Causes
People often suffer from swelling in different parts of the body, which has many causes. Swelling in the eyebrow area is no different. The tumor can be caused by an external factor or an internal disease. The main reasons that can cause swelling of the eyebrows are considered to be the following:
NOTE. The information provided is not a substitute for an actual physical medical examination. Please visit your healthcare provider to determine the exact cause before starting medication.
Swelling due to illness and other factors
The first possible cause of eyebrow swelling is edema - this is swelling that occurs due to the retention of lymphatic fluid in the tissues and cavities of the body.
In this case, a swollen eyebrow is the result of fluid leaking from the capillaries that are located around the eye. Symptoms appear gradually. This swelling may be caused by a hidden infection. Other possible causes include: prolonged sitting or standing, surgery, high altitude, sunburn, pregnancy, and complete lack of physical activity. Serious medical conditions that can cause swelling are arthritis, pulmonary insufficiency, thyroid dysfunction, diabetes and liver disease. Associated symptoms will include:
- Swelling of the skin
- Itching
- Weight gain
- Increased heart rate
- Skin may appear glossy and tight
Treatment in this case most often involves eliminating the infection, if any. Otherwise, therapy will include:
- Diuretics are medications that help increase urination and remove excess fluid through the kidneys.
- Ranibizumab is a medicine approved in more than 85 countries that helps prevent and treat macular edema in diabetes.
- Control of blood vessel growth or therapeutic angiogenesis.
Injury
The eye is one of the most sensitive parts of our body. A hard object coming into contact with this area can cause damage, including a crack in the bone around the eye (orbital fracture), which can cause the eyebrow to swell.
Hard physical contact, such as a punch or ball to the eye, can cause this damage. A traumatologist should examine you and, depending on the extent of the damage, prescribe the necessary treatment.
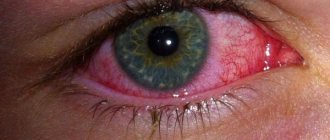
Symptoms associated with orbital bone damage include red eyes, swollen eyebrows, and headaches. A combination of a warm compress and an anti-inflammatory will help relieve the swelling and pain it causes.
Epilation with thread or tweezers
While everything is clear with tweezers, not everyone knows enough about hair removal with a thread. This is an ancient method of hair removal that is more popular in the West. It is mainly done on the eyebrows for cosmetic purposes. This is one of the most hygienic treatments, no chemicals are used and the thread is only used once per person. This technique also reduces the likelihood of contact or atopic dermatitis, given that the only thing that comes into contact with your face is the thread.
Threading is an art and it is now becoming very difficult to find someone who can replicate the technique correctly. If done incorrectly, hair removal can damage the hair follicles, a condition known as folliculitis. Eyebrow pores can become clogged with dead skin cells and sebum or become swollen.
READ ALSO: How to visually hide a high forehead: successful women's haircuts
Eyebrow swelling caused by hair removal with thread or tweezers should not bother you. The symptoms will go away on their own in about a week. You need to keep your face clean and avoid further hair removal until the swelling goes down. Using a warm or cold compress twice a day will also help relieve swelling.
Botox injections
We all strive to maintain youth for a long time, especially women. Recently, cosmetic surgery and other facial procedures have become increasingly common. Research from one of the leading cosmetics companies has found that the number of people who resort to cosmetic procedures is increasing. One of these procedures is Botox injections.
Botox is used to treat certain muscle diseases and for cosmetic purposes to eliminate wrinkles by paralyzing the facial muscles. A drug made from botulinum toxin is injected into the facial muscles in specific locations.
When this procedure is performed poorly or too much Botox is injected, the muscles can swell. Therefore, Botox injections may be a likely cause of eyebrow swelling. Side effects of Botox include an allergic reaction, rash on the face and other parts of the body, itching, pain in the face or neck, muscle stiffness and nausea. If you experience the following symptoms, seek medical attention;
- Breathing problems
- Severe muscle pain
- Bladder control problems
- Itchy skin
- Vision problems
- Severe skin rash
- Irregular heartbeat
Ingrown hairs
Another reason for eyebrow swelling is ingrown hairs. This is a common occurrence among women due to the various methods they use to remove unwanted hair. These methods include waxing, tweezing, threading, and shaving.
When the above procedures are not followed properly, the hair follicles may become damaged. The pores become blocked, making it difficult for hair to penetrate the skin and it grows inwards. The pores can become filled with keratin, dead cells and tissue, forming a tumor, cyst or bump on the eyebrow.
This condition is not life-threatening, but if you notice swollen parotid or cervical lymph nodes, a painful, itchy rash or bumps, you should see a doctor. People with chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer and HIV/AIDS should avoid taking over-the-counter medications without a doctor's prescription.
If there are no such serious diseases, then treatment will include:
- Warm compress at various intervals throughout the day.
- Antibacterial, antiseptic ointments and itching relievers.
- Corticosteroid ointments will help against itching and inflammation.
Allergy or irritation
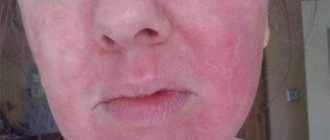
Eyebrow swelling can also be caused by an allergic reaction, such as to foods high in protein or vitamins, or to medications. Cosmetics such as face cream or lotion contain chemicals that can cause swelling due to skin irritation.
You need to see a doctor to find out what is causing this reaction. Avoid using any medications until the cause of the allergy is known.
Waxing
Waxing can also cause eyebrow swelling if not done properly. This occurs due to damage to the hair follicles, which causes clogged pores. It is also possible to have rashes and painful bumps caused by a buildup of keratin and dead skin cells in the pores.
To relieve pain, stop waxing for a while. You can use topical products such as anti-itch creams. If the lymph nodes begin to swell or other cold-like symptoms appear, an infection may be present. Then you need to seek medical help.
Swollen eyebrow piercing
When the piercing is not performed correctly or sterile instruments are not used, it can be a possible cause of tissue infection in the eyebrow area. Some people are also allergic to the metal used to make the jewelry. A wound on the eyebrows can also be a site for bacteria and other pathogens that cause infection if it does not heal for a long time.
READ ALSO: Eyebrow shapes based on face shape: photo, selection rules
When performing an eyebrow piercing, you first need to make sure that the instruments used are sterile and have been disinfected beforehand. Avoid using these instruments repeatedly as you may become infected or pass the infection from one person to another. Do not remove the jewelry immediately after the puncture; let the wound heal first.
After the piercing, you can clean the wound with an antiseptic such as methyl alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. If the swelling does not go away for a long time, or you notice swelling of the lymph nodes, itching and pain in the wound, you should seek medical help.
Swelling after eyebrow tattoo
In the days following the procedure, while your skin is healing, it may be swollen and itchy. This is completely normal. You may be tempted to soothe your brows with a cold compress. While it won't necessarily minimize swelling, a cold compress (NOT frozen), wet tea bags or facial tissues (not wet) applied lightly to the brows will help relieve discomfort. Just don't do this constantly, as repeated attempts to cool already injured tissue can actually increase the likelihood of skin damage and infection. Never apply pressure to your fresh tattoo and be very careful not to rub, scratch, peel or peel the area.
Swollen sinuses
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses (paranasal sinuses) - an empty space located behind the bones of the face and filled with air, which belongs to the nasal cavity. Sinusitis can be caused by fungi, bacteria, a virus, or an allergy. In mild cases, symptoms go away on their own without taking any medications. Depending on the location of the paranovic sinuses, there are several types of sinusitis. Swelling on the forehead or in the eyebrow area is a symptom of frontal sinusitis - inflammation of the frontal sinuses.
This condition is sometimes uncomfortable and painful due to swelling and inflammation. If symptoms do not disappear, you should consult a doctor. In extreme cases, complications and the development of an abscess in the eye area, eyebrows, forehead and even brain are possible.
Ophthalmopathy
Graves' disease (diffuse toxic goiter) is an autoimmune disease associated with the thyroid gland, which, among other things, causes swelling of the eye muscles and soft tissues in the eye socket (ophthalmopathy). When this happens, the eyeball moves forward (exophthalmos) and causes other symptoms. Symptoms typically include swelling of the eyebrows and persistent watery eyes.
This is a serious disorder and to counter this you need to visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Treatment involves preventing the disease from affecting the eyes. Most often prescribed:
- Use of artificial tears
- Medicines and eye drops
- Depending on how severe the symptoms are, surgery may be indicated.
Drug treatment
Treatment will be prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis. These can be either simple nasal vasoconstrictor drops for a runny nose or powerful antibiotics if pain in the eyebrow has become a symptom of an inflammatory process. In the most severe cases (the same advanced sinusitis), surgical intervention is possible. And before visiting a doctor, you can give yourself the following first aid in order to somehow relieve the pain.
NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
These are first aid remedies for eyebrow pain of unknown etiology. They have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. These include drugs that contain:
- metamizole sodium (Analgin, Baralgin);
- acetylsalicylic acid (Upsarin Upsa, Aspirin, Walsh-asalgin);
- paracetamol (Calpol, Panadol, Calpol, Cefekon, Efferalgan);
- ibuprofen (Ibufen, Mig, Dolgit, Nurofen);
- nimesulide (Nimesil, Nise, Nimulid).
They have few side effects and quickly provide pain relief. Together with them, you can take a drug to relieve spasms - no-shpu. If you suffer from vasoconstriction, which can lead to pain in the eyebrow, medications from another group will help.
Caffeine-containing drugs
If the pain is dictated by problems with blood vessels, you can drink a caffeine-containing drug - a complex medicine consisting of several components:
- Citramon;
- Solpadeine;
- Pentalgin;
- Sedalgin;
- Tetralgin.
You need to understand that drugs that relieve pain are a temporary solution to the problem, helping to relieve only the symptoms of the underlying disease. If pain persists, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. In cases of neuralgic nature of pain in the eyebrows, it is recommended to take sedatives.
Sedatives
Modern pharmacology offers its customers a wide range of different sedatives. They help relieve stress, which is the cause of many neuralgic diseases. And they, in turn, cause pain in the eyebrows. Recommended medications:
- Pax Plus;
- Afobazole;
- Persen;
- Phenibut;
- Gerbion;
- Sanason lek;
- Novo-passit.
If you have pain in the eyebrow area, and for some reason you have not yet been able to see a doctor, try to get rid of the pain with the help of recommended medications. Although it is much better in this situation not to swallow newfangled “chemical” pills, but to use traditional medicine that has been proven over the years.
Keep in mind! You cannot constantly take medications without medical advice if you have a headache in the eyebrow area. This is a temporary solution to the problem because the pain will return and may become chronic.
Advice from experienced doctors
In order to prevent the appearance of bumps on the eyebrows and speed up their treatment, you must follow the recommendations of doctors:
- Dress warmly, try to catch colds less often, and treat colds in a timely manner.
- Do not consume foods or contact surfaces that can cause allergies.
- Protect yourself from insect bites and spray with chemicals.
- See a doctor immediately after your eyebrow becomes swollen.
Under no circumstances should you squeeze out the cones yourself.
Lumps on the forehead above the eyebrows can be easily eliminated using special products and procedures. Removing a tumor above the eye under the eyebrow is much easier when the cause of its formation is known.
Diagnostic measures to determine the causes of pain
If you have a headache above the eyebrow or around the eye, you should first be examined by a therapist. He will be able to determine which specialist should be contacted. With such a disease, you may need to consult an otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist or trauma surgeon.
The patient is also sent for a number of tests and studies. A blood test is always done, and an x-ray examination of the cavities of the facial part of the skull is required.
An otolaryngologist can take samples of the nasal mucosa for bacterial culture. The ophthalmologist will examine the fundus of the eye. The neurologist will be interested in the result of the electroencephalogram. To complete the picture, you can do a CT scan of the head.
Diagnosis of eye pathologies
Relief of swelling after epilation (with wax, tweezers or thread)
If the technology of this procedure is not performed correctly or the wrong tools are used, there is a possibility of damage to the hair follicles, and this can cause swelling and inflammation of the eyebrows.
The following tips will help relieve swelling after waxing:
- Cleanse your face with a soothing and antiseptic lotion
- To reduce redness, rub your face with an ice cube
- Use moisturizers such as baby cream
- Avoid wearing makeup.
Typical nature of pain when the eyebrow above the eye hurts
Know! Like any pain, this syndrome is distinguished by strength and frequency. It is also divided according to the nature of its manifestation:
- beam sensations ; an attack of this kind is attacking; syndromes recur after 10-20 minutes and can last up to 3 hours;
- cluster view ; usually occurs at night and can continue until the morning; sometimes radiates in the dental nerves;
- discomfort from tension ; most often occurs in women and older people, is shingles in nature and is accompanied by general weakness and lack of appetite;
- migraine; usually accompanied by temporal pain;
- pathology ; discomfort of this type appears against the background of nausea, fear of light and loud and sudden sounds.
Eyebrows swollen for no reason
Sometimes the eye can become swollen for no apparent reason. If medical examination does not reveal an infection, then it can be assumed that the cause is an autoimmune disorder.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body produces antibodies that begin to fight your own body cells. This can lead to swelling and inflammation of the skin around the affected areas. In most cases, the condition does not go away on its own, and hormonal therapy may be required throughout life. Signs and symptoms of an autoimmune disorder vary from one person to another depending on how strong the immune system is.
The actual cause of an autoimmune disorder is unknown, but the following factors may trigger an attack by the immune system:
- Virus or bacteria attack
- Medicines
- Chemical irritants such as soap or body lotion
- Environmental irritant during climate change
READ ALSO: Sign: why a girl’s or man’s left eyebrow itches
Autoimmune disorders are chronic conditions for which there is no cure yet, but it is possible to relieve symptoms and prevent spread to other parts of the body with the following tips.
- Eat a balanced diet
- Make time for physical activity regularly
- Take Vitamin A
- Limit your time in the sun
- You need to reduce your overall stress level.
Secondary pain above the eye
Let's look at the main reasons why the eyebrow above the eye, eyebrow, eyelid and forehead hurts:
- hormonal imbalance. Attacks of severe pain can occur during puberty, menopause, before menstruation, and during pregnancy. Female hormones affect the elasticity of blood vessels, which leads to unpleasant sensations;
- unsuccessful plastic surgery to eliminate wrinkles;
- trigeminal neuralgia. Although neuralgia affects the left eyebrow, the right one can also hurt, since the processes of the trigeminal nerve go to it. Patients complain of excruciating pain that radiates to various parts of the face;
- With intracranial pressure, objects appear in two before the eyes, and dark circles appear before the eyes. The cause of this condition is a violation of the microcirculation of cerebrospinal fluid or its excessive formation. The condition manifests itself in the form of general weakness and drowsiness. Injuries and neoplasms can lead to increased intracranial pressure;
- neoplasm. An accurate diagnosis can indicate the presence of a tumor;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the causes of pain above the eye
Swelling on the forehead above the eyebrow
The presence of swelling on the forehead may be the most noticeable sign of an infection or a simple allergic reaction to an irritant, also called contact dermatitis. Is this swelling serious or not? For many people, any unexplained swelling can be a cause for concern. For people with a strong immune system or those who exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet, this problem usually goes away within a day or two.
When the swelling is not caused by another condition, then a simple warm compress and the use of anti-inflammatory ointments or gel should help return the facial skin to normal. Otherwise, if the swelling does not go away after a week, you need to undergo a medical examination to determine the cause. Only after a complete examination will the doctor be able to prescribe adequate treatment.
Among all the reasons that cause swelling of the forehead, the most common are the following:
- Contact dermatitis is when the body reacts after physical contact with an irritant. It can lead to an itchy and painful rash on the skin.
- An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body begins to react abnormally to normal and healthy body cells.
- Allergic reaction to food or soap. For many people, various chemical components present in soap can irritate the skin, causing it to swell. Mineral composition in foods such as vitamins and proteins can also cause swelling in the same people.
- External trauma , physical damage to the face with a hard object, can cause swelling of the forehead.
What tests are usually prescribed?
At an appointment with a neurologist, a physical examination of the patient is performed: basic neurological reflexes are checked and the neck muscles are examined.
The doctor writes out a referral for tests: general blood test, biochemical blood test, blood sugar test.
A general blood test with an increase in ESR or an increased content of leukocytes indicates inflammation in the body.
Blood biochemistry may indicate a deficiency of one of the vital elements, which leads to discomfort in the head area.
Low blood glucose levels are often accompanied by cephalgia, dizziness and weakness.
The doctor may write a referral for additional tests:
- The gas composition of arterial blood can reveal cerebral hypoxia.
- A blood test for hormones determines various abnormalities in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
A neurologist can give a referral to one or more diagnostic methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - excludes the presence of various neoplasms (tumors and cysts), aneurysms. The photographs clearly show post-traumatic defects, neurodegenerative abnormalities, and changes in blood vessels affected by atherosclerosis.
- Computed tomography (CT) is the most informative method for studying the brain. It gives a clear idea of pathological changes in the skull and brain, pathology of bone tissue, blood vessels and brain structures. Provides information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries. The disadvantage of this method is the significant radiation dose during the study.
- Electroencephalography gives an idea of the presence of pathological changes in blood vessels and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Doppler ultrasound (ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck) - shows the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries; narrowing and tortuosity of the arteries, leading to brain hypoxia; peripheral vascular resistance.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - gives an idea of the tone and blood flow of blood vessels. Using REG, the following are diagnosed: hypertension, atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- MRI of the cervical spine - the presence of cervical osteochondrosis can cause pain in the head and neck, which intensifies when turning the head.
- Rheovasography of cerebral vessels (RVG) - shows the quality of blood flow through the great vessels, evaluates collateral circulation.
- Radiography will be less known. In the image you can only see the bone structures of the skull, soft tissues are not visible.
The use of anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve swelling
Anti-inflammatory drugs also have a positive effect after reactions associated with tattooing.
They generally relieve inflammation, improving the condition and relieving pain. Such drugs are divided into preparations of internal and local action.
The first include:
- Paracetamol;
- Acetylsalicylic acid;
- Ibuprofen;
- Diclofenac.
Ibuprofen is a remedy that should be in every first aid kit. This drug is listed by WHO as a vital and universal medicine with almost no side effects. The most popular anti-inflammatory local remedies include:
- Radevit;
- Belosalik;
- Voltaren;
- Beloderm;
- Ichthyol ointment;
- Syntomycin ointment;
- Indomethacin ointment;
- Retinoic ointment;
- Tetracycline ointment (with antibiotic).
Causes of pain not related to pathologies
The occurrence of frequent and sometimes chronic pain in the facial part of the head or in the back of the head is often influenced by a number of reasons not related to any pathology. They are a consequence of the lifestyle of the patient himself:
- First of all, frequent pain can be a consequence of alcohol intoxication.
- The second common reason is smoking. A smoker's blood vessels often experience spasm, and hypoxia leads to pain not only in the head, but also in other organs.
- An abundance of fatty, fried and spicy foods in the human diet.
- In people engaged in physical labor, there is a frequent and sharp increase in blood pressure, hence the occurrence of pain in the occipital part of the head.
- Mental work, especially long-term work, often leads to chronic pain.
- Pain in the eyes and in the area around them is a consequence of prolonged work at a computer monitor.
Swollen eyebrow bone and headache
A swollen eyebrow bone is likely to cause severe pain. In most cases, this swelling indicates a more serious condition. This is often caused by damage to the orbital bone, which serves as the socket for the eyeball.
A common cause of orbital bone injury is external trauma and contusion. This can happen as a result of an accident or a blow to the eyebrow with a hard object. Other causes may include improper waxing techniques where severe tension occurs on the skin.
The most common visible symptoms of orbital bone swelling include:
- Strong headache
- Painful sensations in the eye socket
- Swollen eyebrow
- There may also be problems with vision
- Redness of the eyes
- Numbness of cheeks, nose and teeth
- Episodes of nosebleeds may occur.
When treating a damaged bone, you need to be very careful with the type of anti-inflammatory ointments you apply. You should also make sure that the product does not come into contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes, as this can lead to irritation. You can apply a cold or warm compress to your eyebrow to soothe the skin and prevent further swelling.
If symptoms persist or pain and swelling do not go away after a week, contact your doctor.
Treatment with folk remedies
If you feel that you can no longer endure the pain in the eyebrow area, try to relieve it with folk remedies. Perhaps your herbal medicine cabinet contains medicinal herbs that will become your first assistants in this matter.
- Cold compress
Place a towel soaked in cold water or pieces of ice on your forehead and eyebrows.
- Herbal compresses
Rinse the leaves of burdock, cabbage or coltsfoot. Apply to forehead.
- Infusions for internal use
- potato juice;
- nettle infusion;
— viburnum juice with honey;
- a mixture of motherwort (2 parts), thyme (1 part) and mint (2 parts);
- lingonberry infusion;
- Valerian tincture;
- mint decoction;
- propolis tincture.
These folk remedies should help if there is pain in the eyebrow area, but you need to understand that they do not cure, but only eliminate the pain syndrome. Even if you feel relief after them, it will be temporary. Be sure to get examined by a doctor. In addition to the above remedies, always keep in mind a few useful tips that will help you endure these torments.
Bonus recipe. Beetroot compresses are good for pain in the eyebrows. Soak a cotton pad in beetroot juice and apply it to the eyebrow that hurts.
Why is the eyelid above the eye swollen and painful?
A number of reasons:
- Allergy. Flowering plants often provoke the problem. Swelling above the eyes in this case is not uncommon.
- Colds. First, the nasal sinuses swell, then uncontrolled lacrimation occurs. The upper eyelid swells and pain increases.
- Inflammatory process. Many eye diseases cause redness and swelling.
- Development of tumors of various types (benign, malignant).
- Problems with the cardiovascular system. Swelling above the eye often indicates heart pathology.
- Using low-quality cosmetics.
- Crying for a long time.
- Due to hormonal imbalance, the eye may become swollen and painful.
- Formation of xanthelasma. The accumulation of lipids causes swelling.
- Barley. Swelling is the first stage, then an abscess forms. It is impossible to squeeze out the formation. Blood poisoning may occur.
- Conjunctivitis. In a person, the mucous membrane of the eyeball becomes inflamed, which can cause swelling.
- Impaired metabolism. The eyelids may swell for this reason. No redness of the skin is observed.
In addition to swelling, the following symptoms often occur: general weakness, increased irritability.
Take the Attention Test! Find 10 differences! (click right here!)
Associated symptoms
A severe headache associated with unpleasant sensations in the area of the brow ridges may not occur independently, but may be accompanied by additional symptoms. If any discomfort occurs, you need to listen carefully to yourself in order to identify individual signs that a specialist can correlate with the presence of a particular disease.
Signs of frontal sinusitis:
- swelling near the eyes;
- fear of bright light;
- impaired sense of smell;
- increase in body temperature;
- increased discomfort when pressing on the skin;
- discomfort concentrated above the eyebrows, spreading to the frontal part of the skull.
Signs of development of the inflammatory process:
- the pain is insignificant, dull, aching;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- with sinusitis, severe discomfort on the bridge of the nose.
Characteristic symptoms of neuralgia:
- pain is sharp, shooting;
- increasing intensity while pressing;
- noise in ears;
- change in visual function towards its decrease;
- difficulty with pupil movement due to damage to the optic nerve;
- retinal hemorrhage;
- pain in bone tissue.
Migraine has the following symptoms:
- pulsation;
- sharp pain radiating to the temple, eye sockets;
- the duration of unpleasant sensations is up to several days;
- dizziness;
- presence of tinnitus;
- irritability;
- fatigue.
We recommend reading: Is it possible to drink alcohol after eyebrow tattooing?
With encephalitis and meningitis, bursting pain is noted, accompanied by severe discomfort in the occipital and temporal lobes.
Infringement of neck vessels is accompanied by:
- decreased auditory and visual function;
- loss of consciousness;
- difficulties with mental activity and memorization;
- sleep disorders.
In case of injury it is typical:
- bleeding from the site of injury;
- difficulties with orientation in space;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- dizziness;
- the appearance of hematomas.
Any of these diseases, or suspicion of their presence, is a reason to immediately seek medical help.
Treatment
Treatment for a swollen eyebrow can only be performed when the actual cause of the swelling has been diagnosed. Most swelling goes away on its own without any medical help, but when there is a more serious underlying cause, the swelling is likely to return.
You should avoid self-medication. It is optimal for a professional doctor to study the symptoms and make prescriptions. Typically, the following remedies are used to treat a swollen eyebrow:
- Stitching for severe injuries and bruises of the orbital bone
- Ointments for topical use
- Painkillers such as paracetamol
- Vitamin A to strengthen the immune system
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Antibiotics
- Eye drops can be used to protect the eyes from infection.