Many people believe that a urologist is a male doctor. In fact, this specialist treats both men and women, and even children. Parents, when receiving a referral from a pediatrician for their child to urology, often wonder why? In this article you will learn who a pediatric urologist is, when you need to take your child to him, what diseases and how this specialist treats.
When should you contact a pediatric urologist?
There are certain signs of dysfunction of the children's genitourinary system. Parents should definitely show their child to a urologist if:
- changes have appeared in the results of routine (they are periodically carried out for all children) urine tests;
- the child’s urine has changed (an unpleasant odor, color change, turbidity);
- difficulties with urination (pain, rare urination, urinary incontinence);
- complete absence of urination;
- pain in the kidney area (sometimes accompanied by vomiting and bloating).
The boy should definitely be taken to a pediatric urologist if he has:
- swelling (dropsy) of the testicle;
- soreness, swelling, redness in the penis area;
- cryptorchidism (undescended testicle);
- inability to expose the head of the penis;
- other developmental defects.
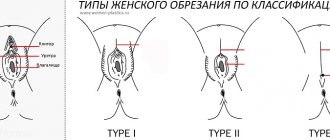
A visit to a pediatric urologist may also be necessary for a girl. Typically, the reasons may be as follows:
- absence (up to 15 years) of menstruation;
- failure of the steady cycle;
- excessive hair growth (visible hair on the chest, upper lip, chin, sideburns);
- vaginal discharge (brown, green, or yellow with a foul odor).
Why does a woman need to see a urologist?
In medicine, such a specialty as female urology has long appeared - this is a section that is conditionally “located” between diseases of the urological and gynecological profile. The direction appeared in the USA in the 60s of the last century.
What does a female urologist do? First of all, he examines and treats the pelvic floor organs in women - the bladder, uterus, rectum and various sexual disorders. One of the “popular” diseases with which women most often consult a urologist is acute and chronic cystitis of various origins.
If you have:
- obvious symptoms of cystitis (pain when urinating, blood in the urine, etc.);
- urinary incontinence;
- feeling of general discomfort in the genitals;
- pain and heaviness in the lower back - do not put off visiting a doctor.
When examining, the doctor always takes into account the age and anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patients who come to him. For example, when young and nulliparous girls get married, they often encounter so-called “honeymoon cystitis.” It occurs when the body reacts to the “invasion” of the partner’s microflora. Also, similar forms of cystitis can appear if a woman’s urethra is located too low. Sometimes such a deviation is subject to minor surgical correction, after which the symptoms of cystitis disappear.
It is recommended that mature and elderly women consult a urologist, especially during menopause and menopause, when the body begins to undergo unpleasant physiological changes. It happens that excess weight and multiple births lead to prolapse of the uterus, pelvic floor and urinary incontinence. All these diseases are treated by a urologist and under certain conditions they can be corrected, the main thing is not to be shy and come to see the doctor in a timely manner.
Preventive examinations
The absence of alarming symptoms does not mean that the child does not need to be taken to a urologist. Preventive examination is required before 1 year, at 3 years and 14 years.
- Up to a year, a visit to pediatric urology will allow you to determine genetic malformations of the genital organs: narrowing of the foreskin, undescended testicles, reduction of the penis and testicles. It is better to treat such diseases as early as possible.
- Three years is the age when boys may develop diseases such as hernia and dropsy. They should also be identified as early as possible.
- A 14-year-old boy is likely to develop testicular vascular diseases, so a visit to a urologist is also required.
Why do men go to the urologist?
The genitourinary system in men has a complex structure, as a result of which it is prone to a certain “bouquet” of diseases. In the worst cases, tumor processes occur in the kidneys, testicles and prostate. That is why preventive examinations by a urologist are a vital necessity for any man. The sooner a man seeks help from a doctor, the sooner the doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
During an objective examination, the doctor examines the man’s external genitalia for possible developmental abnormalities and inflammatory processes. The doctor also examines the prostate rectally and prescribes tests.
If a man has:
- erectile dysfunction;
- itching appears when visiting the toilet;
- premature ejaculation is observed;
- there is a general feeling of discomfort in the genitals -
You should definitely seek help from a urologist.
Free consultation on training issues
Our consultants are always ready to tell you about all the details!
How is an appointment in pediatric urology performed?
An appointment with a pediatric urologist begins with collecting an anamnesis (heredity, past illnesses, health information). Next, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination: assesses the condition of the baby’s genitals and kidneys, and examines his abdomen. Examination of a small child is always carried out in the presence of mom or dad. If necessary, additional diagnostic tools are used:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, pelvis, scrotum;
- uroflowmetry;
- radiography;
- videocystoscopy;
- laboratory tests (PCR, ELISA, biochemical, bacteriological and general clinical tests).
The equipment of the urological clinic with modern diagnostic equipment is one of the clearest proofs of its quality.
What does a urologist do during an appointment?
A urologist is a specialist whose competence includes:
- diagnostics,
- treatment
- prevention
pathologies of the urinary system in men and women.
Some people mistakenly contrast urologists with gynecologists.
This is incorrect - a urologist eliminates pathologies that have arisen in the urinary organs, regardless of the patient’s gender.
What does a urologist do during an appointment?
- First of all, the doctor listens to the patient's complaints.
He asks him about when the first symptoms of the disease appeared, what circumstances preceded this, etc.
Thus, he compiles the patient's medical history.
The anamnesis data also includes information about possible treatment attempts made by the patient before he consulted a doctor.
If they occurred, find out what drugs were used for this and for how long the patient took them.
- After collecting anamnestic data, the doctor examines the patient’s external genitalia (scrotum, penis, vulva, inguinal lymph nodes) for the possible presence of discharge, rash, hyperemia or swelling of the tissue.
- In men, the prostate gland is examined.
For this, either the usual digital method through the rectum can be used. Or transrectal ultrasound using a special sensor.
- If necessary, during the initial appointment, the urologist can conduct additional instrumental studies (cystoscopy, urethroscopy, ultrasound of the scrotum and pelvis, Doppler sonography).
- The doctor takes a swab from the urethra or vagina.
A smear is taken using special instruments - a probe, a spatula, a bacteriological loop. In men, a smear is taken from the urethral canal using a disposable thin probe - it is inserted into the lumen of the urethra to a depth of 3-4 cm, and then removed back with rotational and forward movements. The resulting smear is placed on a clean glass slide or in a sterile tube and sent to the laboratory for testing. The smear can be examined unstained (native) and after staining using various methods (Romanovsky-Giemsa, etc.). A smear from the vagina and cervix in women is obtained during a gynecological examination on a chair using vaginal speculum. A sterile instrument is inserted into the vaginal lumen without touching the vulva, and material is obtained. If necessary, instead of a smear, a scraping of the epithelium of the genitourinary tract is taken (to diagnose chlamydia).
The smear is examined for flora using light microscopy and for sexual infections using PCR.
Bacterioscopy makes it possible to detect STI pathogens such as gonococci, trichomonas, yeasts, and gardnerella in the urogenital discharge. This study makes it possible to determine the presence of inflammation in the urogenital tract by detecting an increased number of leukocytes, epithelial cells and mucus. When there is bleeding in the genitourinary tract, the smear contains red blood cells.
PCR smear allows you to diagnose almost any urogenital infection. Due to its high sensitivity and specificity, this method makes it possible to accurately detect the genome of the infectious agent even at its minimum concentration in the test sample and in the patient’s body. Due to this, PCR is the best method for diagnosing latent and asymptomatic sexually transmitted infections.
In addition to microscopy and PCR, the resulting urogenital smear can be used for bacteriological examination or cultural inoculation. To do this, biological material is sown on special nutrient media and placed in a thermostat for 5-7 days, where microorganisms are cultivated at a certain temperature. After this time, the tubes are removed and the grown colonies of the microbial pathogen are identified. This makes it possible to accurately diagnose most bacterial sexually transmitted infections, both specific and nonspecific. In addition, it is possible to determine the highest sensitivity of microorganisms to antimicrobial drugs.
- Blood can be taken for examination using ELISA or RIF, as well as urine for sediment microscopy or PCR. Serological studies are based on identifying specific immunoglobulins in the patient’s blood serum - antibodies to the infectious agent. Thus, serodiagnosis is the only method for verifying the diagnosis of syphilis. Serological analysis is widely used to diagnose chlamydia and viral infections (cytomegalovirus, viral hepatitis B and C, HIV, etc.).
- In men, a spermogram, a study of prostate juice, and a blood test for hormone levels can be performed.
In most cases, a spermogram and semen analysis for sexually transmitted infections are done for certain diseases of the testicles (orchitis, epididymitis), sexual dysfunction, as well as for suspected infertility. The secretion of the prostate gland is examined for lesions of the prostate (acute or chronic prostatitis, vesiculitis, prostate adenoma) - the secretion is obtained using a finger massage. Prostate juice can be examined using bacterioscopy, culture and PCR. A blood test for a hormonal profile is carried out in combination with other methods in the diagnosis of hormonal disorders, sexual dysfunction of endocrine origin and infertility.
How to prepare for a visit to the urologist
You cannot go to an appointment with a urologist spontaneously; before visiting a doctor, you must comply with a number of mandatory conditions. The following rules will help the patient effectively prepare for a urological examination.
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse. Ejaculation and sexual contact are excluded a couple of days before going to the urologist. This will allow the specialist to take the necessary tests at the first appointment.
- Bowel movement. A rectal examination of the prostate involves a preliminary bowel movement. If there are difficulties with bowel movements (constipation), a cleansing enema will help.
- Prohibition of urination. The bladder must remain full for the most informative study of the genital and excretory organs. You should not urinate about two hours before your urological examination.
Of course, before going to the urologist, take a shower and put on fresh underwear.
Endoscopic diagnostics
If we talk about what methods of studying the urinary system exist, we should not forget about endoscopic diagnosis. An endoscope can be used to examine the internal surface of an organ.
This diagnostic method includes:
- Urethroscopy. During the study, the doctor evaluates the condition of the urethral mucosa along its entire length.
- Cystoscopy. During this procedure, a specialist examines the inside of the bladder.
- Chromocystoscopy. During the study, the patient is injected with a contrast agent, which is ultimately excreted by the kidneys. This process is monitored by a urologist. Based on the results obtained, he will be able to draw conclusions regarding the excretory capacity of the kidneys.
You can't jump higher than your dad and grandpa with their size
— How to assess simply visually whether a teenager’s sexual development is proceeding harmoniously: is the length of the penis sufficient for his age, is everything good with sex hormones?
— Everything is purely individual. Many people ask about their 5-year-old son, and how everything will be for him in 15 years, during puberty. However, until puberty ends, no one can say for sure. If dad and grandfather are okay with their size, then that means the boy will have someone to grow into. The level of sex hormones cannot be adequately assessed until they have started working as intended. Sex hormones are produced not only by the testes, but also by the adrenal glands.
Here problems occur at the intersection of specialties, when the boy seems to be large, but secondary sexual characteristics are not formed or the testicles do not grow. This is primary or secondary hypogonadism, which is treated by endocrinologists. In this situation, the urologist only gets involved when the testicle is out of place.
Indications
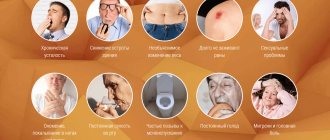
A urological examination of men should be carried out with the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower back, groin, perineum, rectum, testicles (it can have a different nature and duration);
- swelling of the face and/or arms, legs;
- too frequent, or, on the contrary, too rare urge to empty the bladder; discomfort during emptying the bladder;
- involuntary release of urine;
- presence of blood in ejaculate or urine;
- inflammatory process in the urethra (may be accompanied by pain, itching, burning, as well as secretion of mucus or pus);
- the appearance of a rash, swelling, redness and itching in the intimate area; discomfort during intimacy;
- enlargement of the lymph nodes that are located in the groin area.
Among other things, a preventive examination by a urologist should be carried out 1-2 times a year. The fact is that urological pathologies are often asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. A preventive examination will allow you to detect and treat the disease on time.
You should not engage in amateur activities, as this can cause severe damage to the body. Only a urologist can perform the examination and treatment correctly.
Examination by a urologist
How a woman is examined by a urologist is of interest to many patients. First of all, the specialist asks the woman if she has any pronounced symptoms, then proceeds to palpation of problem areas, as well as measuring body temperature.
Based on this initial diagnosis, a competent specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis and then prescribe a series of tests to confirm it. Often the following studies are prescribed for this:
- blood and urine donation;
- biochemical blood test to determine the amount of urea, creatinine and reactive protein;
- passing urine within 24 hours;
- smear on vaginal microflora;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder.
If after these studies the diagnosis still remains inaccurate, magnetic resonance or computed tomography, pyeloscopy or urethroscopy may be required.
After making a diagnosis, the specialist prescribes therapeutic measures that should be strictly followed.
Otherwise, the disease may provoke the development of other pathologies or become chronic. Share: