Author of the article
Anatoly Shishigin
Reading time: 3 minutes
AA
Each of the human organs is part of a specific body system that is responsible for its functions and the overall integrity of the life process. One of these important organs is the bladder, which is part of the genitourinary system.
This organ is elastic and unpaired, located in the pelvic area. Urine filtered by the kidneys enters the bladder through the ureters, and leaves the body through the urethra, the urethral tube. There is no exact data on the size of the organ, but on average it ranges from 500 to 1000 ml.
Leukoplakia of the bladder in women
In recent years, there have been changes in both the symptoms of chronic cystitis in women of all ages and approaches to the treatment of chronic cystitis. One problem is leukoplakia of the bladder, areas of which are found in 72% of women with urinary disorders. Leukoplakia of the bladder photo is always located in the area of the cervix and Lieto's triangle, it begins with individual small spots that gradually merge, completely or partially covering the bladder triangle with a crust of melted snow.
Why is leukoplakia of the bladder in the area of Lieto's triangle
Such a clear connection of leukoplakia of the bladder to Lieto’s triangle can be explained by the fact that the bladder triangle and the vagina originate from the same embryonic tissue, and the areas of leukoplakia of the bladder are hormone-dependent, changing during pregnancy and the phases of the menstrual cycle.
The main types of diseases of the Lieto triangle
Very often, various pathologies and neoplasms arise in this area, and inflammatory processes arise. The most common are: cancer, leukoplakia, trigonitis, urethrotrigonitis.
Leukoplakia of the bladder
Leukoplakia literally translated from Greek means “white plaque.” Leukoplakia of the bladder is a pathology in which the normal mucous membrane of the organ becomes keratinized. In women, leukoplakia is observed much more often than in male patients, and this is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the genitourinary system. Most often, leukoplakia occurs in the bladder triangle, where the mucosa is absolutely smooth. Inside the bladder, the surface forms folds. It is at the bottom of this organ that leukoplakia plaques are attached.
More on the topic: How does bladder endometriosis manifest and how to treat it?
Diagnosis of leukoplakia is most often done in a complex of procedures to identify other diseases, such as:
- cystitis in the chronic stage. Its symptoms are very similar to leukoplakia, the differences can only be found when a biopsy is performed during cystoscopy. Instrumental methods confirm inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder, on which there are no whitish spots of leukoplakia with an altered epithelial layer;
- cancer in the bladder, which is asymptomatic or manifests itself as leukoplakia. Cystoscopy reveals small ulcers and other similar changes in the epithelial layer. A biopsy reveals atypical epithelial cells characteristic of cancer.
The diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted only after an endoscopic examination supplemented by a biopsy.
Trigonite
Trigonitis is an inflammation of the bladder, affecting its bottom, Lieto's triangle. Most often, this disease can be found in the chronic form of cystitis than in its acute stage. The disease usually affects women and is of a stagnant nature. In this case, blood circulation at the bottom of the bladder and in its neck is disrupted, the uterus is in the wrong position with the vaginal wall lowered in front. As a rule, all this is accompanied by chronic inflammatory processes in the parametrium.
Symptoms are mild, only slightly more frequent deurination, slight discomfort when urinating, slight hematuria. There are no changes in the urine itself or they differ only slightly from normal values. Cystoscopy will show looseness of the mucous membranes in Lieto's triangle, swelling and hyperemia.
Trigonitis is dangerous due to the occurrence of reflux, when urine flows back into the bladder, as well as the formation of ascending type pyelonephritis.
Urethrotrigonitis
Utretrotrigonitis is one of the types of trigonitis that affects the bladder triangle. It is characterized by inflammation of the mucous surfaces of the urethral canal and the very bottom of the bladder. It is most often found in cases of gonorrhea.
Symptoms of leukoplakia of the bladder
Leukoplakia of the bladder
may be an abnormal response to bladder inflammation, irritating the trigone region. Leukoplakia of the bladder becomes the site of least resistance to infection, as bacteria can more easily adhere or penetrate into this area than into normal urothelium. Leukoplakia of the bladder is an area of the bladder covered with squamous epithelium; normally, the mucous membrane of the bladder is lined with transitional epithelium. Studies have shown weakened tightness of the altered epithelium to urine. Unlike transitional epithelium, squamous epithelium lacks tight intercellular junctions, therefore, urine can penetrate into the submucosal layer and cause inflammatory changes. Accordingly, pain receptors in the bladder triangle are irritated, with the subsequent development of an increased urge to urinate.
What is special about the vesical triangle?
The Lieto Triangle has a unique feature. It consists of a collection of many nerve endings. There are similar nerve ganglia inside the bladder, as well as scattered neurons, which are part of the autonomic nervous system. But it is in the area of the bladder triangle that their concentration is especially high.
Lieto's triangle of the bladder is the most firmly fixed of all the anatomical parts in its structure. This area does not change or increase over time. The most developed layer in it is the muscular one, called the detrusor. It is thanks to his efforts that during contractions the natural release of urine occurs.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia of the bladder
Cystoscopy does not reveal inflammatory changes in the area of the bottom, apex and walls of the bladder. At the same time, the mucous membrane of the bladder triangle and the neck of the bladder was covered with a white coating like snow
, clearly demarcated from the normal, non-hyperemic rest of the bladder mucosa. Histological examination of such areas showed signs of chronic cystitis, with pronounced and widespread squamous metaplasia of the transitional type epithelium, focal sclerosis of the mucous membrane.
Features of the structure of the bladder
The bladder has its own structural features. It often changes size and shape depending on how much fluid it fills. A full organ is round and very voluminous, but when empty it is wrinkled and flat, like a plate.
There is a special free-type region in the organ, which has a triangular shape. It is because of this structure that it received the name vesical triangle. The edges located at the very bottom perform the function of an internal urethral opening. The remaining two angles are needed for the openings of the ureters. The basis is made up of transversely lying striated muscle fibers. With its sides it is moved towards the ureter, tightly adjacent to the walls of the bladder.
Treatment of leukoplakia of the bladder
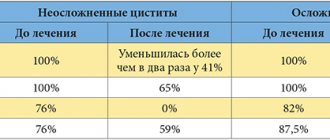
Most women with leukoplakia of the bladder receive repeated courses of antibiotic therapy and instillation of anti-inflammatory drugs into the bladder. The effectiveness of treatment for leukoplakia is weak and insufficient.
TUR vaporization of bladder leukoplakia
In our clinic, patients successfully undergo endoscopic treatment of bladder leukoplakia
TUR with vaporization of leukoplakia of the bladder under spinal anesthesia. Surgical treatment of bladder leukoplakia occurs without complications, macrohematuria is not observed in the postoperative period, catheterization of the bladder is not required, but antibiotic therapy and pain relief are required. A few days after the operation, there was a disappearance of frequent urge to urinate, pain when urinating, and a decrease in nighttime urges. A month later, epithelization of the bladder mucosa occurs in the place where there was leukoplakia.
Therapeutic tactics aimed at cauterizing leukoplakia of the bladder are quite widely used by urologists. Treatment of leukoplakia of the bladder - TUR vaporization of the bladder suppresses the hyperactivity of many receptors located in the neck of the bladder, reduces the symptoms of bladder overactivity, on the other hand, does not cause scarring of the bladder mucosa.
What is Lieto's triangle of the bladder?
Trigonum vesicae, Lieto's triangle, vesical triangle is a special formation in the bottom of the bladder, limited by the ureters on the sides and the internal opening of the urethra below. It is named after the French anatomist, court physician of the 18th century Joseph Lieto.
The bladder triangle is considered the main landmark during the ureteral catheterization procedure during cystoscopy. It is located only 2.5 cm from the delta of the ureters, and at the same distance from the internal opening of the urethral canal. When the organ is full, the distance doubles, and the internal opening is located near the highest point of the triangle. At the same time, this point is also recognized as the lowest located mark of the bladder. Due to the presence of mucous membranes, a small bump forms behind this hole.
More on the topic: Causes of bright urine
There are no folds in the mucosa in places where the openings of the ureters are open in the bladder. Lieto's triangle has its own mucosa, which has not very large glands and branches, which are clusters of transitional epithelial cells. It also has the names Brunn's nest. Due to the high density in connective tissue, the entire submucosal layer is a smooth surface. A feature of the bladder triangle is the frequent occurrence of leukopalkia, neoplasms and inflammation, trigonitis.
Frequently asked questions about the treatment of bladder leukoplakia in Moscow
How to prepare for surgery to remove leukoplakia of the bladder?
To undergo surgery to remove leukoplakia of the bladder or TUR-vaporization of the bladder, it is necessary to undergo a preoperative examination for surgery under general anesthesia. Make an appointment by phone for surgery to remove leukoplakia of the bladder. On the eve of the operation, it is necessary to shave the surgical field - pubis, inner thighs
Will the stitch be visible after surgery to remove leukoplakia of the bladder?
The operation of cauterization of leukoplakia of the bladder is endoscopic, performed through the urethra, so there is simply no stitch
What are the guarantees that there will be no recurrence of bladder leukoplakia after surgery?
We have been treating bladder leukoplakia
and we have excellent results in the treatment of leukoplakia. If you follow the doctor's recommendations after surgery, the result is guaranteed. Relapses after surgery to remove bladder leukoplakia are very rare in our practice. There were mainly cases of relapse of leukoplakia of the bladder after 7-8 years, which required re-operation TUR-vaporization of the bladder
Are there other treatments for bladder leukoplakia?
Unfortunately, there are no other methods of treating bladder leukoplakia. The only way to treat leukoplakia of the bladder is TUR-vaporization of leukoplakia. Unfortunately, laser ablation does not give a lasting result and we abandoned it
What recommendations should be followed after removal of bladder leukoplakia?
Restrictions on physical activity and sexual activity for up to two weeks. There are no further restrictions