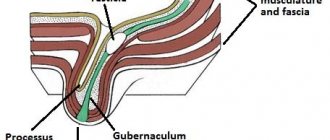
Ureterohydronephrosis of the kidney is a condition manifested in the form of an increase in the volume of the renal pelvis and calyx and the ureteric canal.
These changes are accompanied by a decrease in the performance of the organ and atrophy of its functional cells. The physiological consequences of megaureter are poor patency of the ureter in the pelvis.
The reasons for the development of megaureter are multiple, determined both by congenital predispositions and defects, and by the influence of the environment and human lifestyle. What most often influences the occurrence of this pathology?
Causes
Ureterohydronephrosis on the left, right or bilateral occurs, as a rule, for the following reasons:
- stones in the kidneys and ureters;
- diabetes;
- some prostate diseases;
- ureteral disorders due to anemia;
- constant spasm of the urethral sphincter;
- congenital valve;
- injuries of the genitourinary system.
In addition, the risk is increased by the uncontrolled use of analgesic drugs and delirium drugs, alcohol consumption and exposure to radiation. All these factors increase the pressure inside the kidney, disrupt renal blood flow and increase the amount of urine in the collecting part of the organ.
The presence of a congenital urethrovalve and sphincter spasm are mainly characteristic of children, although regarding the first case there are exceptions when adults are also susceptible to these manifestations. Ureterohydronephrosis may occur during pregnancy. Sometimes ureterohydronephrosis is diagnosed in the fetus.
Pain relief for renal colic for a long time without contacting a specialist can lead to a significant deterioration of the condition due to constant use of analgesics.
Complications
The most common complication of urolithiasis is an inflammatory process in the kidney - acute pyelonephritis
, which can lead to bacteriotoxic shock or urosepsis. If a stone remains in the kidney for a long time, especially if the stone is coral-shaped, chronic pyelonephritis may develop, which can periodically worsen and lead to severe irreversible complications: renal failure, shrinkage and death of the kidney. KSD can lead to the development of hydronephrosis, ureterohydronephrosis, which also in the future, if untreated, will lead to the death of the kidney.
Classification of the disease and its stages
The disease is classified according to three main characteristics. By reason of occurrence, they are divided into primary, which appeared as a result of the innate characteristics of the body, and secondary, i.e. acquired as a result of disease or traumatic exposure.
Ureterohydronephrosis on the right
According to localization, there is unilateral or bilateral ureterohydronephrosis, depending on whether one or two kidneys are affected by this pathology.
Finally, depending on the degree of obstruction, three types of pathological changes are also distinguished - obstructive ureterohydronephrosis, narrowing the ureter below, refluxing, caused by the reverse flow of contents, leading to expansion of the canal equally throughout the ureter, and combined, when both pathologies are observed.
Ureterohydronephrosis according to ICD-10 is coded as N13.2. There are five main stages of this kidney disease.
If the first stages are characterized by a relatively noticeable decrease in the tone of the ureteric canals, then in the last stages the kidney atrophies and ceases to perform its functions - the function of absorption of substances from the blood is impaired.
Acute manifestations of ureterohydronephrosis cause renal colic, problems with urination, changes in the composition (including an increase in the amount of blood) of urine, and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Symptoms of ureterohydronephrosis are similar to the manifestations of some other kidney diseases, so correct diagnosis, especially at an early stage, is very important.
Infantile hydronephrosis: a hidden threat
According to statistics from the Novosibirsk Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 1, the number of detected hydronephrosis is growing every year. Maxim Klimovich, a pediatric urologist-andrologist and surgeon at Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 1, explained why this disease is insidious and how not to miss the alarming symptoms.
Hydronephrosis is a disease in which the renal cavity expands, resulting in the obstruction of urine flow. The disease is dangerous because, if detected late and without proper treatment, it leads to irreversible consequences in the kidney tissue. Fortunately, modern diagnostics make it possible to detect hydronephrosis at the very initial stages, which contributes to the successful treatment of this pathology.
Alarming numbers
According to statistics from the Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 1 of Novosibirsk, in 2011 there were 176 cases of hydronephrosis, in 2012 there were 190, in 2013 - 191, and in 2014 there were already 202.
About 30% of children on this list are sent for surgery every year. We asked pediatric urologist-andrologist, surgeon Maxim Klimovich to comment on these figures, as well as talk about the features of diagnosis and treatment of hydronephrosis.
– Maxim Valerievich, what is the reason for the increase in hydronephrosis?
– The increase in the statistics of childhood hydronephrosis is associated, first of all, with the widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics. Previously, this disease was most often detected in adults, but with the advent of perinatal screenings and modern ultrasound machines, we can detect this disease at a very early stage and, in most cases, treat it successfully.
Before and after birth - What types of hydronephrosis occur in children?
– Speaking about hydronephrosis, it is necessary to understand that it can be congenital and acquired. In the first case, the pathology occurs due to the narrowness of the transition of the renal pelvis to the ureter. This may be caused by a narrowing of the ureteral structure or abnormal narrowing of an accessory vessel.
Hydronephrosis is often hereditary; it can also occur if the female body during pregnancy was exposed to unfavorable factors - stress, smoking, alcohol, hazardous production or taking certain medications.
Acquired hydronephrosis occurs, as a rule, as a result of urolithiasis, as well as injuries to the abdominal cavity, which provoke the formation of scars that can disrupt the functioning of the kidney, leading to its atrophy.
– What symptoms can a child experience with hydronephrosis?
– Parents should suspect something is wrong if the child feels unwell, has pain in the lumbar region, or experiences an attack of renal colic. Possible nausea, vomiting, difficulty urinating, and blood may appear in the urine.
This disease is very insidious due to its asymptomatic course, so parents should be attentive to their children: they need to monitor the baby, be sure to undergo a medical examination and take all the necessary tests.
Early diagnosis - How is intrauterine hydronephrosis detected?
– Every pregnant woman should understand the importance of routine examinations during pregnancy. At the first ultrasound screening at 10-12 weeks, the doctor may already notice renal pathology. If an ultrasound scan reveals cavitary enlargement of the fetal kidneys, then the expectant mother is prescribed additional studies in a few weeks.
It happens that the diagnosis is removed. If the doctor sees a progressive situation, then the woman is told about the risk of developing hydronephrosis in the baby and is closely monitored until birth. There are cases when a serious expansion of the abdominal system is detected at the earliest stages and is bilateral in nature. Then the woman is sent to a perinatal commission, where the issue of terminating the pregnancy is decided, since the prognosis in this case is unfavorable.
– Can this disease be treated in utero?
– Abroad, methods of antenatal surgery are used, when the child is operated on before birth, but in Russia this practice is not yet widespread.
– If a woman is told about hydronephrosis in the fetus during pregnancy, then what should she be prepared for after childbirth?
– After the baby is born, an ultrasound examination is performed in the maternity hospital and the size of the enlargement is looked at - if it is small, the baby is sent home under the supervision of a local pediatrician and nephrologist. If the dilation is serious, changes in the urine are observed, then the mother and baby are hospitalized in our department for examination.
Observe or operate?
– What tests are prescribed for a child to clarify the diagnosis?
– A number of special tests are performed, ultrasound, x-rays, intravenous urography and cystography are done. In some cases, computed tomography and dynamic scintigraphy are indicated.
If stage 1 or 2 hydronephrosis is established, the child is constantly monitored - it is possible that the disease will go away with age. If stage 3 is staged, then a surgical operation is indicated, which can be performed in two ways: a standard incision on the corresponding side of the lumbar region or a laparoscopic method.
The scope of the operation in both cases is the same, but with laparoscopy the hospital stay is shorter and the cosmetic effect on the skin is greater.
– At what age can such operations be performed?
– Some clinics, if possible, prefer to wait up to five to six months until there is a decrease in the physiological functions of the kidneys. Our hospital has techniques that allow us to successfully operate on children from birth. After all, if the problem exists, then why wait until six months? Surgery cannot be avoided anyway.
– What is the prognosis for stage 3?
– The earlier the disease is detected, the better the prognosis. The difficulty of hydronephrosis is that it can be asymptomatic for a long time, as a result of which the kidney is increasingly damaged.
Fortunately, this organ has great compensatory abilities: even if both kidneys are damaged, we can cure most children.
Prevention issues
– Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of hydronephrosis?
– No, there is no specific prevention of this disease. But, it should be understood that the better a woman takes care of her health during pregnancy, the higher the chance of giving birth to a healthy child. To do this, you need to eat right, drink high-quality water, protect yourself from stress and from the effects of negative factors such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
The same is true for young children: a healthy lifestyle and natural food without chemical additives help maintain kidney health for many years.
Treatment
Unfortunately, with a disease such as ureterohydronephrosis, treatment most often consists of surgical intervention, because medications are usually not effective enough and often cannot stop the development of pathoprocesses. To minimize the impact, minimally invasive surgery methods are used.
A small percentage of patients can be cured with medication, and in some, especially rare cases, ureterohydronephrosis is stopped due to natural processes occurring in the body - age-related changes, serious and long-term fluctuations in hormonal levels, etc.
In most cases, the specialist recommends surgery. Usually, such manipulations as the introduction of a special expansion catheter, surgical correction of defects, excision of the narrowing site, and ureterostomy are carried out promptly. In the most difficult cases, the functions of the ureter are assigned to the small intestine.
Surgical intervention is a rather complex process, and it is impossible to replace it with any other measures. At the same time, the process of preparation for invasive intervention and the course of the recovery process are of great importance. Both medications prescribed by a doctor and traditional methods can help with this.
If megaurethria is suspected, in addition to a hepatologist, it is imperative to consult a specialist in gastroenterology.
Traditional methods of treatment
First of all, it is worth noting that the use of any traditional medicine must be agreed with specialists.
This applies to the preoperative period, and, to an even greater extent, to the period of rehabilitation treatment following the operation.
Natural remedies cannot cure the disease, but can significantly influence the effect of certain chemical pharmaceuticals, enhancing or, conversely, neutralizing their effect. So, failure to involve a treating specialist can significantly complicate the healing process.
In case of illness, both fairly simple and complex remedies help. A very simple, but quite effective recipe based on cornflower.
2 teaspoons of the color of this plant should be poured with two glasses of boiling water.
Leave the resulting infusion in a warm place for half an hour.
Take half a glass three times a day before meals. This will significantly reduce inflammation.
Bearberry has also long been known as a remedy for diseases of the urinary system. A tablespoon of the crushed plant should be poured into three glasses of cold water and boiled over low heat, then a third of the liquid should be evaporated. Cool the resulting broth, covering the container with a lid, and drink three times a day after meals, so that all the resulting liquid is drunk in one day.
Various complex fees also have an effect. Some of them are sold in pharmacies, but many can also be prepared yourself. A very popular recipe is one that includes 1 part burdock root, 1 part bearberry, 1 part wormwood, two parts each of rose hips and celery root.
All ingredients are mixed and then steamed in a thermos at the rate of 2 tablespoons per glass of boiling water. You need to take one glass half an hour before meals, morning and evening, after straining.
A simpler method is to collect equal amounts of dandelion root, birch leaves and juniper fruits. The collection is poured with boiling water - one liter of water per 2 tablespoons, and boiled for at least ten minutes over very low heat.
The liquid is poured into a thermos and left for 12 hours. You need to take the decoction half an hour before meals, 100-150 ml. The course of treatment is 1.5-2 months.
And finally, a decoction of equal parts of horsetail, reed, nettle, crushed birch leaves, adonis and oat grains relieves inflammation quite well. The preparation of this infusion is similar to that described above.
The medication is taken one glass per day after meals. The course of treatment is at least 4 months, after which it is necessary to take a two-week break.
Pharmacies sell ready-made renal preparations, which can also be used as a maintenance and preventative agent, but only after consultation with a treating specialist.
Research results
The structural and functional state of the renal parenchyma in all patients was significantly changed (Table 1).
Table 1. Structural and functional state of the renal parenchyma in patients with “late” hydronephrosis before drainage of the renal parenchyma (n=34).
| Stage of hydronephrosis | Research methods | |||
| Ultrasound (renal parenchyma, mm) | Echo-Dopplerography (arcuate artery resistance index) | MSCT (renal parenchyma, mm) | DFT (%) | |
| Terminal A or B | 7,9±2,7 | 0,69±0,05 | 7,3±4,7 | 8 – 25 |
UMPs in these patients, as a rule, were represented by giant pelvises and calyces with fixed bends of the upper third of the ureter (Table 2).
Table 2. The degree of dilatation of the maxillary sinus according to ultrasound data in patients with late stages of hydronephrosis before drainage of the urinary bladder (n=34).
| Stage of hydronephrosis | Degree of dilatation of the maxillary joint (cm) | |
| Pelvis* | Calyxes | |
| 3rd (terminal A or B) | 4,1 – 14,0 (8,54) | 1,5 – 7,0 (3,28) |
* — the transverse size of the pelvis is indicated
Microscopy in the wall of the pelvis revealed thinning and death of the smooth muscle bundles of the inner layer and a massive proliferation of connective tissue between the remaining muscle bundles (Fig. 1). The thickness of the muscular layer of the pelvis was about 28% of the total thickness of the wall, which indicated significant degenerative changes in the pelvis and confirmed the need for extended resection of the pelvis as a necessary component of the operation.
Fig.1. Microslide. Wall of the pelvis. PAS reaction. x 420. Explanation in the text.
The final assessment of the structural and functional state of the renal parenchyma in patients with late stages of hydronephrosis was carried out no earlier than 7-10 days after nephrostomy or stenting of the upper bladder. The specified time interval is necessary to restore renal hemodynamics after unblocking the kidney (1, 2).
In accordance with the results of our studies, terminal B stage of hydronephrosis was established in 8 patients: despite the drainage of the renal parenchyma, the renal parenchyma was still not determined by ultrasound and MSCT, or its fragments were visualized, as a rule, at the poles of the kidney, not exceeding 3-5 mm. Renal blood flow and radiopharmaceutical accumulation curve were absent. The patients underwent nephrectomy. Macroscopically, the kidneys were represented by a connective tissue sac. Microscopically, diffuse nephrosclerosis and hyalinosis (thyroid kidney) were determined (Fig. 2, 3).
Rice. 2. Macropreparation.
Fig.3. Microscopic specimen of a removed kidney. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, x 200.
An immunomorphological study in the removed kidneys revealed a pronounced expression of α-SMA and vimentin by myofibroblasts and fibroblasts, indicating diffuse nephrosclerosis (Fig. 4, 5). The lack of expression of α-SMA and CD34 by the vessels of the peritubular space indicated complete degradation of the microvasculature. The absence of VEGF expression indicated the onset of irreversible, truly terminal changes in the renal parenchyma.
Fig.4. Expression of α-SMA. Fig.5. Vimentin expression.
Thus, the results of the immunomorphological study were consistent with the data of clinical diagnostic methods, confirming the true irreversibility of the terminal B stage of hydronephrosis. Organ-removal tactics in this category of patients are justified.
26 patients had terminal A stage hydronephrosis. 7 – 10 days after drainage of the UMP, the thickness of the renal parenchyma increased to an average of 12 mm, parenchymal blood flow began to be recorded, the resistance index decreased to 0.6, and the DPF exceeded 30%. The patients underwent organ-saving surgery.
A comparative, dynamic assessment of the structural and functional state of the kidney, comparison with the results of immunomorphological studies in patients with “late” hydronephrosis showed that stage 3A of the disease, which was considered truly terminal, is essentially not such, and the changes that have arisen are largely reversible. As illustrative material, we present a clinical observation of a patient with terminal A stage hydronephrosis.
Patient B, 16 years old. Diagnosis: stenosis of the LMJ and giant “late” left-sided hydronephrosis. The pelvis is more than 10 cm in diameter. The parenchyma is not determined, the blood flow is not recorded, the radiopharmaceutical accumulation curve is close to the isoline (Fig. 6, 7, 8).
Fig.6. Echodopplerogram.
Fig.7. MSCT. Axial scan.
Fig.8. Dynamic nephroscintigram. Explanations in the text.
After drainage of the left IMP with a catheter-stent for 10 days, the thickness of the renal parenchyma was 12 mm, and renal blood flow comparable to the opposite kidney began to be recorded (Fig. 9a, b). Resection of the pelvis, upper third of the ureter, and ureteropyelostomy were performed. At surgery, the kidney was of normal size, color, and turgor (Fig. 10 a, b). Due to the gigantic pelvis, which is not capable of contraction, its extended resection was performed. Light microscopy reveals grade 2 morphological changes, focal nephrosclerosis, but the structural organization of most nephrons is preserved (Fig. 11).
Fig.9 a. Echo-dopplergram.
Fig.9 b. MSCT. Axial scan.
Rice. 10 a. Operation stage.
Rice. 10b. Intraoperative Doppler echogram.
Fig. 11. Microslide. Kidney tissue. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, x 200.
In an immunomorphological study, the level of vascular markers is reduced, the level of vimentin is higher than normal, which indicates focal nephrosclerosis. Expression of VEGF by nephrothelium is reduced, but sufficient. The organization of most tubules is preserved (Fig. 12 a, b, c, d). Thus, the morphological criteria reasonably allowed us to hope for further restoration of the structure and function of the renal tissue.
Fig. 12a. Expression of α-SMA.
Rice. 12b. CD34 expression.
Fig. 12c. Vimentin expression.
Fig. 12d. VEGF expression.
6 months after the operation, the function of the kidney and UMP was significantly restored, as evidenced by ultrasound, MSCT, static nephroscintigraphy and Doppler echo (Fig. 13a, b, c, d, e).
Rice. 13a. Echogram after 6 months.
Rice. 13b. Doppler echogram after surgery. after 6 months after operation.
Rice. 13th century MSCT. Axial scan after 6 months. after operation.
Rice. 13 MSCT. 3-D reconstruction after 6 months. after operation.
Rice. 13d. Static nephroscintigram after 6 months. after operation.
Thus, the reverse transformation of seemingly irreversible changes in the renal parenchyma against the background of drainage of the IMF allows patients with terminal A stage of the disease to save the kidney by performing reconstructive surgery.
Diet
The consequence of certain dietary recommendations is also very important. Proper nutrition significantly enhances the effect of medications and alleviates the manifestation of the disease.
The basic rule of nutrition for this disease is to avoid any foods that burden the kidneys and urinary system.
You should completely stop eating pickles and generally significantly limit your intake of salt and acidic foods. It is also not recommended to eat spicy food - it can provoke inflammation.
Prohibited are fatty meats and broths, legumes, confectionery, carbonated drinks and any seasonings in the form of sauces and ketchups, especially factory-made ones. The patient's diet should be based on eating light foods, and the amount of protein should not be too high - this creates a load on the kidney.
But it is impossible to completely eliminate or even greatly minimize proteins, especially after surgery - without them, recovery processes will worsen.
The basis of the diet should be porridge, all kinds of vegetable dishes, dairy products, poultry and beef liver, as well as boiled potatoes.
It is allowed and even necessary to consume a lot of fruits and natural juices and fruit drinks, especially from fresh grapes, cherries, blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, cherries, citrus fruits and watermelons. It is allowed, in the absence of contraindications such as diabetes, the use of all kinds of dried fruits.
Meat consumption should be seriously limited. It is best to choose dishes from lean fish and lean white meat, observing their consumption in moderation. Alcohol and any flavoring additives, canned food, and dyes are absolutely excluded.
Eating foods that contain significant amounts of protein is undesirable. However, with certain indicators of the body, products can be introduced into the diet on the recommendation of a specialist.
Diagnostics
- Initial examination by a urologist.
- Laboratory diagnostics
: general blood test, biochemical blood test, general urine test, urine test according to Nechiporenko. - Radiation diagnostic methods
: ultrasound of the urinary system, plain radiography and with the use of intravenous contrast agent (excretory urography), computed tomography (CT). - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
When treating patients with urolithiasis in our clinic, a comprehensive examination is carried out, after which treatment tactics are selected for each patient individually.
To treat urolithiasis, our clinic uses modern high-tech treatment, which relieves stones in patients even with severe concomitant diseases. We have all the latest methods
getting rid of the treatment of urolithiasis.
In our clinic, about 6-10 operations (!) are performed daily just for urolithiasis, so we can confidently say that we have a wealth of experience
in treating patients with urinary tract stones.
At the same time, we give preference ONLY to non-invasive (external lithotripsy) and minimally invasive (contact laser ureterolithotripsy, minipercutaneous and percutaneous nephrolithotripsy, laparoscopic uretero- and pyelolithotomy) treatment methods. Despite the huge number of surgical treatments performed for urolithiasis, the number of open operations does not exceed 2-3 cases per year (!)
.
Sign up for a consultation
For treatment of urolithiasis, please call the number listed on the website.
Video on the topic
A pediatric urologist explains what ureterohydronephrosis is in children, treatment and prognosis:
In general, no natural remedies combined with diet can cure ureterohydronephrosis. However, their use, in combination with a thoughtful nutritional plan, can significantly improve a person’s well-being and help speed up post-operative recovery. Therefore, the use of such drugs and, especially, diet can be recommended as additional measures, after consultation with doctors.