The kidneys, due to their anatomical position, are to a certain extent protected from external influences. However, they are often damaged by trauma to the abdomen, lumbar region and retroperitoneum. In 70-80%, kidney injury is combined with damage to other organs and systems. Most patients are admitted to urology departments with isolated kidney injuries. Victims with combined injuries are often referred to general surgical departments.
Epidemiology
Gunshot injuries (wounds) of the kidneys occur mainly in wartime. According to the experience of the Great Patriotic War, they accounted for 12.1% of all injuries to the genitourinary organs. In subsequent military conflicts, an increase in the number of kidney injuries by 2-3 times was noted, which, apparently, is associated with a change in the nature of firearms. The main feature of modern gunshot injuries is the formation of a cavity along the wound channel, significantly exceeding the diameter of the wounding projectile, with a large area of destruction and necrosis, while the frequency of combined injuries exceeds 90%.
In peacetime, among patients in urological hospitals, the share of patients with closed kidney injuries accounts for 0.2-0.3%.
Classification
Mechanical kidney injury is divided by type into:
- Closed (blunt or subcutaneous) kidney injury: Kidney contusion (multiple hemorrhages in the renal parenchyma in the absence of macroscopic rupture of the subcapsular hematoma).
- Damage to the fatty tissue around the kidney and/or the fibrous capsule of the kidney.
- Subcapsular rupture without penetration into the collecting system. In this case, a large subcapsular hematoma is formed.
- Rupture of the fibrous capsule and kidney tissue with penetration into the pyelocaliceal system.
- Kidney crush.
- Trauma to the vascular pedicle or separation of the kidney from the vessels and ureter.
- Contusion (with extracorporeal lithotripsy - ELT).
- Bullet wound.
Depending on the nature of the damage:
- Isolated T.
- Combined T.
The area of kidney damage must also be indicated:
- Damage to the upper segment.
- Damage to the lower segment.
- Damage to the kidney body.
- Damage to the vascular pedicle.
Depending on the presence of complications:
- Complicated injury.
- Uncomplicated injury.
Closed kidney injury
The mechanism of damage may be different. What matters is the force and direction of the blow, the place of its application, the anatomical location of the kidney and its topographic relationship with the 11th and 12th ribs, the spine, the physical properties of the organ, the development of muscles, subcutaneous fatty tissue and perinephric tissue, the degree of intestinal filling, the amount of intra-abdominal and retroperitoneal pressure. Renal rupture occurs either as a result of direct trauma (lumbar bruise, fall on a hard object, body compression) or from indirect impact (fall from a height, bruise of the whole body, jumping). The impact of these factors can cause compression of the kidney between the ribs and transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae, as well as hydrodynamic effects due to increased fluid pressure (urine, blood) in the kidney.
In the presence of pathological changes in the kidney preceding the injury (hydronephrosis, pyonephrosis, kidney anomalies, chronic pyelonephritis), kidney damage occurs with minor impacts - the so-called spontaneous rupture of the kidney.
A special type of closed injury includes accidental damage during instrumental examination of the upper urinary tract. The development and implementation of new technologies in clinical urological practice has led to the emergence of a special type of closed kidney injury, which includes shock wave lithotripsy.
Anatomical changes in the damaged organ can vary from minor hemorrhages in the tissue to its complete destruction. Traumatic damage can occur without a clear violation of the integrity of the organ. In these cases, histological examination reveals morphological signs of circulatory disorders and dystrophic changes in the parenchyma. Functional disorders with such kidney injury can be even more pronounced.
Causes of kidney failure
Decreased renal circulation
Causes:
- Large blood loss.
- Serious cardiac dysfunction - cardiogenic shock, heart failure, severe arrhythmia,
- Severe decrease in blood pressure. Blood pressure drops below 80 mm Hg. Art. even for a short period leads to a sharp deterioration in blood flow in the kidney tissue.
- Mechanical rupture of blood vessels (trauma, surgery).
- Liver failure.
- Drugs that reduce blood flow.
Nephron damage
Causes:
- Exposure to toxic substances - poisons of organic and inorganic origin, medications (for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys - acute glomerulonephritis, tubulointerstitial nephritis
- Tumors leading to kidney damage.
- Other diseases leading to the destruction of nephrons, including autoimmune diseases.
- Severe allergic reaction.
- General infection (sepsis).
Blockage of the urinary tract
Causes:
- Obstruction (narrowing) of the urinary tract due to urolithiasis.
- Tumors of the genitourinary organs.
Open injury (wound) of the kidney
The causes and conditions for the occurrence of open kidney damage are different. Particularly severe open injuries to the kidneys are observed when they are wounded by modern firearms. This is due to the complex structure of the wound channel, the extensive area of tissue damage around the wound channel, and frequent combined lesions of several adjacent areas. Such injuries are often complicated by traumatic shock and massive blood loss.
Most gunshot wounds to the kidneys can rightfully be classified as severe. Complete crushing of the kidney is quite common. Injuries from shotguns are especially severe. The possible separation of the kidney from the vascular pedicle does not always lead to fatal bleeding, since the inner lining of the artery is screwed into the lumen of the vessel.
Knife wounds most often take the form of linear cuts, which can be located both radially and transversely in relation to the renal vessels. The latter circumstance has a certain significance for the choice of the volume and nature of surgical intervention. The closer the wound is to the renal pedicle, the greater the risk of damage to large vessels and the larger the infarction area with subsequent suppuration and melting. If the pyelocaliceal system, ureter is damaged and surgical intervention is not performed, urinary infiltration occurs with the development of phlegmon of the retroperitoneal space, and with injuries penetrating into the abdominal cavity - peritonitis.
What to do if you have a kidney injury and how to properly treat the injury
Any pathological changes due to kidney injury leave a mark for the rest of life and lead to the death of any part of the nephrons - the structural units of the kidney. A kidney bruise does not lead to rupture of the organ capsule and extremely rarely causes life-threatening bleeding, but it never goes away without a trace .
Photo 1. Kidney bruises, even mild ones, do not go away without leaving a trace.
Symptoms
Symptoms of closed injuries
Kidney damage is characterized by a severe condition of patients, heavy bleeding, severe pain, often urine leakage into surrounding tissues, urination disorders (dysuria) and dysfunction of internal organs, which often contributes to the development of both early and late complications.
Clinical manifestations are varied and are largely determined by the type and severity of the injury. Kidney damage is characterized by a triad of symptoms:
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Swelling of the lumbar region.
- Hematuria (blood in the urine).
The nature of the pain can be dull, sharp, colicky in nature, with irradiation to the groin area. Nausea, vomiting, bloating, symptoms of peritoneal irritation, and increased body temperature often cause diagnostic errors.
Hematuria is the most common and significant sign of kidney injury. Microhematuria is detected in almost all patients with such damage.
In addition to the listed symptoms, kidney injury may be accompanied by atypical, but important from a diagnostic point of view, signs:
- Dysuria up to complete urinary retention due to bladder tamponade due to blood clots.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Symptoms of peritoneal irritation.
- Gastrointestinal tract (GIT) dysfunctions.
- Signs of internal bleeding.
- Fever (as a result of the development of post-traumatic pyelonephritis and suppuration of urohematoma).
Depending on the clinical picture, there are 3 degrees of severity:
- Mild kidney injury - the general condition of the victim is slightly impaired, there is moderate pain in the lumbar region, short-term minor micro- or macrohematuria, there is no perinephric hematoma, there are no signs of peritoneal irritation. This type of injury is referred to as kidney bruise .
- Kidney injury of moderate severity - the general condition quickly changes from satisfactory to moderate severity (pulse quickens, blood pressure decreases), hematuria is pronounced and may continue to increase. The accumulation of blood in the bladder can cause dysuria (impaired urination), up to complete urinary retention. Under the skin in the area of injury, in some patients, a hematoma is clearly visible. The pain is insignificant and often radiates to the lower abdomen, groin area, and genitals. Obstruction of the ureter by blood clots can lead to the development of renal colic. Urohematoma can lead to the development of symptoms of peritoneal irritation.
- Severe kidney injury - collapse and shock come to the fore, severe pain in the lumbar region on the affected side, profuse and prolonged gross hematuria are observed. Urohematoma and signs of internal bleeding tend to increase.
Symptoms of an open injury (wound)
Open kidney injuries (wounds) are in many ways similar to closed ones in terms of clinical manifestations, principles of diagnosis and treatment. Main symptoms of injuries:
- Pain in the wound area.
- Hematuria.
- Urohematoma.
- Presence of a wound and wound channel.
- Leakage of urine from the wound.
The leakage of urine from a wound, although the most reliable symptom, is rarely encountered in the early stages after injury. If a kidney injury is suspected, the Nessler reagent technique can be used to determine urine in bloody discharge from the wound. Urohematoma rarely forms due to kidney injuries.
Pain in the lumbar region varies in intensity and depends on the condition of the wounded person and the degree of damage not only to the kidney, but also to other organs. Pain causes protective tension in the abdominal muscles, and the earlier it appears and the more severe it is, the more reason there is to suspect simultaneous damage to the abdominal organs.
Hematuria, as with closed injuries, is the leading and most common symptom of kidney injury. Blood in the urine appears quite quickly after injury; Already during the first urination or during catheterization of the bladder, the urine contains a large number of blood clots, which can lead to bladder tamponade. The degree of hematuria cannot judge the type and extent of kidney damage. On the contrary, the most severe injuries to the renal hilum area may not be accompanied by the appearance of blood in the urine, and small tears in the renal parenchyma sometimes lead to profuse hematuria.
Kidney bruise: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of injury | By the kidneys
Causes and symptoms of organ damage
Kidney bruise is a consequence of injuries of various types. It can be triggered by factors such as:
- an unsuccessful fall on a hard surface or various objects;
- strong compression that lasts quite a long time;
- striking the lumbar region;
- injuries in road accidents;
- domestic traumatic circumstances.
Very often, broken kidneys can be diagnosed immediately. All symptoms appear almost immediately. The most common manifestations of bruises from falls and other injuries are the following:
- pain syndrome;
- swelling in the lumbar region;
- discharge of blood when urinating.
Most patients complain of pain immediately after receiving an injury. The pain is quite intense and sharp, characterized by localization at the site of injury. A kidney injury can be immediately identified by the release of blood along with urine. The severity of the injury can be judged by the duration of hematuria.
In some cases, these symptoms do not appear. This does not indicate the severity of the damage. Rather, on the contrary, there is a risk of separation of the ureter or vascular pedicle of the organ. If blood is excreted in urine for a long enough time, anemia can develop.
Sometimes hematuria can appear some time after injury.
Swelling in the lumbar region is the second most important sign of organ damage. It is a consequence of intramuscular hemorrhage. In severe cases, urine may be added to the tissue behind the abdominal cavity and around the kidneys. As a rule, this circumstance may indicate a violation of the integrity of the kidney.
In addition, clinical signs such as:
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- temperature increase;
- abdominal bloating;
- bad feeling;
- decrease or increase in blood pressure.
If the kidney injury is complex, you may have symptoms that are similar to those of acute appendicitis. Often this state of affairs indicates the development of peritonitis. Organ damage may be accompanied by rib fractures, lung or liver damage.
Diagnostics
First of all, it is necessary to determine hemodynamic parameters. In cases where hemodynamics are not stable, surgical treatment is indicated. If hemodynamic parameters are stable, a complete examination of the patient is possible.
The presence of kidney injury may be indicated by hematuria (micro- and macrohematuria), pain in the lower back, in the lateral abdomen and lower chest, swelling and hemorrhages, as well as tension in the abdominal muscles, rib fractures, combined injuries of the abdominal organs, the presence of gunshot or stab wounds in the projection of the kidney, fractures of the spinous processes of the vertebrae.
Laboratory diagnostics
- Determination of microhematuria (blood in the urine not visible to the eye).
- Hematocrit (control).
- Hemoglobin (control)
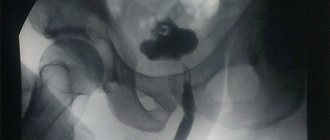
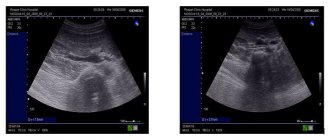
Instrumental diagnostic methods
- X-ray methods.
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Angiography.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose AKI, an initial examination by a doctor and a number of mandatory laboratory and instrumental tests are required.
Blood chemistry:
- Determination of the level of metabolic end products in the blood. The most specific indicator is the amount of creatinine. The higher it is, the more severe the degree of decline in renal function is diagnosed.
- Establishing the level of blood acidity (detection of acidosis).
Urine tests - general and biochemical. Impaired kidney function is indicated by increased levels of potassium and phosphorus, and decreased levels of sodium.
Hardware studies: ultrasound and CT (computed tomography). They are done to visualize the size of the kidneys and bladder, the presence of hydronephrosis (fluid in the kidneys), and urinary tract obstructions.
First aid
Treatment of a kidney injury should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. The most important task of first aid is to quickly transport the victim to a medical facility.
If you hit the kidney and there is pain, this is a reason to call an ambulance. Sometimes a bruise can be “silent” (not produce symptoms), but ultimately lead to serious consequences.
Algorithm for providing emergency care for a lower back injury:
- Place the victim on a hard horizontal surface.
- Place a cushion or something similar under your knees. This technique will reduce intra-abdominal pressure and reduce swelling.
- If your kidney hurts a lot after a blow, apply ice. A cold compress will not only reduce pain, but also slow down the growth of the hematoma.
Following these recommendations greatly increases the effectiveness of subsequent treatment.