Causes of the disease
- Excessive sex life, frequent masturbation in youth.
- Thoughtfulness, melancholy, melancholy, intense grief.
- Fear that impairs kidney function.
- The liver is in charge of muscles and tendons, male genital organs, if “the aspirations of the heart have not been crowned with success” - a bad, even angry mood; the liver loses the ability to function normally (circulating fluids), the male genital organs are helpless.
- The flow of “moisture” and “heat” syndromes downwards, the male organs are weakened.
- Eating is incorrect, disordered, and monotonous. Frequent consumption of fatty foods, smoking, drinking.
Omens
- Obesity . There is no increase in appetite, life is also ordinary, and body weight, however, is constantly growing. Even if you exercise for two hours every day, success is not entirely satisfactory. Even if a small number of people are able to establish a connection between shenxu and fatness, nevertheless, the fact is clear: one of the causes of the “disaster” is precisely shenxu. And there is no way to deny this.
- Acceleration of baldness : are you no longer delighted with your blue-black long hair as you once were? Recently they have faded, dried out, and even thinned out. You wash your hair with the best hair care products, do special procedures once a week, but this does not save you from an awkward situation. Then you urgently need to think about whether there is a connection between your problem and a decrease in kidney activity. And on the eve of the medical examination, we wish you good luck!
- Puffiness of the eyes : in the morning, when you get out of bed, the eye areas are dry and rough, maybe you think that this is due to the fact that you sat at the computer for a long time the day before. Take your time, look carefully to see if your lower eyelids are too swollen? Attention is a signal about shenxu, which indicates the inability of the kidneys to normally produce urine, with the help of which the body removes toxins.
- Sexual apathy : at thirty, you should be, as the saying goes, “like the wolf and the tiger,” but you have “turned into a nun in a temple.” The culprit is Shenxu.
- Premature menopause and concerns about it : rush of blood, night sweats, late menstruation, mental anxiety... If these symptoms of menopause visited you at the age of 30, go for an examination to see if you have kidney problems. Chinese medicine believes that the property of deficiency syndrome (emptiness) is aging. Long-term overwork harms the kidneys, and aging due to “empty kidneys” occurs at a faster pace.
- Fear of the cold : In the office, when other people find the temperature quite comfortable, do you shiver from the cold? And it’s difficult to reach a consensus with colleagues about the temperature of the air conditioner...And don’t you also have more clothes on than others? Having a cold, you also suffer from diarrhea. Chinese medicine believes that all this is “created” by shenyangxu (kidney yang deficiency).
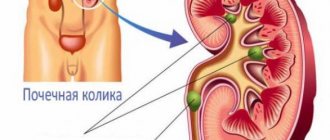
Diagnosis and causes of kidney stones in women
A kidney stone or salt stone is a manifestation of urolithiasis. Crystallization of salts occurs asymptomatically until the movement of the formed macrolite begins through the urinary tract system. Exit is accompanied by intense pain, fever and inflammatory processes. Symptoms of kidney stones in women are masked by diseases of the retroperitoneal space and gynecological pathologies, so diagnosis and treatment is carried out by a nephrologist in tandem with a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- Causes of urolithiasis in women
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic measures
- Basic treatment methods
- Risks of the disease
- Prevention of urolithiasis
Causes of urolithiasis in women
Signs and symptoms of shenxu in women
- Chloasma (facial skin pigmentation).
When there is not enough kidney qi, it is impossible to “glow” with moisturized skin. “Moth” shaped spots, pale yellow, tobacco-colored or pale dark “plaques”, with a light border, constantly appear on the cheekbones, moreover, with irregular and troublesome periods.
- Black circles under the eyes.
In Chinese medicine theory, black is the color “representative” of the kidneys. Dark eye sockets indicate shenxu. In addition, it can be not only shenxu, but also many other diseases of the organs, which after a long time can multiply and reach the kidneys. We have an everyday expression: “a long illness reaches the kidneys” (jiubing jishen) - this is precisely about the “dark” eye sockets.
- Fear of cold.
Kidney yang is the basis of yang qi of the whole body. Life is entirely based on the movement of yang qi; if the yang of the kidneys is not enough, it is impossible to “warm up” the body with liquids, and fear of cold is possible.
- Menses are disharmonious.
Chinese medicine believes that if kidney qi is saturated, only then qi and blood (qixue) are in harmonious movement. The Chung-Mai and Ren-Mai meridians function normally, only then the monthly cycle is regular and predictable. Therefore, kidney yang deficiency is an important factor in irregular periods. Shenxu also causes chronic dizziness, weakness, softening of the legs and lower back, and bloating of the lower abdomen.
- Infertility.
If there is not enough kidney yang, it is impossible to “capture” the jing seed and become pregnant. Often the color of menstruation is also pale, lower back pain, dizziness, fear of cold, exhaustion and impotence.
- Lower back problems.
Chinese medicine believes that “the lower back is the palace of the kidneys.” The reaction to shenxu may be pain in the lumbar region, the peculiarity of which is that it is gradually felt after a grueling load at work.
- Loose bone tissue.
Reason: the kidneys “manage” the bones, shenxu manifests itself in loose bone matter. Often found in women in youth, middle age and old age.
Kidneys in Chinese medicine
The character Kidney 肾 consists of three parts. The lower one indicates that this is one of the organs. One of the top ones represents a servant who bows before his master. The second top one is about firmness and determination.
Kidneys are servants of human Life. And at the same time, they are about control and strength, which are so necessary for Life.
Tamara Khestanova
Founder of the clinic
Hardness is also about the solid structures of our body, such as bones, teeth, bone marrow, which are controlled by the Kidneys. We remember that the Kidneys, according to Wu Xin, live in the house of water, and seasonal Qi is Metal.
The kidneys are the lowest-lying Yin organs in the body. Also in the back of the body. They humbly desire to be useful to all other organs, to provide Qi for a person’s daily affairs.
The kidneys are responsible for energy production, consolidation and storage. This process is reminiscent of the duties of the Secretary of the Interior to conserve natural resources for use in difficult times of crisis, change and daily life of the country. Kidneys are the source of vitality, endurance, strength. Intellect, creativity, and our abilities are born in them. Our ability to grow and reproduce depends on the Kidneys.
Young people have strength, stamina, ambition, motivation, shiny hair, strong teeth and bones. Enough strength for both work and rest. After a night with friends in the club they can fully work out the day. With age, the amount of kidney qi decreases, and you think, how could I stand at the operating table overnight and go to school in the morning?! Youth and a sufficient amount of Kidney Qi….
An important function of the Kidneys is to store Jing (Essence). This is the energy that is transmitted to every person from their parents.
The meaning of the character Jing is four selected germinating grains of rice, and the color of germinating plants. This is a kind of image of the germination of life. Jing stored in the Kidneys is the basis of our Qi and the seed of Life.
In Chinese, Jing and sperm have the same name. For women, Jing is menstrual blood.
Jing can be compared to genetic information encoded in DNA. And if in Chinese medicine they talk about the hereditary constitution, then they talk about Jing. Jing is called one of the “three treasures”.
Each person has a different amount of Jing at birth. Some have more, some have less. It is impossible to increase its quantity. You can save what you have.
Jing can be compared to an alkaline battery that has a certain resource. Once it is used up, it cannot be recharged. So it is with Jing, there is as much as we received from our parents. And you can squander everything very quickly, even if you received a lot. But you can spend it wisely, sparingly, then it will last for a long time, even if you didn’t receive that much. What cannot be replenished can be saved.
Acupuncture is a method that preserves Jing.
Kidney Jing, or rather its quantity, determines our birth, development, puberty, maturation, old age and death.
From the moment of birth, it opens up more and more, reaching its maximum at the time of puberty, and then we begin to deplete.
Jing with Miracle Meridians controls seven-year cycles in women and eight-year cycles in men. Because excess Essence (Jing) circulates in the eight Miraculous meridians. Kidney Jing is important for conception, “ensuring” pregnancy.
From the Kidney Essence, Brain Matter is produced. Not to be confused with the concept of “bone marrow” in Western medicine. In Chinese medicine, it is the substance from which bones, bone marrow, spinal cord and brain are formed. That is why memory, concentration, ability to think, willpower depend on the strength of the Kidneys.
Dangers
Medical research has made it possible to understand that if the shenxu in men has not yet reached the peak of fullness, various kinds of symptoms may appear during that period. For example: shenxu can cause chronic bronchitis, emphysema, high blood pressure; Chinese medicine believes that the main coronary heart diseases: weak pulse, blood stagnation are also the result of insufficient interaction between the heart and kidneys; Chronic diarrhea in the elderly is closely related to spleen and kidney yang deficiency. Shenxu can also provoke prostatic hyperplasia (obesity). In addition, diabetes, chronic nephritis, and other diseases associated with shenxu.
We also cannot ignore the harm caused by shenxu to women. Likewise, if you do not “get what you need” in abundance in a timely manner, you can also deal with a number of medical complications. First of all, it (shenxu) manifests itself in early menopause or in the destruction of your “maternal dream”. Secondly, it causes swelling of the eyelids, circles under the eyes, and a pale complexion. In addition, there is also a clear fear of the cold. In addition, for this reason you may also lose your vision, feel dryness and heat throughout your body, have difficulty concentrating, and even increase your blood pressure.
In addition, hearing sensitivity, breathing, scalp hair growth, and salivation are closely related to the kidneys. Therefore, the kidneys in Chinese medicine are by no means a separate organ; they cover the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, endocrine system, reproductive system, and urinary system. If there is harm from shenxu, this will certainly affect the functioning of the main systems of the body.
Chinese kidney tea Shenshitong: composition, principle of action, instructions, reviews
Urolithiasis occurs in a huge number of people, and many of them will undergo surgical treatment or crushing of stones. It turns out that there are natural herbal preparations that help normalize kidney function and remove stones from the urinary system.
Medicinal tea Shenshitong is a tea drink, dietary supplement, traditionally used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of nephrological and urological diseases, especially kidney stones. The tea comes in the form of instant granules in bags, which contain many useful substances in the form of extracts. It is approved for use by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and other CIS countries. The price of the product is about 420 rubles for 10 bags of 15 g each.
Shenshitong tea is recommended to be taken as a stand-alone remedy or in combination with other medicinal drugs. Its naturalness is beyond doubt, as is its effectiveness. Almost 90% of those who have tried it note a positive result.
This is not surprising - the composition is very rich, yet balanced and ideally selected to provide a therapeutic effect on the kidneys, bladder and the entire urinary system. The product must be taken strictly in accordance with the instructions and with the approval of a doctor.
Compound
The sachets contain the following components of plant origin:
- Ligodium japonica;
- Loosestrife of Christina;
- Thousand-head sowing;
- Bird's knotweed;
- Double-pronged solo color;
- The carnation is lush;
- Elecampane British;
- Sage multiroot.
The composition also contains one component of animal origin - the inner lining (film) of the chicken stomach.
Properties and principle of operation
The active components of Shenshitong tea work together to provide excellent results in the fight against urolithiasis. For example, loosestrife has astringent and healing properties, relieves pain and eliminates stagnation. Thousand-headed - a powerful diuretic and analgesic plant, knotweed cleanses the blood, regenerates, quickly relieves inflammation, and reduces the permeability of vascular walls.
In combination with each other, all herbs and animal ingredients normalize metabolism, in particular, they positively change the chemical composition of urine. Also they:
- Relieves pain and spasm in the ureters and kidneys.
- Relieves signs of renal colic in nephrolithiasis.
- They help reduce the size of stones and painlessly remove them with urine.
- Improves glomerular filtration rates.
- Increase urine volume.
- Relieves inflammation and is active against urinary tract microbes.
- Eliminate congestion in the pelvic area and retroperitoneal space.
- Reduces swelling of the mucous membrane of organs.
The drug works both as a therapeutic and as a prophylactic agent. It prevents salts from accumulating in the kidneys, therefore it prevents the progression of urolithiasis or its development in the presence of predisposition and risk factors. Shenshitong tea is also useful after surgery or laser or ultrasonic crushing of stones - to prevent complications.
Indications
The stone-dissolving, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects of the drug allow it to be used for the following diseases:
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Uric acid diathesis.
- Microlithiasis.
- Dysmetabolic nephropathy.
- Pyelonephritis – acute, chronic.
- All forms of glomerulonephritis.
- Ureteral infections.
- Cystitis
- Urethritis.
Tea has been proven to help dissolve almost all types of stones, especially urates and oxalates. Tea is also indicated after kidney surgery to remove stones, including after minimally invasive interventions, for the prevention of urolithiasis.
The product can even be used in cats suffering from various forms of kidney pathologies. Together with other drugs, Shenshitong is successfully prescribed in the treatment of adnexitis.
The results of using tea will largely depend on the location of the stones, their size and quantity, as well as the chemical composition and structure. Based on these data, the timing of tea intake is assigned. For small stones (up to 1-1.8 cm in diameter), dissolution occurs in 7-14 days; larger stones dissolve in 2-4 weeks. Stones located in the renal pelvis take longer to heal than those located near the ureters. It also takes longer to work on spike-shaped stones compared to round and oval stones. The order of application is as follows:
- Dilute a 15 g sachet in 0.2 liters of boiled warm water (water temperature - 37-40 degrees).
- Drink Chinese tea regardless of meals.
For urolithiasis, it is enough for an adult to take 2 sachets per day, preferably at the same time during the course of treatment. As the stones move, the dosage is increased - one portion every hour until the stone passes and the pain stops. For people over 60 years of age, the dosage is reduced by 2 times. In case of severe urolithiasis, the dosage regimen is different: in the morning - 2 sachets per 500 ml of water, in the afternoon and evening - 1 sachet per 200 ml of water. For pyelonephritis, drink 1 sachet per 250 ml of water twice a day.
Instructions for use of Shenshitong tea
Contraindications
Children under 15 years of age, cancer patients, lactating women, pregnant women, patients with severe forms of diabetes mellitus, people with severely reduced immunity, or those with allergies to the components of the drink should not be treated with tea.
special instructions
If any side effects occur - reactions from the gastrointestinal tract, severe pain, allergic reactions - the drug should be discontinued. To maintain the normal color of tooth enamel, you need to drink the drink through a straw, and also brush your teeth immediately after taking it.
Reviews from urological specialists indicate that the effect of the drink resembles that of medications intended to dissolve stones - Urolesan, Palin, Fitolysin. Therefore, doctors advise using the drink in treatment regimens for nephrolithiasis.
It should be remembered that some conditions (acute cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis) require urgent initiation of antibacterial therapy, and tea as a monotherapy will be practically useless.
Patient reviews of Shenshitong tea are also positive. After application, many formations actually decrease in size, mainly urate stones. The drug has the most effective effect on small stones - they are easily removed from the kidneys and ureters. The only negative is that in the first days many people note soreness of the kidneys, which goes away by the middle of the course. In the video, how to distinguish original Chinese Shenshitong tea from a fake:
Treatment
Diagnostics.
Shenxu indicates insufficiency of yin or yang energy-jing of the kidneys. There are many types of shenxu, among them the most common are the “emptiness” of kidney yin and the “emptiness” of yang. Diseases caused by shenxu are varied, there are many different external factors, but they lead to shenxu. Specifically, we can talk about the main ones: 1. congenital deficiency; 2. sensory disorder; 3. immoderate sex life; 4. long-term illness that damages the kidneys; 5. weakness of the body in old age.
Treatment.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the most important thing is immediate, correct treatment. Shenxu “transforms” into various diseases; in no case should you rush to reinforce the body with a large number of medications, but it should be treated using leisurely methods. You can add gozhi berries to the course of treatment, for example, eat them with food. In a few months you can improve your health. The main essence of the treatment is to activate the Jinglo system (literally, “restore communication in the Jing channels, revitalize collaterals), promoting effective blood circulation in the lumbar region, oxygen exchange in the blood, which can also have a positive effect on strengthening the intervertebral areas.
Restoration of the kidneys (bushen - nutrition of the kidneys) is different, in the case of yin emptiness, yang emptiness, jing emptiness, qi emptiness. Nutrition of the kidneys - nutrition of the kidneys, adding kidney yin, increasing kidney qi, replenishing kidney jing. These are all different methods and different medicines. However, during this period, an erroneous treatment path is likely. Health drugs mainly “nourish the emptiness” (bushui), “emptiness nutrition” mainly nourish the kidneys (bushen), and kidney nutrition mainly nourish the kidney yang, which causes “overstimulation” of the yang (for example, sexual arousal ), and this can be considered stimulant abuse.
What to look for.
- Overdose of cold, cold foods that harm the kidneys, such as bitter gourd, pork, goose meat, beer.
- Men harm their kidneys when they come into contact with detergents. In the house, you should wash dishes, vegetables and fruits with less detergent, and avoid getting any detergent residue into your body.
- A suitable "type of mobility" can slow down aging, but the strain should not be severe. You need to choose the type of activity according to your capabilities; it will promote blood circulation, eliminate blood stagnation and lack of qi. Walking, slow running, fast walking or goose steps on small pebbles can increase blood circulation and play a healing role in the case of shenxu.
Reasons for Shenxu
- Abuse of painkillers. If you take anti-inflammatory drugs for a long time, for example, painkillers, methindole, paracetamol, aspirin, you can harm your kidneys.
- Excessive use of Chinese medicines. Chinese medicines that have been clinically identified to harm the kidneys are: Wilford's three-winged plant (Leigongteng), Manchurian kirkazon (Guanmutong), morning glory seeds (Qian Niuzi), Siberian cocklebur fruits (Tsang Erzi), poppy boll (Yingsuqiao), Chinese aconite (Chinese aconite). shengcao-wu), Indian quisqualis (shiqunzi), weak kirkazon root (qingmusyan), stephania four-stamen (guangfangzi). Among them, the most harmful to the kidneys is leigongteng, followed by guanmutong.
- Addiction to carbonated and sweet drinks. Soft drinks and energy drinks in large quantities are harmful to the kidneys. The body's pH is 7.2, and these drinks increase acidity, that is, they change the pH.
- Excessive consumption of doughy bread. Bread and biscuits contain a food additive - potassium bromate, which gives a feeling of porosity. However, infatuation with such bread harms the central nervous system, blood and kidneys.
- Drink a lot, eat a lot. Today, people gather for social dinners more often, and the possibility of overeating on “delicacies” is quite likely. This “food waste” passes through the kidneys in large quantities. Drinking and eating in excess, without a doubt, increases the load on the kidneys.
- After alcoholic drinks, drink strong tea. Some believe that drinking strong tea after wine or something stronger can remove intoxication. In fact, this is not only ineffective, but also harmful. Experts say the theophylline in tea leaves can affect kidney function and speed up urination. At this time, the alcohol has not yet been broken down and begins to be excreted by the kidneys, as a result, the kidneys take in large quantities of ethanol, which is an irritant factor, hence the harm.
- There are salty foods. If foods are highly salted, this leads to increased blood pressure. The kidneys cannot maintain normal flow, leading to kidney disease.
- Regular urinary retention. Some people, being busy with work, do not go to the toilet for a long time. Experts remind that urine retention can lead to urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis (kidney inflammation). This type of infection is a recurring disease that results in a chronic infection that is difficult to cure.
- Drinking little water. If you don't drink water for a long time, the amount of urine decreases. The concentration of waste from the food cycle and poisonous toxins increases in the urine. Cases of kidney stones and uronephrosis (enlargement of the renal pyelocaliceal segment) are clinically recorded.
- Hypothermia;
- Neglect of going to bed on time, as well as a disordered daily routine;
- Excessive physical activity, as well as imbalance of work and rest, physical labor and recovery;
- Anesthesia and surgical interventions;
- Frequent air travel.
Kidney disease syndromes
According to the teachings of Chinese traditional medicine, the original yin and the original yang accumulate inside the kidneys, literally translated from Chinese as “hiding”, which a person must reliably preserve, avoiding their use or depletion, because kidney diseases in most cases refer to states of emptiness or depletion. Kidney diseases are divided into two main groups in Chinese medicine.
1. Emptiness of kidney yang. 2. Emptiness of kidney yin.
Kidney Yang Emptiness
Depending on the clinical manifestations and pathological changes, this condition is classified into four types.
1. Emptiness and weakness of kidney yang. The emptiness of the kidney yang is a consequence of the patient's constitutional weakness or the result of chronic illness, excessive overexertion, or exhaustion of the yuan-li of the lower heater. Other causes may be senility or kidney yang deficiency, which can also lead to emptiness and weakness of the kidney yang. Main symptoms: feeling of cold in the body and limbs, lack of energy, weakness in the lower back, knees, impotence. The patient has a light tongue with a white coating, a deep, slow pulse, devoid of strength when palpated in the “qi” position of both wrist joints (ching qu point, 8th point of the lung meridian). Explanation . When the kidney yang is empty, the patient is deprived of energy, he feels chilly, and has cold hands and feet. According to Chinese medicine, the lower back is the region of the kidneys, and the kidneys are in charge of the bones. When kidney yang is insufficient, there is therefore weakness in the lower back, sacrum and knees, since the latter relate to the bones. When the kidney yang is empty and weak, sexual function is also weakened; impotence may occur. The patient has a light-colored tongue with a white coating, a deep and slow pulse, devoid of strength when palpated in the cabbage soup position of both wrist joints (8th point of the lung meridian). Therapy . Warming kidney yang, as well as replenishing and toning it.
2. Lack of kidney qi strength. This condition may result from prolonged weakness combined with depletion of kidney yang or insufficient treatment and nutrition of a chronically ill patient. In this case, there is a weakening and decrease in the functional origin of the kidneys. The kidneys have lost their ability to store, strengthen and receive, so the kidney qi is not strong enough. Main symptoms: spermatorrhea, premature ejaculation, impotence, discharge of clear urine, dripping after urination, frequent urination or urinary incontinence, pain and weakness in the lower back, pale face, weakened hearing, light-colored tongue with a white coating, thin, weak pulse. Explanation . The concept of spermatorrhea, often used in Chinese medicine, is difficult for Western doctors to understand. Therefore, kidney function should be considered according to Chinese medicine theory. According to this theory, in a patient suffering from spermatorrhea and premature ejaculation of semen due to the emptiness of kidney qi, there is insufficient strength of the so-called seminal barrier, as a result of which the ejaculation of semen occurs. The bladder is in close connection with the kidneys but of the “superficial-internal” type. For this reason, emptiness of kidney qi leads to uncontrolled bladder function and urinary incontinence occurs, i.e. a high frequency of passing clear urine or dripping urine after urination is complete. Since the lumbar and sacral region is a renal region, in a state of kidney emptiness, pain occurs in the sacrolumbar region. The key to diagnostic understanding of the kidneys is the ears. When the qi of the kidneys is empty, the qi loses its ability to rise up and does not reach the ears, which leads to their insufficient supply, and hence to decreased hearing. For the same reason, paleness of the face, light coloration of the tongue, a thin weak plaque, and pulse appear, which corresponds to the general symptoms of emptiness of the kidneys. Therapy . Strengthening and receiving kidney qi.
3. The kidneys do not accept qi. This condition often occurs in patients with kidney emptiness and weak qi. Damage to kidney qi can be caused by chronic diseases accompanied by coughing and asthma, the patient’s particular obesity, which according to Chinese medicine is often associated with emptiness of qi, as well as bouts of excessive sweating or damage due to various kinds of overexertion. Main symptoms: shortened breathing (the patient exhales more than inhales), shortness of breath after physical exertion, bouts of increased sweating, cool hands and feet, fear of wind and cold, swollen, pasty face, empty and superficial pulse, light body of the tongue. Explanation. According to Chinese medicine, the lungs are responsible for breathing, and the kidneys are responsible for receiving qi. When the kidney qi is empty, the function of the kidneys is disrupted, a condition called “emptiness below, excess above” occurs, and shortened breathing and shortness of breath appear, with a stronger exhalation than inhalation. When the yang of the kidneys is empty, they are not able to perform the function of converting water in the body and thus resist yin, so swelling of the face occurs. In a state of emptiness and weakness of the yang of the kidneys, the yang of the protective forces is also weakened, so the patient experiences attacks of increased sweating, coldness of the extremities, and fear of wind and cold. Therapy . Strengthening, toning the kidneys, receiving qi.
4. Empty kidneys with flooding. This condition is in most cases the consequence of emptiness and weakness of the constitutional order or the consequence of poor treatment of a chronic disease. In this case, there is a weakness of kidney qi, as a result of which the functions of evaporation of body fluids are disrupted. This leads to a breakdown in communication with water, causing flooding; the water rises in the opposite direction, passes into the skin and muscles, forming edema, which, according to Chinese medicine, is a sign of empty kidneys with flooding. Main symptoms: edematous swelling throughout the body, primarily in the lower extremities, and after pressing with a finger, an indentation remains, pain in the lower back, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, scanty urine output, shortened breathing, mucus in the throat, swollen and light-colored body of the tongue, white coating on the tongue, deep, thin pulse. Therapy . Warming yang, removing water.
Emptiness of kidney yin Emptiness of kidney yin occurs in most cases as a result of damage to the substance, loss of blood, and deterioration of the body's juices. Possible causes of kidney yin emptiness include damage to the kidneys as a result of an acute illness associated with fever, or under the influence of yin emptiness of other dense and hollow organs. Kidney yin emptiness occurs due to excessive use of warming and drying medications, which deplete yin. Main symptoms: dizziness, flickering in the eyes, deafness, tinnitus, loose teeth, insomnia, dry mouth and throat, mental anxiety, night sweating, pain in the lower back and knees, red tongue, thin, fast pulse. Explanation. The kidneys are in charge of the accumulation of the substance. When the yin substance is empty, the latter are deprived of the ability to limit yang or keep it under control. When empty, yin yang becomes extremely strong, according to Chinese medicine. Therapy. Nourish and replenish or tonify kidney yin.
Kidney meridian (KD ) Kidney (足少陰腎經, zúshàoyīn shènjīng) - 27 acupuncture points , paired, belongs to the yin system, water element. The movement of energy along the centro meridian is rapid. The energy comes from the bladder meridian and is transferred to the pericardial meridian. The period of maximum activity of the kidney meridian is from 17 to 19 hours.
The kidney meridian originates below the little toe, runs to the sole of the foot and then to the outer ankle, which it surrounds. Next it runs along the inner side of the lower limb behind the liver meridian and the spleen meridian. From the back of the thigh, it approaches the lower end of the spine (Chang-Qiang point, 1st point of the ruler’s vessel), passes along the spine to the kidneys, from where its branch leaves, leading to the bladder.
The other branch originates from the kidney, ascends to the liver, passes through the diaphragm, enters the lungs and meets the pericardial meridian.
Inside the lungs, this branch branches into two parts. The first connects to the heart and spreads inside the chest. The second runs along the neck, ending at the root of the tongue. Clinical acupuncture diagnostics
| Meridian I (lungs) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Pain in the back and shoulder | Pain in the collarbone and chest area |
| Shoulder muscle tension | Feeling of numbness and coldness of the upper limb |
| Temperature increase | Increased sensitivity |
| Loud cough | Hoarse cough |
| Redout | Dizziness |
| Tonsillitis | Dry throat |
| Bronchial asthma | Skin disorders, itching |
| Palm hot to the touch, hot sweat | Cold sweat |
| Meridian II (large intestine) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Constipation | Diarrhea |
| Abdominal pain, bloating | Rumbling stomach, intestinal disorders |
| Headache, dizziness | Emotional discomfort, anxiety |
| Pain in the fingers, forearm, shoulder and back | Numbness in the forearm and shoulder area |
| Muscle tension in the cervical-occipital region | Weakness of the upper limb and a feeling of weakness in the fingers |
| Chills | Bronchial asthma, pharyngitis |
| Meridian III (stomach) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Bloating, belching, constipation | Rumbling in the stomach, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Hunger | Lack of appetite |
| Muscle tension in the front of the neck | Shoulder muscle tension |
| Chest pain | Pain in the abdominal muscles |
| Pain along the front of the thigh, shin and knee | Numbness and coldness in the thigh and lower leg area |
| Pain and cramps in the stomach area | Slow digestion, feeling of fullness in the stomach |
| Agitation of a patient with a high fever | Mental depression, frequent yawning |
| Dry mouth, cracked oral mucosa | Swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat |
| Pain and limitation of movement in joints | drooping corner of the mouth, swelling of the face |
| Meridian IV (spleen - pancreas) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Bloating, feeling of fullness in the abdomen, constipation | Poor digestion, feeling tired after eating, diarrhea |
| Pain and feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium, chest | Pain in the epigastric and epigastric regions |
| Pain in the joints of the legs | Weakness and paresis of the lower limb |
| Nausea, belching of air | Vomit |
| Pain in the foot, limited movement of the first toe | Venous congestion in the legs |
| Food intoxication | Skin disorders |
| Meridian V (heart) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Pain in the heart area | Palpitations and shortness of breath during exercise |
| Hyperemic face | Pale face |
| Feeling of heat in the palms, pain in the shoulder and forearm | Coldness of the inner surface of the shoulder |
| Feeling of heaviness in the limbs | Dizziness due to lack of circulation |
| Feeling of fullness in the stomach | Diseases of the organs of the lower chest (heart, liver) |
| Mild euphoria, increased excitability | Feelings of sadness, fear, longing |
| Meridian VI (small intestine) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Pain in the navel and lower abdomen, constipation | Decreased nutrition, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea |
| Headache | Ringing in the ears, hearing loss |
| Torticollis, muscle cramps in the neck and back of the head | Swelling of the lower jaw and neck area |
| Pain in the back of the shoulder and forearm | Weakness in the limbs and a feeling of coldness in them |
| Meridian VII (bladder) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Frequent urination | Rare urination |
| Painful spasmodic phenomena from the genitourinary organs | Swelling and swelling of the genital area |
| Pain and tension in the muscles of the back (spine) | Hypotonia of the muscles of the neck and spine, hip immobility |
| Pain and spasms of the muscles of the lower limb | Feeling of heaviness and weakness in the lower extremities |
| Headache in the fronto-occipital region | Dizziness |
| Nosebleed | Haemorrhoids |
| Excessive tearing and eye pain | Weakness of the back and fifth toe |
| Meridian VIII (Kidney) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Urinary retention | Urinary incontinence |
| Dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue | Profuse sweating |
| Feeling of heat in the legs | Feeling cold in your feet |
| The foot feels warm to the touch | Foot feels cold to the touch |
| Pain in the sacrum, lower back, inner thigh | Feeling of numbness and weakness in the lower extremities |
| Increased sexual potency | Decreased sexual potency |
| Nausea | Intestinal disorders |
| Feeling of inner excitement | Feeling of fear, indecisiveness |
| Meridian IX (pericardium) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Feeling shy, angry, heart problems | Depression, fatigue, palpitations |
| Upper limb pain and shoulder muscle tension | Upper limb weakness |
| Headache with flushing sensation | Dizziness with anemia |
| Chest pain | Feeling of heaviness in the chest |
| Redness of the eyes | Yellowness of the sclera |
| Constipation | Diarrhea |
| Meridian X (three parts of the body) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Urinary disorder, polyuria | Breathing disorders |
| Heat intolerance | Cold intolerance |
| Pain in the area of the shoulder blade, neck and back of the head | Numbness and weakness in the shoulder and neck area |
| Noise, ringing in the ears | Deafness |
| Hyperemia, facial sweating | Pale face |
| Fever with high temperature | Moderate fever |
| Irritability | Mental and physical fatigue |
| Meridian XI (gallbladder) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Bitterness in the mouth, nausea | Vomiting bile |
| Headache, pain in the thigh and leg area | Dizziness, weakness in lower extremities |
| Swelling of the neck and chin with redness of the skin | Swelling of the foot and popliteal fossa |
| Throat disease | Eye diseases, yellowing of the sclera |
| Increased excitability, sleep disturbance | Drowsiness |
| The outer surface of the foot is hot to the touch | Night sweats |
| Meridian XII (liver) | |
| Redundancy | Failure |
| Headache | Dizziness |
| Pain on the inner surface of the leg and thigh, pain in the lower back | Lower limb weakness |
| Yellowness of the skin | Pale skin color |
| Menstrual irregularities | Tendency to prolapse of the uterus and vagina |
| Feeling angry | Feeling of fear |
| Sleep disturbance | Weakness, powerlessness |
| General emotional discomfort | Depression |
All information on the site is for reference only and is not a public offer as defined by the provisions of Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.