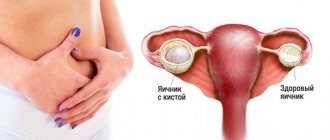
A kidney cyst is a benign cavity formation on the kidney, usually round in shape and filled with clear or yellowish fluid. This disease occurs in patients of any gender, but more often people over 50 years of age suffer from the disease. If a cyst occurs on one of the kidneys, then we are talking about a single formation. Polycystic kidney disease refers to formations on both kidneys.
It is very important to promptly seek qualified medical help to prevent serious consequences, and above all, kidney failure. Nephrologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide complex therapy for kidney cysts. Surgery is performed according to indications. Urologists are fluent in kidney surgery techniques. Surgical interventions are performed using both modern endoscopic equipment and lumbar access.
What kind of disease is this?
Kidney tissue has a special structure that has its own functional tasks: it filters blood, retains necessary components and removes toxic metabolic products.
A congenital kidney cyst can form in the prenatal period, which is influenced by genetic factors and adverse external influences. The development of an acquired kidney cyst can be caused by certain provoking factors. The size of the cyst varies from one millimeter to several centimeters. The biggest problem is represented by multiple cysts in the kidneys. Such formations are dangerous because, penetrating the kidney tissue, they disrupt the functioning of a large volume of the filtration system. Due to dysfunction of part of the parenchymal tissue, the activity of the kidneys is disrupted.
Causes of tumors in the kidneys
Despite the fact that kidney cyst is a disease that occurs quite often, experts have not yet figured out the reliable causes of this pathology. As a result of traumatic, hereditary or infectious factors, abnormal tissue growth is possible, which leads to the formation of a kidney cyst. Accordingly, this disease can be classified as either acquired or congenital.
Experts believe that a genetic predisposition to cysts in the kidneys occurs due to a lack of connective tissue in the body. If complications arose during the mother's pregnancy (there were injuries, infections), then the likelihood of the child developing a kidney cyst increases significantly.
Acquired kidney tumors can occur both at the site of a hematoma due to trauma, and when the site of infection is not stopped in a timely manner.
The age factor is also important, playing a role in the formation of kidney cysts. Most often, people over 50 years of age suffer from this disease.
So, the provoking factors for the development of the disease are:
- age-related changes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- malignant tumors;
- injuries,
- prostate adenoma in men.
The risk of developing a kidney cyst increases in people suffering from hypertension and urolithiasis, frequent colds, which are complicated by inflammation of the kidney parenchyma.
Make an appointment
Consequences of kidney puncture
Renal puncture is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. When the painkiller stops working, the patient may experience minor pain, which should disappear soon. If the condition, on the contrary, worsens, we can argue about the development of complications.
Unpleasant consequences of kidney puncture can be:
- Pneumothorax. This is a pathology characterized by the accumulation of gases in the pleural cavity. This leads to serious problems - poor circulation and respiratory function.
- Renal colic. Sharp and acute pain in the kidneys occurs due to blockage of the urinary tract and problems with the outflow of urine.
- Increased body temperature. Development of infectious inflammation.
- Kidney infarction, hypotension.
- Paranephritis of purulent type.
- Arteriovenous fistula.
All these complications occur very rarely.
In the first days after surgery, the physician will be able to easily notice the development of pathologies and prevent their progression. A course of antibiotics will help prevent the development of complications. In the first days after the puncture, the patient may complain of feeling unwell. From time to time, attacks of nausea and headaches, fever, pain, and blood in the urine occur. Any deviations from the norm should be reported to your doctor immediately. Share:
Types of kidney cysts
The following types of cystic anomalies of the kidneys and upper urinary tract are distinguished:
- Simple renal cyst;
- Multicystic kidney;
- Polycystic kidney disease;
- Multilocular cyst;
- Solitary renal cyst;
- Parapelvic cyst.
The most common are simple renal cysts. They are a single-chamber cavity filled with serous contents. Multiple kidney cysts can be located in both organs.
Multicystic kidney is a congenital anomaly in which the renal parenchyma is replaced by cysts of various sizes. The mechanism of development of a multicystic kidney is based on atresia of the ureteropelvic anastomosis during the embryonic development of the fetus.
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetically determined disease that is manifested by the formation of numerous cysts on both kidneys. They gradually grow, causing atrophy of the organ parenchyma.
Multilocular cyst is a rare, poorly studied developmental anomaly. It has other names: adenoma, cystic lymphangioma, cystic hamartoma, multilocular cystic adenoma, Wilms cystic tumor, cystic nephroma, adenomatous polycystic tumor. Multilocular cyst occurs in patients of different ages - from birth to 80 years. In half of the cases, developmental anomalies are detected in children. Kidney cysts are diagnosed more often in women than in men.
A multilocular cyst is located in the right or left kidney; sometimes doctors detect bilateral and diffuse damage. It is characterized by the following criteria:
- One-sidedness of the lesion;
- Multi-chamber;
- Lack of communication with the pyelocaliceal system;
- Lack of connection between individual cavities;
- The presence of epithelial connective tissue cords;
- Lack of differentiated kidney elements.
A solitary renal cyst is a round-shaped cystic formation that is not associated with the collecting system of the kidney. There are simple solitary and dermoid cysts. A simple cyst does not contain septa or inclusions and is filled with serous contents. Located in the cortical layer (parenchyma) of one of the kidneys.
Parapelvic cysts of both kidneys are located in the region of the pelvis or sinus of the organ. They are a type of simple cyst. They are a hollow, round-shaped formation that has a fibrous membrane, lined with cubic epithelium and filled with fluid.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a kidney cyst directly depend on its size. So, if the cyst is small, it does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient. If the cyst increases in size, this leads to pain in the lumbar region on one or both sides (polycystic kidney disease). When the cyst reaches such a size that it compresses the ureters, its symptoms may manifest as follows:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- reduction in single volume of urine;
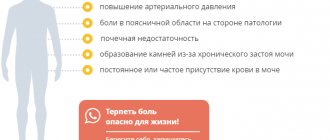
- increase in blood (“lower”) pressure.
Advanced cases - when the kidney cyst compresses the parenchyma, ureter, neighboring tissues, may be accompanied by the following conditions:
- discomfort, nagging pain in the lumbar region, especially pronounced after physical activity;
- palpable tumor;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- increased body temperature, chills.
The development of arterial hypertension is a fairly common sign of cyst localization in the parenchymal tissue of the kidneys. As the tumor grows, compression of the tissues of the organ occurs, disruption of its nutrition and metabolism. As a result, the production of renin, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure, increases. “Renal” hypertension is manifested by an increase in diastolic pressure.
With a weakened immune system, there are frequent cases of infection and the development of an inflammatory process. Infectious damage to the kidney (pyelonephritis) is manifested by the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- painful and frequent urination;
- aching constant girdle pain;
- increase in body temperature.
A laboratory examination of urine reveals an increased level of leukocytes, as well as casts and red blood cells.
Lack of timely, competent treatment threatens the patient with the development of chronic renal failure, which is characterized by polyuria (increased urge to urinate), weakness, thirst, and increased blood pressure.
With large cysts, compression occurs not only of the ureters and renal pelvis, but also of important vessels, which can result in ischemia and atrophy of the affected organ.
If a kidney cyst ruptures, the symptoms become acute: pain appears in the abdomen and lower back, body temperature rises, and the patient is tormented by constant thirst. When a cystic formation ruptures, there is an increase in the volume of urine, a change in the color of the skin, the appearance of chills, and swelling of the tissues. In this situation, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor for emergency surgery.
Make an appointment
When is puncture of a kidney cyst necessary?
Kidney cyst
- This is a benign formation, which is a round sac filled with liquid. This is a common disease, most often asymptomatic, and the patient first learns about its existence only after an ultrasound. However, sometimes a cyst can make itself felt with such manifestations as nagging pain in the lower back, arterial hypertension, and blood in the urine. The most dangerous complication is kidney cyst cancer. Therefore, if you are diagnosed with a kidney cyst, the doctor recommends you treatment, which should not be postponed - even if unpleasant symptoms have not yet appeared. In uncomplicated cases and small cyst sizes, non-surgical treatment is possible.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of kidney cysts is carried out using the following methods:
- Survey radiography;
- Excretory urography;
- Retrograde ureteropyelography;
- Nephrotomography;
- Pneumoretroperitoneum.
These techniques do not satisfy the requirements of nephrologists. With the help of excretory urography, it is possible to detect radiological signs of the presence of a kidney cyst in 26.7% of cases, intravenous urography - in 1-2%.
A more accurate diagnosis of kidney cysts is possible using the following research methods: isotope techniques, angiography. They are not without their shortcomings. Computed X-ray tomography is used to diagnose cysts at the Yusupov Hospital. It is the “gold standard” for recognizing cystic kidney formations. The information content of the study is close to 100%. At the Yusupov Hospital, radiologists use equipment with high resolution. It makes it possible to establish the correct diagnosis in the presence of cysts that reach 5 mm in diameter. Computed tomography does not provide complete confidence in the reliability of the diagnosis for parapelvic cysts and for a tumor in the cyst. It is possible to identify cystic formations that do not communicate with the renal pyelocaliceal system with the introduction of radiocontrast agents.
Unlike computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the frontal and sagittal sections confirms the presence of such cysts. The method allows us to identify the multi-chamber nature of the cystic formation. Results are less operator dependent than with ultrasound. Using MRI, one can judge the presence of serous-purulent or hemorrhagic contents in the cyst, and clearly differentiate a parapelvic cyst against the background of concomitant hydronephrosis and sinus lipomatosis.
At the Yusupov Hospital, if a kidney cyst is suspected, doctors perform an ultrasound examination using the latest equipment. Often, using this method, a kidney cyst is detected by chance. Ultrasound examination is especially informative in the differential diagnosis of solid and liquid formations of the kidneys. Normally, the cyst of the left and right kidney has the following dimensions:
- Length – from 100 to 120 mm;
- Thickness – from 40 to 50 mm;
- Width – 50-60 mm;
- The thickness of the parenchyma is no more than 23 mm.
On ultrasound, the parietal component of the renal cyst can be seen. Ultrasound examination has many advantages:
- Non-invasive research;
- Does not cause inconvenience to patients;
- Easy to do;
- Does not require patient preparation;
- Does not depend on the functional state of the kidneys;
- Does not expose the examiner to the risk of radiation;
- Allows for dynamic observation and use as a screening test.
Under ultrasound guidance, urologists perform a puncture of the cyst. Its contents are sent for cytological examination. If the cyst in the kidney is solid, tissue is collected for histological examination. Cystography increases the diagnostic value of percutaneous cyst puncture. The study carries a large radiation dose and is performed only when ultrasound and CT data are questionable.
In recent years, laparoscopy has been increasingly used to diagnose cystic kidney lesions. The method makes it possible to carry out a differential diagnosis of a cyst with malignant kidney tumors, and to take pieces of tissue for biopsy in doubtful cases. Laparoscopy is of diagnostic value in the study of parapelvic cysts.
Treatment methods
When selecting treatment tactics, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use an individual approach and take into account a number of important features: the type and stage of the kidney cyst, the severity of symptoms, the age and health of the patient.
Conservative therapy for kidney cysts is aimed primarily at relieving the symptoms of the disease. It can be prescribed to relieve inflammation, pain, and lower blood pressure. In addition, drug treatment helps normalize kidney function and promotes rapid recovery of patients in the postoperative period.
For small cystic formations that are not accompanied by severe symptoms, patients are usually offered dynamic observation. However, in the case of intensive growth of the tumor, changes in its structure and dysfunction of the urinary system, surgical intervention is recommended.
To carry out surgical treatment at the Yusupov Hospital, the most modern, gentle, minimally invasive methods are used. Laparoscopic surgical interventions are performed through small incisions, thereby minimizing blood loss and the risk of postoperative complications.
Treatment of a kidney cyst is carried out using another minimally invasive procedure - percutaneous puncture and aspiration of the cyst, the process of which is monitored by ultrasound or CT. A sclerosing substance is necessarily injected into the cyst capsule to “glue” the walls together. Sclerotherapy can significantly increase the effectiveness of the procedure. At the Yusupov Hospital, the most modern sclerosants, which have a minimum number of side effects, are used to carry out this manipulation.
Performing puncture and aspiration of a kidney cyst involves the use of local anesthesia. The procedure is carried out in several successive stages:
- inserting a needle into the cavity of the cystic formation;
- evacuation of cyst contents;
- cytological examination of the fluid obtained by aspiration for the level of proteins, creatinine, fats, and malignant cells;
- administration of a sclerosing drug.
Puncture of a cyst is almost never accompanied by the development of complications.
Kidney removal may be prescribed in rare cases - in case of serious organ damage or signs of malignancy.
How is a kidney cyst treated at the N. I. Pirogov Clinic?
For surgical treatment, doctors at the N.I. Pirogov Clinic perform a modern intervention - puncture of a kidney cyst with sclerotherapy. This is a minimally invasive procedure that is indicated for single-chamber simple kidney cysts with homogeneous contents and smooth contours. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia. In a pre-made access on the skin measuring only 0.5 cm, the doctor, under careful visual ultrasound control, inserts a special needle into the cyst cavity, removes fluid and injects a drug that glues the walls of the cyst. Within three hours after the procedure you can go home.
Is surgery necessary?
A kidney cyst is a benign formation and removal of a kidney cyst (laparoscopy or other methods) is a truly justified treatment method. Often, patients are diagnosed with a cyst during random or routine examinations (ultrasound, x-rays).
The formation of a cyst on the kidney occurs without visible symptoms and does not cause any harm to human health. Surgical intervention in the presence of small benign formations may not be required at all. However, a patient with a similar diagnosis still needs to visit a specialist to monitor and prevent the growth of tumors at least twice a year. Regular examinations will also help prevent the degeneration of benign formations into malignant ones.
In some cases, surgery is still necessary. If the patient experiences severe pain in the lumbar region, the functioning of the kidneys is impaired, kidney tumors are larger than 5 centimeters, surgical intervention is the only correct and necessary solution.
Surgeons at the Yusupov Hospital in most cases remove the cyst with capsule. Our doctors use minimally invasive techniques that involve removing the contents of the cyst through a small puncture of the skin in the lumbar region. If the cystic formation is located deep in the parenchyma of the organ, the option of removing the kidney itself is considered.
Conservative treatment includes the use of modern broad-spectrum antibiotics and painkillers in the postoperative period.
Make an appointment
Preparing the patient for surgery
Before surgery, the patient must undergo thorough preliminary preparation. If the recommendations of the treating specialist are not followed, the planned operation may be postponed. Preparation includes the following points:
- the patient must avoid hypothermia, which can lead to colds;
- You should not take medications that reduce blood clotting;
- Urine and blood tests are performed, as well as an ECG;
- consultation and conclusion of a therapist is necessary;
- it is possible to prescribe additional examinations of the kidneys and blood vessels;
- 2-3 days before surgery, it is recommended to remove flour products, vegetables and fruits from the diet;
- Before the operation you cannot eat or drink anything; on the eve of the operation a cleansing enema is given.
It is also necessary for the patient to undergo standard medical procedures, examinations and a set of tests before the operation. The specialist may additionally decide to puncture the kidney cyst. Computed tomography and abdominal MRI examination data will also be required. If a cyst is found in the kidney, the size for the operation is critical - it should be over 5 cm.
Immediately before the operation, the patient is put under anesthesia. There are two possible ways. The first involves the use of medications. However, there are also contraindications to this type of anesthesia - it is not suitable for patients who may develop an allergic reaction to the components of the medications used. In this case, the doctor prescribes epidural anesthesia for the patient suffering from the disease (removal of the kidney cyst under epidural anesthesia).
The advantages of epidural anesthesia include complete anesthesia of the lower part of the body, preservation of consciousness, verbal contact between the doctor and the patient, active mobility of the patient, which allows the doctor to puncture the kidney in a timely manner, and monitor the condition of the patient on the operating table. Epidural anesthesia is recognized in the medical community as an adequate and controlled process. With the development of progress in the field of medicine and pharmacology, the arsenal of local anesthetics has also increased.
Preparing for a kidney biopsy
It will help to avoid complications during and after the procedure.
- General examination (blood tests, urine tests, x-rays, ultrasound, ECG and others).
- 2 weeks in advance - abolition of medications, blood thinners, anti-inflammatory drugs.
- 3 days before - giving up alcohol.
- The last meal of the day is 8 hours before surgery, and the last drink is 2-4 hours.
Tell your doctor what medications you take every day and what you are allergic to.
After the operation, you need to lie on your back for 10 hours, you can already eat and drink. At this time, the staff measures the patient’s pulse, blood pressure, and takes urine for analysis.
Surgical methods for removing a kidney cyst
Currently, the Yusupov Hospital uses several modern effective methods to remove a cyst on the kidney.
Laparoscopic method
Laparoscopy of a kidney cyst involves the following actions by the surgeon: the doctor makes small incisions (punctures) on the skin in different places, most often in the side and on the anterior abdominal wall, and through them inserts a laparoscope (probe with a video camera) and instruments. Laparoscopic removal of a kidney cyst is one of the most gentle and adequate methods, which is the most popular in medical circles. The recovery time after laparoscopy of a kidney cyst is quite short, no more than 2-3 days.
If the cyst is located directly in the kidney tissue, resection of the kidney cyst may be performed during the procedure. The surgeon may change tactics and remove part of the organ itself. The doctor warns the patient in advance about possible options for undergoing surgery. Typically, surgery to remove a kidney cyst lasts about 1 hour. Patients can receive more detailed answers to questions - how to remove a kidney cyst laparoscopically, cost and terms of payment - from the consultants of the Yusupov Hospital by phone.
Percutaneous removal method
The doctor makes an incision in the patient's lumbar region, through which an endoscope with an instrument is inserted. This type of endoscope in urological surgery is used when operating on the affected kidney when the cyst is located on the back of the organ. The operation itself using percutaneous removal is performed under general anesthesia. This open method has been used extremely rarely in modern surgery lately. It is considered risky due to its high morbidity. In addition, recovery after removal of a kidney cyst is very long and very painful.
Intrarenal retrograde method
Removal of a kidney cyst with a laser is considered low-traumatic. In modern medicine it is quite controversial. This is a modern type of surgical intervention; when it is used, no incisions are made on the patient’s skin; it is the fastest and most painless. Resection of a kidney cyst is performed using a laser. But it is mainly used in medicine in cases where other types of surgical intervention are difficult to apply. If the operation is successful, the cyst turns into a scar and no longer bothers the patient.
Make an appointment
Surgical treatment of kidney cysts
A kidney cyst is a benign thin-walled neoplasm in the form of a sac, filled with a yellowish liquid without turbidity. It can have an ellipsoidal or spherical shape, be simple (single-chamber) or complex (consisting of several segments). As the tumor grows, it begins to put pressure on the kidney, thereby disrupting its normal functioning. As a rule, the size of the cyst varies from 1 to 10 cm, but there are also larger variants. This structural organ disorder can appear at any age, but is most often diagnosed in people over 50 years of age. When the cyst reaches a size that causes pain and discomfort to the patient, a decision is made to remove it surgically.
Indications for surgery
Surgical treatment of kidney cysts is prescribed for the following indications:
- large cyst size;
- abscess cyst (appearance of purulent complications)
- cyst rupture;
- presence of blood in the urine;
- compression of the kidney or ureter by a cyst;
- pain syndrome.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical intervention is not performed if:
- asymptomatic course of the disease;
- severe polycystic kidney disease;
- the patient is taking blood thinning medications (surgery is possible 7 days after they are discontinued);
- a patient's blood clotting disorder;
- exacerbation of diabetes mellitus;
- decompensation of respiratory diseases;
- decompensation of cardiovascular diseases.
Types of surgeries to remove kidney cysts
Percutaneous puncture
What kind of operation is this? This is an outpatient procedure to remove the contents of a kidney cyst without open surgery, after which medications are injected into the tumor cavity to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
In what cases is it carried out? Percutaneous puncture is performed in the presence of the above indications for surgery if the location of the cyst allows its puncture without risk to the tissues and structures surrounding the organ. In other cases, laparoscopic or open surgery will be required.
How it is carried out. To perform a percutaneous puncture, a team of doctors is required, consisting of a urologist, an ultrasound diagnostic specialist and an operating room nurse. The procedure is carried out under ultrasound control with local anesthesia. After completing the preoperative preparation, the patient is placed in the position determined by the doctor during a preliminary ultrasound examination (on his side or on his back). A marker on the body indicates the puncture point, and the area itself is treated with antiseptic drugs. After this, the doctor inserts the needle layer by layer. When its tip reaches the cyst cavity, the contents of the formation are removed, followed by biochemical, cultural and cytological studies. By injecting a small amount of air or contrast agent, the doctor should ensure that the cyst is isolated from the renal cavity. After this, sclerotherapy is performed. It involves the introduction of medications into the tumor cavity that cause contraction and sclerosis of the cyst.
Laparoscopic resection
What kind of operation is this? Laparoscopy is a surgical treatment with minimally invasive intervention, in which all manipulations are performed using endoscopic devices through small incisions in the projection of the operated organ. This method is often used today in urology, for example, to treat urolithiasis when lithotripsy is ineffective.
In what cases is it carried out? The laparoscopic method allows for any surgical intervention, including nephrectomy (kidney removal). This operation is used for the resection of multiple, solitary, bilateral cysts, large formations or those located in areas of the kidney inaccessible for puncture.
How it is carried out. Laparoscopic cyst resection will require an expert surgical team. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. During laparoscopy, the surgeon injects a gas substance into the surgical field to expand the working area. After this, punctures (usually 3) are made in the area of the kidney projection, through which the laparoscope and other instruments are inserted. At the same time, through the camera located in the device, an enlarged image of what is happening is transmitted to the monitor, which makes the operation safe and minimally traumatic. Using instruments, the surgeon removes and extracts cystic formations from the kidney area, brings drainage tubes to the operated area and sutures the punctures. Sometimes, along with the cyst, it is necessary to remove a certain amount of kidney tissue, and sometimes the entire organ. The patient is warned in advance about all possible complications.
Indications for removal of a kidney with a cyst
It should be emphasized that kidney removal (nephrectomy) is a necessary treatment method only in cases where the organ is affected by a malignant tumor. Accordingly, if the cyst on the kidney is benign, then we cannot talk about nephrectomy. Such factors that can lead to kidney removal may include an abnormality in the development of the kidney, which interferes with the normal functioning and functioning of the organ. Severe damage caused by trauma may also be a reason to remove the kidney.
How to behave after a kidney biopsy?
In general, the following recommendations should be followed for 2 weeks after the biopsy:
- Physical activity should be avoided.
- It is necessary to avoid shaking the body (it is not even recommended to go down the stairs).
- It is not recommended to take a hot bath, so the patient should choose to shower only.
- Do not lift heavy objects;
- It is necessary to avoid all activities that could lead to injury to the lumbar or abdominal region.
2-3 weeks after the kidney biopsy, the patient can return to his usual routine, provided there are no complications.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Rehabilitation period
After surgery to remove benign tumors on the kidneys, the patient remains in bed for two to three days. If the course of events is positive, he is allowed short walks without serious physical exertion. As for the postoperative period for open interventions, it takes a little longer.
It is necessary to strictly monitor the patient's diet. Fatty, fried and spicy foods are excluded. After 1-1.5 months, the patient can return to his usual lifestyle, but food restrictions will still have to be observed to prevent the condition from worsening.
Particular attention is paid to controlling the amount of fluid consumed. Based on the doctor’s decision, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and painkillers. To avoid the appearance of new formations, it is recommended to visit a specialized specialist and undergo the necessary examinations at least 2 times a year.