processes (reactive, precancerous, tumors). When other laboratory methods identify an infectious agent (human papillomavirus, bacterial and parasitic infections), the cytological method allows one to evaluate the body’s response to the infectious agent, the presence or absence of signs of damage, proliferation, metaplasia or transformation of the epithelium. It is also possible, by examining a smear, to determine the cause of changes in the epithelium (the presence of inflammation with an approximate or confident determination of pathogenic microbiota (microflora), pathological processes associated with hormonal, medicinal, mechanical, radiation effects on the woman’s body and the cervix, conditions fraught with the risk of dysplasia and cervical cancer, and when they develop, establish the correct diagnosis.In this regard, cytological examination is used both for screening (smears from a visually normal cervix) and in the presence of changes in the mucous membrane visible during a gynecological examination.
Receiving material
Cervical cancer most often develops in the transformation zone, it is preceded by background processes and intraepithelial lesions (epithelial dysplasia), which can be located in small areas, so it is important that material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the junction of squamous and columnar epithelium . The number of altered cells in a smear varies, and if there are few of them, then the likelihood increases that pathological changes may be missed when viewing the specimen. For effective cytological examination it is necessary to consider:
- During preventive examinations, cytological smears should be taken from women, regardless of complaints, the presence or absence of changes in the mucous membrane. Cytological examination should be repeated at least once every three years;
- it is advisable to obtain smears no earlier than on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation;
- you cannot take material within 48 hours after sexual intercourse, use of lubricants, vinegar or Lugol’s solution, tampons or spermicides, douching, insertion of medications, suppositories, creams into the vagina, including creams for performing ultrasound examinations;
- pregnancy is not the best time for screening, as incorrect results are possible, but if you are not sure that the woman will come for examination after childbirth, it is better to take smears;
- for symptoms of acute infection, it is advisable to obtain smears for the purpose of examining and identifying pathological changes in the epithelium, the etiological agent; Cytological control is also necessary after treatment, but not earlier than 2 months. after completing the course.
Material from the cervix should be taken by a gynecologist or (during screening, preventive examination) by a well-trained nurse (midwife).
It is important that the smear contains material from the transformation zone, since about 90% of tumors come from the junction of the squamous and columnar epithelium and the transformation zone, and only 10% from the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal.
For diagnostic purposes, material is obtained separately from the ectocervix (vaginal portion of the cervix) and endocervix (cervical canal) using a spatula and a special brush (such as Cytobrush). When conducting a preventive examination, Cervex-Brush, various modifications of the Eyre spatula and other devices are used to obtain material simultaneously from the vaginal part of the cervix, the junction (transformation) zone and the cervical canal.
Before obtaining the material, the cervix is exposed in “mirrors”; no additional manipulations are performed (the cervix is not lubricated, mucus is not removed; if there is a lot of mucus, it is carefully removed with a cotton swab without pressing on the cervix). A brush (Eyre spatula) is inserted into the external os of the cervix, carefully guiding the central part of the device along the axis of the cervical canal. Next, its tip is rotated 360° (clockwise), thereby obtaining a sufficient number of cells from the ectocervix and from the transformation zone. The instrument is inserted very carefully, trying not to damage the cervix. Then the brush (spatula) is removed from the canal.
Treatment of leukocytes in a smear
Based on the results of a complete comprehensive diagnosis, our gynecologist individually selects a treatment regimen for the inflammatory process. It is a full examination that will reveal the true reason why there are many leukocytes in the smear and treatment in this case will be effective. It is TREATMENT , and not treatment until the next exacerbation, as happens in most cases.
Rarely, there is a situation where good treatment has been carried out, but the leukocytes in the smear remain elevated. This is one of the most difficult problems to solve. It seems that in such cases this is due to dysbiosis at the level of the vagina and cervix. Even multiple courses of antibiotic therapy often do not help; infections after treatment with antibiotics may also not be detected. And the leukocytes in the smear are elevated and remain at a high level. In such cases, it is recommended to periodically conduct courses of local sanitation (suppositories with antibacterial components) and persistently fight to maintain normal intestinal microflora.
Preparation of drugs
Transfer of the sample to a glass slide (traditional smear) should occur quickly, without drying out or losing mucus and cells adhering to the instrument. Be sure to transfer the material to the glass on both sides with a spatula or brush.
If it is intended to prepare a thin-layer preparation using the liquid-based cytology method, the brush head is disconnected from the handle and placed in a container with a stabilizing solution.
Fixation of strokes
performed depending on the intended staining method.
Papanicolaou and hematoxylin-eosin staining are the most informative in assessing changes in the cervical epithelium; any modification of the Romanovsky method is somewhat inferior to these methods, however, with experience, it allows one to correctly assess the nature of the pathological processes in the epithelium and the microflora.
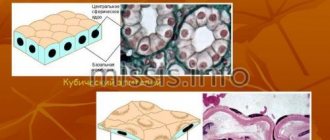
The cellular composition of smears is represented by desquamated cells located on the surface of the epithelial layer. When adequate material is obtained from the surface of the mucous membrane of the cervix and from the cervical canal, the cells of the vaginal portion of the cervix (stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium), the junction or transformation zone (cylindrical and, in the presence of squamous metaplasia, metaplastic epithelium) and cells of the cervical canal enter the smear. columnar epithelium). Conventionally, cells of multilayered squamous non-keratinizing epithelium are usually divided into four types: superficial, intermediate, parabasal, basal. The better the epithelium’s ability to mature, the more mature cells appear in the smear. With atrophic changes, less mature cells are located on the surface of the epithelial layer.
Physiological leukocytosis
Associated with the redistribution of leukocytes, they move from the parietal pool (reserve) into the general bloodstream.
Physiological types of leukocytosis include:
- Digestive. 2-3 hours after eating, leukocytes are released from the depot into the blood, and it flows to the gastrointestinal tract for better digestion. Immune cells are necessary for the submucosal layer of the stomach and intestines for protection, since microorganisms contained in the air, water and on products enter the body with food.
- Myogenic (muscular). Intense muscle work triggers a cascade of reactions, stimulating the work of all organs, tissues and cells. During and after physical activity, the number of white blood cells can be 3-5 times higher than normal.
- Elevated leukocytes during pregnancy are a necessary measure to protect the mother’s body from infection entering the blood. If in the first trimester leukocytosis is relative, but by the third trimester the leukocytes exceed the norm by 2 times and this is not considered a pathology. In addition, leukocytes are involved in stimulating uterine contractions during childbirth.
- In the first 2-3 days of life, elevated leukocytes in a child are the norm. During pregnancy, the mother's immune system protects the fetus. After birth, all formed elements are actively released into his blood from the depot. Leukocytes are necessary to protect the child’s body from an aggressive external environment.
- Painful. When pain receptors are irritated, blood vessels constrict, blood pressure and adrenaline levels increase. This is a stress reaction, in response to which leukocytes are redistributed and released from the parietal reserve into the blood, leading to short-term leukocytosis.
- Stress. Emotional outbursts cause changes in blood vessels, hormonal surges, increased blood pressure and heart rate. In response to this, the number of leukocytes in the blood increases, as during painful stimulation.
With physiological leukocytosis, there is a slight increase in the number of leukocytes without changes in the leukocyte formula (the ratios of all 5 fractions of leukocytes). This phenomenon is short-term and harmless.
Interpretation of cytological examination results
The most common at present is the Bethesda classification (The Bethesda System), developed in the USA in 1988, to which several changes have been made. The classification was created to more effectively transfer information from the laboratory to clinical doctors and ensure standardization of treatment of diagnosed disorders, as well as follow-up of patients.
The Bethesda classification distinguishes squamous intraepithelial lesions of low grade and high grade (LSIL and HSIL) and invasive cancer. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions include changes associated with human papillomavirus infection and mild dysplasia (CIN I), high-grade - moderate dysplasia (CIN II), severe dysplasia (CIN III) and intraepithelial carcinoma (cr in situ). This classification also contains indications of specific infectious agents that cause sexually transmitted diseases.
To designate cellular changes that are difficult to differentiate between reactive states and dysplasia, the term ASCUS - atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (squamous epithelial cells with atypia of unclear significance) has been proposed. For a clinician, this term is not very informative, but it directs the doctor to the fact that this patient needs examination and/or dynamic monitoring. The Bethesda classification has now also introduced the term NILM – no intraepithelial lesion or malignancy, which combines normal, benign changes, and reactive changes.
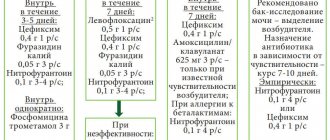
Since these classifications are used in the practice of a cytologist, below are parallels between the Bethesda classification and the classification common in Russia (Table 22). Cytological standardized report on material from the cervix (form No. 446/u), approved by order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated April 24, 2003 No. 174.
The reasons for receiving defective material are different, so the cytologist lists the types of cells found in the smears and, if possible, indicates the reason why the material was considered defective.
Cytological changes in the glandular epithelium
| Bethesda Terminology developed in Bethesda (USA, 2001) | Terminology adopted in Russia |
| ASSESSMENT OF SWIM QUALITY | |
| Full material | The material is adequate (a description of the cellular composition of the smear is given) |
| The material is not complete enough | The material is not adequate (a description of the cellular composition of the smear is given) |
| Unsatisfactory for evaluation | Cellular composition is not enough to confidently judge the nature of the process |
| Satisfactory to evaluate, but limited by something (identify reason) | |
| Within normal limits Metaplasia (normal) | Cytogram without features (within normal limits) - for reproductive age Cytogram with age-related changes in the mucous membrane: - atrophic type of smear - atrophic type of smear with leukocyte reaction Estrogenic type of smear in a postmenopausal woman Atrophic type of smear in a woman of reproductive age |
| BENIGN CELL CHANGES | |
| Infections | |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Trichomonas colpitis |
| Fungi morphologically similar to the genus Candida | Elements of Candida fungus detected |
| Cocci, gonococci | Diplococci located intracellularly were found |
| Predominance of coccobacillary flora | Flora coccobacillary, possibly bacterial vaginosis |
| Bacteria morphologically similar to Actinomyces | Flora of the Actinomycetes type |
| Other | Flora of the type Leptotrichia |
| Flora – small sticks | |
| Flora – mixed | |
| Cellular changes associated with Herpes simplex virus | Epithelium with changes associated with Herpes simplex |
| Possibly chlamydial infection | |
| Reactive Changes | |
| Inflammatory (including reparative) | The changes found correspond to inflammation with reactive changes in the epithelium: degenerative, reparative changes, inflammatory atypia, squamous metaplasia, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and/or others. |
| Atrophy with inflammation (atrophic | Atrophic colpitis Atrophic type of smear, leukocyte reaction Mucosal epithelium with hyperkeratosis Mucosal epithelium with parakeratosis Mucosal epithelium with dyskeratosis Reserve cell hyperplasia Squamous metaplasia Squamous metaplasia with atypia |
| Radiation changes | Epithelium of the mucous membrane with radiation changes |
| Changes associated with the use of intrauterine contraceptives | |
| PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE FLAT EPITHELIUM | |
| Squamous epithelial cells with atypia of undetermined significance (ASC-US*) Squamous epithelial cells with atypia of undetermined significance not excluding HSIL (ASC-H) | The changes found are difficult to differentiate between reactive changes in the epithelium and dysplasia. Cells were found that were difficult to interpret (with dyskaryosis, enlarged nuclei, hyperchromic nuclei, etc.) |
| Changes in squamous epithelium (non-tumor, but worthy of dynamic observation) | |
| Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL): human papillomavirus infection, mild dysplasia (CIN I) | Epithelium of the mucous membrane with signs of papillomavirus infection. The changes found may correspond to mild dysplasia. |
| High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL): moderate, severe dysplasia and intraepithelial carcinoma (CINII, CIN III) | The changes found correspond to moderate dysplasia. The changes found correspond to severe dysplasia. The changes found are suspicious for the presence of intraepithelial cancer. |
| Invasive cancer | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma with keratinization Small cell squamous cell carcinoma |
| Glandular hyperplasia The changes found correspond to endocervicosis | |
| Atypical glandular epithelial cells (possible assumptions): – Unclear significance (AGUS); – suspicious for neoplasia; – endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS); – adenocarcinoma | Glandular hyperplasia with atypia of the dysplasia type (I, II, III) Adenocarcinoma |
| Endometrial cells are cytologically benign (in a woman in menopause, etc.) | |
| Endometrial adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma of another location Adenocarcinoma without additional characteristics | Adenocarcinoma, possibly endometrial adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma NOS (not otherwise specified) |
| Other malignant tumors (if possible, determine the nosological form) | |
| Assessment of hormonal status | |
* whenever possible, ASCUS should be defined as similar to reactive, reparative or precancerous processes;
** changes associated with exposure to human papillomavirus, previously designated as koilocytosis, koilocytic atypia, condylomatous atypia, are included in the category of mild changes in squamous epithelial cells;
*** If possible, it should be noted whether the changes relate to CIN II, CIN III, whether there are signs of cr in situ;
****hormonal assessment (carried out only on vaginal smears): – the hormonal type of smear corresponds to age and clinical data; – the hormonal type of smear does not correspond to age and clinical data: (decipher); – hormonal assessment is impossible due to: (specify the reason).
The role of ethnicity
About half of the women in the study were Hispanic, and the rest were not. The authors provide evidence of higher rates of cervical cancer in Hispanic women. They sought to discover any ethnic factors that may lie beyond "lack of screening" or "unequal access to healthcare."
Some data has been found that supports this. For example, Hispanic women in the study were more likely to have low levels of vaginal Lactobacillus populations and higher populations of Sneathia bacteria.
This may suggest that the different composition of the vaginal microflora in Hispanic women may be a potential risk factor for the development of cervical cancer in this population.
Integration of various laboratory methods
In the diagnosis of cervical diseases, clinical data and microflora test results (classical microbiological (culture), ANC methods (PCR, RT-PCR, Hybrid Capture, NASBA, etc.) are important).
If it is necessary to clarify the pathological process (ASC-US, ASC-H), cytological examination is, if possible, supplemented with molecular biological ones (p16, oncogenes, methylated DNA, etc.).
HPV detection tests have low prognostic significance, especially in young women (under 30 years of age), due to the fact that in most patients in this age group, HPV infection is transient. However, despite the low specificity of the test for intraepithelial tumors and cancer, it can be used as a screening test in women under 30 years of age, followed by cytological examination. Sensitivity and specificity increase significantly with the combined use of the cytological method and research to detect HPV, especially in patients with questionable cytological data. This test is important in the management of patients with ASC-US, during follow-up to determine the risk of relapse or progression of the disease (CIN II, CIN III, carcinoma in situ, invasive cancer).
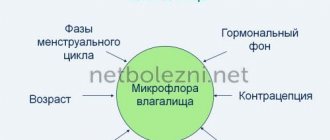
How are vaginal microflora and cervical cancer related?
Infection with certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV) is a long-known risk factor for the development of cervical cancer.
However, scientists from the University of Arizona (Phoenix) suggest that there are other factors that affect the condition of the cervix.
An article published in the journal Scientific Reports said that patients with cervical cancer or precancer were found to have a different composition of vaginal bacterial flora compared to women who did not have changes in cervical conditions .
It is assumed that there is a direct connection between beneficial bacteria and a healthy cervix, as well as harmful bacteria and various pathologies and an increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
In patients with cancer and precancer,” explains senior study author Melissa M. Herbst-Kralovec, who is an assistant professor at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, “lactobacillus—the good bacteria—is replaced by a mixture of bad bacteria.
Types of leukocytes
Leukocytes are divided into two large groups:
- granular, which are characterized by the presence of a large segmented (divided into parts) nucleus and granules in the cytoplasm (the main semi-liquid mass of the cell, its internal environment). They are also called granulocytes.
- non-granular, which do not have specific granules in the cytoplasm (internal environment of the cell). Their second name is “agranulocytes”.
Each group has its own types of leukocytes. They differ in structure, appearance, properties and functions.
Granular leukocytes:
- Neutrophils.
- Eosinophils.
- Basophils.
Non-granular leukocytes:
- Lymphocytes.
- Monocytes.
Let's look at each subgroup in detail.
Neutrophils
They are the first to arrive at the site of injury - to places where tissues have been damaged and/or where microorganisms have penetrated.
The main task of neutrophils is to capture and digest microorganisms (bacteria and viruses).
A sharp increase in neutrophils in the blood (neutrophilia) indicates an acute inflammatory process, presumably of a viral nature. Most often, the proportion of immature forms—juvenile and rod forms—increases.
Eosinophils
Leukocytes with pronounced granularity of the cytoplasm (internal environment of the cell).
The main task of eoisnophiles is the destruction of parasites and participation in allergic reactions.
An increase in eosinophils in the blood is called eosinophilia. Its presence indicates the presence of a parasitic, allergic (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis) or cancer (eosinophilic leukemia, Hodgkin's disease) disease. In addition, eosinophilia is characteristic of bronchial asthma.
Basophils
The smallest population of leukocytes with fine granularity.
The main task of basophils is to release histamine, which is necessary for the inflammatory process and allergic reaction.
An increase in the content of basophils in the blood is called basophilia.
Basophilia indicates increased sensitivity of the immune system, which is typical in allergic reactions. For example, with urticaria or serum sickness.
Lymphocytes
Non-granular leukocytes with a large rounded nucleus. By size they are divided into large, medium and small.
There are 3 types of lymphocytes:
- T lymphocytes. The main components of cellular immunity. They destroy foreign particles, direct and regulate the activity of other immune cells and inhibit an excessive immune response.
- B lymphocytes. Participate in humoral immunity. They recognize foreign structures (antigens) and produce protective proteins (antibodies) to destroy them.
- NK lymphocytes. Destroys cells affected by bacteria and viruses, as well as tumor cells.
The main task of lymphocytes is to provide a specific immune response.
An increase in lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphocytosis. It is characteristic of acute infections and blood diseases (leukemia).
Monocytes
The largest leukocytes. They are not grainy, but have a large core.
Monocytes are macrophages, cells capable of absorbing and digesting large solid particles. After phagocytosis, macrophages, as a rule, do not die.
The main task of monocytes is to “clean up” the lesion from damaged or dead cells and microorganisms.
An increase in monocytes (monocytosis) occurs during infections, blood diseases, cancer, after surgery and during the recovery period.