Home / Other
Back
Published: 10/23/2020
Reading time: 12 min
0
174
- Normal and deviations What discharge should be normal
- Characteristics of the disease
- What does ammonia smell like?
- Mechanism of occurrence
- Physiological causes Dehydration
- Vaginal candidiasis
- Methods
- Oral medications Etiological treatment
- Effective traditional medicine recipes
Norm and deviations
Normal discharge is a small amount of vaginal mucus that does not have any unpleasant odors and is uniform in consistency. They help maintain healthy microflora, preventing the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
If the mucus acquires foreign aromas, then this is a sign of the development of pathology.
During the period of ovulation, the produced vaginal secretion acquires a yellowish tint and a sticky consistency. Then it becomes transparent again, but changes again before and after menstruation: the norm during this period is the appearance of slight yellowness.
The ammonia smell of discharge in women is considered a pathological sign. The causes may be various diseases of the reproductive system.
What discharge should be normal?
Normally, the secretion secreted by the vagina is odorless and transparent. A slight sour aroma is allowed. When the discharge smells like ammonia, this indicates problems in the genitourinary system. This is beyond the norm and requires consultation with a gynecologist or urologist.
Vaginal secretions may acquire a yellowish tint only during the period of ovulation. Its consistency also changes. The secret becomes sticky. Once ovulation is complete, color and consistency return to normal. Slight yellowness may appear before menstruation. This must be taken into account in a specific phase of the menstrual cycle. In women, yellow discharge with the smell of ammonia is a symptom that signals problems in the body.
Characteristics of the disease
In general, the smell of urine is due to its volume, richness and the content of various chemicals that are filtered by the kidneys from the liquid part of the blood mass. Normally, the daily volume of urine is about 1.6-1.8 liters, and fresh, freshly excreted urine has virtually no odor. Many foods consumed can cause different odors. Concentrated urine (less water content) is also accompanied by some kind of olfactory tint. In addition, the smell of urine appears when it remains in any, even closed, container after a short time. Its delays in the body have a similar effect.
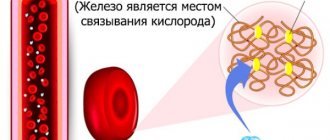
In the human body, ammonia is a byproduct of amino acid metabolism. In a normally functioning body, the liver quickly converts it into urea, which is quietly excreted in the urine. The smell of ammonia in the urine indicates that free ammonia molecules have appeared, which means that the liver has not coped with its function. At the same time, the reverse process of decomposition of urea into ammonia can occur in the kidneys if there is an excess amount of urea. In any case, ammonia is a fairly toxic substance, meaning the presence of ammonia in urine should be a cause for concern.
It should be noted that the smell of ammonia in the urine is much more common in women than in men, which is caused by understandable physiological differences. This is facilitated by both the structure of the genitourinary system with the specific microflora of the vagina, and hormonal changes during menopause or pregnancy.
What does ammonia smell like?
The gas has a sharp, specific odor, similar to the aroma of rotten eggs. To get an idea of what it smells like, you can smell ammonia, which is an ammonia solution.
When trying to sniff ammonia, you must be careful, keeping the open bottle away from your nose. Acute inhalation of vapors can cause headaches, watery eyes and nausea.
There is always a small amount of ammonium phosphate in the urine. If urine sits for a long time, the element begins to decompose. A visit to a public toilet that is rarely cleaned can give you an idea of the ammonia odor.
Mechanism of occurrence
In the body, acetone is found in the form of ketone bodies (KBs) - acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetone itself. When they are overproduced, ketosis occurs, in which CTs accumulate in the blood (hyperketonemia) and appear in urine (ketonuria). If urine smells like ammonia in women, this is a sign that excess ketone bodies are being excreted. They are released along with exhaled air, urine, and sweat.
Ketone bodies serve as the basis for the synthesis of lipids in the brain and peripheral nerves. However, in high concentrations they have a toxic effect (this condition is called ketoacidosis), resulting in the following:
- a shift in electrolyte balance towards increased acidity (metabolic acidosis);
- damage to phospholipids from which cell membranes are formed;
- changes in protein structure;
- impaired binding of hemoglobin to oxygen;
- narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels (including in the brain);
- decrease in circulating blood volume;
- a decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood, which leads to an imbalance in the biochemical balance, dizziness, and loss of consciousness;
- irritation of the gastric and intestinal mucosa (abdominal pain, vomiting);
- a narcotic effect on the central nervous system, causing lethargy, lethargy, loss of consciousness and coma.
In a healthy woman, the content of acetone bodies in the blood ranges from 34-430 µmol/l, and 20-50 mg are excreted in the urine per day. Such a low concentration is not detected in conventional laboratory tests, so in clinical practice it is generally accepted that CT scans should be completely absent. To detect acetone in urine, qualitative methods are mainly used, the results of which are rated from 1 to 4 “pluses” (“++++”). 3 pluses correspond to an increase in the concentration of the substance by 400 times, and 4 – by 600.
Pathological causes
There are a number of fungal, infectious inflammatory and viral diseases for which this symptom is characteristic:
- Vaginal candidiasis, more popularly known as thrush. The causative agent is the Candida fungus, which is present in any organism. The impetus for its activation and population is the weakening of the body’s protective properties under the influence of illness or intense psycho-emotional stress. In answer to the potential question: could thrush be the cause of the ammonia smell?, it should be noted that this is individual for each woman. Basically, curdled impurities in the discharge emit the smell of fermented milk products, but in some cases there may be a subtle odor of ammonia. The disease is accompanied by itching and burning in the groin area. If symptoms of thrush are detected, both partners must undergo appropriate examination, since the disease is almost instantly transmitted through unprotected sexual contact. With timely and effective treatment, the causative agent of the disease can be neutralized relatively quickly.
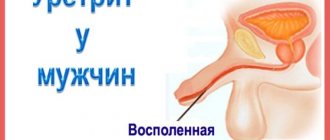
- Urethritis. It represents the course of inflammatory processes in the urethra. It can develop as a result of unhindered colonization of the body by Candida fungi. A fairly common disease among the female population. In addition to the smell of ammonia, the following symptoms indicate it: pain and stinging when urinating; blood in the urine; the appearance in the discharge of atypical mucus of a transparent or light yellow hue.
- Cystitis. The symptoms are quite similar to urethritis. The main reason for the development of the disease is hypothermia, as a result of which the mucous membrane of the bladder becomes inflamed. The main symptoms include: frequent urge to urinate; dark-colored urine with possible blood and ammonia odor; the temperature may rise to subfebrile levels; severe pain when urinating.
- Kidney diseases such as pyelonephritis and pyelitis can also be the cause of the smell of ammonia in the intimate area. They are characterized by: intense pain from the back in the lumbar region; high fever that does not subside for several days; profuse sweating; dizziness and headaches accompanied by general weakness; in some cases, nausea is possible; dysfunction of the genitourinary system.
- Sexually transmitted diseases, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis and others.
- Diabetes mellitus in the early stages of development. A high concentration of ketone in the body causes the smell of acetone or ammonia to appear in the throat area. Ketones that are not processed by the liver are spontaneously eliminated through urination, leaving a characteristic odor. More intense odor symptoms indicate diabetic dehydration.
- Viral form of hepatitis. This infectious liver lesion is determined by specialists based on the following characteristics: yellowish tint of the skin and eyeballs; dark colored urine with a strong odor of acetone or ammonia.
- Vaginosis or vaginal dysbiosis. The development of the disease is due to the predominance of harmful microorganisms in the microflora of the intimate zone. As a result, the previously mentioned odor appears, accompanied by itching, burning, as well as swelling and skin irritation of the labia;
- Furunculosis of the vulva is determined by yellow or green discharge characteristic of the disease;
- Endometriosis. It is an inflammation of the lining of the uterus. At the same time, it increases in size and bleeds. These discharges have a strong ammonia smell. In addition, the disease is determined by the characteristic swelling of the abdominal cavity and pain during sexual intercourse;
- Malignant neoplasms on the genital organs. They are characterized by colorless or light red discharge with a specific odor.
- Vaginal fistula is a pathology that appears as a result of mechanical stress. The main causes include childbirth and genital trauma. A fistula is an empty space between the organs of the genitourinary system. It is treated exclusively through surgery.
- Parasitic microorganisms present in 70% of the population. The waste from most of them can emit an ammonia odor.
Note! Each of the pathologies listed above requires individual and immediate treatment. The symptoms that appear should not be ignored, as this is fraught with serious consequences, including death. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Associated symptoms
Hyperammonemia in women and men is accompanied by signs of hepatic encephalopathy. The neurotoxic effects of ammonia on the body cause the following phenomena:
- inappropriate behavior (drowsiness, lethargy or agitation, decreased mental abilities, memory loss);
- frequent intermittent breathing;
- convulsions;
- gait disturbances, loss of orientation;
- refusal of meat, vomiting;
- headache.
Violation of the acid-base state against the background of poor elimination of toxic metabolic products is combined with ketonuria, an increase in the anion gap, and an increase in the level of blood ketones. Severe cases lead to coma and death.
Diagnostic measures
Quite informative is the titrimetric method for determining ammonia using the indicator - methyl orange and setting up a color reaction with Nessler's solution.
Normally, plasma ammonia should not exceed 7-22 µmol/l. In urine there are 10-30 mcg/100 ml, and its daily amount includes 30-60 mmol (0.5-1 g).
Methods
The amount of ammonia in biological fluids is extremely small, which makes it difficult to determine its true level. To study samples, in addition to titrimetric methods, photometric, gas chromatographic, and potentiometric methods are used.
To clarify the reason for the increase in this value, it is recommended to undergo an additional examination, including the following diagnostic measures:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical tests (renal, liver, protein, albumin);
- bacteriological culture of urine for microflora;
- indicators of acid-base status;
- water and electrolyte balance;
- antiglobulin test - Coombs test to detect hemolytic anemia;
- donate blood for markers of viral diseases.
It is also recommended to conduct an ultrasound examination to determine the extent of damage to internal organs.
Features of preparation
Serum is used to study the level of hydrogen nitride. To obtain it, a test tube with an anticoagulant is completely filled with venous blood and mixed thoroughly. At the same time, it is important to avoid the destruction of red blood cells, as well as contact of the biomaterial with the patient’s sweat - this can cause a false overestimation of the results. If transportation is necessary, plasma is frozen.
Urine is collected in a disposable plastic container after thorough toileting of the external genitalia. Women should wait until their period ends.
It is important to know! After collection, urine is examined as soon as possible. If it stands for a long time, there is a high probability of loss of ammonia or its increase under the influence of microorganisms. If it is not possible to perform the analysis immediately, a preservative is added to the sample and stored in a cool place.
On the eve of the test, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- refrain from sexual intercourse and heavy physical activity;
- maintain your usual drinking and eating regimen;
- limit the consumption of vegetables, fruits, meat products;
- with the permission of the doctor, temporarily stop taking barbiturates, narcotic painkillers, diuretics;
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun;
- exclude smoking, alcohol, visiting the bathhouse, sauna.
It should be borne in mind that the concentration of ammonia in the body increases during fasting, as well as in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Possible reasons for the occurrence of ammonia-smelling discharge in women
Discharge in the groin area is a natural process indicating the normal state of the body's reproductive functions. This liquid prevents the formation of harmful fungi and bacterial infections on the mucous membrane of the genital organ. The discharge has a specific odor. Its intensity depends on the personal characteristics of the body and on the hormonal background, namely.
- changes occur in the body associated with entering menopause. Entering menopause is inextricably linked with a decrease in estrogen production. This hormone is responsible not only for female reproductive function, but also for the body’s resistance to infection;
- the patient takes medications and dietary supplements. Some medications, especially B vitamins, can give urine an unnatural odor;
- the body is dehydrated. During the day, about one and a half liters are excreted from the body. urine, therefore it is recommended to drink more than 1.5-2 liters per day. untainted water. Dehydration can result from excessive sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting. If a person does not replenish the required supply of water in the body, dehydration occurs and, as a result, the concentration of urine increases. Urine acquires a specific smell due to the huge amount of chemical compounds in poop;
- the lady is carrying a baby. During pregnancy, the body experiences hormonal changes. During this period, the expectant mother is especially vulnerable to various genitourinary infections. In addition, there is 24-hour pressure on the bladder, which leads to stagnation of water (suitable conditions for the growth of pathogenic microbes).
- If a pregnant woman drinks fairly clean water, but the discharge still smells like ammonia, you can suspect a disorder in the metabolic processes. The consequence of the violation is the accumulation of acetone and acetoacetic acid in poop, causing an uncharacteristic odor. In addition to this symptom, a pregnant woman may notice a deterioration in health, weight loss and a decrease in blood pressure;
- there are kidney pathologies. Inflammatory processes in the kidneys may be accompanied by a disorder in the excretion of urea and hydrogen. The consequence of this violation is a strong ammonia odor in the urine;
- pathogenic microflora spreads. Bacteria and fungal infections are the reasons why vaginitis appears. The foul odor of urine is characteristic of this disease. A symptom of an infectious lesion can also be cloudiness, the appearance of sediment and the discharge turning black;
- The pancreas produces the missing amount of insulin. When you have sweet diabetes, urine can emit not only an ammonia, but also an acetone smell. This happens due to the accumulation of ketones in the body, which are breakdown products.
If the usual smell of urine has changed to ammonia, it is worth trying to increase the amount of clean water you drink per day
Complications
Delayed treatment or complete ignoring of vaginal odor can lead to complications such as:
- inflammatory or infectious processes in the vagina, uterus and appendages, ovaries and urinary canal organs;
- predisposition to sexually transmitted diseases;
- increased risk of complications after surgery on the genitourinary system.
To prevent the formation of complications, it is best to contact a gynecologist at the first signs for consultation and treatment, and under no circumstances try to get rid of them on your own. It is important to remember that after childbirth, the occurrence of discharge and odor is a completely normal process. Only a rotten smell should cause alarm.
Discharge with the smell of ammonia: determining the cause
Sometimes it happens that the smell of vaginal discharge takes on a specific character, which, of course, alarms all representatives of the fairer sex. What does ammonia-smelling discharge mean in women and how to get rid of it, you can find out in this article.
Nature arranges it in such a way that the work of each of our organs is accompanied by the products of its vital activity. The reproductive system mostly consists of mucous tissues, which have many glands that produce secretions. Thanks to it, a barrier function is carried out: the retention of foreign microorganisms. This way, the natural microflora is preserved, and all unnecessary bacteria are removed along with the mucus.
Normally, this is a moderate amount of transparent mucus, without foreign odor and uniform consistency. As the menstrual cycle progresses, this characteristic may change: the secretion becomes sticky and yellowish during ovulation, before or after menstruation.
If the discharge begins to smell strongly of onions, rotten fish, iron, rot, acetone or ammonia, acquires a white, gray or other unnatural color, its composition becomes heterogeneous, and discomfort in the form of itching, burning, and pain increases, then we are talking about a violation. Let's consider the problem of having discharge with a pungent odor of ammonia or ammonia.
It is known that the lifestyle, quality of nutrition and general health of a woman are reflected in the characteristics of the secreted sexual secretion and its aroma. Therefore, the reasons for the ammonia smell may be as follows:
- Lack of fluid intake, which causes urine to become concentrated, giving rise to such a smell.
- Excess protein in the diet, which makes it difficult for the liver to process it into amino acids.
- Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause, and in girls during puberty leave an imprint on the aroma of secretion. For the same reason, menstrual bleeding in the first days may smell like ammonia.
- Improper hygiene when discharge or urine residues accumulate in the inguinal folds.
- Some medications or multivitamin complexes change the composition and smell of the discharge.
- Most often, this phenomenon occurs due to dysfunction of the liver, which cannot cope with the processing of a metabolic byproduct - ammonia. During normal liver function, it is excreted in the urine. When its activity is disrupted in the body, toxic substances accumulate, finding release in the form of vaginal mucus. That is why the smell from the genitals can bother not only a woman, but also a girl who is not sexually active.
The causes of discharge with the smell of ammonia in women are also pathological.
- Urethritis, in which the urethra becomes inflamed, develops due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the microflora. The symptoms include the smell of ammonia, cutting pain when urinating, discharge from the urethra appears, and urine may have a brown tint and contain mucus.
- Cystitis is another inflammatory process of the bladder. It develops due to harmful microorganisms and due to hypothermia, and in menopause cystitis is an even more frequent “guest” due to age-related changes. Symptoms of urethritis may include fever and general malaise.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys and their pelvis, which gives such an odor and is accompanied by frequent urination, lower back pain, chills, weakness, increased sweating, and dizziness.
- In diabetes mellitus, ketones - acetone compounds - are present in the urine in excessive quantities. In high concentrations they can give a similar fragrance.
- If white lumps in the mucus begin to stand out or they become yellowish, the described smell appears, and unbearable itching and burning are felt, then this is a fungal disease called Candidiasis, popularly known as thrush.
- Bacterial vaginosis may be a prerequisite for the appearance of discharge with an ammonia odor. This aroma of discharge is diluted by the smell of rotten fish, and the mucus takes on a grayish tint. She can express herself with particular force after sexual contact. Symptoms are also expressed by a burning sensation with itching.
- Any other sexually transmitted infections, such as trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis and others can provoke such a fragrance from the vagina.
Find out in the article at the link why it can be painful to go to the toilet during your period.
A woman may confuse vaginal secretion with minor urine leakage, which is a sign of overactive or neurogenic bladder syndrome.
If the discharge begins to smell like ammonia, you should contact a medical professional. It’s worth starting with a gynecologist to rule out female diseases. Also consult a urologist and endocrinologist, because most often such a symptom is the result of these specialists.
For the above diseases, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs are used, and in severe cases, antibiotics. These medications are supplemented with immunostimulants and restoratives.
Treatment is possible at home. Local suppositories, douching with solutions with the mentioned medications, baths based on medicinal herbs, and warming are suitable. But under no circumstances self-medicate. First of all, contact a competent specialist.
To prevent the disease, follow simple preventive measures:
- Eat a balanced diet, avoid strict diets and bad habits.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Don't get too cold.
- Do not neglect colds, as they are often the cause of diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Keep your blood sugar levels under control at all times.
- Maintain intimate hygiene, wash yourself often, paying attention to the groin area.
- Choose genital care products correctly: without fragrances, dyes, plant-based, maintaining ph balance.
- Eliminate synthetic underwear from your wardrobe, leaving only natural, comfortable shapes.
- Protect yourself with condoms if you do not have a regular sexual partner.
As numerous reviews show, colorless, white and yellow discharge with the smell of ammonia in women is a common problem that can be eliminated quite easily. It is important to notice in time, find out the cause and receive the correct treatment. Be healthy!
Therapy
The treatment method depends on the type of pathology that provoked the appearance of an uncharacteristic odor. Before prescribing medications to a patient, the necessary tests must be done.
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of an unpleasant symptom may include:
- healthy lifestyle;
- compliance with the drinking regime;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of colds;
- blood sugar control;
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene;
- refusal to wear synthetic underwear;
- using condoms.
Prevention measures
Every girl can prevent her vagina from stinking. You just need to follow a number of preventive measures:
- Don't forget about a healthy lifestyle.
- Avoid overcooling and treat colds promptly.
- Take time to drink regularly.
- Observe hygiene rules.
- Eat normally.
- Control blood sugar.
- Do not wear underwear made of synthetics.
- Engage only in protected sex.
- Visit doctors more often.
Nothing difficult to do. The main thing is to consult a specialist if you notice a ammonia-like odor from your vaginal discharge.
Diagnostics
When a woman notices that her discharge is more yellow than what is considered normal for her, she goes for a consultation with a gynecologist. This specialist listens to complaints and conducts an examination in a gynecological chair, during which he takes a smear from the vaginal epithelium and cervical canal.
If the diagnosis is not obvious from clinical manifestations, then the patient is referred for blood and urine tests, which can be used to determine whether inflammation or the causative agent of the disease is present in the body.
To determine sexually transmitted diseases, the doctor may prescribe an ELISA test, bacteriological examination or PCR diagnostics.
conclusions
A strong odor of ammonia in the urine of women and men may be a physiological reversible phenomenon or indicate the development of more dangerous pathological processes. If a specific pungent odor of urine is present for a long time, you should immediately consult a doctor, undergo a full diagnostic examination, and determine the exact concentration of the toxic substance in all biological fluids and tissues of the body. Identifying the true causes of hyperammonemia will allow timely identification of the presence of metabolic diseases and development of adequate treatment tactics.
Sources
- https://medslovaru.ru/vydelenija-pahnut-ammiakom-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://AptekaTamara.ru/bolezni/vydeleniya-pahnut-ammiakom.html
- https://dieta.pochke-med.ru/pochki/trusy-pahnut-ammiakom/
- https://tden.ru/health/mocha-pahnet-ammiakom-u-zhenshhin
- https://fraumed.net/kidneys-urination/changes-urine/mocha-paxnet-ammiakom-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://dermatologpro.ru/info/pahnet-ammiakom-iz-intimnoj-zony/
- https://vit-klinika.ru/zapah-izo-rta/zapah-atsetona-na-prokladke.html
- https://rdbkomi.ru/zhenskoe-zdorove/pochemu-vydeleniya-pahnut-ammiakom.html
- https://MedWords.ru/ginekologiya/vydeleniya/s-zapahom-ammiaka
- https://sculpturica.ru/info/vydelenija-pahnut-ammiakom-u-zhenshhin/
- https://silazdorov.ru/vydelenija-pahnut-ammiakom-u-zhenshhin-prichiny-neprijatnogo-zapaha.html
- https://UroMir.ru/diagnostika/zapah-mochi/pahnet-ammiakom-u-zhenshchin.html
- https://simptzabol.ru/zapax-acetona-iz-vlagalishha.html
- https://onlinedoktors.ru/vydeleniya-pahnut-nashatyrem.html
[collapse]