Information about the disease
The conjunctiva is a thin, transparent film that covers the eye and extends to the inner surface of the eyelid. It produces the mucous part of the tear fluid, which is necessary to moisturize and protect the eye from negative external influences.
Conjunctivitis accounts for about 30% of all eye pathologies. The disease affects the transparent mucous membrane and the inside of the eyelid. At the initial stage, the pathological process does not affect vision in any way, but if left untreated, serious complications can occur. This may be keratitis, dry eye syndrome, scarring of the eyelids and cornea.
The prevalence of the disease is associated with the high sensitivity of the conjunctiva to negative external influences. In its normal state, the membrane is completely transparent, through which you can see blood vessels and meibomian glands. As the disease progresses, the mucous membrane becomes rough, cloudy, and scars may form on it.
REFERENCE. It will take about a week to treat acute inflammation. With low immunity or the presence of concomitant pathologies, therapy may be delayed, and the acute form will turn into chronic. Treatment can be prescribed by a family doctor; in severe cases, monitoring by an ophthalmologist is necessary.
Causes
There are a large number of reasons for the development of conjunctivitis. Provoking factors:
- Infectious flora. The disease can be caused by chlamydia, bacteria, fungi or a virus. Infection occurs when using low-quality, expired cosmetics or rubbing the eyes with dirty hands. The infection can enter the organs of vision through the blood. This happens with ARVI, chicken pox or measles.
- Prolonged exposure to an allergen. Damage to the conjunctiva may be a symptom of an allergic reaction. The allergen can be a chemical or pollen.
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation causes snow blindness.
- Sensitivity to certain drugs. The body's response can be through tearing, irritation and redness.
- Violation of the rules for wearing contact lenses. This is one of the most common reasons as a result of which an infection enters the mucous membrane of the eye.
Conjunctivitis can occur due to a lack of vitamins, overwork, hypothermia and metabolic disorders.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the type of conjunctivitis and the reasons that caused it. General symptoms:
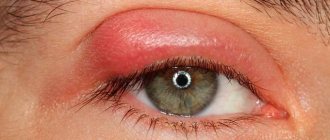
- swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva;
- hemorrhages;
- granulomas;
- burning and itching;
- photophobia;
- discharge from the conjunctival sac.
A decrease in visual acuity is possible only in particularly advanced cases. With bacterial conjunctivitis, there is virtually no itching, and profuse purulent discharge is observed. The acute epidemic form is characterized by severe swelling and the presence of purulent mucous discharge. Symptoms of an allergic form are associated with exposure to a specific allergen. The clinical picture of chemical conjunctivitis depends on the chemical substance.
Diagnostics
The disease is characterized by vivid symptoms, so diagnosis is not difficult. To establish the cause of the development of the pathological condition, a microbiological study of the discharge is carried out. As a result, the doctor receives information about the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Diagnostic methods:
- A scraping or smear from the surface of the conjunctiva of the eye. A special tool is used for this. The collected material is transferred to the laboratory.
- Cytological examination. Using microscopes, the cellular composition of the scraping is studied. Based on the results obtained, the cause of the inflammatory process is determined.
- Microscopic analysis of scrapings for the presence of mites of the genus Demodex. These parasites can affect not only the epidermis, but also the mucous membrane.
- General blood analysis. The number of different types of leukocytes in the blood helps to clarify the cause.
- Serological study. This will require tear fluid or blood. This is a reliable method for diagnosing infectious inflammation of the eye.
If non-infectious conjunctivitis is suspected, allergy tests are prescribed. To do this, a specialist applies a small amount of a possible allergen to the mucous membrane and monitors the reaction. Based on the results obtained, therapy is prescribed.
If conjunctivitis of a specific etiology is suspected, consultation with a venereologist, infectious disease specialist, or phthisiologist may be required. For the viral type, an appointment with an otolaryngologist is required.
A differential diagnosis with uveitis, keratitis and an acute attack of glaucoma is prescribed.
Useful video
An ophthalmologist on the diagnosis and treatment of conjunctivitis:
Treatment
The therapeutic regimen varies depending on the type of conjunctivitis. The first step is to eliminate the causative agent of the disease. General strengthening treatment involves the use of astringent drops. The choice of medications depends on the severity and type of disease.
The use of antibiotics in the form of drops has a good effect. The use of Levomycetin or Tobrex is prescribed. In case of bacterial infection, antibacterial ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect are used. They relieve irritation and soften the skin of the eyelids.
How to restore a healthy look if conjunctivitis does not go away: effective treatment methods
Every day the eyes experience enormous stress, so it is very important to prevent visual impairment .
To do this, you need to consult an ophthalmologist in order to promptly diagnose and begin treatment of diseases that cause a lot of inconvenience to our eyes and become chronic.
ontakte
Odnoklassniki
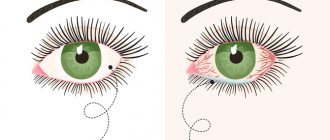
Conjunctivitis is considered the most common eye disease. The disease has characteristic symptoms:
- redness of the eyes due to inflammation of the outer transparent membrane of the conjunctiva;
- increased tearfulness;
- irritation and itching;
- pain in the eyes , especially after prolonged work at the computer.
In case of inflammation, it is imperative to find out the cause of the disease and make the correct diagnosis.
Doctors note several types of conjunctivitis:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- allergic (reaction to various external irritants such as contact lenses, plant pollen).
What are the symptoms of conjunctivitis?
Finding out the cause of redness and irritation of the conjunctiva is a mandatory step in the process of treating the disease.
The risk of contracting a viral or bacterial disease increases especially during the cold season.
The following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute form of conjunctivitis;
- chronic illness.
Infectious conjunctivitis is caused by chlamydia. Possible eye damage due to a fungal infection. The non-infectious form of the disease involves an allergy to various external factors. The disease can manifest itself at certain periods of the year or when encountering an external irritant. Inflammation begins if any chemical substance gets into the eye, for example, shampoo or cheap cosmetics.
Different forms of eye inflammation disease have their own symptoms. Viral conjunctivitis is accompanied by:
- excessive tearing;
- redness;
- severe itching and visual fatigue.
The peculiarity of the infection is that initially it can affect only one eye, and then spread to the healthy organ of vision.
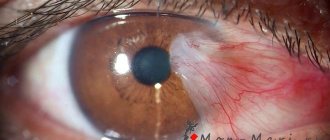
Photo 1. Accumulation of pus in the eyes, when it becomes difficult to open the eyelids - a sign of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis:
- Accumulation of pus in varying quantities. Often patients cannot open their eyelids in the morning, so many have to rinse their eyes well first.
- Swelling of the lower or upper eyelid may occur , which affects the functional functioning of the organ.
- Severe uncontrolled lacrimation.
- Redness and inflamed eyelids.
- One eye may be affected, but if hygiene is insufficient, the infection spreads to the healthy organ of vision.
The allergic form of the disease is characterized by:
- irritation;
- severe itching;
- uncontrolled lacrimation accompanied by severe sneezing;
- swelling of the eyelids
Important! Often conjunctivitis is a sign of existing diseases , such as tonsillitis, purulent tonsillitis, and influenza.
To avoid complications, you need to start fighting the disease in time. A dangerous consequence of conjunctivitis is keratitis, which can lead to loss of vision.
Why does conjunctivitis in adults not go away for a long time?
The acute form of the disease occurs with pronounced symptoms. The discomfort they cause prevents the patient from leading his usual daily routine and working fully, especially if the activity is related to a computer.
Therefore, every adult patient has a logical question: how long will it take to recover and why does the disease not go away for a long time? The answer largely depends on a number of factors:
- from an accurate diagnosis ;
- from following the doctor's recommendations ;
- from observing hygiene rules;
- on the form of the disease;
- depending on the type of disease;
- from the cause of eye inflammation (trauma to the organ of vision, vitamin deficiency, herpes, etc.);
- the presence of other chronic pathologies
- from the characteristics of changes in the mucous membrane of inflamed eyes.
The patient will be able to clarify the time frame for recovery only after consulting a doctor. The doctor, after studying all the examination materials and the patient’s symptoms, will accurately tell you the duration of treatment.
Wrong diagnosis
Inaccurate diagnosis leads to incorrect selection of medications to combat the disease.
Today, every advanced Internet user can easily determine the presence of conjunctivitis, but only a doctor can find out the cause of the disease by conducting a series of tests and the necessary examination.
Most of the symptoms of different forms of conjunctivitis are similar . There are specific medications for each form of the disease.
Incorrect or incorrect diagnosis leads to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and to the transition of the acute form of the disease to chronic. In this case, treatment may last indefinitely.
Attention! The longer it takes to treat conjunctivitis, the less effective the medications taken by the patient become. Viruses and fungal pathogens gradually become immune to the components of the drug.
The ophthalmologist is obliged to prescribe therapy as soon as the disease is confirmed. A smear is first taken to determine the causes of the disease in order to adjust the course of treatment based on the results of the study.
What factors determine the duration of therapy?
The duration of treatment depends on many factors. This is the type of conjunctivitis, the correctness of the diagnosis and the time of initiation of therapy.
Duration of treatment for various types (write an introductory sentence and for each type write the cause, brief symptoms, in general terms what is treated and how long the disease lasts
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the pathogen. For each type of conjunctivitis there is a separate therapeutic regimen. The duration of treatment depends on the form and timeliness of diagnostics.
Viral
Viral conjunctivitis is most often diagnosed in the cold season. It is contagious and can occur in association with upper respiratory tract infections. The infection is transmitted by contact through a handshake.
The incubation period is from 4 to 12 days. Main symptoms:
- redness;
- lacrimation;
- itching;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eye;
- photophobia.
First, serous discharge is observed in one eye, and then spreads to the second. As a complication, clouding of the cornea and decreased vision may occur.
Antiviral drops with interferon are used for treatment. The use of Oftalmoferon gives a good effect. This medicine has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antiviral effects. The optimal dosage is 1-2 drops 6-8 times. Recovery occurs in 1-2 weeks.
Bacterial
This type of conjunctivitis occurs as a result of bacterial infection. Risk factors:
- sinusitis;
- immunodeficiency state;
- non-compliance with the rules of wearing contact lenses;
- contact with an infected patient;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- use of a contaminated instrument during an ophthalmological examination;
- chronic diseases;
- systemic disorders;
- low immunity.
With this eye disease, staphylococci, pneumococci, gonococci and diphtheria bacillus are often detected.
Signs of the pathological process:
- feeling of discomfort in the eyelids;
- itching;
- blurred vision due to discharge;
- redness.
Patients with a weak immune system complain of general malaise in the form of frequent headaches and fever. This condition is caused by the negative effects of toxins released by bacteria.
Treatment consists of using broad-spectrum antibiotics. The medicine may be in the form of drops or ointment. To remove crusts and discharge, saline solution is used.
The maximum duration of treatment is 2 weeks. The chronic form can last from 1 to 2 months.
Purulent
The purulent form of conjunctivitis occurs as a result of untreated allergic, bacterial or viral conjunctivitis. A characteristic sign is the presence of purulent discharge.
This pathology often occurs in children, including infants. Symptoms of the purulent form change as the patient's condition worsens. In the first days, the discharge may be mucous in nature, but then it becomes purulent.
As the pathological condition develops, swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, itching and burning appear. Patients often complain of increased body temperature. The inflammatory process may involve the upper respiratory tract. In adult patients, the lymph nodes become enlarged, thereby causing pain.
Causes of protracted conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes in ophthalmology is defined as conjunctivitis. This is a common type of pathology that has characteristic symptoms. There are differences in the course of a certain type of disease. Each requires specific treatment, taking into account the etiology of the pathology. Only an ophthalmologist can determine the specific type of disease after a full examination and appropriate tests.
The duration of therapy depends on the treatment method. If conjunctivitis does not go away for a long time, then this will be a sign of self-medication and a neglected condition. It is possible that re-infection has occurred and complications have arisen. Also, the reason lies in improper treatment and the addition of other infections. Compliance with hygiene rules is of particular importance. Usually one eye is initially affected, and then the infection spreads to the second.
If the first symptoms of the disease occur, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. Don't wait for severe symptoms to develop. Dangerous signs are headache, increased body temperature, decreased visual acuity.
When the cause of conjunctivitis is eliminated, all signs of the disease disappear. The risk of dangerous complications is also reduced. The success of the result depends on timely treatment. It is important to understand that only a doctor can establish a diagnosis after examination and laboratory tests.
Why does it take an adult so long to recover?
In order for recovery to occur as quickly as possible, you need to choose the right treatment and start therapy on time. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing a chronic form, which requires longer treatment.
Wrong diagnosis
Correct diagnosis is of great importance. To do this, you need to contact a specialized specialist who will determine the causative agent of the pathological process and select the appropriate medications. To avoid mistakes, differential diagnosis is prescribed.
Some types of conjunctivitis are mistaken for dry eye syndrome. It manifests itself in the form of burning, itching and irritation of the visual organs. Patients, as with conjunctivitis, complain of a sensation of a foreign body in the eye and increased sensitivity to light. In most cases, simply using moisturizing drops is prescribed.
In order for the doctor to correctly determine the type and form of the disease, the patient must provide detailed information about previous diseases and unfavorable working conditions. Treatment is prescribed only after determining the cause of the pathological condition.
Wrong treatment
Improper treatment can lead to transformation of the acute form into a chronic form with subsequent loss of vision. Before starting therapy, the doctor must determine the cause of the pathological condition. Based on the information received, medications are selected. The patient must first make sure that there is no allergic reaction, otherwise his condition may worsen.
Treatment not started on time
An important condition for a quick recovery is the timely initiation of therapy. Self-medication can lead to a delay in the process and the development of complications. In particularly advanced cases, eliminating the chronic form may take several years.
Chronic allergic conjunctivitis
Most allergic conjunctivitis occurs chronically, manifesting itself mainly in adults: their symptoms are irregular and worsen only at certain periods under the influence of any allergen. They quickly take on a protracted form, requiring complex complex treatment by specialists in two areas: an allergist and an ophthalmologist. The course of the disease is characterized by the following signs: moderate burning in the eyes, slight redness of the mucous membrane, scanty discharge. Symptoms may differ in the spring-summer season (if the allergen is pollen of certain plant species or UV radiation) or vary depending on other external factors. Thus, with prolonged contact of the eye shell with any irritating foreign body (contact lenses, ocular prostheses or sutures after surgery), growths are found on its surface. The reason for their appearance is an allergic reaction to an irritant. They provoke unbearable itching, mucous discharge and noticeable drooping of the eyelids.
Prevention of relapses and chronic forms of pathology
To avoid the re-development of conjunctivitis, you need to follow simple preventive rules. Key points:
- Refusal to use items that have been in contact with a sick person.
- Disinfection of bed linen and pillows.
- Washing hands after going outside.
- Eye wash.
- Regular visits to the ophthalmologist.
- Compliance with all personal hygiene rules.
- Daily ventilation of the house and periodic wet cleaning.
- Timely treatment of ARVI and other diseases.
- Use only personal hygiene items.
You should avoid going to the pool for some time after treatment. Getting chlorinated water into your eyes can cause complications. It is recommended to use only boiled water for washing. It is better to replace the face towel with disposable napkins.
Particular attention should be paid to strengthening the immune system. It is recommended to take vitamin complexes and a nutritious balanced diet. Vitamin A is present in liver, greens and carrots; to replenish ascorbic acid reserves, you need to add citrus fruits, black currants and kiwi to the menu.
If conjunctivitis was of an allergic nature, then all possible contacts with the allergen must be eliminated. Experts recommend using moisturizing eye drops with vitamins. They improve metabolism and protect the organs of vision from ultraviolet radiation.
To avoid the development of chlamydial and gonococcal lesions in newborns, it is necessary to promptly treat chlamydial infections and gonorrhea during pregnancy. If there is a tendency to allergic conjunctivitis, preventive local and general therapy is required in anticipation of a possible exacerbation of the pathology.
Useful video
Types of conjunctivitis in children and adults!
Treatment period for viral conjunctivitis
The duration of treatment for conjunctivitis in both adults and children depends, first of all, on the type and form of the disease. For example, inflammation of the eyes caused by a viral infection may go away on its own. This type of disease mainly includes cold conjunctivitis caused by an adenovirus. It usually passes quickly and is tolerated quite easily by both adults and children. But if the disease is complicated by other pathologies or caused by the herpes virus, then the recovery time can take up to three weeks.
The treatment method for all viral conjunctivitis is based on increasing the body's defenses. And to speed up the healing process, antiseptic solutions are used to wash and disinfect the eyes. But in the case of herpetic conjunctivitis, treatment must be supplemented with antiviral drugs.
It is important to note that if viral inflammation is not treated, it can go away on its own and without consequences in about three weeks.
But you should always remember that viral conjunctivitis is a common cause of the development of eye diseases such as keratitis, which leads to clouding of the cornea and can even cause blindness. Therefore, there is no need to take risks and hope that the disease will go away on its own. It is better to spend a few hours visiting an ophthalmologist than to spend your entire life paying for your arrogance with vision problems.
Factors influencing the recovery time of conjunctivitis
In the successful treatment of any form of conjunctivitis, properly selected medications play an important role. After all, if you use antibacterial drops to treat viral conjunctivitis, you can cause even more harm to your eye health and complicate the already severe course of the disease. But one should not discount the general principles of treating inflammation, which apply to absolutely any type of conjunctivitis. Effective therapy is not limited to drugs. Following simple hygiene rules and performing a number of important procedures will help speed up the healing process. The patient must have personal household items, wash his hands frequently, not communicate with possible carriers of infection, and not visit public places.
Before the instillation procedure, it is imperative to rinse your eyes, clean your eyelids and eyelashes from dried residues of mucous secretions and pus. This rule, firstly, will help to avoid re-introduction of infection into the eyes, and secondly, it will ease and speed up the course of the disease.
Duration of treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis
In some cases, a few days are enough to eliminate bacterial conjunctivitis, and in difficult situations, treatment can take up to five weeks. The duration of therapy for this type of inflammation is influenced by a combination of factors, which include:
- spectrum of action of the antibacterial drug prescribed by the doctor;
- the use of other drugs as part of complex therapy;
- the patient has chronic diseases;
- type of pathogenic microorganism.
Duration of allergic disease
The inflammatory process of the mucous membrane (conjunctiva) is caused by the influence of various endogenous factors. It occurs predominantly in the younger generation and in approximately 20% of the population.
With atopic conjunctivitis, simultaneous damage to two eyes is initiated. The current type of eye disease, unlike viral and enterobacterial ones, is not contagious. Allergens contribute to the formation of this type of conjunctivitis.
When selecting medications, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis is diagnosed by conducting general consultations with an ophthalmologist, dermatologist and allergist.
At the same time, an anamnesis is compiled based on its typical external indicators and symptoms, and a decision is made on subsequent adequate treatment. It is better to start it at the very beginning of symptoms and after a clear diagnosis.
Treatment of conjunctivitis begins with isolating the allergen. Next, antihistamine medications are prescribed for oral administration. In parallel with this, it is recommended to instill eye drops several times a day. Steroid drugs are prescribed by a doctor only for complex and severe symptoms of the disease. It goes away in 10–14 days.
Allergic conjunctivitis should always be treated with corticosteroids carefully and in compliance with the dosages prescribed by the doctor. It is advisable to discontinue the drug gradually.
Preventive actions for allergic conjunctivitis are focused on eliminating contact with the most popular allergens and are directed against house dust, animal hair, cosmetics and household chemicals.
Duration of viral disease
Viral conjunctivitis is provoked by colds and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract (ARVI, acute respiratory infections). Significant factors in infectious inflammation are:
- continuous irritation, increasing redness and eye fatigue;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- high sensitivity;
- uncontrolled tearing;
- formation of discharge;
- glued eyelids in the morning.
It is considered an extremely dangerous and contagious form of infectious mucous membrane of the organ of vision. Moves easily through contact from a sick person to a healthy person. Ways of transmission of conjunctivitis:
- communication with the patient;
- aerogenic;
- general household and hygiene items.
If the inflammation does not go away for a long time, rinsing with disinfectants is used. How long does enteroviral conjunctivitis last? Depending on the severity of the disease, from 7 days to 2 months. During the treatment of conjunctivitis, medications are used in the form of antibiotics and any antiviral ointments and drops. In order to strengthen the body's immunity, vitamin preparations are prescribed.
By regularly using a disinfectant based on Furacilin to wash your eyes, you can successfully overcome the disease in a short time. The resulting crusts on the eyelids are removed with a piece of bandage soaked in boiled water, tea leaves, or infusions of calendula, sage, and chamomile flowers.
It is advisable not to violate the established rules so as not to become infected with conjunctivitis. You should not hope and wait that the disease will go away on its own. In the absence of adequate treatment, the process becomes protracted, which is fraught with further deterioration or loss of vision.
general characteristics
How to understand that conjunctivitis has passed
It seems that you were not in the wind, and nothing got into your eyes, but a pain appears, comparable to the feeling of a handful of sand thrown into your eyes. The next morning, everything seems to be fine, but you should wipe your eyes, as pain, redness and the ability to get microscopic fragments, sharp edges reminiscent of glass shards, appear in them again.
These are signs of conjunctivitis, which affects both normal and nearsighted and farsighted eyes, that is, any. And the reason is damage to the mucous membrane around the eyeball. There are three main types of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial,
- allergic,
- viral.
Bacterial and viral are highly contagious and easily transmitted. Typically, any type of conjunctivitis can become chronic. Damage to the lacrimal ducts, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, damage to the nasal mucosa can become an impetus for the development of conjunctivitis.
A condition in which the eyes become inflamed cannot be called joyful. Conjunctivitis is an unpleasant phenomenon that you want to get rid of as quickly as possible. Especially if it concerns a small child. Anyone would be interested in how many days should one wait until the illness goes away?
How long will it take for the disease to be cured, and why in some cases does it take a long time to treat conjunctivitis, longer than one month?
Bacterial conjunctivitis is often diagnosed in adults. It usually goes away within 5-7 days. It happens that it takes two weeks to heal. The duration is explained by: The type of bacteria that caused the disease.
The therapeutic methods used. General health of the patient. Most often, conjunctivitis in adults is caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. A similar bacterium is present in the ocular microflora.
But not everyone suffers from the inflammatory process, only those whose immunity weakens. The conjunctiva becomes inflamed due to the activity of staphylococci quite often.
The disease is indicated by glued eyelashes after waking up and strong purulent discharge. True, the inflammatory process passes quickly. To get rid of unpleasant discomfort, you can use antiseptic agents to wash the organs of vision. The disease is rarely cured with antibiotics.
The conjunctiva is the mucous membrane that covers the front of the eyeball, the upper and lower fornix of the eye, and the back of the eyelids. Among eye diseases, conjunctivitis is the most common and accounts for about 50% of all outpatient visits.
There are many etiological factors of the disease and, depending on them, the following types of conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- Bacterial - caused by gonococcus, diplobacillus, diphtheria or staphylococcus.
- Viral - occurs under the influence of herpes viruses (simple or zoster), measles, rubella, adenoviruses, picornaviruses.
- Fungal.
- Chlamydial - trachoma and paratrachoma.
- Parasitic.
- Allergic - there are spring, phlyctenulosis and pollen.
- Conjunctivitis that occurs under the influence of physical and chemical factors or under the influence of endogenous substances - against the background of somatic diseases, infectious-toxic, endocrine and metabolic disorders.
- Drug.
- Autoimmune.
According to the flow, acute and chronic processes are distinguished. The incidence depends on seasonality, and the etiology depends on climatic conditions. In the autumn-winter period, the frequency of viral and bacterial conjunctivitis is high, and in the spring-summer period - allergic.
In cold and temperate latitudes, the cause of the disease is mostly pneumococcus, and in hot climates, epidemic Koch-Wicks conjunctivitis is more common. In Russia, staphylococcal inflammation of the eye mucosa is common.
Based on the type of inflammatory process, the following forms of conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- Catarrhal is an allergic, adenoviral inflammation of the eye mucosa.
- Purulent - staphylococcal infection.
- Follicular - trachoma, paratrachoma.
- Membranous - for diphtheria and pneumococcal lesions.
Conjunctivitis also occurs due to a number of factors that increase the risk of the disease:
- Damage to the eyeball.
- Presence of a foreign body.
- Inflammatory processes of the oral cavity and/or nasopharynx.
- Hypothermia.
- Visual fatigue.
- Having contact with a patient with viral or bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Previous blepharitis, dacryocystitis, keratitis.
Duration of treatment for fungal conjunctivitis
Until recently, fungal conjunctivitis was considered a fairly rare disease. Typically, the source of such infection was soil, plants, vegetables, fruits, a sick person or animals. But recently, eye mycoses have become quite common. And this is due, first of all, to people’s uncontrolled use of eye drops containing antibiotics or corticosteroids, as well as non-compliance with hygiene rules when wearing contact lenses. Treatment for fungal conjunctivitis can last for years. It is complicated by the fact that inflammation of this type develops very slowly and, as a rule, always takes a chronic form. Today, about 60 species of various fungi are known, which are clinically isolated in pathologies of the organs of vision. It is the persistent and prolonged course of the disease, which can lead to perforation of the cornea and complicates the treatment process.
Therefore, when prescribing treatment, it is very important to determine the type of fungus that provoked the development of the disease. Only by laboratory determination of its nature and the correct choice of antifungal agent can one get rid of such an unpleasant and dangerous disease. Typically, the course of treatment for fungal conjunctivitis is 4-6 weeks, and it must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
It is important to know that only complete recovery, which must be confirmed by laboratory tests, can guarantee that the disease will not take a latent form.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye in children
Newborns are a special category of patients; they are most often infected in the maternity hospital, during passage through the birth canal, or from medical personnel who do not follow hygiene rules.
A child can become infected from the mother if she has genital tract infections - gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc. During childbirth, the mucous membrane of the eye is the first to come into contact with the microflora of the mother's genital organs, and therefore inflammatory processes develop in it first.
To prevent ophthalmia in the maternity hospital, all newborns are given eye drops with an antibiotic - Tetracycline or Tobrex. Such measures are very important, since in children the cornea and other structures of the eye are involved in the pathological process, which can lead to blindness.
If, despite preventive measures, a newborn develops conjunctivitis, immediate treatment with antibacterial agents is necessary.
In older children, inflammation of the conjunctiva is a fairly common disease and is largely caused by bacterial flora.
The pathology is characterized by abundant purulent discharge, which prevents the child from opening his eyes in the morning, hyperemia is pronounced, the eyelids swell, and burning and itching bothers him. Children begin to rub their eyes, which leads to injury to the mucous membrane and deepening of inflammation.
Children have weak local immunity, so inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye occurs very often. If a child has already developed conjunctivitis, it is necessary to seek help from a specialist in time.