Lebedeva E.N., children's speech therapist, speech pathologist-defectologist, Children's Clinic "Markushka"
Dyscalculia is a specific term that recently appeared in our society, and, unfortunately, is unfamiliar even to teachers. What is it, and what do parents, especially those with children – preschoolers and primary schoolchildren, need to know?
Dyscalculia in children
- a specific disorder of mathematical abilities, characterized by the child’s inability to successfully master even the simplest arithmetic functions.
Diagnosis of dyscalculia
Children with this specific disorder are characterized by:
- Difficulty determining and comparing the number of items;
- Difficulties in distinguishing between the concepts “more” and “less” without specific recalculation;
- It is difficult for them to name the sequence of the number series in both forward and reverse order;
- Difficulties arise in remembering the composition of a number, in understanding the semantic significance of arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division);
- Students have great difficulty memorizing addition and multiplication tables, mathematical terms are incomprehensible, and solving the simplest problems leads to a dead end if there is no visual subject line;
- Errors in writing and naming numbers are also common.
Classification
Taking into account the predominant nature of the deficiency, the following types of dyscalculia are distinguished:
- Verbal. Difficulty recognizing numbers and understanding listening problems. Normal performance of written tasks in the absence of mental arithmetic ability.
- Prognostic. The translation of specifics into abstraction and vice versa is disrupted. It is impossible to create a symbolic diagram for a practical problem.
- Lexical. Difficulty reading numbers and arithmetic operations. Auditory perception is normal, but problems appear when reading.
- Graphic. Oral mathematical operations are performed without errors, but the child does not understand what to do when asked to write down the problem.
- Ideognostic. Inability to mentally operate with mathematical concepts without relying on drawings, sticks, or notes.
- Operating room. Understanding and comparing numbers does not suffer; difficulties are noted when solving both oral and written examples.
Causes of dyscalculia
In studying the causes of such a disorder, scientists agree that the main thing is a disruption in the functioning of the cerebral cortex. This can be either a consequence of mental retardation, mental retardation, or a variant of a genetic hereditary malfunction, as well as a consequence of strong psychotraumatic factors. Impaired functioning of the visual analyzer, impaired processing of received information, difficulties in analytical and synthetic activity can also be the cause of dyscalculia. Therefore, we should talk about dyscalculia proper in cases of intact intelligence, against the background of which difficulties in mastering simple mathematics appear.
Dyscalculia in children can manifest itself independently, or in combination with reading (dyslexia) and writing disorders (dysgraphia).
Causes
There are psychogenic, organic and genetically determined variants. In many children, pathology occurs under the simultaneous influence of several factors, one of which is decisive. Identifying this factor allows you to select the optimal correction program, so experts pay great attention to identifying the leading cause of dyscalculia.
- Unfavorable heredity. Most parents of young patients experienced the same difficulties in childhood, indicating a genetic predisposition.
- Negative learning experience. Excessive punishment, conflict and coercion cause the child to lose confidence, provoke fear and aversion to the exact sciences.
- Organic brain lesions. The problem may be associated with dysfunctional changes due to complications of gestation, bad habits of the mother, intrauterine infections, traumatic brain injuries and infectious lesions of the central nervous system suffered in the first years of life.
Classification of dyscalculia
At the moment, several types of dyscalculia are known, each of which has its own characteristic signs. But as practice shows, the “pure” type is extremely rare, so the diagnosis of dyscalculia should be carried out by a specialist who, during the examination, will be able to see the whole picture.
In modern correctional pedagogy and psychology, graphic, verbal, lexical (numerical), operational, practical-gnostic and spatial dyscalculia are distinguished, as well as arithmeria (inability to master the calculation process) and pseudodyscalculia (underdevelopment of mathematical abilities due to lack of desire to learn, lagging behind in the curriculum or incorrect training program, when assignments are not based on the material covered).
Dyscalculia in schoolchildren. Most common types
| Type of dyscalculia | Characteristic |
| Graphic | Characterized by a violation of “coding”. Difficulties arise when writing the named number, errors in determining the grapheme related to the spoken number or the named mathematical term. Inability to graphically indicate a geometric figure written in a problem or spoken aloud in a verbal formulation. |
| Verbal | Characterized by difficulties in naming numbers, symbols, quantities, reading formulas and mathematical operations. |
| Practognostic | Inability to abstractly count objects, distribute them depending on quantity, shape or other characteristics in a given order. |
| Lexical | Lack of understanding of arithmetic functions, inability to solve mathematical examples or equations as a result of unawareness of operations with symbols, violations of spatial-visual processes. |
Symptoms
Signs of unstable behavior due to pedagogical neglect and social disadvantage are often observed. In most cases, along with dyscalculia, dysgraphia (problem of spelling and poor handwriting) is noted. But a child can write and read quite well.
Let us indicate some difficulties that are signs of specific dyscalculia :
- Misunderstanding what a number means, what its bit structure is.
- Lack of understanding of how numbers are connected and what their internal structure is.
- Misunderstanding what zero means, the left and right components of a number.
- Inability to build automated digital and ordinal series.
- Inability to add numbers past ten, subtract, divide and multiply.
- Inability to recognize number signs.
- Inability to relate numbers when performing arithmetic.
- It's difficult to learn the multiplication tables.
- Inability to solve problems that require understanding the meaning and carrying out two or more logical operations and the need to keep certain actions in memory.
- Lack of understanding of the mathematical content of diagrams and pictures that contribute to the correct solution.
- Inability to perform logical-abstract operations in the fields of algebra, geometry, trigonometry, and physics.
In other words, the child can easily count within ten, but does not operate with larger numbers. He is not able to understand the structure of numbers, to correlate the number and its spelling using numbers. Therefore, a child often has difficulty learning to tell time, practically does not remember dates, phone numbers, formulas, and at school cannot keep up with drawing, physics, and chemistry. If these symptoms appear, do not delay solving the problem.
Without the skills and abilities that mathematics provides, it is difficult to perform many basic daily functions. In addition, mathematics is one of the main subjects of many higher and secondary vocational educational institutions, which will be almost impossible for a child with dyscalculia to enroll in. A gradually developing fear of mathematics, generated by regular failures in class, can create many problems for a student.
Correction of dyscalculia
Corrective work to overcome dyscalculia should be carried out under the guidance of specialists. It is best when several specialists work with the child at once: a defectologist, a speech therapist, a psychologist, a neuropsychiatrist. Due to little knowledge of this disorder, most often all the work falls on the shoulders of a speech therapist or speech pathologist.
The developed speech therapy and defectology programs include a set of classes aimed at developing specialized mathematical actions and general life concepts, such as: more and less, number composition, mental counting, with the subsequent transition of actions into skills.
Particular attention is paid to the development of thinking, the formation of abstract thinking. At the same time, a program for speech development is being built to expand the vocabulary of children, and the ability to verbally compare, analyze and contrast is being taught.
Timely and complete classes for the correction of dyscalculia
allow you to successfully overcome this disorder, which helps to improve schoolchildren’s performance in mathematics and improve the child’s psychological state.
Development mechanism
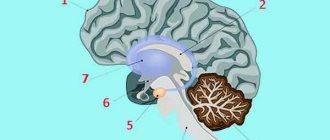
The pathogenesis is based on dysfunction of neurons in the intraparietal sulcus, insufficiency of connections between the parietal lobe and adjacent areas responsible for recognizing symbols and performing mathematical operations, and spatial perception. As a result, the processes of deciphering numbers and signs and comprehending tasks are disrupted. The situation is complicated by a decrease in concentration, a decrease in the amount of RAM, a lack of planning and a low speed of information processing.
How to treat the disease?
Treatment for dyscalculia may vary depending on the nature and severity of the disorder. But given the specific nature of the disease, therapeutic approaches such as cognitive rehabilitation are used to overcome it, and no drug treatment is provided. Once a child has identified learning problems and cognitive impairments associated with dyscalculia, the specialist develops a plan to overcome them. This is possible by tailoring the lesson to the child's individual needs, focusing on what causes him the most difficulty. The goal is to create a stable foundation for skill development. Helping your child develop math skills requires a hands-on approach. For example, you can use concrete material objects, such as colored glass stones, figurines, toys, etc., to teach your child how to count and perform simple arithmetic operations in the form of a game.
Classification and types of dyscalculia
- Verbal dyscalculia is a violation of the verbal designation of mathematical concepts.
- Lexical dyscalculia is a disorder in reading mathematical symbols.
- Graphic dyscalculia is a violation of the recording of mathematical symbols or signs, as well as a violation of the correct reproduction of geometric figures.
- Operational (or ideological) dyscalculia is the inability to operate with numbers and perform simple mathematical tasks.
- Practognostic dyscalculia is the inability to count or compare concrete, visual objects or their symbols.
Historical aspect
The term dyscalculia dates back to approximately 1949. It comes from the ancient Greek word δυς, meaning "bad" and the Latin calculāre, meaning "to count." In 1974, a Czechoslovakian scientist defined dyscalculia as “a structural disorder of mathematical ability.” His research proved that learning disabilities were caused by problems in certain parts of the brain that control mathematical calculations, and not because people with these symptoms were “mentally retarded.” Nowadays, researchers sometimes use the terms "mathematics dyslexia" or "mathematics learning disability" when referring to this condition.
The term is often used to refer to the inability to perform arithmetic operations, but is also defined by some educators and cognitive psychologists, such as Stanislas Dechen and Brian Butterworth, as a more fundamental inability to conceptualize numbers as abstract concepts of comparative quantities. Researchers consider this skill to be fundamental, the one on which other mathematical abilities are built.
More often, dyscalculia develops as a genetically determined learning disability that affects a person's ability to understand, remember, or manipulate numbers or number facts (such as the multiplication tables). Symptoms of dyscalculia include problems with simple counting, inability to remember simple arithmetic facts such as addition, subtraction, etc. But to date, few symptoms of the disease are known as little research has been done.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 3,500 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 2,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 2,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 6,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 25,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 48,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Hypnosis (1 session) | 10,000 rub. |
| Hypnotherapy course (5 sessions) | 45,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 8,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 9,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 2 persons | 11,500 rub./day |
| Ward for 2 persons Comfort | 12,500 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 16,500 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Treatment
The basis of therapy is psychocorrective exercises that stimulate the development of neural connections. Educational psychologists and speech therapists who know how to treat dyscalculia work with the child. According to indications, nootropics are additionally prescribed. The emphasis is on the formation of such functions as:
- Spatial. Skills in working with the concepts of length, width, height appear. Children learn to determine how objects relate to each other and to pictures.
- Speech. Sufficient vocabulary and the ability to articulate clearly provide a foundation for working with mathematical terms. Patients master arithmetic concepts and learn to use them freely in conversation.
- Arithmetic. They move to this stage after mastering the previous ones. Work includes listening, visual demonstration, oral reproduction, and writing of number operations. Patients learn to understand the meaning, remember the conditions, and choose the logic for solving a problem.