Wet hair and strong wind
We are constantly in a hurry and, having washed our hair in the morning without drying it properly, we rush to work or run errands.
We rushed out into the street, and this is the result - our wet head was blown by the wind. Unpleasant symptoms appear: temperature 37 and above, shooting in one ear, pain in the left or right side of the skull and ear. All this is due to the fact that it blew.
All this is due to the fact that it blew.
Main symptoms
Typically, symptoms appear very quickly, while the clinical picture can be acute and increase rapidly. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the chance of a quick recovery and avoiding complications.
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 –>
If you have a wind blowing through your neck and head (usually patients point to the right or left side of the head), then the most common symptoms are as follows:
p, blockquote 5,0,1,0,0 –>
- Weakness and aching sensation in the bones, teeth may hurt.
- It is difficult or completely impossible to turn your head.
- Headache. The head can hurt both from the inside and outside in the area of the hair roots. It can be localized on the left or right side of the skull, as in migraines. The back of the head may hurt, shoot in the temples, or there may be aching pain in the crown area.
- An increase in temperature, accompanied by muscle tremors, increased heart rate and breathing.
- A feeling of heaviness, both in the skull and throughout the body, dizziness, nausea, decreased performance.
- Noise, feeling of pulsation, shooting in the ears.
- A head cold can cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
- The lymph nodes in the neck become inflamed.
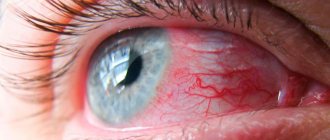
- Watery eyes and redness of the eyes.
- Sometimes the scalp hurts.
- Photophobia, chills, tremors throughout the body.
- In chronic diseases of the heart muscle, instability of blood pressure may occur.
These are not all the signs of a head cold, although they are characteristic of many different diseases. We do not recommend dealing with each symptom separately; the best option is to call a doctor at home. Thanks to a correct diagnosis and competently prescribed treatment, it is possible to exclude the development of complications and promptly identify the possibility of the occurrence of concomitant diseases.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 –>
We do not recommend dealing with each symptom separately; the best option is to call a doctor at home.
The true causes of neck pain
Drafts are the most innocent reason for a cold neck. People with “sedentary” professions often complain about a sore neck, especially those who are forced to remain in one position for a long time - pianists, drivers, PC operators, etc. Due to a tense position, the blood supply to the muscles is disrupted.
Painful sensations up to sudden attacks appear if there is:
- Infections. Viral infections are one of the most common causes of neck pain. From the tonsils the infection spreads to the muscles. This happens with ARVI, influenza, syphilis and tuberculosis. If the inflammation is caused by a fungus or purulent infections, surgical treatment and removal of pus is necessary.
- Autoimmune causes. Inflammation in the neck muscles is often the reason that the body begins to fight itself by producing antibodies. In this case, the pain will be very severe, often this symptom accompanies rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or sclerederma.
- Parasites. Toxoplasmosis, trichinosis and other diseases caused by parasites in the body often provoke muscle inflammation.
- Poisoning. Alcohol abuse, drugs, drug overdose, or bites from venomous reptiles and insects cause severe spasms and the neck may become inflamed.
- Neck injuries. Bruises, cuts, hypothermia, sprains during physical activity - all this can cause inflammation and swelling. A hernia in the neck can pinch a nerve.
purulent inflammation;
Drug treatment of myositis
It is impossible to treat a cold neck without the use of special ointments and creams. These funds differ in type and principle of action:
| Type of ointment | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Warming |
| Name | Diclofenac, Nice, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam | Finalgon, Menovazin, Bystrum-gel, Apisatron |
| Operating principle | Stop the inflammatory process, relieve pain and swelling | Improve blood circulation, tissue trophism, reduce pain |
You can use irritant and anti-inflammatory agents together, alternating them according to the instructions.
If your neck has a cold, a pepper patch will help you quickly cope with the pain. It relieves pain and warms by strongly irritating the skin with the essence of red pepper. Apply the patch to the inflamed area for 3-5 days for 12 hours. Before the first use, you should check whether there is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
Before the first use, you should check whether there is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
Natural ointments
Badger fat, unsalted pork fat or butter are suitable as a fat base for homemade ointments. Medicinal ingredients include chamomile flowers, lilac flowers, horsetail herb, willow buds and bay leaves. Each of the plant components can be used separately or in the form of collections.
The plants should be crushed into powder, combined with a fat base and kept in a water bath for several hours, preventing the mixture from boiling. Place the cooled mixture in a glass container and leave in a dark place to harden and infuse for 10 days.
The ointment is applied to the painful area up to three times a day in the form of warm compresses. It is better to prepare the product in advance and store it in the refrigerator as “first aid” for bruises, myositis, radiculitis, and sprains.
Boil 20 fresh physalis fruits in 500 ml of distilled water for 15 minutes.
Causes of head colds
You can get a cold in your head in different ways. Beware of drafts, strong winds, and air conditioners. People who have a head cold are at risk for a number of complications.
People who have a head cold are at risk for a number of complications.
Cervical myositis. Why does my neck hurt?
Myositis
– inflammation of skeletal muscles with the formation of nodules inside them and aching pain. As a rule, a person finds out about the disease either in the morning or after some time if he catches a cold in his neck during the day. His muscles swell and spasm, and any movement of the head touches the nerve endings. This gives rise to aching pain, which can intensify with movement, when pressing on the area of redness, and “give” to other parts of the body, for example, the shoulder, forehead or shoulder blade.
Is it possible to protect yourself from cervical myositis? Yes, it's possible. First, you need to avoid prolonged and frequent stress - this directly affects the immune system. Stress causes muscle contraction as a protective reaction of the body. This leads to their spasms and possible inflammation.
It is also necessary to monitor the temperature in the room, avoid drafts and hypothermia. The easiest way is to purchase special climate control equipment for these purposes.
Another reason for the appearance of cervical myositis may be incorrect posture and constant tension of the neck muscles due to the profession: drivers, violinists, office workers and others. If you sit for a long time at a computer, book or in front of a screen in an uncomfortable position, you should think about changes in the workplace. This position causes the muscles to contract more often and contributes to their spasm.
If you slept in an uncomfortable position, this can also cause cervical myositis.
Myositis is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, to summarize all of the above:
- Play sports - it will give you strength and energy and strengthen your body.
- Take a contrast shower or harden yourself - myositis often occurs as a complication after viral diseases: acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, colds, and so on.
- Maintain healthy sleep - at least seven hours.
- Proper nutrition is the key to excellent health and mood.
Now let’s find out what symptoms accompany myositis and why it is dangerous.
Just keep in mind that palpation will also increase the pain.
Diagnostics
When patients come to see a doctor, they say: “I can’t turn my head” or “I have a cold neck, how to treat it.” For diagnosis, in most cases, an external examination and collection of patient complaints is sufficient. In some cases, it will be necessary to additionally donate blood for analysis, undergo x-rays, electromyography and biopsy.
Under such conditions, inflammation spreads to the neighboring muscles of the esophagus and larynx, causing disruptions in their work.
What symptoms indicate that you have a headache?
The development of the disease is based on a certain mechanism. In the smooth muscles of the skull or neck, under the influence of a flow of cold air, local (limited) non-purulent inflammation occurs. Tonic tension occurs in the muscles, that is, spasm. It contributes to disruption of blood flow in small vessels, as a result, biochemical breakdown products begin to accumulate in the affected area, pain and tissue compaction appear.
The head is blown (symptoms and treatment in adults are described later in the article), which means that in 90% of cases there will also be stiffness when moving the neck and heaviness in the back of the head. It is caused by an inflammatory process in the muscles of the cervical spine or changes in the cranial nerve plexuses. As a result of hypothermia, these structures can swell, increase in size, and compress nearby organs.
Therefore, patients often complain of:
- one- or two-sided migraine-like pain in the occipital, temporal, vertex, parietal region of the head, intensifying when trying to turn or tilt the head; in more rare cases, pain is localized in the facial area;
- lumbago in the area of the eyes, ears, face, back of the head, forehead;
My head blew. Symptoms and treatment - a feeling of stiffness in the neck and shoulders, stiffness in head movements;
- loss of sensitivity and sensation of “crawling goosebumps” (paresthesia), pulsation at the temples;
- rare dizziness, blurred vision or spots before the eyes, ringing in the ears;
- moderate general malaise, weakness, apathy, weakness;
- chills, temperature rise to low-grade levels (37.5-38°);
- long periods of falling asleep, frequent awakenings, nightmares, night sweats;
- increased anxiety, irritability, tearfulness.
Characteristic manifestations
If you have a head cold, a person experiences a whole range of characteristic symptoms. Their appearance is associated with general intoxication of the body, as well as an increase in the amount of intracranial fluid. These manifestations can be complemented by more serious disorders, for example, inflammation of the facial nerves.
The first signs of a cold appear within a few hours.
The main symptoms that indicate that the head has blown are the following:
- Severe headache, even migraine. If you have a headache due to a cold, there is a specific feeling as if the roots of your hair hurt. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the back of the head, forehead, temples;
- Dizziness;
- Feeling of heaviness in the head area;
- Shooting pains in temples;
- A sharp increase in temperature;
- Periodic, short-term, but intense pain in the forehead, chin, cheeks, nose. A similar symptom indicates that the trigeminal nerve has been chilled;
- Nasal congestion, runny nose;
- Photophobia;
- Noise and pulsation in the ears;
- Pain in the neck muscles;
- Pain in the neck that gets worse when you try to turn it to the side;
- Chills;
- Redness of the eyes and areas around them;
- Changes in blood pressure;
- Drowsiness, general weakness;
- Decreased concentration.
If the right side of the head hurts, which is complemented by unpleasant sensations in the ear area, we are talking about myositis - a phenomenon in which the head is blown out and the neck muscles become inflamed. With myositis, the pain is initially aching in nature, then becomes more intense. The right eye may also become watery.
Pain in one of the sides of the head and ear may also indicate otitis media, which develops due to exposure to drafts.
If your head is blown and characteristic symptoms occur, it is important not to ignore them, but to immediately consult a doctor: if the head is hypothermic, neuralgia may develop. The condition is characterized by the appearance of burning pain along the occipital or trigeminal nerve, the occurrence of spasms of the facial muscles, and profuse sweating. Neuralgia can lead to paralysis of one half of the face.
Read how to treat occipital neuralgia.
The appearance of convulsions, bouts of vomiting, pain when turning the head to the sides are characteristic symptoms of the development of meningitis. In this case, it is important to transport the patient to a medical facility as soon as possible.
Probable Causes
The head is blown (symptoms and treatment in adults depend on the degree of hypothermia), which means you need to start therapy without delay. The treatment regimen is determined based on the cause of the development of symptoms and the severity of the pathological process.
Air conditioner
The cause of the disease can be prolonged exposure to air conditioning during the hot season, especially being under a direct stream of air. Therefore, office workers who are forced to stay at their workplace for 4-6 hours can often complain of a cold head.
Wet hair and strong wind
It can easily blow the head of athletes or dancers who sweated during training and immediately went out into the cold air. In addition, going outside with undried hair or sleeping at night with wet hair in a cold room can cause this condition.
Constant exposure to a cold air stream contributes to the development of a cold in the head, so this often happens when fishing, during a hiking trip, while hunting, or when working in the garden. A sweaty head under a hat can also cause a cold if there is a piercing cold wind outside.
Open doors and windows
It can get drafty when ventilating a room, with open windows on a train, on a bus, especially when there is a large difference in temperature outside and indoors.
Draft in the car
The driver's head was blown - a typical situation when driving at high speed with the windows open. Truck drivers often complain of a head cold. Symptoms that arise in adults require close attention and differentiation from other head diseases. If treatment is not started on time, serious consequences may develop.
Other Possible Causes
Other possible reasons include:
- Swimming and diving in cold springs, ice holes and natural reservoirs. Prolonged stay in water with low temperature contributes to the launch of inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the head.
- Walking without hats in the cold season. This is how young boys and girls get headaches, trying to dress according to fashion, and not according to the weather.
- Riding on open water boats at high speed, especially after swimming in rivers, seas, lakes. On the water, the risk of hypothermia increases, which is associated with high air humidity, so high-speed walks on water transport can provoke the development of colds.
- Accommodation in regions with low temperatures (Yakutia, Chukotka and others). In these areas, you can catch a cold even in warm clothes, since at times gusts of wind and weather conditions reach critical levels.
- Chronic stress and constant physical fatigue. In these cases, the muscles of the body are always tight, blood circulation and lymph outflow are difficult, so you can catch a cold at any time from a light breeze.
The head is blown (symptoms and treatment in adults may vary due to concomitant diseases) - people with a predisposition who have chronic diseases often complain about this:
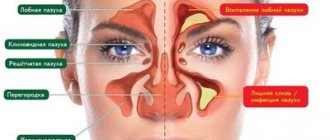
- sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- cervical osteochondrosis, cervical myositis, glenohumeral periarthritis;
- otitis, eustachitis;
- conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis;
- lymphadenitis; extensive furunculosis;
- erysipelas, eczema, abscesses on the face, neck, head;
- neuritis of the facial, trigeminal, oculomotor nerves;
- stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, deep caries, formation of cysts in the oral cavity;
- injuries, wounds, bruises of the soft tissues of the face and skull.
With all these pathologies, inflammatory processes are localized in the cranial-occipital or facial part of the head, so with any hypothermia they can spread to nearby tissues.
It is easier to get a cold in people with a weakened immune system, suffering from severe chronic pathologies and acute infectious diseases.
Special risk groups include:
- People with immunodeficiencies - persistent disorders in which one or more parts of the immune system cannot protect the body from infections. With physiological deficits that accompany critical stages in the development of the body, it is easy to get a cold. Although the disease will take longer and be more difficult than in healthy people, recovery will be complete. But with primary or secondary immunodeficiencies, the disease can become seriously complicated or its treatment may be delayed for a long period. Common immunodeficiencies include DiGeorge, Duncan, Bruton, Louis-Bar syndrome, blood and lymph diseases.
- Patients with autoimmune pathologies. A malfunction occurs in their body, immune cells begin to “absorb” healthy human tissues, as a result, a chronic inflammatory process develops, which under unfavorable conditions (hypothermia, infection) begins to spread to other organs. Common autoimmune disorders include scleroderma, vasculitis, lupus erythematosus, and others.
- Patients suffering from diabetes, gout, and inflammatory diseases have a reduced immune status and a weakened body. Because of this, it is easier for them to catch a head cold than for healthy people.
Consequences for the human body
A cold threatens with a number of unpleasant and even dangerous complications. Even after a slight draft that blows through the back of your head, you can get:
- neuritis, in particular, neuritis of the facial nerve;
- tendonitis (tenosynovitis, tendobursitis), arthritis;
- inflammatory processes in the maxillary and frontal sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis);
- otitis, meningitis;
- arachnoiditis;
- conjunctivitis;
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- infectious brain abscess.
All of these diseases are serious, require difficult and long treatment, sometimes threaten irreversible complications, and require referral to different specialists.
Neuritis of the facial (trigeminal) nerve
If the left side of the head or the right is blown, there may be inflammation of the nerve innervating the facial muscles on one side of the face. As a result, their weakness (paresis) and even complete paralysis of facial movements develops.
People with an anatomically narrow bone canal are more prone to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Due to deterioration of blood supply and pinched nerve, tunnel syndrome is observed.
Pathology occurs due to the fact that the head is blown by the wind or blown by a fan. People sitting near air conditioning or constantly exposed to drafts are at high risk.
Meningitis
Meninitis does not occur from hypothermia; it is infectious or bacterial in nature. However, if an adult or child constantly has a cold head, this indicates a decrease in immunity. This means that the body is especially susceptible to various viruses and bacteria.
Meningitis is a very dangerous disease, so if, after blowing through the right or left side of the head, you experience pale skin, weakness, lethargy, anxiety, drowsiness, or severe headache, you should urgently consult a doctor who will prescribe medication treatment.
Otitis
Otitis is a group of inflammatory diseases of the ear, which manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- pain when opening the mouth;
- pain in the ear;
- swelling and redness of the ear;
- pus from the ear;
- increased body temperature;
- itching and congestion in the ear.
If all these symptoms occur after the back of the head or neck has been blown, you should urgently consult an otolaryngologist.
Infectious brain abscess
This is the name of the purulent-inflammatory process that occurs in the brain tissue. Most often, this complication affects people who have a cold, have a weakened immune system, or have a history of severe chronic diseases.
Often the cause of an abscess is untreated purulent otitis media - also a consequence of a frozen head.
The disease is accompanied by:
- high temperature;
- chills;
- weakness and pallor;
- blood leukocytosis and increased ESR;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- nausea and vomiting.
The course of the disease is acute, severe, and requires immediate medical attention.
Inflammation of the maxillary or frontal sinuses
Acute inflammation of the maxillary and frontal sinuses, resulting from a blown head, is usually severe and accompanied by severe pain in the head and forehead.
Sinusitis
This is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which is almost always a consequence of a severe runny nose and colds, poorly or unfairly treated. Symptoms of the disease are:
- temperature rise to 37-38 degrees;
- loss of sense of smell, as the nose begins to become stuffy;
- heaviness in the head;
- pain in the temples and bridge of the nose;
- decreased performance;
- memory impairment.
Frontit
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses occurs with prolonged runny nose and sinusitis. Symptoms:
- nasal congestion;
- temperature increase;
- fever in children;
- pain in the forehead;
- decreased sense of smell or its complete loss.
Treatment is complex with the use of antibiotics. How long your headache will hurt depends on proper therapy.
Tendinitis
Often a complication of a cold neck is temporal tendonitis - inflammation of the tendon of the masticatory muscles. With the disease, pain is felt when moving the jaw, which radiates to the neck and head.
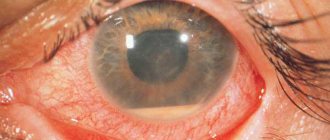
Conjunctivitis
With conjunctivitis, swelling of the eyelids, redness, burning, itching of the eyes, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign object in the eye, as well as purulent, mucous discharge develop. Eyelashes tend to stick together in the morning.
If the disease is not treated, headache, enlarged lymph nodes, and weakness may occur. How to treat conjunctivitis caused by a cold? Antiviral ointments and drops are prescribed.
Arthritis
Temporal arthritis, as a complication of hypothermia of the head, develops when nerve endings are damaged. The disease is accompanied by acute, shooting pain at the site of inflammation, usually only on one side of the head.
Painful attacks occur spontaneously, as if for no reason.
Lymphadenitis
Pain under the jaw and slightly below the ear, slight swelling and tenderness in this place indicates the development of lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes. Ear pain also bothers me.
This complication is treated by heating with dry heat (semolina, salt) or semi-alcohol compresses.
Arachnoiditis
Inflammation of the lining of the brain, leading to the formation of cysts and adhesions, is called arachnoiditis. The pathology can appear several months after the head cold, and is characterized by a gradual increase in symptoms. Among them:
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- weakness and fatigue;
- irritability;
- epileptic seizures;
- headaches.
Differentiation of diagnosis if the head is blown
The head is blown (symptoms and treatment in adults may be similar to inflammatory diseases of brain tissue), which means that differential diagnosis needs to be carried out as soon as possible. There are often situations when it is necessary to identify symptoms that distinguish a head cold from more severe diseases caused by the penetration of bacteria or viruses into the body.
Distinguishing signs of a head cold from brain infections:
| Diseases | Signs | Treatment |
| Cold | It begins gradually, causing moderate heaviness and pain in the back of the head. Patients maintain satisfactory general condition and performance; the temperature is rare and does not rise above 37.5-38°. The duration of the acute phase of a cold is 2-5 days. | It is carried out at home, the basis is symptomatic remedies and a properly organized diet and rest. |
| Meningitis, encephalitis | It begins acutely with a rise in temperature to 38.5-39° and above. The general condition of the patients is extremely serious, accompanied by severe weakness, severe headaches, nausea, and vomiting. The duration of the disease is 7-14 days, rehabilitation after the disease is long. | Urgent hospitalization is required. In a hospital setting, intensive antibacterial and infusion therapy (drips are placed) is carried out. |
An important diagnostic distinguishing feature of inflammation of the meninges from a common cold of the head is the presence of a source of bacterial infection, that is, contact with the patient. But cases of the disease spreading upward, due to acute inflammatory pathologies of the ENT organs or as a complication of pneumonia are not excluded.
Common methods of diagnosing a head cold include:
- collecting complaints and studying the life history of patients (lifestyle, profession, chronic diseases, injuries, bad habits);
- an objective examination reveals hyperemia, swelling and hardening of soft tissues, the presence of lymphadenitis, injuries;
- instrumental diagnostics using ultrasound scanning, computed tomography, x-rays, and MRI is necessary in cases of suspected infectious processes, trauma, or neoplasms;
- laboratory methods make it possible to identify the causative agent of infection (using smears), analyze the biochemical composition of the blood, and indirectly determine the degree of inflammatory changes using a general blood and urine test.
Symptoms of a cold head
If you have a cold in your head, it is important to pay attention to the area where the pain arose and the nature of this pain
Symptoms of the disease depend on the part of the damaged area of the head, which organs and tissues were exposed to the inflammatory process. Pay attention to the following ailments:
- Heat
- Shiver
- Migraine
- Sudden changes in blood pressure
- Dizziness
- Noise in ears
Important: you must first pay attention to the area where the pain occurred and its nature.
If pain is felt in the forehead and nose, this may indicate the occurrence of frontal sinusitis and sinusitis.
If there is shooting pain in the mouth, eyes, forehead, cheeks, it is difficult to drink cool liquids, or acute pain occurs when there is wind, then most likely the inflammation has affected one of the nerves of the face.
If the ear area or behind the ears hurts, then it is otitis media.
Red eyes, pain and a feeling of a foreign body in the eyeballs are a signal that conjunctivitis has begun.
Pain under the lower jaw and swelling indicate the development of lymphadenitis.
Acute pain in the head, which is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, nausea - these signs indicate meningitis. If, when changing body position, a person experiences severe pain, cannot tilt his head, or has a high temperature, then immediately call an ambulance. Since convulsions and other unpleasant manifestations of meningitis complications are possible.
If a person experiences a severe headache when exerting himself, jumping, and if he has insomnia, impaired memory and depression, then this indicates the development of arachnoiditis.
A cold in the head causes decreased vision if the optic nerve is affected, and leads to dental disease with an inflamed trigeminal nerve and other complications.
Without treatment, a cold head can lead to pathologies, including cardiac ones.
Often a person does not pay attention to the symptoms of a head cold. Everyone thinks that they have a cold, which can be treated with the usual medications, and no complications will arise.
But if you do not start treating the head in a timely manner, at the first signs, then this leads to unpleasant consequences, and pain in the head will accompany the person constantly. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent a head cold, and if this happens, then start treatment in a timely manner.
First aid
If you experience pain due to a head cold, you can take painkillers (Citramon, Spazgan and others) and go to bed. You can moderately insulate your head - wear a scarf or tie a scarf. It would be rational to increase the water regime, this will help to quickly remove harmful substances from the body. It is useful to drink herbal teas with an anti-inflammatory effect, containing chamomile, St. John's wort, and calendula.
It is important to ensure information peace, turn off the loud sound of the TV, radio or reduce it as much as possible.
If taking painkillers and proper rest has brought significant relief and no new complaints have arisen, you can continue treatment at home. If the condition worsens, then it is time to contact your local physician for examination and treatment.
Can you blow your head?
Many patients are skeptical that the unpleasant sensations were blown by the wind, which is why they do not carry out the necessary prevention of the disease. It is important to remember that an unfavorable condition can develop not only in cold weather. Increased risk factors are present on hot days and when staying in a stuffy room.
Reasons why you might get a cold:
- refusal to wear a hat in cold or windy weather, with low immunity;
- refusal to use an umbrella when it rains;
- staying outside with poorly dried hair, especially in the presence of wind;
- staying under a running air conditioner or being in a drafty room;
- a sharp transition from a hot room to cold outside in winter and a change from a warm street to a cooled room in summer;
- traveling in a car or public transport with the windows open;
- swimming in cold water;
- heavy consumption of ice cream or iced drinks in the heat.
You will learn about the effect of air conditioning on the development of pathology here.
Air conditioning is one of the reasons for a cold head.
If you get a headache, you need to act quickly. You should not rely on your immunity and refuse treatment. Ignoring symptoms can lead to inflammation of the nerves of the neck, face and head. With the development of the inflammatory process, the development of sinusitis, otitis, and tendovaginitis is likely. Inflammation of the lymph nodes and the onset of conjunctivitis are possible. In complex cases, the pathology spreads to the brain, causing meningitis, arachnoiditis, and the formation of abscesses.
How to treat a cold head in adults
The head is blown (symptoms and treatment in adults are determined depending on the severity of the disease), which means you need to start taking symptomatic medications.
Drug treatment
To reduce fever or relieve chills use:
- Aspirin;
- Paracetamol;
- Ibuprofen;
- Cefikon.
In order to reduce pain, the following are prescribed:
- Analgin;
- Spazgan;
- Nice;
- Ketarol.
The following will help reduce swelling and inflammation of soft tissues:
- Arthrozan;
- Diclofenac;
- Ortofen.
The following will help strengthen the body's overall resistance:
- Combilipen;
- combined vitamin and mineral complexes;
- biological supplements containing omega-3 acids.
If the head is blown out along with the neck and shoulder girdle, the following is added to the treatment:
- warming and anti-inflammatory ointments;
- several physical procedures (ultrasound, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy);
- exercise therapy;
- massage.
If lymphadenitis occurs, antibacterial therapy is prescribed (a course of intramuscular injections of Ceftriaxone).
Head colds caused by viral infections may require the use of antiviral drugs and interferons:
- Arbidol.
Arbidol for adults - Amexin.
- Ingaverin.
Home treatment assistance
At home, a light stroking massage of the head and neck can help. It is important to perform movements in the direction from the crown and crown down, from the back of the head and temples down, that is, in accordance with the blood flow through the capillary plexuses.
Where exactly does it hurt
It is very important to determine exactly where the person’s head blew. Symptoms in adults and children are approximately similar, but what can you expect from a child if even a respectable uncle with a higher education sometimes cannot pinpoint exactly where he experiences discomfort? But this is very important for making a diagnosis!
- Frontal pain. In most cases - above the eyebrow and on the right. This is a clear manifestation of the consequences of a draft.
- Shot in the temple. Also most often on the right side, and usually when touched. This is clearly not a “headache” - the symptoms clearly indicate more serious problems.
- Aching pain in the temple, rising in peaks and falling sharply. Characteristic of cervical osteochondrosis. Not accompanied by temperature.
- “Shoots” at the crown of the head. These are so-called referred pains. That is, something else hurts you, but it just radiates to your crown. A full and thorough examination may be required.
- Shot in the back of the head. Another sign that you have a headache. Or, if observed in the morning and in the absence of drafts, during sleep you rarely turned around, and your head was in a rather uncomfortable position.
- Rising and falling pain, intensifying in a lying position, may indicate a diseased tooth.
- Shoots in the ear and the side of the head hurts on the same side - most likely otitis media. It is also caused by “blowing” and can radiate to the entire area of the forehead and to the back of the head.
If you can more accurately describe your feelings (at least for yourself), and you yourself will know what to do before you get to the clinic, and the doctor will make a diagnosis more accurately and quickly.
Possible consequences if left untreated
The inflammatory process may worsen if, at the height of the disease, patients refuse to wear warm hats during the cold season, stay in a draft for a long time, or continue swimming in bodies of water with low temperatures. Serious consequences arise not only without treatment, but also as a result of negligent attitude towards health.
Neuritis of the facial (trigeminal) nerve
The disease begins suddenly and is accompanied by:
- severe, burning pain;
- numbness;
- facial paresthesias.
Then one-sided asymmetry and lack of facial expressions appear.
Treatment of the disease is long-term, complex with active use:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- local anesthetics;
- hormones;
- biostimulants.
Meningitis
This is an acute infectious disease accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- stiff neck;
- high temperature;
- severe intoxication.
Patients with meningococcal infection are hospitalized, and a course of antibacterial therapy is carried out in the hospital.
Otitis
Inflammatory process in one or more parts of the hearing aid. It is characterized by sharp shooting pains in the ear, the appearance of serous or purulent exudate from the ear canal. The disease can be treated with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammation of the maxillary or frontal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis)
As a result of the spread of the pathological process along the descending pathways, inflammatory changes can affect the sinuses located in the forehead and nose. Mucous or purulent contents begin to actively accumulate in them.
The result is:
- pressing headaches;
- runny nose;
- snoring during sleep;
- sometimes a rare cough.
The basis of treatment for these diseases is the use of antibiotics and vasoconstrictor drops.
Tendinitis
This is a disease of the musculoskeletal system that affects the tendons. It manifests itself as difficulties in moving the limbs, dull, prolonged pain.
The following are used in treatment:
- non-steroidal drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- vitamins;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy.
Conjunctivitis
This is an ophthalmological pathology associated with inflammatory changes in the outer shell of the eyes.
Signs of the disease are:
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eye;
- burning;
- itching;
- photophobia;
- thick discharged exudate from the conjunctival sac.
Treatment of the disease consists of frequent instillation of eye drops with an antimicrobial effect.
Lymphadenitis
The pathology is expressed in enlargement and pain of regional lymph nodes located at the site of localization of the inflammatory process. Without treatment, the disease can spread to other lymphatic vessels. The basis of treatment for lymphadenitis is the intramuscular use of cephalosporin antibiotics.
Arachnoiditis
Arachnoiditis refers to diseases of the nervous system and is characterized by pathological changes in the arachnoid membrane of the brain or inflammation of the spinal cord.
Signs of the disease include:
- persistent headaches;
- dizziness;
- pathologies of vision and hearing;
- epileptoid seizures.
Treatment tactics depend on the type of inflammation and its location; it is divided into medicinal and surgical.
A headache is a common problem. Symptoms and treatment in adults are often overlooked. It is enough to exclude the factors that provoked this condition, carry out symptomatic therapy, and the patient’s health is restored within 5-7 days. It all depends on the cause of hypothermia, the general immune status of the patient and concomitant diseases. In general, the prognosis for a head cold is favorable; only in advanced cases can complications arise that require long-term treatment or emergency hospitalization.
Effective methods for treating a cold neck
Treatment of a cold neck or myositis is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Pathology can develop at any age. Symptoms of the disease increase during movement or when touching the affected muscle.
- 1. Clinical picture
- 2. Drug therapy
- 3. NSAIDs and massage
- 4. Application of ointments
- 5. Folk remedies
The first obvious symptom of myositis is pain. For many patients, it appears in the morning when they try to get out of bed or turn their neck. During the night, inflamed muscles swell and spasm, irritating nerve fibers. The pain is aching in nature and increases with any movement. It localizes asymmetrically (depending on which side was penetrated or pulled).
In severe cases, irradiation is observed in the shoulder, temples, ears, forehead, and on the back in the area of the shoulder blades. A feature of the disease in a child is a rapidly rising body temperature. At the same time, my head hurts a lot. In adults, symptoms of fever are rare. Children are more likely to develop complications.
Acute and severe pain in the neck is a reason to contact a neurologist. After examination, the doctor must rule out spine pathology. What to do if the patient has a cold or a sore neck, the doctor will decide in each case individually. If necessary, consultation with a physiotherapist and surgeon will be required.
Recommendations for the treatment of myositis:
- 1. The neck muscles should be calm.
- 2. A warming agent is applied to the diseased part of the body, wrapped in a warm scarf.
- 3. If there are no ointments, it is recommended to apply a warm compress with vodka, but only for adults.
- 4. Therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- 5. Self-massage. The manipulation is performed during or after applying a warming ointment. Massage is contraindicated in the presence of inflamed lymph nodes.
- 6. Taking antipyretics for body hyperthermia (Paracetamol, Nurofen).
- 7. Attacks of unbearable pain must be stopped in a hospital setting, where the doctor carries out a novocaine blockade.
If self-medication at home does not bring relief within 2-3 days, you need to contact a specialist. Standard course of treatment to combat myositis:
- 1. Bed rest, especially if the disease appeared as a result of professional activity. A diet is prescribed that excludes fatty, fried, spicy foods and alcohol.
- 2. Antibiotic therapy (Sumamed, Gentamicin) when diagnosing the infectious etiology of the disease. With a purulent form of myositis, you need to open the abscess and treat the wound with antiseptics.
- 3. Relieving inflammation and pain using NSAIDs.
- 4. Relieving pain and muscle spasms with warming ointments and gels. Dry heat in the form of a heating pad works great.
- 5. Physiotherapeutic procedures - massage of the cervical-collar area, acupuncture. After pain relief, exercise therapy is prescribed.
If the pathology is parasitic in nature, the patient is prescribed anthelmintic drugs. Additionally, manual therapy and vasoactive treatment are prescribed. Drug therapy for myositis is aimed at blocking inflammation. For this, the patient is prescribed painkillers (Ketorolac, Metamizole).
In case of an acute attack of pain, the use of non-steroids (Ibuprofen, Amizon, Reopirin) is indicated. The following features are characteristic of medications of this pharmacological group:
- do not use intravenously for concomitant ulcers;
- Take medications with water only;
- they cannot be combined;
- During therapy, drinking alcoholic beverages is contraindicated.
New generation NSAIDs provoke fewer adverse reactions. Such means include:
- Movalis. Available in the form of capsules, suppositories and injections;
- Celecoxib is an anti-inflammatory drug effective for myositis;
- Arcoxia is taken orally;
- Xefocam.
The analgesic effect of the drugs lasts for 12 hours. At the same time, it is recommended to visit a massage therapist. The goal of this therapy is to relieve inflammation and stagnation. More often, massage is combined with reflexology. Superficial massage is combined with warming compresses.
In the first 2 hours after the manipulation, it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises. The load increases gradually, and the duration of one session is 20 minutes. Treatment of myositis in children is carried out with the help of physiotherapy, manual treatment, exercise therapy, while their activity is limited. If it hurts a child to turn his head, light self-massage is indicated.
A comprehensive fight against a cold neck includes taking gels and ointments. Such medications improve the flow of lymph and blood, relaxing problematic muscles and increasing tissue elasticity. At the same time, local metabolism accelerates and pain decreases. The therapeutic properties of ointments depend on the components included in the composition (warming up muscles, relieving swelling).
If your neck is cold, use the following external medications:
- 1. Apizartron. One of the components is bee venom. The ointment quickly relieves inflammation by warming up the tissue. It is applied to the problem area, rubbing in with massage movements. Virapin ointment has a similar effect.
- 2. Viprosal is a drug prepared from snake venom.
- 3. Sanitas. It contains essential oils and turpentine. Used for rubbing.
- 4. Gymnastogal is a warming agent that has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- 5. Heparin ointment is a vasodilator and absorbable agent that is applied to the bandage.
- 6. You can use Gevkamen distracting ointment. It contains menthol and paraffin.
- 7. Efkamon gel is used as an analgesic. It is used for massage.
- 8. For allergies, Richtofit ointment is recommended. It is developed on a plant basis and easily relieves inflammation. Long-term therapy with Richtofit promotes the restoration of damaged tissues.
- 9. Plant-based Venoruton activates blood circulation, reducing pain and muscle tension.
- 10. Finalgon ointment is used for heating. It is applied to the skin with a special applicator.
- 11. If the pathology is bactericidal in nature, turpentine ointment is used. It has an analgesic effect.
All ointments do not contain non-steroids and do not cause intoxication.
You can eliminate myositis with folk remedies. You must first consult with your doctor. Common recipes:
- 1. Lard and horsetail. The lard is finely ground and mixed with horsetail powder (ratio 4:1). The ointment is placed in a glass container, tightly closed with a lid and stored in the refrigerator.
- 2. Bay oil - add 10-15 drops of vegetable oil to 1 liter of warm water. The product is thoroughly mixed. A small piece of cloth is moistened in it and pressed to the problem area. The pain should subside within half an hour.
- 3. Burdock leaf compress: several fresh burdocks are thoroughly washed and treated with boiling water. Then they are put in a pile, applied to the sore spot and wrapped in a woolen scarf. It is recommended to wear the bandage for several hours.
- 4. Chamomile flower ointment: powder from dried flowers is mixed with butter in a ratio of 1:4. The product is stored in a glass container in a cool place. Apply to the right or left side of the neck, depending on the pain, 4 times a day.
- 5. Tincture from barberry bark: crushed bark is poured into a glass container and filled with 70% alcohol (proportions 1:10). You need to insist in a warm place with regular shaking of the sediment for 10 days. The composition relieves inflammation from the muscles.
To treat muscle inflammation, it is recommended to use various essential oils, before using which you need to make sure there are no allergies. To do this, the oil is applied to the skin and left for 20-30 minutes. If there is no reaction, then myositis can be treated with these drugs.
To protect the neck muscles from inflammation, you need to avoid overstraining the cervical spine, regulate the time of work and rest, protect the muscles when working in cold and drafty conditions, and promptly treat colds and infections.
New generation NSAIDs provoke fewer adverse reactions.
Traditional medicine
Hypothermia of the head is not recommended to be treated only with traditional methods, because they may not be enough. You should turn to traditional medicine to achieve recovery faster. It is worth remembering that anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as painkillers, can only be prescribed by a doctor. It is highly not recommended to select them yourself.
When the head is blown, people often use Nimesil. It effectively eliminates inflammation, lowers body temperature, and also relieves pain. Most people tolerate it well and also note rapid improvement in their condition. But at the same time, it is not allowed to be given to children, and also to be used if there are contraindications.
If a person has a headache, the doctor may recommend using Movalis to relieve the pain. Warming ointments will be useful for muscles, but they can be used in the absence of fever. Sometimes, when your head is blown, your ears may hurt. In such a situation, Otinum drops are recommended; they quickly relieve the negative symptom.
In a situation where a person is treating himself, but his head continues to hurt, he should immediately consult a doctor. There is a risk of serious complications, so you should not postpone your visit to the hospital.
The patient must comply with bed rest; it is extremely important not to go for street walks, not to be in a draft, and to get plenty of rest.
Systemic medications
The most common drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used primarily for pain relief and swelling. Any form is suitable - tablets or injections.
NSAIDs include:
- Nimesulide. A drug for pain relief. Not recommended for long-term use as it has an adverse effect on the liver.
- Ibuprofen. It is used to reduce body temperature and relieve pain in myositis of various origins.
- Indomethacin. Recommended mainly for the treatment of arthritis and bursitis. For myositis it is used if the mobility of the cervical spine is impaired.
- Naproxen. The drug has many side effects - for the nervous system, liver, skin, gastrointestinal tract, and is therefore not recommended for long-term use.
- Piroxicam. The drug has a prolonged action, therefore it is used once a day to relieve inflammation and relieve pain in disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
- Ketoprofen. Belongs to the category of vital drugs. It is better tolerated than all the drugs described above, so it is used for a long time for joint pain and myositis.
- Dexketoprofen. Modified preparation of ketoprofen. Valid for 4 – 6 hours after administration. Relieves swelling and has an antitumor effect.
In the treatment of myositis, muscle relaxants can be used:
- Mydocalm. The drug is powerful, but it must be used with caution by those people who have abnormalities in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, nervous system, and gastrointestinal tract.
- Sirdalud. The drug is used on the principle of increasing dosage to determine the safe concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma. Possible decrease in blood pressure, nausea, drowsiness.
- Muscoflex. It is used in the form of injections. Side effects may include stomach pain, diarrhea, and allergies.
Analgesics used at home without a prescription:
- Paracetamol.
- Analgin.
- Mialgin.
- Phenacytin.
Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs for rapid relief of severe pain are used only as prescribed by a doctor. This group of drugs has many negative side effects, and therefore requires individual selection of dosages.
Vasodilators help increase the lumen of capillaries and improve blood circulation. Used for muscle spasms and swelling.
- Pentoxifylline. Changes the properties of blood, reducing the resistance of the walls of blood vessels.
- A nicotinic acid. Dilates small blood vessels.
- Dibazol. Reduces blood pressure, dilates blood vessels, relieves swelling.
- Trental. An analogue of pentoxifylline, has the same properties.
- Sermion. The drug helps with cerebral circulation disorders if the vertebral arteries are narrowed due to muscle spasm.
- Vazonite. Active ingredient: pentoxifylline.
- Suprilex. The action is to reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of blood vessels.
Vasodilator drugs for myositis are taken in a course of 1 to 3 days along with NSAIDs.
At the same time, the lateral muscles of the neck become tense.
Treatment with traditional methods
When your neck gets cold, traditional medicine recommends using compresses, ointments or rubbing at home. Choose one of the proposed recipes, after making sure that you are not allergic to its components.
Few people know that if you have a cold neck, you can significantly alleviate the condition without harmful medications.
First aid
When it is obvious that the problem is a cold in the head, it is better in this case not to leave the house, but to invite a doctor to your place. Before the specialist arrives, you should not take medications or resort to physical therapy. But there is a list of manipulations that can quickly alleviate the patient’s condition and reduce the risk that the disease will lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Required activities when your head gets stuck:
- bed rest, refusal of physical activity and physical activity - attempts to cope with the disease “on your feet” will only complicate the situation;
- drinking tea with raspberries, rose hips or honey - the drink should be warm, but not hot;
- insulation of the patient and the room in which he is located. You need to make sure that there are no drafts in the room and carry out ventilation according to all the rules;
- if you have a sore throat, rinse it with a solution of baking soda or a decoction of oak bark;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- warm your head using “dry heat”; to do this, you need to wrap it in a down scarf;
- heat a little salt in a frying pan, put it in a cloth bag and apply it to the areas where the headache is concentrated;
- also, for cephalalgia, you can rub a little mint essential oil into your temples or the hollow on the back of your head;
You can learn more about treating pathology with essential oils here.
- It’s worth giving up eating heavy food for a while; it’s better to limit yourself to hearty but light dishes.
Often the listed manipulations are sufficient to speed up the healing process. If time passes and the condition does not improve, be sure to consult a doctor. In this case, you will need to take medications and perform physiotherapeutic procedures.
You will learn about treatment methods for long-term cephalalgia in this article.
The approach should be comprehensive and non-aggressive.
Compresses for a sore neck
Most often, at home, one of the three recipes given below is used, choosing the one that is best suited for a particular patient.
- A potato compress perfectly warms the neck and significantly reduces swelling of muscle fibers, allowing you to relieve pain. To prepare it, you need to boil 4 large potatoes in their skins (using peeled potatoes is useless) until very soft. After this, you should prepare a puree from them by grinding them together with the peel. Next, the mass is wrapped in cotton cloth and applied to the neck. The top of the compress is insulated with a woolen scarf in several turns. Leave this vegetable medicine until it cools completely. After removing the compress, rub the neck with vodka and wrap it again with a scarf. Treatment lasts until complete recovery. The procedure should be carried out before bedtime, since after such deep warming the body needs rest.
- A horseradish compress is an excellent warming agent that allows you to relieve all unpleasant manifestations of the disease in the shortest possible time. To do this, 200 g of grated horseradish root is wrapped in two layers of gauze and applied to the neck. After this, the compress is fixed with cotton cloth and left for as long as possible, but no more than 12 hours. Depending on individual sensitivity, each patient can tolerate the burning sensation for a different period of time: one cannot stand it for more than 30 minutes, while another will warm up for 12 hours without much discomfort. As soon as the burning becomes unbearable, remove the compress and wipe the neck with vegetable oil or rich cream. Treatment continues until pain and stiffness disappear completely.
- A compress with garlic and mustard is a powerful warming agent that can eliminate even severe pain. To prepare it, 3 tablespoons of dry mustard are poured with a small amount of warm (but not hot) water and mixed with 1 teaspoon of gruel made from garlic. The resulting mass is spread in an even layer on a cotton cloth and applied to the neck through it. If the medicine comes into direct contact with the skin, the risk of burns is very high. The compress is fixed with a woolen scarf and left to act, depending on the patient’s ability to tolerate the burning sensation, for 2–4 hours. This therapy can last no more than 6 days.
This therapy can last no more than 6 days.
First aid to a patient
If you feel unwell, you should go to bed and avoid physical activity. If a person has a cold, a characteristic symptom is an increase in body temperature. As first aid, it is recommended to take analgesics (Aspirin, Paracetomol, Nurofen). Such remedies from your home medicine cabinet can help reduce discomfort and fever. You need to drink warm tea with lemon and honey, rosehip infusion, cranberry juice. Drinks contain large amounts of vitamin C, which strengthens the immune system.
The patient is advised to eat light food and should avoid fried, spicy, and smoked foods for several days. Dry heat helps a lot, for this purpose a woolen scarf is tied around the sore spot or a hat is put on.
Folk remedies for head colds
Ginger tea is good for colds.
Weakness, slight fever, headache and runny nose - these symptoms are familiar to many. They cause discomfort, but they can be managed without medication. For minor ailments, folk remedies can compete with pills. The main rule in fighting a cold is to drink more fluids. Useful for restoring health:
- tea with ginger or raspberries;
- infusion of chamomile, linden, sage;
- warm water with lemon and honey;
- dried fruits compote.
To treat a runny nose, instillation of fresh beet juice is recommended. The vegetable contains vitamins and microelements. Its juice thins mucus, reduces swelling, and has an anti-inflammatory effect. The solution is prepared with water, proportion 1:1. 3-4 drops are dripped into each nasal passage.
High temperature is a frequent companion of a cold. It can be reduced not only with antipyretic drugs, but also with folk remedies. Tea made from linden flowers, raspberry jam or compote, and a compress of vinegar mixed with water are effective.
When treating with folk remedies, it is important to monitor the dynamics of the disease. At the first signs of deterioration, you should see a doctor and start taking medications.