November 30, 2017
November 30, 2017
- Indications for use
- What does a head CT scan show?
- Brain
- Paranasal sinuses
- Temporal bones
- Facial bones
- Brain vessels
- Jaw
- Eye sockets
- Larynx
- Teeth
- Soft tissues of the neck
- Scull
- Inner ear
CT scan of the head is an accurate, highly informative and irreplaceable method for studying the entire bone structure of the head and internal organs. The examination is based on the principle of layer-by-layer scanning of the head with X-rays.
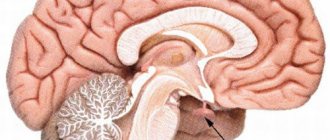
The head is the most important part of the human body, since it contains the brain and other vital organs.
In case of prolonged headaches, nausea, or a sharp decrease in visual or hearing acuity, it is important to investigate its condition.
To diagnose the condition of the head, the following CT examinations are prescribed: the brain, paranasal sinuses, temporal bones, facial bones, cerebral vessels, jaw, orbit, larynx, teeth, soft tissues of the neck, skull and inner ear.
In many cases, in conjunction with the above studies, CT scans of the vessels of the head and neck are performed.
Indications for use
A referral for an examination is issued by a neurologist, ENT doctor, oncologist, traumatologist, psychologist, surgeon or therapist. The main purpose of the study is to make an accurate diagnosis, refute or confirm a previously made diagnosis.
A CT scan of a specific part of the head is prescribed for the following indications::
- Frequent headache of unknown etymology;
- Convulsions;
- Rapid deterioration of vision or hearing without serious reasons;
- swelling of the face or neck;
- Presence of head injury;
- Pathologies of coordination;
- Lack of balance;
- Suspicion of oncology;
- Constant increase in blood pressure (blood pressure);
- Foreign bodies;
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
Computed tomography allows you to diagnose the presence of minor pathologies and serious diseases at any stage, which is of great importance for patients with diseases for which treatment must begin immediately.
Indications
CT is prescribed to detect inflammatory processes, brain tumors, hemorrhages and the consequences of traumatic brain injury (TBI).
In addition, computed tomography is one of the methods for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation for various diseases - the bones of the skull, membranes and structures of the brain, blood vessels and paranasal sinuses are clearly visible in the images.
A computed tomography scan of the brain may be prescribed by the attending physician (therapist) or a neurologist in the following cases:
- suspected swelling, inflammation, hemorrhage after TBI;
- acute circulatory disorder (stroke);
- abscess and cysts of the brain;
- infectious diseases (encephalitis, meningitis);
- oncopathology (tumors, metastases);
- abnormalities in the development of brain structures and blood vessels;
- pathologies of blood vessels (thrombosis, aneurysm);
- hydrocephalus (“dropsy” of the brain - excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricular system of the brain);
- convulsions, visual disturbances, dizziness, decreased sensitivity, confusion - neurological symptoms for no apparent reason;
- causeless headaches for 2-3 months or more;
- preoperative examination;
- individual contraindications to MRI (presence of a pacemaker, insulin pump, metal prostheses).
Facial bones
The facial bones are an important component of the skull and are included in the masticatory apparatus (paired maxillary bone and lower jaw). A recommendation for testing is given for headaches, swelling of the soft tissues of the facial area, nasal discharge, rapid deterioration of visual acuity and frequent pain in this area. Diagnostics reveals damage, deviated septum, the presence of a foreign body and pathological changes in blood vessels.
It lasts about 30 minutes, and the average price in Moscow ranges from 3,000 to 4,900 rubles.
Brain CT machine
The equipment consists of several parts. This is a special table-couch on which the patient lies. The main element is the ring. It contains a device that emits X-rays and sensors that record the weakening of the density of the rays as they pass through the tissues of the head and transmit this data to a computer.
Modern technologies make it possible to enlarge any image to obtain even more detailed information. Since the quality of images largely depends on the number of slices in a single segment, and when examining the brain it is important to find even the smallest pathological foci, it is recommended to undergo scanning using multi-slice devices. Optimal equipment performance is from 16 cuts per step.
CT scan of the brain: video
You can watch a video of how a CT scan of the brain is performed - for example, on our website or on the Internet resources of clinics offering this type of diagnosis.
CT scan of the brain in the photo
The results of a CT scan are called images. By photo in this case we mean images of the CT process itself. In the photographs posted on the Internet, including on our website, you can see what the tomograph looks like.
It is useful to look at such pictures before undergoing a CT scan of the brain, since for some patients studying the scanning process is the most important component of psychological preparation for the examination.
Inner ear
The inner ear is a system of canals in which the auditory and vestibular analyzers are located. The main reason for prescribing a diagnosis: a sharp deterioration in sound quality, pain in the ear, fluid from the ear canal, noise and injury. CT images can detect the following pathologies: damage or displacement of bones, infectious or inflammatory processes, as well as angioma.
On average, diagnostics takes 5-10 minutes, and the cost ranges from 4,500 to 6,000 rubles.
Share link on social networks
When is a brain CT scan with intravenous contrast performed?
Basically, CT scans of the brain are performed with contrast if there are suspicions of benign or malignant brain tumors, as well as aneurysms, malformations and other vascular disorders (as part of CT angiography of the vessels of the head).
An iodine-based radiopaque agent administered through the cubital vein allows one to reliably and informatively determine the nature of the tumor, its exact size and degree of development, and the relationship with neighboring structures and tissues of the brain.
Contraindications to CT with contrast
Contraindications to CT with contrast include:
- presence of a confirmed allergy to iodine;
- acute or chronic renal failure due to the possibility of complications due to the administration of a contrast agent;
- blood creatinine level above 100 µmol/l;
- severe diabetes mellitus (risk of complications from contrast enhancement while the patient is taking medications containing metformin);
- some thyroid diseases.
It is possible to do a computed tomography scan with contrast during breastfeeding. You just need to exclude lactation within 48 hours after the study.
Questions
Is it possible to do a CT scan during pregnancy?
Any form of X-ray diagnostics is contraindicated at any stage of pregnancy. Computed tomography uses well-known x-rays, which have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, CT scanning for pregnant women is performed only in exceptional cases when it comes to saving the life of the mother. If there is a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, they will try to carry out a tomography using a low-dose program, covering the tummy as much as possible with a special lead blanket that reflects X-rays. But even these precautions cannot exclude the possibility of the development of abnormalities in the fetus. The likelihood of this threat depends on the stage of pregnancy. The use of computed tomography in the early stages of pregnancy is strictly undesirable, since this may be fatal to the embryo, and the woman will have to terminate the pregnancy. According to the observations of expert radiologists:
- in pregnant patients who were irradiated at 1-2 weeks due to radiation from CT scans, in 98% the fetus died or stopped developing;
- in women irradiated at 2-5 weeks of pregnancy, in 70% of cases there was a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy, and in 20% the fetus had malformations of the liver, heart, and thyroid gland;
- In pregnant women who underwent computed tomography at 6-12 weeks, in 80% of cases the child developed multiple pathologies of organ development.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after x-rays and fluorography?
In case of medical necessity, an X-ray or fluorography examination can be combined with a computed tomography session on the same day. The main thing is to ensure that the total radiation dose does not exceed 15-20 mSv. On average, X-rays provide 0.2 mSv of radiation exposure per scanning session. The level of radiation exposure on MSCT is significantly higher and depends on the scanning area. It can range from 1 mSv to 15 mSv per examination.
Is it possible to do CT scans for children?
Computed tomography is a radiological form of diagnosis. It is not recommended for children under 14 years of age unless absolutely necessary. X-rays have a negative impact on the formation of the central nervous system in a child and increase the chances of cancer in children under 5 years of age. The dose of radiation that a child receives during a tomography session leads to an increase in the number of cells with mutations in the P53 gene, which is responsible for the development of cancer, and increases the chance of developing leukemia and brain cancer by 35%. Therefore, a child’s CT scan is performed only as prescribed by a doctor and in the presence of compelling medical reasons, when the benefits of the examination outweigh the health risks associated with it. Doctors strive, whenever possible, to replace computer scans with safer forms of diagnostics - ultrasound or MRI.
Is it possible to do a CT scan at a temperature?
Temperature is not a contraindication to native tomography, but it may be a limitation for contrast-enhanced CT. Changes in a person's temperature may indicate an inflammatory process in the body, and in such a state, the introduction of iodine-containing contrast can provoke a crisis.
Can I do a CT scan with dental implants and braces?
The short answer is yes. X-rays do not in any way affect dental implants, crowns and braces, no matter what material they are made of. Dental implants also cannot affect the quality of the tomograms obtained. They do not produce any artifacts on CT images.
Is it possible to do CT with titanium and metal plates?
Metal in the body is not a contraindication to CT, regardless of the alloy composition of your metal inclusion. Therefore, computed tomography can be used as an alternative form of diagnosis when, due to the metal in the patient’s body, magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed on the patient.
Is it possible to do a CT scan with a pacemaker?
If you have a pacemaker of any model, you can do a CT scan. CT scans use X-rays and they do not have any negative effect on any artificial pacemakers. Therefore, CT is used as an alternative to MRI if the patient has a pacemaker, neurostimulator, or insulin pump, which can fail in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. But it is safe for such patients to undergo examination with a CT scanner.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after chemotherapy?
A CT scan may be ordered after a series of chemotherapy treatments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. The decision about when control images need to be taken is made by the attending physician. Chemicals used in oncological treatment are not a contraindication to CT. The only thing you should always remember is that X-rays tend to accumulate in the human body, so the recommended interval between CT examinations for an oncological diagnosis should be 2-3 months. For diagnostics, you should also choose spiral low-dose units.
How to interpret pathologies from CT images?
After the scan, the doctor compares the resulting images with normal indicators of the condition of the skull and brain, and evaluates the speed of blood flow. The specialist also pays attention to the presence of foreign bodies, signs of fluid accumulation, and disruption of the structure of nerve fibers.
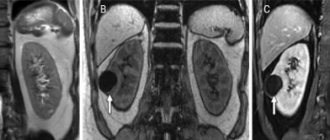
One of the common diseases - ischemic stroke - is visualized by dark spots on the brain tissue, hemorrhagic stroke is determined by white spots on CT images of the brain, as shown in the photo below.
The images also distinguish cystic formations from tumors - during a contrast study, a tumor neoplasm, unlike a cyst, accumulates contrast and appears more clearly in the images.
Note that the diagnosis of tumors is based on identifying direct (shadow of the formation) and indirect signs (swelling of brain tissue, hydrocephalus, etc.). Some features, such as areas of brain tissue with high density, are detected only if a contrast agent is injected. Also, many large formations or located deep in the brain are diagnosed by expansion, compression or displacement of the cerebral ventricles.
The patient does not have any brain disorders if the brain itself, blood vessels, and skull bones are of normal size, there are no symptoms of bleeding, there are no accumulations of fluid, the integrity of the bone tissue of the skull is not compromised, there are no neoplasms, damage to nerve fibers, enlargement or expansion of the ventricles of the brain and other signs of disease.
Only a radiologist should interpret the images, but not the patient himself, since interpretation of the results is a complex process, and incorrect interpretation of the data can lead to an incorrect diagnosis and lack of correct treatment.
Contraindications
X-ray radiation and contrast agents cannot be called completely harmless, therefore there are a number of contraindications to CT scans of the brain. You cannot undergo the procedure if you have severe pain syndromes or hyperkinesis, when you cannot remain completely still. Contraindications to contrast administration are diabetes mellitus, iodine allergy and renal failure. It will not be possible to find out what a brain tomography shows if the procedure is necessary for a pregnant woman at any stage - the radiation can negatively affect the fetus. Nursing mothers will have to wean their baby off the breast for two days until the contrast wears off. Patients with acute mental illness, as well as claustrophobia, will need to either choose a different research method or undergo a CT scan under anesthesia.
How often can a CT scan of the brain be done?
You can’t just find out what a CT scan of the brain shows. The procedure is prescribed by the attending physician if there are a number of symptoms indicating disturbances in the functioning of the brain, as a rule, no more than once a year. In severe cases, you can undergo tomography up to three times a year with an interval of at least 4 weeks.
Alternative Methods
If for a number of reasons it is impossible to find out what a CT scan of the brain shows, you can undergo an MRI
. This procedure will allow you to examine the structure of the brain in detail and identify any abnormalities. CT is aimed at studying the chemical structure of tissues that absorb x-rays, depending on their density. MRI does an excellent job of visualizing soft tissue. It often happens that CT and MRI are prescribed together to obtain a more detailed picture. However, it is worth knowing that magnetic resonance imaging makes it practically impossible to examine the bones of the skull; in this case, computed tomography better shows all structural changes.