A rash under the eyes is a pathology that occurs in both children and adults. The causes of its appearance may be allergic reactions or other diseases developing in the body. If you experience rashes in the eye area, you should consult a doctor.
Only a specialist will understand why the rash under the eyes occurred and will help get rid of it. Lack of qualified and timely treatment leads to complications that can threaten the patient’s life.
Kinds
Rash around the eyes is classified as follows:
- Stains. They do not rise above the epidermis and are not accompanied by changes in the surface of the skin. Characterized by redness of the skin;
- Small pimples. They are a small red rash around the eyes. They rise above the epidermis, and inside there is a purulent substance;
- Nodules. They are small seals under the epidermis. They may be accompanied by an inflammatory process, or they may occur without it. Nodules, in turn, are divided into several types: soft, hard and semi-hard seals;
- Bubbles. They are a formation with a bottom, a tire and a cavity. They are located inside the skin or rise above it. The cavity is filled with liquid, which flows out with light pressure;
- Ulcers. Outwardly they resemble bubbles, but inside there is a purulent substance of a yellow or white hue.
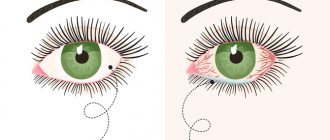
The rash is red. Depending on the species, the epidermis around the eyes remains unchanged or changes shade to pink. Soft tissues often swell.
Ophthalmic herpes zoster –
Herpes in the eyes can be caused not only by the herpes simplex virus (Herpes simplex, types HSV-1 and HSV-2), but also by the herpes zoster virus type HSV-3, which causes herpes zoster (synonymous with herpes zoster). When the herpes zoster virus worsens, the eyes can also be involved in the process, and herpetic eruptions occur along the 1st branch of the trigeminal nerve.
The very first symptom that appears in the prodromal stage of the disease (i.e., before the onset of herpetic eruptions) is an indication at the tip of the nose. In the acute phase of the disease, the symptoms are usually very pronounced, and also appear as rashes on the eyelids, the skin around the eyes, the skin of the forehead, and also very often on the tip of the nose. There may be very strong pain in the forehead, severe swelling of the eyelids, and photophobia.
In more than half of all cases, inflammation of all tissues of the anterior and sometimes posterior parts of the eye occurs. Eye herpes caused by Herpes Zoster can be severe and is often accompanied by scarring of the cornea. The consequences may include cataracts, glaucoma, chronic uveitis, corneal scarring, postherpetic neuralgia, etc. (all these complications impair vision).
Diagnostics -
The diagnosis is made based on the characteristic rash on the forehead, tip of the nose and eyelids, as well as on the results of an eye examination. Traces of herpes zoster in the past in the eye area can be indicated by atrophic hypopigmented lesions that have arisen at the site of past herpetic eruptions on the forehead. Herpetic lesions of the forehead and skin around the eyes, which have not yet spread to the eyeball, indicate a high risk and require urgent consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Why does a rash appear?
A rash around the eyes appears for the following reasons:
- Allergic reaction to external or internal irritants. This could be food, facial care products and other factors. Antihistamines will help get rid of eye rashes, but first you need to eliminate contact of the allergen with the body;
- Unstable emotional background. Frequent stress contributes to problems with the epidermis, which also manifest themselves in pimples under the eyes. Antidepressants will help solve the problem;
- Fungal infections of the epidermis. In this case, not only a rash appears in the eye area, but also itching and peeling. Therapy consists of the use of antifungal medications. After this, the rash will disappear;
- Pathologies caused by infections. In this case, a rash in the eye area is a symptom of the disease;
- Dermatitis. The rash is accompanied by itching, burning and peeling. Treatment should be based on getting rid of the cause that provoked the appearance of rashes on the epidermis.
The appearance of red spots under the eyes is also provoked by a short and poor quality night's rest.
Treatment methods
The causes and treatment of rashes (spots or pimples) are related - the doctor prescribes appropriate medications and therapeutic methods depending on the specific causative agent of the disease.
Treating spots under the eyes
Regular hygiene is important when treating macular rashes around the eyes. The cause of the spots may be poorly chosen prescription glasses, sunglasses, or swimming glasses - it is important to change them. Symptoms can be relieved by eliminating contact of the skin around the eyes with these objects. In addition, it is important that a person using prescription or cosmetic eye lenses use hypoallergenic products that do not cause rashes. To relieve itching and irritation around the eyes in adults, hydrocortisone medications prescribed by a doctor are used in exceptional cases. Under-eye rashes can be relieved by applying cold compresses or cucumber slices.
Treatment of acne under the eyes
For effective treatment, it is important to know the possible cause of the problem. If the rash is part of a seasonal allergy, antihistamines are used in therapy to relieve rhinitis, sneezing, and skin symptoms (including rash around the eyes). You should also reduce your exposure to known allergens – pollen, dust, animal allergens.
In newborns
Acne in newborn babies is not an independent pathology, but is part of the symptoms of other diseases, and if a rash occurs in the eye area of a baby, this may be evidence of the appearance of dermatitis or eczema. If we are talking about allergic dermatitis, then accompanying symptoms also appear - rashes on the epidermis that are red. Red spots also appear under the child's eyes. The cause of this problem is usually dry air in the children's room. Regular ventilation and the use of ionizers help to avoid this situation.
Rashes under the eyes also appear due to the use of synthetic fabrics. These can be scarves, diapers, bed linen and other wardrobe accessories with which the child has constant contact.
A rash under the eyes of a child may be an allergic reaction of the body to the following irritants:
- Food allergens. The appearance of a skin rash around the eyes in infancy is often provoked by new foods that the baby has never eaten. In this situation, rashes may appear in the child’s oral cavity. If after the introduction of complementary foods a rash appears on the epidermis, it is recommended to switch to the previous nutrition system;
- Children's cosmetics. A rash under a child's eyes often appears due to the fact that parents are addicted to using creams, oils and other similar products. Stopping the use of these products will help get rid of the problem;
- Dust. If the baby has small spots or a small rash, this may indicate a lack of regular wet cleaning in the house;
- Animal fur. If there are cats, dogs and small rodents living in the house, then there is a high probability that the child will be allergic to their fur. The rash on the eyes will not disappear as long as the baby is in contact with animals. Even antihistamines will not help solve the problem, and you will have to give the animals to other people in good hands.
Exanthema is another cause of rash in children's eyes. This pathology most often occurs in infancy. The disease appears due to viruses that penetrate the bloodstream. They spread throughout the body through the blood, including the epidermis. Exanthema also appears due to immune reactions to the pathogen. Typically, rashes occur due to measles, rubella and herpes stage 6.
Circles under a child's eyes also occur due to lack of sleep. If the baby has a disturbed sleep-wake pattern, then there is a high probability of redness in the visual area. The problem disappears without therapy after a full and quality night's rest.
Allergy on the eyelids: symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention (with video)
The group of allergic diseases of the eyelids includes: urticaria, Quincke's edema, eczematous and contact dermatitis, toxicoderma. All these pathological conditions are the body’s immune response to exposure to an allergen, and occur with a violation of the integrity of the tissue.
What causes eyelid allergies?
Antigens that can cause allergic inflammation include:
- some medications;
- plant pollen;
- animal hair;
- bird feather;
- cosmetical tools;
- Food;
- various chemicals;
- ultra-violet rays;
- cold exposure, etc.
An allergic reaction can occur immediately, approximately fifteen to thirty minutes after contact with the allergen, or develop after six to twelve hours.
Depending on the time of manifestation, immediate type eyelid allergies are distinguished:
- hives;
- angioedema;
- simple dermatitis;
and slow:
- toxicoderma;
- eczema of the eyelids.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
Common symptoms of allergic diseases of the eyelids include swelling; intense itching, lacrimation.
With urticaria, blistering rashes appear on the eyelids. The eyelids itch unbearably. The eyeballs are tense. My eyes are constantly watering. General malaise occurs, the patient shudders, and the body temperature rises.
The course of urticaria can be acute or chronic. The first case is characterized by transient rashes, when blisters may disappear a short time after their appearance.
In the case of chronic urticaria, allergic inflammation of the skin lasts for weeks and sometimes months.
What you need to know: hives are most often caused by food or drug allergens.
Angioedema or Quincke's edema is a type of urticaria and is a limited swelling localized on the mucous membranes, skin, and subcutaneous tissue. Most often, patients discover this problem in the morning, after waking up.
Angioedema is usually located on the face (cheeks, lips, forehead), arms and legs; The tongue and soft palate, neck and skin over the joints, and the membranes of the brain may swell.
Before edema appears, the patient may have a headache, a feeling of weakness, and asthenia. Angioedema on the eyelids, according to the degree of severity, is divided into minor, when the palpebral fissure is only slightly narrowed, and severe, in which the eye fissure is completely closed.
What you need to know: not only the eyelids can swell, but also the cornea, iris, uveal tract of the eye, retrobulbar tissue, which threatens the organ of vision with complete death.
Allergic dermatitis of the eyelids usually affects both eyes. The disease manifests itself as rapidly increasing redness of the eyelids. The patient is bothered by severe itching and burning. Due to swelling of the skin of the eyelids, the palpebral fissure is narrowed.
A local allergic reaction develops within six hours after contact with one or another allergen, which can be cosmetics or medications, etc.
Eczematous lesions of the skin of the eyelids are characterized by an acute onset followed by a transition to a chronic process, occurring with remissions and relapses. Blistering, papulopustular rashes appear on the skin of the eyelids. The eyelids are swollen and hyperemic. My eyes are constantly watering.
Deep cracks appear in the corners of the eyes. Subsequently, the pustules containing serous fluid are opened. The exudate flows out, which causes the skin to become wet, and its drying out leads to the formation of yellowish scales.
After the inflammatory process subsides, the stratum corneum of the skin is restored and exfoliated. Subsequently, the affected skin takes on a healthy appearance.
The rash with toxicoderma can be represented by white or red blisters, erythematous-scaly elements, formations with pinpoint hemorrhages. It can appear on different areas of the skin, including the eyelids. As a rule, this is an allergic reaction of the body to certain medications, certain foods, and various chemicals.
What you need to know: recently this problem has been increasingly associated with the widespread use of various chemical fertilizers and poisons in agriculture. Consumption of products grown in such conditions can lead to toxicoderma.
Diagnostics
When collecting anamnestic data, take into account:
- presence of hay fever (seasonal allergies);
- duration of pathological manifestations;
- one or two-sided process.
During a physical examination, visual acuity is checked, an external examination of the eyes is carried out, and their structure (edges of the eyelids: anterior and posterior, cornea and connective membrane, ciliary edge) is also examined in detail using an optical device - a slit lamella.
Laboratory tests include scrapings from the connective membrane (conjunctiva) and tear fluid. Skin tests are carried out with various allergens.
Allergy on the eyelids, accompanied by swelling, is differentiated from swelling that occurs due to various inflammations, with Milroy-Meige syndrome.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
Allergic diseases of the eyelids are treated by an ophthalmologist together with an allergist.
Treatment methods
The goal of treatment of allergic diseases of the eyelids is to eliminate the cause that caused them, achieve stable remission, and prevent the occurrence of possible complications (anaphylactic shock, papilledema, etc.)
Treatment begins with identifying the allergen and eliminating it. Desensitizing therapy is carried out with glucocorticoids and antiallergic drugs. If a secondary infection occurs, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
For local treatment, cold lotions are used to relieve itching and swelling, and alcohol solutions of anesthesin, novocaine, and menthol are used for rubbing.
The following antihistamines are prescribed for internal use: diazolin, claritin, citrine, pipolfen, cetirizine, fenistil, chloropyramine. For intravenous administration, use a 10% calcium chloride solution.
For frequent relapses, subcutaneous injections of histaglobulin and the administration of small doses of corticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone) are indicated. For local use, glucocorticoid ointments and creams are used (hydrocortisone, dexamethasone ophthalmic ointment, as well as prednisolone, Celestoderm B, Flucinar, Sinalar, histimet ointments.
Instillations of cromoglycic acid and antazoline/tetrizoline are performed into the conjunctival sac. If the optic nerve is affected by allergic inflammation, subconjunctival and retrobulbar injections of corticosteroid drugs (hydrocortisone emulsion, dexamethasone solution) are given.
To relieve edema, diuretics are prescribed (diacarb, furosemide, triampur, clopamide). For exudative phenomena, applications with a solution of rivanol or Burov's liquid are indicated. After the release of exudate stops, the affected areas are treated with salicylic-zinc paste (Lassara) or ointments (triamcinolone, prednisolone, Celestoderm B, etc.
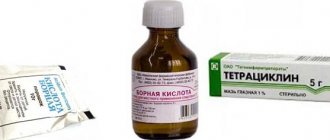
In case of eczematous lesions of the skin of the eyelids, lotions with lead water, boric acid solution, and Burov's liquid are applied to problem areas.
Treatment of associated infection is carried out with antibacterial eye drops of a solution of gentamicin, norfloxacin or tobramycin.
What you need to know: If your eyelid allergies are caused by food, you need to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Persons with a complicated course of the disease are hospitalized and treated in a hospital setting.
Severe damage to the conjunctiva, cornea and eyelid skin requires surgical intervention.
Prevention and prognosis
What you need to know: people with this problem need to avoid contact with the allergen, undergo annual preventive treatment, and strengthen their immunity.
In the absence of frequent relapses, we can talk about a favorable outcome of the disease, otherwise, there is a violation of the outflow of lymph and overstretching of the skin.
information about eyelid dermatitis
Source: //zdravstvuy.info/?p=5786
In older children
Bacterial infections and allergic reactions are the two main causes of rashes on the eyelids and around the eyes in older children.
If we are talking about allergies, then the rash is a reddish rash on the epidermis. In another way, such rashes are called urticaria. Accompanied by itching and burning.
Pathology therapy is based on identifying the allergen and protecting the child from contact with it. Sometimes these measures are enough for the rash to go away on its own without any medication.
If the rash under the eyes occurs due to bacterial pathologies, then it will also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of soft tissues in the area of the rash;
- pain in the area of the affected epidermis;
- itching and burning.
For pathologies caused by bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. This helps to cure the disease itself, as well as get rid of the rash on the epidermis.
Fungus is another cause of eye rashes in older children. It usually appears due to poor personal hygiene. Constant rubbing of the eyes with dirty hands can cause not only a rash, but also other more serious pathologies of the visual organs.
If your eyes become swollen due to hives
One of the most life-threatening complications is angioedema, which can develop with urticaria. Treatment of this condition must be immediate, as there is a high risk and threat to the patient’s life.
Why can swelling develop with urticaria?
What does angioedema look like? The basis of any allergic reaction, including urticaria, is an immune response to the penetration of all kinds of irritating and foreign substances into the human body.
At the very first contact with this factor, only increased susceptibility to it develops, that is, the body remembers, but practically does not react clinically at all.
But in the case of all subsequent contacts, a response in the form of an allergy always develops.
All symptoms that appear with urticaria occur under the influence of histamine, which is produced almost instantly after the penetration of the allergen.
As a result of the synthesis of histamine, the vascular permeability of the skin increases, which leads to the formation of redness and swelling.
Angioedema with urticaria occurs when the process spreads deep into the tissue, into the subcutaneous tissue, affecting the mucous membranes.
Urticaria and angioedema can occur not only in the face and larynx, which is most often diagnosed, but also in the lower leg, chest, internal organs, and genitals. But, nevertheless, angioedema with damage to the mucous membrane of the larynx is considered the most life-threatening.
What can cause the development of angioedema?
Urticaria and angioedema have the same causes of development. The development of this type of reaction is not always necessary as a result of direct ingestion of the allergen, that is, with food. Sometimes simple contact, inhalation of vapors, particles is enough.
Most often, swelling with urticaria can be caused by the following factors:
- Food products, and, as a rule, these are substances belonging to the highly allergenic class. Among them are nuts, honey, citrus fruits, seafood, eggs, as well as any red fruit.
- Medicines that are most often capable of causing the development of allergic reactions and swelling are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and radiocontrast drugs. Also, an edema reaction can be caused by the administration of immunoglobulins, as well as vaccines.
- Often, urticaria and angioedema occur in response to insect bites, especially hymenoptera (wasp, bee, bumblebee).
- Also, the most frequently diagnosed causes include pollen of various flowers and plants, and animal hair.
It is important to clearly know and remember what substance caused the development of such reactions, and try to prevent contact with it in the future. Since in most cases, repeated episodes of the disease are much more complex and stronger than the previous ones in their condition and course.
What does angioedema look like?
Angioedema of the eyes Urticaria and angioedema have somewhat similar developmental symptoms. Sometimes angioedema develops immediately after direct contact with an irritating substance, and sometimes this condition occurs a short time after the onset of urticaria symptoms.
Let's look at the clinic and all the symptoms that may indicate the development of edema.
Angioedema with urticaria is a dangerous condition, often life-threatening for a patient of any age. It is accompanied by a sharp development of swelling of the skin in any one area or part of the body or even throughout the body. Gradually, the process begins to spread to the subcutaneous fat.
On palpation, the swelling of the tissues is dense and warm. Skin color usually does not change. Symptoms of itching are rarely present.
When urticaria and angioedema occur simultaneously, a red rash in the form of blisters appears on the patient’s skin. And in this case, there is both itching and burning.
Most often, this type of edema develops in the larynx and in this case requires immediate action to relieve this allergic reaction as soon as possible. The fact is that when the larynx area is damaged, suffocation often develops literally in a matter of minutes and the person can die.
With the development of edema in the eye area, vision is impaired, and with damage to the genitourinary organs, urination changes and becomes difficult.
What does the patient need to know?
Sudden swelling with urticaria is a rather unpleasant condition. Anyone who has experienced it at least once should know all the symptoms that have developed and try under no circumstances to allow such reactions to develop again.
It is advisable to always have with you a “passport of an allergy patient”, where the diagnosis will be written, all provoking factors are listed and basic recommendations are given. This is especially important if you are intolerant to any medications.
If it was not possible to identify the cause of this phenomenon, then it is advisable to remember the following:
- It is recommended to avoid prescribing and taking medications such as Aspirin and any others belonging to the Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory group.
- We must give up smoking and alcohol.
- Replace hot baths with showers.
- In cases of diagnosing Arterial Hypertension, it is recommended to exclude the use of ACE Inhibitors (Enalapril, Lisinopril and others), since it is this group of drugs that can cause an edema reaction if it is predisposed.
- A hypoallergenic diet is required, especially during the period of symptoms.
In addition, you must always have one of the Antihistamines with you, so that in case of sudden development of allergy symptoms or swelling, you can help yourself in time and prevent the condition from worsening.
Treatment of angioedema
Treatment of this pathology must be carried out in a very short time in order to relieve an attack of an allergic reaction. It is almost always necessary to admit the patient to a hospital department. This is due to the fact that even if it was possible to quickly relieve inflammation, this does not mean that it cannot arise again after some time, especially in cases of an undetected reagent.
Urticaria and angioedema require the following treatment:
- Mandatory exclusion of the suspected provoking factor.
- Antihistamines help relieve the first signs of edema.
- If necessary, treatment with hormonal drugs (Prednisolone) is prescribed.
- Treatment with Enterosorbents is also necessary, which helps remove the allergen from the body faster.
- It is advisable to carry out detoxification therapy in combination with diuretics.
- A good effect is achieved by prescribing hyposensitizing drugs (Sodium Thiosulfate)
Source: //geraklionmed.ru/esli-pri-krapivnitse-opuhayut-glaza/
Causes in adults
Factors that provoke the appearance of a rash around the eye of an adult:
- Taking certain medications. This also applies to the use of oral contraceptives;
- Consumption of certain foods. These include certain types of fish, meat, pizza and nuts, as well as consumption of honey, chocolate and soy foods;
- Constant contact with household allergens. These include household chemicals, pet hair, and so on;
- Use of cosmetics. Most often, a rash near the eyes in an adult appears due to the use of low-quality products for caring for the epidermis around the eyes. In this case, you can get rid of the problem by abandoning the means that provoked its occurrence;
- Decorative cosmetic products. Rashes around the eyes in an adult also appear due to poor quality eye shadow or mascara. To avoid such a problem, experts recommend purchasing cosmetics only from trusted manufacturers in retail outlets that value their reputation;
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In this case, the rash on the eyes is an allergic reaction to the sun's rays. Sunglasses or protective agents applied to the epidermis before going outside will help to avoid its occurrence;
- Use of sunscreens. The situation here is different than with the sun's rays. A rash in the eye area in this case is an allergy to the use of sunscreens;
- Unstable emotional background. Cases have been recorded where stress led to the formation of rashes on the epidermis in the eye area;
- Cold. Sometimes the epidermis reacts to changes in air temperature. This happens for many reasons – deterioration of the body’s defenses, poor nutrition and others;
- Health problems. Any pathology leads to a deterioration of the immune system. As a result, a person develops a household allergy from which he did not suffer before;
- The presence of the herpes virus in the body. It usually manifests itself as a cold in the mouth area. Herpes on the eye is a rare phenomenon, but such cases have been recorded.
Red eyelids or spots under the eyes occur for many reasons. The main thing is to determine the factor that led to the problem. Therapy is based on identifying the cause of the pathology and eliminating it. In some cases, it is enough to just get rid of the factor that triggered the rash in the eye area.
However, it happens that to cleanse the epidermis, treatment of the rash itself may be required. Only a doctor can prescribe it after diagnosis and based on the individual characteristics of the patient. Any independent measures can lead to a worsening of the situation and complications that threaten the patient’s life.
Causes of red rash
The first thing to note is that dermatitis or eczema, which causes a red rash under the eyes, includes many different skin conditions and different symptoms.
If you are lucky enough to not have eczema on your face, know that it is a common problem. Let's look at the most common causes of a red rash and redness of the eyelids.
Atopic eczema
Atopic eczema or atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema with long-lasting and chronic symptoms. Appears in many forms, often in combination with other allergic rashes, asthma, hay fever. The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but dermatologists believe that atopic spots may be caused by a combination of hereditary and environmental factors, including changes in weather. What is characteristic of the disease? Itchy rashes causing scratching. The result is swelling, cracks, and peeling.
Atopic eczema can affect anyone, regardless of gender or age, but most commonly causes a red rash around a child's eyes. Symptoms vary individually, and the disease appears differently in each person. Typical manifestations:
- rashes, itching, dry skin under the eyes and on the eyelids;
- redness with small red pimples resulting from skin inflammation;
- the presence of a rash on other parts of the body.
Contact dermatitis around the eyes
Unlike atopic eczema, the first symptoms of a contact dermatitis rash occur when the skin is directly exposed to an irritant or allergy-causing factor. This type of eczema is associated with the negative effects of a substance that causes an unwanted reaction upon contact with the skin. A common factor that irritates the skin, causing signs of skin allergies and rashes, is the use of decorative cosmetics (eyeliner, mascara and eye shadow).
A common reaction to the use of these products in some people is an allergy, which causes a small rash under the eyes (in adults), especially on the sensitive skin around the eyes.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis or eczema include red patches, burning skin around the eyes, dryness, cracking of the skin, and small (small) blisters.
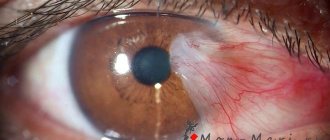
Borreliosis
This bacterial infectious disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, mainly transmitted by ticks. Red rashes with an uneven surface appear around the area of the tick bite, but in some people the rash can spread to areas of the dermis where there was no contact, such as the eye area.
Other symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, chills. If the disease is not treated, it can develop into serious health problems such as nervous system disorders, arthrosis and other joint complications.
Important! If you develop a rash along with the other symptoms listed above, consult your doctor immediately!
Reaction to certain types of medications
The appearance of rashes and pimples under the eyes can be caused by exposure to a certain drug or substance, whether taken orally or injected. The immune system develops hypersensitivity when exposed to an allergy-causing substance. Further contact with this substance causes an allergic reaction - a rash.
Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
Is the skin under your eyes swollen, red, and covered in rashes? You may suffer from atopic keratoconjunctivitis, a disease in which the immune system produces more antibodies in response to an allergen. The disease is genetically induced and is not just a cosmetic problem. In addition to developing a rash and damaging the skin, it can also lead to sensitivity to light, burning and itching of the eyes.
Allergic (contact) conjunctivitis
The next possible cause of redness and rashes in the eye area is contact conjunctivitis, when inflammation, rash, and redness of the eyelids occurs as a result of allergies. Inflammatory processes in the upper eyelids can cause swelling, burning, a feeling of dryness in the eyes, pain, and a feeling of sand in the eyes.
Other reasons
The appearance of a rash on the eye, red itchy lesions can be caused by the following reasons:
- hay fever;
- exposure to direct sunlight without protection;
- injury;
- chronic excessive stress;
- herpes viral infection on the eye;
- psoriasis.