What is conjunctivitis
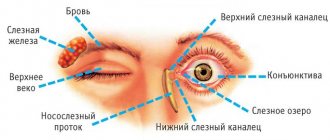
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
This is exactly the disease that many people face throughout their lives. Some people are bothered by this pathology several times a year, which imposes certain restrictions on their lifestyle. This disease is contagious. It is necessary to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene to avoid infecting others. The appearance of conjunctivitis leads to redness and swelling of the eyelids, the appearance of mucus or pus, watery eyes, a burning sensation and itching. Conjunctivitis is the most common eye disease in the world, accounting for about 30% of all eye pathologies. There are several classifications of this disease, which are based on different signs. The following forms are distinguished:
- blepharoconjunctivitis—inflammation of both the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- keratoconjunctivitis - a combination of inflammation of the conjunctiva with inflammation of the cornea;
- episcleritis is a condition in which almost the same tissue damage occurs as with conjunctivitis, but lacrimation and discharge from the eyes are not observed.
Depending on how severe the symptoms of the disease are and how quickly they develop, there are:
- acute conjunctivitis - the disease is pronounced and causes a lot of inconvenience, reducing the quality of life;
- chronic conjunctivitis - the symptoms of the disease are somewhat erased, but make themselves felt for a long time;
- subacute conjunctivitis - a form that occupies a transitional position between the two mentioned above;
- recurrent - the disease periodically affects the patient's eyes, often around the same time of year.
What is giant papillary conjunctivitis? Symptoms and treatment of the disease
The cause of papillary (papillary) conjunctivitis often lies in the use of reusable contact lenses.
In addition, multiple mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the upper eyelid and other types of irritation cause swelling of varying complexity.
With proper treatment and preventive measures, inflammation of the conjunctiva can be minimized.
In this case, irritation of the mucous membrane is non-infectious in nature .
Other common causes include the absence or improper care of sutures in the area of the eye membranes after surgical interventions.
The cause may also be the use of an eye prosthesis in violation of the instructions.
The difficulty in identifying pathology lies in its very long incubation period , which can reach up to 4 years.
According to statistics from ophthalmological clinics and hospital departments, the frequency of diagnosis of giant papillary conjunctivitis reaches 15% of patients who seek help.
- The occurrence of an allergy to the solution containing contact optical devices or to the material from which they are made;
- Corneal dystrophy;
- Improper care or storage in violation of standards for means of increasing visual acuity;
- Mechanical irritation of the mucous membranes during the process of placing or removing lenses from the eyes ;
- Accumulation of tear fluid on the shell of the optical device;
- Surgical interventions in the organs of vision.
To reduce the risk of developing this type of disease, many ophthalmologists recommend that patients use daily optical lenses with their timely renewal.
Symptoms
In addition, other associated symptoms :
- prolonged and persistent burning in the eyes;
- with periodic exacerbation, constant itching;
- increased sensitivity to bright or too intense light sources;
- mucous discharge from the eyes;
- mild form of blurred vision;
- a feeling that there is some foreign object in the eyes or that something is preventing you from blinking, creating some discomfort;
- drop in visual acuity;
- Peculiar small growths appear on the inside of the upper eyelid.
Most reported presentations with symptoms of papillary conjunctivitis involve irritation in both eyes.
Such manifestations occur only when using soft-type vision correction products. Owners of hard lenses do not experience this reaction.
Treatment
When papillary conjunctivitis is treated immediately, patients often receive prompt and very effective help.
In this case, the symptoms disappear in just a few days.
If the disease drags on, then measures to eliminate it are much more complicated and for each individual case depend on many factors.
- Application of “artificial tears” to the mucous membranes. This eliminates the main symptoms within a couple of hours or days;
- Regular application of cold compresses;
- Medicinal elimination of discharge from the mucous organs of vision;
- Stop using vision correction products for a while
When fighting different types of conjunctivitis, ophthalmologists often prescribe topical medications.
As practice shows, they are the ones that are distinguished by the highest efficiency.
Priromecaine, trimecaine and lidocaine are available in the form of eye drops and are used to relieve the main symptoms.
They are also prescribed to continue treatment after all signs and discomfort have been eliminated.
A solution of furatsilin or potassium oxycyanate is excellent in reducing symptoms and speeding up recovery after washing the eyes.
These products are never used in pure, undiluted form.
Such actions can lead to burns of the mucous membranes or decreased visual acuity.
Therefore, it should be used only after consultation with a doctor and a full diagnostic examination.
Solcoseryl is prescribed to restore visual acuity as a result of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the eye.
The high rate of metabolic processes that appears in the patient’s tissues is due to the content of calf blood in the preparation.
Complications
If treatment for papillary conjunctivitis , patients risk encountering the following psychological and physical complications :
- psychological and emotional stress;
- herpes infection;
- lingering discomfort.
With regular use of contact lenses, this type of conjunctivitis can turn into a chronic disease.
Treatment prognosis
If the patient began therapy at an active or advanced stage, then the likelihood of the disease chronic is very high .
In such cases, it may not always be possible to restore lost vision.
Although the symptoms and signs of the disease will still be cured.
More complex treatment will require papillary conjunctivitis, which is accompanied by blurred vision, the addition of herpetic and other infections, and a feeling of constant discomfort in the eyes.
Can conjunctivitis develop while wearing contact lenses?
Some people believe that constantly wearing contact lenses can cause conjunctivitis. We cannot agree with this statement, nor can we refute it. In fact, the optical products themselves are absolutely safe, and their use cannot lead to ophthalmological diseases. But under one condition - the lenses are processed as stated in the instructions.
Proper care of contact optics plays an important role and guarantees safety for the visual organs. It is very important to promptly change the containers used to store lenses, as well as replace tweezers, suction sticks or other accessories that are used when wearing ophthalmic products. Optical products can only be cleaned and disinfected with fresh solution. It is prohibited to use liquid that was previously filled in the container for this purpose.
Is it possible to wear contact lenses if you have conjunctivitis?
Usually in the first days of illness a person does not experience discomfort due to the use of contact lenses. But after some time, he begins to be bothered by itching, burning, redness of the eyes, and watery eyes. As soon as these symptoms occur, optical products immediately become carriers of pathogenic microorganisms: bacteria, microbes, viruses. For this reason, eye doctors do not recommend continuing to use lenses during illness. This prohibition by doctors is due to the fact that conjunctivitis when wearing contact lenses is more difficult to cure. During illness, their use often causes a lack of tear fluid, which helps moisturize the cornea. In the viral form, especially when accompanying colds, lenses quickly become sources of viruses. This can happen when you cough or sneeze. The treatment loses its effectiveness, the inflammatory process continues to progress.
Contact lenses are a foreign body to the eyes. Very often their use becomes an obstacle in the treatment of conjunctivitis. This is especially true for traditional models, as well as prolonged wear, which can be used for several days in a row without taking them off. Having a foreign body in the eyes for several days and sometimes weeks does not contribute to treatment in any way, but only worsens the patient’s condition. Lenses intended for one to three months of use should also not be worn while sick. Optical products themselves become sources of infection and interfere with the treatment prescribed by the ophthalmologist. Their use can cause various complications and significantly increase the duration of the disease. In especially severe cases, the disease can become chronic.
Wearing lenses for conjunctivitis is not recommended for another reason. These optical products fit tightly to the cornea and impede the movement of the eyelids, which contribute to the release of mucous or purulent contents. In bacterial and viral forms of the disease, this is especially important, since in the absence of the possibility of exit, the discharge becomes the cause of the development of microbial flora.
Reasons for the development of conjunctivitis
The causes of conjunctivitis can be divided into two groups: infectious pathogens and allergic agents.
Pathogens of infectious nature
1. Bacterial conjunctivitis:
- Staphylococcus;
- Pneumococci;
- The Koch-Wicks bacterium is the cause of the development of epidemic conjunctivitis;
- Streptococci;
- Chlamydia (trachomatous conjunctivitis is caused by one of these types of bacteria);
- Gonococci;
- The causative agent of diphtheria;
- Other bacteria.
2. Viral conjunctivitis:
- Herpetic conjunctivitis;
- Measles;
- Smallpox;
- Adenoviral and others.
Due to unsatisfactory environmental conditions in which the body develops and grows, allergic conjunctivitis becomes one of the leaders in the overall morbidity structure. Allergic conjunctivitis, causes:
- Pollen and plant seeds;
- Cosmetical tools;
- Food allergens, as well as substances that are currently added to products to increase their shelf life;
- Medications with long-term use;
- Household chemicals;
- Bacteria that infect other areas in the body may not directly affect the conjunctiva, but produce substances that are allergens for humans
- Contact lenses - due to the way they are worn, often cause conjunctivitis. However, recently companies have been developing increasingly inert substances from which lenses are made. They are less likely to cause allergies in patients.
Other causes of conjunctivitis:
- Impact of harmful physical factors in enterprises;
- Exposure to ionizing radiation;
- Excessive exposure to light energy on the human visual organ;
- Accidental contact with eyes of dust, soot, small chemical particles, etc.;
- Impaired refraction - myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism;
- Avitaminosis;
- Inflammation in the sinuses.
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis
It is not difficult to make a direct diagnosis of conjunctivitis. The doctor sees with the naked eye all the changes occurring in the patient’s eyes. The main thing in diagnosis is to determine the cause of the disease, without which it is impossible to carry out effective specific treatment.
What are the risks of wearing lenses longer?
Another rule that must be followed when using lenses is to strictly adhere to the wearing period. It is indicated on the packaging by the manufacturer. If ophthalmic products are intended for a month, then they can be worn for no more than 30 days. This period is counted from the moment the blister is opened - the original packaging in which the contact lenses were stored before use. Therefore, even if a person has not worn them for several days, this does not extend the period of wearing them.
Various complications are associated with wearing lenses too long. First of all, the problems are associated with corneal hypoxia - an insufficient amount of oxygen reaching it. This disrupts the metabolism of the cells of the cornea. When wearing contact lenses longer than the period indicated on the package, the body tries to independently replenish the supply of cells. Vessels located outside the cornea are actively involved in this process. This leads to the fact that they grow through the stroma, causing eye hyperemia.
Wearing lenses too long increases the risk of developing an eye infection. This mainly occurs due to violation of hygiene rules. For example, you should not touch contact optics with dirty hands. If a person wants to remove lenses from his eyes, he must wash his hands and only then perform any actions with optical products. Failure to comply with this rule may cause the development of conjunctivitis.
Causes
This disease develops for various reasons, mainly related to prolonged interaction of the mucous membrane of the eye with a foreign object. These can be contact lenses, dentures, postoperative sutures. For example, sutures after surgery to replace a clouded lens or keratoplasty.
Among the causes of papillary conjunctivitis associated with wearing contact lenses and using eye prostheses, the most common are the following:
- Violation of the wearing regime, namely the timing of replacement of products and the duration of their presence on the surface of the eyes. Long-term sleep in lenses not intended for extended wear.
- Violation of recommendations for the care of lenses/prostheses.
- Using damaged contact lenses, such as those with scratches or tears.
- Wearing lenses with deposits formed on the surface.
- Allergic reaction to the composition of the care product.
- Purchasing lenses without first consulting an ophthalmologist, since there are eye pathologies for which wearing these products is unacceptable.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Depending on what caused the inflammation, the symptoms of the disease may vary.
| Name | Symptoms |
| Acute conjunctivitis | - Lacrimation; - Pain in the eyes; - Burning sensation; - Photophobia; - Eyelids are swollen/swollen; - The conjunctiva is red; - Pus is released, the eyelids stick together; - Runny nose and general symptoms of a “cold” (fever, weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite). |
| Chronic conjunctivitis | — Unpleasant sensations in the eye area; - Feeling of a foreign body in the eye; — Cloudiness of the cornea; - Eyelids are red. |
| Bacterial conjunctivitis | - Pain and pain in the eyes; - Dryness of the mucous membrane and skin of the eyelids. |
| Viral conjunctivitis | — Severe inflammatory reaction of the conjunctiva; — Inflammation of the conjunctiva occurs almost simultaneously in both eyes; — There is no copious purulent discharge; — Inflammation is accompanied by an increase in temperature and inflammation of nearby lymph nodes. |
| Allergic conjunctivitis | - Severe itching and burning of the eyelids and mucous membranes of the eyes; - Severe swelling and redness; - Lacrimation and photophobia. |
Specific manifestations of conjunctivitis depend on the form of the disease. But the course of conjunctivitis is still characterized by a number of common symptoms. These include:
- swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eyelids and transitional folds;
- discharge of mucous or purulent secretion from the eyes;
- itching, burning, lacrimation;
- sensation of “sand” or foreign body in the eye;
- photophobia, blepharospasm.
Papillary conjunctivitis - symptoms, treatment and prevention
Papillary conjunctivitis is a pathology of the mucous membranes of the eyeballs, which is inflammatory in nature. Develops when using contact lenses of any type. But it is more often observed in people who use soft lenses that do not require removal during sleep, as well as lenses with a long service life (up to six months).
Giant papillary conjunctivitis is considered a relatively new eye disease. This is an inflammatory, non-infectious condition caused by improper use of ocular prostheses, soft lenses, or open ends of surgical sutures.
The cause of the development of the disease may be poorly cleaned soft lenses or the reaction of the mucous membrane of the eyes to their material. The incubation period can last up to 4 years. Scientists estimate the incidence of the disease from 2 to 15%.
Symptoms of the disease
This type of conjunctivitis is characterized by:
- redness of the eyeballs;
- burning;
- itching;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- papillae on the inside of the eyelids;
- blurred vision.
Signs of giant papillary conjunctivitis develop when using only soft lenses; hard ones do not contribute to the appearance of papillary conjunctivitis, which is usually bilateral.
Rehabilitation therapy
In the presence of giant papillary conjunctivitis, treatment is as follows:
- elimination of mobility of the lens and mucous secretions;
- stop using lenses;
- applying a cold compress to the eyes;
- using artificial tears for relief.
The effectiveness of topical preparations that are instilled directly into the eyes has been proven. Drops injected into the eye sac relieve pain because they contain anesthetics. These are Trimecaine, Priromecaine, Lidocaine. They quickly relieve pain. Next, the edge of the eyelids and the mucous membrane of the eyeball are cleaned.
For washing, use a weak solution of potassium permanganate. You can use Dimexide, Furacilin, Oxycyanate.
In case of acute disease, Spersallerg or Allergoftal is recommended 2 times a day; for burning eyes - Vidisik, Oftagel.
As a result of inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyeballs, visual acuity is likely to decrease. And after long-term therapy there may be discomfort.
You can restore damaged mucous membranes using topical medications. Typically, experts recommend Solcoseryl gel, produced using the blood of calves.
The gel awakens metabolic processes in cells, the membranes of the eyes are quickly restored. Treatment with Solcoseryl can last up to 3 weeks. But the use of the medication is possible only with the permission of an ophthalmologist.
Complications and eye hygiene
Treatment of conjunctivitis cannot be delayed. Otherwise, you can cause physical and psychological injuries:
- lingering discomfort;
- herpes infection;
- emotional and mental stress.
Conjunctivitis can become chronic if contact lenses are used regularly.
The best way to prevent the development of papillary conjunctivitis is to adhere to hygiene rules. After diagnosing the disease, it is recommended:
- do not touch your eyes with your hands;
- wash your hands thoroughly and only with soap;
- use a towel only for the face;
- do not temporarily use cosmetics, especially mascara;
- Do not violate the instructions for using contact lenses.
Therapy with traditional recipes
Treatment with recipes from traditional healers can only be an additional remedy.
Traditional medicine offers:
- washing the eyes with plantain infusion;
- apply a cloth moistened with dill juice to your eyelids for 20 minutes daily;
- apply lotions from rose hips, after infusing them for 2 hours;
- instill honey water;
- make compresses from fresh datura leaves.
When resuming wearing lenses, it is advisable to choose a different type. Change the design and material of the lens. It is advisable to replace them more often.
It is necessary to select a new disinfection solution that is not capable of causing an allergic reaction to the eyeballs. But it is better to use disposable lenses.
Clinical guidelines
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must immediately stop using lenses. Papillary conjunctivitis is a very serious problem; delaying treatment is very dangerous.
To avoid aggravating the situation, you must follow hygiene rules, do not wash your face with water containing a lot of chlorine, and visit public places less often.
Timely treatment will eliminate the symptoms of the disease in the shortest possible time. But drugs for therapy should only be selected by an ophthalmologist.
Vision correction products for children and adolescents
Children are allowed to wear lenses only from the age of 10. They do not pose a danger to the organ of vision. The human eye adapts to them from childhood. An indispensable condition is compliance with operating instructions.
Experts consider a one-day vision correction product to be the optimal choice. It requires no maintenance. It is completely safe for the eyes of children and teenagers.
Lenses that must be replaced within a month require daily care. Doctors recommend wearing them for teenagers who can responsibly approach the doctor’s requirements.
It is better not to use a long-term vision correcting product for children. The organ of vision will be susceptible to infection, this is very dangerous for the health of children.
Source: https://o-glazah.ru/konyunktivit/papillyarnyj.html
First aid before contacting a specialist
Some procedures are carried out to help the patient:
- rinse the affected eyes with saline or saline solution (dissolve a tablespoon of table salt in a liter of boiled water);
- instill 2 drops of a 0.3% solution of chloramphenicol or a 20% solution of albucid, repeat every 3 hours;
- If problems begin with one eye, additional drops are given to the second. Just use a clean pipette so as not to accidentally introduce an infection;
- do not use lotions, bandages or warm compresses, so as not to provoke the spread and intensification of the inflammatory process.
Differences between conjunctivitis in adults and children
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis in children often accompanies diseases of the nasopharynx, otitis media, and sinusitis.
Conjunctivitis in children is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the eyes. In children under 4 years of age, conjunctivitis accounts for up to 30% of all cases of all pathologies. With age, this indicator progressively decreases, and refractive errors begin to dominate in the structure of morbidity in pediatric ophthalmology.
In childhood, conjunctivitis can lead to the development of serious complications - visual impairment, keratitis and others. In this regard, conjunctivitis in a child requires special attention from specialists and does not allow for self-medication or self-medication.
There is not much difference in the course of conjunctivitis in adults and children, except during treatment; not all “adult” drugs are acceptable for use in children.
What are the different forms of conjunctivitis?
Bacterial and viral forms of the disease differ from allergic ones by being highly contagious. This means that it is very easy to become infected with them from another person who already has conjunctivitis. The disease is quickly transmitted through household contact and airborne droplets. Infection can occur if hygiene rules are not followed: using other people's towels, handkerchiefs, decorative cosmetics, household items, etc. Sources of pathogenic microorganisms are saliva, tears, and nasal mucus.
In children's groups, the bacterial form of conjunctivitis is very common and often becomes the reason for quarantine. Infection mainly occurs due to violation of hygiene rules. The infection is transmitted through dirty toys, sand getting into the eyes, and during contact with animals. The inflammatory process itself is often called the “disease of unwashed hands.” The viral form of the pathology is usually associated with a viral infection that has entered the body. It can be of herpetic or adenoviral etiology. Viral conjunctivitis often “accompanies” the course of diseases such as:
- ARVI;
- acute respiratory infections;
- sinusitis;
- chicken pox;
- herpes;
- otitis;
- measles.
In adults, conjunctivitis can develop against the background of chronic blepharitis, dacryocystitis, and dry eye syndrome. The disease can occur due to irritation of the visual organs by tobacco smoke, household dust, and exposure to ultraviolet rays. Workers in the chemical industry are most susceptible to the disease. Conjunctivitis often occurs due to a lack of vitamins and a weak immune system of the body.
The allergic form is considered the most harmless of all existing ones. Largely due to the fact that this type of conjunctivitis cannot be contracted from another person. The disease occurs due to the body's hypersensitivity to an antigen. Allergic conjunctivitis can be caused by plant pollen, household chemicals, medications, animal hair, etc. Often the inflammatory process occurs against the background of spring hay fever, psoriasis, atopic eczema and other diseases of autoimmune etiology.
Quick treatment of conjunctivitis using traditional medicine
To get rid of conjunctivitis, you can use not only pharmaceutical drugs, but also folk remedies. They have an equally strong effect, but they should only be used in conjunction with medications. The most effective:
- Chamomile infusion has a gentle effect on the eyes, but at the same time perfectly relieves the inflammatory process. To prepare it, you need to take a spoonful of the dry plant and pour a glass of boiling water. The product must be infused for several hours. Chamomile infusion is used for rinsing and as a lotion on the eyes, which is done for 15-20 minutes up to 5 times a day.
- You can also use regular tea. This remedy is even used to treat a newborn child. It is necessary to brew tea, moisten a cotton pad in it and apply it to the inflamed eyes, removing mucous and purulent discharge from them.
- Dill juice therapy - this remedy has a specific smell. To prepare it, you need to take a bunch of dill, chop it and squeeze out the juice. Soak a cotton pad in the liquid and apply it to the eyes for 15 minutes.
- Dill seeds, horsetail, chicory and marshmallow root are taken in equal quantities and mixed. A tablespoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water. After the infusion has cooled, a disc is moistened in it and applied to the eyes. Before this, instill a few drops of the product.
- Pour two teaspoons of ground rose hips into a glass of water, bring to a boil and remove from heat. When the broth has cooled, rub your eyes with it. Repeat the procedure up to 4 times a day.
It is worth noting that the use of each remedy should be coordinated with your doctor. Conjunctivitis is a complex ophthalmological disease that, without proper and timely treatment, can lead to serious complications. These include complete loss of vision and soft tissue necrosis. After getting rid of the disease, you should remember about preventive measures and do not forget to apply them.
Eye conjunctivitis: treatment in adults
For correct and effective treatment of conjunctivitis, it is necessary to first determine the cause that caused the disease. Many conjunctivitis goes away on its own, but the use of medications significantly speeds up healing.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by cytological and virological studies, as well as on the basis of the enlargement and sensitivity of the parotid lymph nodes.
As a treatment, the doctor prescribes antiviral eye drops with interferon.
Treatment with eye drops can be supplemented with antiviral ointments. The drugs should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Before applying the ointment, you need to rinse your eyes with infusion of sage, chamomile or tea. After this, apply drops to the infected eye. The ointment must be applied thirty minutes after instillation.
READ MORE: What material is better to wear contact lenses from?
For more effective treatment, it is possible to prescribe antibacterial drugs in combination with an antibiotic.
Treatment for low myopia is aimed at correcting vision with glasses and contact lenses.
Will drops help with allergic conjunctivitis? You will find the answer in this article.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
In adults
If the infection is caused by bacteria and is confirmed by laboratory tests, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics in the form of eye drops, and the infection will resolve within a few days.
For conjunctivitis of viral etiology, the basis of treatment is antiviral drugs intended for general and local use.
In especially severe cases of the disease, the use of local drugs containing hormones, diphenhydramine and interferon is allowed.
In case of acute conjunctivitis, it is forbidden to blindfold or tape your eyes, as this greatly increases the risk of developing inflammation of the cornea.
In children
Before being examined by a specialist, it is better not to self-treat the child. But if urgent help is required, you can wash your eyes with a chamomile solution. Observing the direction of movements from the temple to the nose. If you are sure that this is an allergic reaction, then you should not wash your eyes.
In the case where only one eye is inflamed, the procedure still needs to be done with both eyes - the infection easily passes from one eye to the other.
Place only those drops into your eyes that have been prescribed by your doctor. If the doctor recommended eye ointment, then it is carefully placed under the lower eyelid.
Eye conjunctivitis: treatment in adults
Treatment for the disease can vary significantly depending on what caused its development. Therefore, it is important for doctors to know the cause of the disease. It is important to give doctors a chance to cope with the disease as quickly as possible by seeking help in a timely manner. You also need to remember that the disease is contagious and long-term self-treatment can lead to infection of other people.
Viral conjunctivitis
Drops and ointments containing antibiotics significantly speed up the healing process without affecting the patient’s entire body, as happens when taking pills and injections. If the symptoms are not very developed and the patient’s body is strong, then the disease will largely go away on its own, without the help of medications.
Antihistamines are excellent for helping patients with this form of the disease. They block the action of the inflammatory mediator and prevent the allergen from causing a cascade of inflammatory reactions in the conjunctiva. They can be used in the form of eye drops and tablets. Artificial tear drops can reduce all unpleasant symptoms and improve the patient's well-being.
READ MORE: Allergy to contact lenses symptoms - Allergy
In especially severe cases, it is possible to use local medications containing hormones, diphenhydramine and interferon.
For patients with any form of the disease, it is important to remember that it is extremely undesirable to touch the eyes with your hands, since this can either allow bacteria to enter there or spread the pathogen. It is important to especially carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene and use only your own towel to protect loved ones from the pathogen.
Can I use lenses?
The optimal solution for conjunctivitis is glasses. Ophthalmologists do not recommend wearing contact lenses, since the transparent material acts as a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic organisms. Also, patients often note increased itching, burning and pain on the second day of wearing the corrective product.
To treat the disease, Albucid drops are used, which are not recommended for use with contact lenses.
Doctors explain the discomfort by saying that the process of removing and putting on ophthalmic devices often provokes the appearance of microtraumas, which quickly regenerate when the eyes are healthy. However, during inflammatory processes, scratches aggravate the disease and can provoke the formation of ulcers and blurred vision. Also, treatment of conjunctivitis includes instillation of eye drops - Albucid, Visina, Furacilina, the contact of which with lenses is undesirable. A constant procedure of removing and putting on with a mandatory break of 15-20 minutes. causes additional discomfort.
What to do with lenses during conjunctivitis?
If you have conjunctivitis, wearing contact lenses is strictly prohibited. Features of the treatment of this disease require unhindered access of oxygen to the cornea and strict adherence to hygiene rules. During illness, it is recommended to replace the lenses with glasses, which are the optimal solution for many ophthalmological diseases. Treatment of bacterial, viral and allergic conjunctivitis is not allowed when using lenses.
Ophthalmologists do not recommend wearing contact lenses if you have conjunctivitis due to the fact that their material provides an excellent environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. This applies to hydrogel and silicone hydrogel models. Discomfort when using ophthalmic products is often associated with the fact that when removing or putting them on, a person can accidentally damage the cornea, and this aggravates the course of the disease.
Treatment for conjunctivitis includes the use of eye drops, such as:
- "Albucid";
- "Florenal";
- "Tobrex";
- "Levomycetin".
They cannot be used when wearing contact lenses. Contact of the drug with the material from which they are made can lead to deterioration of optical characteristics. This is another reason why wearing lenses during illness is not recommended. It's better to replace them with glasses. If the ophthalmologist has diagnosed “conjunctivitis,” then the lenses should be removed immediately, since during the incubation period they have already “adopted” some of the pathogenic microorganisms. Such optical products pose a danger to the visual organs and may interfere with treatment prescribed by the ophthalmologist. It is impossible to disinfect lenses with conjunctivitis using a disinfectant solution. This product is intended for cleaning optical products from dust particles and decorative cosmetics that accumulate on their surface during use, as well as for disinfecting them. It cannot be used to combat pathogenic microorganisms that cause conjunctivitis.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
To prevent conjunctivitis, it is enough to follow a few simple rules:
- Wash your hands with soap before touching your face and eyes;
- Individual towels: If someone in the family has conjunctivitis, you should provide them with a separate towel and avoid close contact with others. In particular, in case of acute conjunctivitis, it is not recommended to sleep on the same pillow; it is better to temporarily sleep in different sleeping places;
- In case of allergic conjunctivitis, do not be near the allergen to prevent its contact with the mucous membrane;
- Wearing glasses, respirators and other protective equipment that are necessary to perform the profession. tasks;
- Do not touch your eyes with dirty hands. (This rule especially applies to children);
- Use of individual cosmetics: girls should not use common mascara, eye shadow, or napkins.
Knowing that conjunctivitis is mainly of an infectious nature, you should refrain from visiting public events and places with large crowds of people, especially during periods of exacerbation of colds. In order to prevent conjunctivitis, care should be taken to reduce the number of contacts during the illness. It is especially important to avoid contact with newborn children.
How is conjunctivitis transmitted?
The thin transparent tissue covering the outside of the visual organ is called the conjunctiva. Inflammation of this connective tissue is accompanied by the development of a very unpleasant disease - conjunctivitis. The disease has extremely uncomfortable symptoms and can appear at any time. The main signs of the inflammatory process are pain, a feeling of sand in the eyes and a burning sensation. Such symptoms cause discomfort and prevent a person from seeing a clear image.
Is conjunctivitis contagious? If so, how does infection occur? What measures will help prevent inflammation of the mucous membrane?
Types of eye disease
There are three types of inflammation of the conjunctiva:
- bacterial;
- allergic;
- viral.
Chronic and allergic conjunctivitis are not contagious. But the infectious form of the disease is contagious and is easily transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through contact and everyday interaction. The main causes of the disease are viruses and bacteria. It is quite easy to become infected with infectious conjunctivitis, since the infection process occurs:
- when in contact with a sick patient;
- through common household and hygiene items;
- airborne method.
Viral conjunctivitis: mechanism of infection
This form of the disease is the most dangerous and, if not treated in a timely manner, can develop into a chronic form or have serious consequences for vision.
In total, there are two types of viral disease, which depend on the type of pathogen:
- Isolated conjunctivitis. The cause of inflammation is a specific virus. Enterovirus, adenovirus, herpes infections, as well as herpes zoster and Coxsackie virus can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
- An eye disease caused by a certain viral infection. In this case, conjunctivitis occurs against the background of diseases such as: mumps (mumps); measles; rubella; flu; chicken pox (chickenpox).
In 70% of cases, conjunctivitis has a viral basis. Hospitalization of patients with this pathology is considered a necessary measure, since the infection is easily transmitted during interaction with a sick patient.
At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms appear in only one eye. However, over time, the characteristic signs extend to the second one. In any case, the virus affects both eyes at once.
From the moment of infection to the full manifestation of viral conjunctivitis, it can take from 3 to 12 days. The main signs of infection are:
- redness and fatigue of the visual organ;
- tearfulness and itching;
- formation of serous discharge;
- corneal clouding;
- pain when pressing;
- purulent discharge;
- feeling of sand in the eyes;
- photophobia.
There are cases when the symptoms of eye pathology disappear on their own within seven days. However, consultation with a doctor and drug therapy are mandatory, as the disease can become chronic. In addition, it is worth noting that the entire cornea of the eye is restored over several years after the elimination of viral conjunctivitis. Therefore, you should not neglect your own health, and when the first symptoms appear, visit a specialist.
Bacterial conjunctivitis: causes
This form of the disease is less contagious. In other words, bacterial conjunctivitis is not transmitted by airborne droplets, so a healthy person staying in the same room with an already infected person is not in danger. But the disease is still transmitted by contact:
- during physical interaction with the patient, that is, through kissing, shaking hands or hugging;
- when sharing household and personal hygiene items.
To avoid infection, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- do not wear other people's glasses;
- do not use other people’s socks and towels;
- do not sleep in the same bed with a sick person;
- wash your hands regularly with soap;
- touch the organ of vision less often.
Allergic conjunctivitis: is infection possible?
The main factor in eye disease is the human body’s reaction to irritants. This form of conjunctivitis is not contagious. But there is one “but”. Due to allergies, the mucous membrane of the eye becomes more sensitive, so there is a possibility of pathogenic microorganisms entering the conjunctiva. If an infectious form occurs in parallel with the allergic form, then infection is quite possible. And it can happen through the use of common hygiene items.
How to prevent the development of conjunctivitis?
Absolutely everyone is susceptible to eye disease, regardless of age or condition of the visual organ. But children are most predisposed to developing the disease. This is especially true for preschoolers and schoolchildren. Infection occurs within a few hours, and an entire group or class may be affected. Therefore, it is very important to know what precautions will help avoid infection for both children and adults:
- Try to touch your eyes as little as possible, especially with dirty hands.
- Wash your hands often with soap.
- If something gets into your eye, remove the foreign particles immediately. Use a clean cotton pad or paper towel for this.
- Change bed linen and towels regularly. In addition, wash such items in hot water with added detergent.
- Try not to wear decorative or colored lenses.
- Never wear someone else's lenses.
- Ophthalmologists recommend using glasses instead of contact lenses to correct vision, so the eye is less susceptible to infection.
- Before using eye drops or ointments, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly. The same should be done when treating an eye disease in your child.
- Do not use other people’s household and hygiene items (glasses, towels, cosmetics).
- If you or your baby develops infectious conjunctivitis, isolate yourself and your child from others until complete recovery.
Conjunctivitis is a serious eye disease. Therefore, do not neglect preventive recommendations, this will keep your eyes healthy.
Contact lenses and features of wearing them
contact lenses. These ophthalmic products can be called the optimal solution for people with poor vision. Lenses can be used for visual impairments such as:
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism,
- presbyopia.
glasses that have been worn for many years to modern models of contact lenses. Today they are produced by companies in many countries, including Russia. A significant advantage of contact correction means is the ability to provide both central and peripheral vision. Glasses, unfortunately, cannot cope with this task. Lenses provide more natural vision correction than glasses. This is due to the fact that the contact optics moves simultaneously with the movement of the pupil. Thanks to this, it is possible to avoid distortions, inaccurate transmission of dimensions and a decrease in the field of view. Many people encounter such problems when using glasses.
You can wear lenses in any weather conditions. When it rains or snows, the glasses fog up, affecting visibility, while contact lenses continue to provide clear vision. Unlike glasses, lenses can be worn while playing sports. They do not prevent a person from leading an active lifestyle. You can wear them for morning jogging and professional sports. This is one of the reasons why contact lenses are very popular today among people who need vision correction. Many people do not think about whether it is possible to wear lenses during illness. The use of optical products is commonplace for them, so it is difficult for them to imagine even one day without lenses. Many people have been correcting their vision using contact optics for many years. Typically, they continue to use lenses during treatment of the disease, including conjunctivitis.