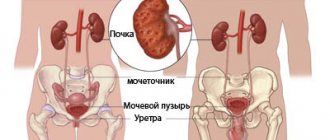
A kidney cyst is a disease in which the excretory function of the kidneys may be impaired. In this case, patients need not only treatment, but also dietary nutrition. A diet for kidney cancer is also necessary. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors take an individual approach to treating patients with kidney diseases.
Doctors conduct a comprehensive examination using equipment from leading American and European manufacturers. Nephrologists and oncologists treat patients according to Russian and international protocols. Medical staff provides professional care for patients. The chefs prepare dietary dishes that are healthy and taste as good as home cooking.
Nutrition for kidney cysts
For kidney cysts, regardless of the type of treatment and stage of the disease, the dietary table according to Pevzner No. 7 is used. The diet for kidney cysts is individual. The cooks at the Yusupov Hospital take into account the culinary preferences of patients when preparing dishes.
Fatty, fried, smoked foods and pickles are completely excluded from the patient's diet. Limit fluid and salt intake, which can increase daily diuresis. Patients are advised to refrain from drinking alcohol, hot spices and sweet carbonated water. Due to the risk of complications, all patients with kidney cysts must avoid hypothermia and heavy physical labor.
Allowed and prohibited products for kidney cysts
The diet for kidney cysts includes permitted foods:
- Fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Vegetable soups without adding fish and meat broths;
- Day-old bread (which has no protein);
- Dairy products;
- A small amount of lean meat and fish;
- Greenery;
- Weak green tea;
- Unsalted and low-fat cheese and cottage cheese.
The following foods are excluded from the diet:
- White bread;
- Alcohol;
- Rich meat and fish broths;
- Canned food;
- Chocolate;
- Canned food;
- Salty and fatty cheeses;
- Beans;
- Carbonated drinks.
The cooks at the Yusupov Hospital prepare dishes from high-quality products for patients with kidney cysts, providing balanced nutrition rich in vitamins and minerals.
General ideas about the disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common form of PKD and is caused by inheritance of defective PKD1 and PKD2 genes. The probability of the disease occurring in children with a hereditary predisposition is 50%.
It is important to know! Mostly both kidneys are affected; Unilateral LBP is rare and develops into cancer in 10% of cases. Cysts in the kidneys crowd out healthy tissue and gradually limit kidney function.
Patients experience the following symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- arterial hypertension;
- enlarged kidneys;
- blood in the urine (hematuria);
- excessive urinary protein excretion;
- frequent urination.
Symptoms usually appear between the ages of 30 and 50. The first sign is hypertension, which is difficult to control. During the course of the disease, many organs are affected - the liver, brain, heart and digestive system.
For PBP, both surgical and medical treatment measures are prescribed. Alternative non-medical remedies are not indicated.
Diet for kidney cysts and polycystic disease
Diet No. 7A is used to treat polycystic kidney disease, which is accompanied by renal failure. The diet is based on reducing protein and reducing the load on diseased kidneys due to increased excretion of protein breakdown products. Food should contain no more than 20 grams of protein per day. The patient is allowed to consume no more than 0.5 grams of salt per day. It is found in cooked foods. To ensure that the finished food has a good taste and is not monotonous and bland, it is allowed to use citric acid and herbs in cooking.
Meals should be fractional, in small portions, 5-6 times a day. Fish and meat, spices and herbs, and legumes are excluded from the diet. It is necessary to control daily fluid intake. You can drink no more than 0.5 liters per day. The daily calorie content of table No. 7A is 2200 kilocalories.
Diet 7B is prescribed when a kidney cyst is complicated by renal failure and is accompanied by an increased level of nitrogenous protein products in the patient’s blood. The patient receives 40 grams of protein per day from food. The amount of salt consumed is reduced to 0.5 grams per day. You cannot add additional salt to dishes; salt is allowed only in foods.
The diet includes fish and lean meat, in small quantities and boiled. Cereals are also subject to restrictions. You can consume no more than 600 ml of liquid per day. Meals in fractional portions, 5-6 times a day. The total daily caloric content of the diet should be about 2400 kilocalories.
The diet for polycystic disease is aimed at eliminating excess protein and fat to relieve the load on the kidneys. Dietary table No. 7 B is prescribed to patients with polycystic kidney disease, which is accompanied by loss of protein in the urine. Nutrition is aimed at replenishing the amount of lost protein, lowering the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and reducing edema. The amount of food containing protein increases, and the amount of food that contains fats, mainly of animal origin, decreases. Preference should be given to products rich in components that can break down fats.
The amount of salt consumed per day is limited to two grams per day. Their diet removes herbs and spices, reduces the amount of simple carbohydrates found in sweets, starch, and flour products. Meals should be taken in small portions no less than 5 times a day. Daily calorie content should not be lower than 2800 kilocalories.
Dietary table No. 7G for polycystic kidney disease is prescribed if the kidney cyst is accompanied by end-stage renal failure, and the patients are on extracorporeal hemodialysis (hardware blood purification). The patient should receive the following ingredients with food:
- Protein – up to 60 grams;
- Salt – up to 2-2 grams;
- Liquid – up to 700ml.
Meals are fractional, 5 times a day. The total daily calorie intake should be no more than 3000 kilocalories.
Traditional methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease
This article will tell you how polycystic kidney disease can be treated with folk remedies to achieve the maximum possible effect. Herbal medicine is aimed at eliminating symptoms: facilitating urination, reducing inflammation and pain. Reviews about the plants vary because they have a heterogeneous mechanism of action.
Efficiency and benefits of traditional medicine
Folk remedies for polycystic kidney disease are ineffective and should not be used for medical purposes. Some dietary supplements can reduce the symptoms of the disease, but do not cure the underlying cause. Before use, you should consult your doctor. Clinical studies have only been conducted with a limited number of plants, which will be listed below.
In alternative medicine, decoctions, tinctures, solutions or powders of medicinal plants are used. Herbal medicines can be administered rectally, orally and intranasally (essential oils).
Description of popular remedies: recipes, application diagram
Treatment with folk remedies for polycystic kidney disease sometimes does more harm than potential benefit. Self-medication is prohibited. In folk medicine, onions, garlic, lingonberry leaves, burdock and other remedies are used to relieve pain and spasms in PBP.
Attention! Beetroot juice, kvass, sodium bicarbonate, acetone and other ineffective drugs should not be taken with PBP.
Garlic
Garlic is rich in allicin, a sulfur-containing compound that is traditionally used for intestinal disorders: flatulence, cramping pain, colds or flu. They have bactericidal properties, so they are able to fight pathogenic microorganisms and parasites.
A Norwegian study found that aqueous extracts of garlic can kill bacteria that have already developed resistance to antibiotics.
Burdock
In traditional herbal medicine, burdock is usually applied topically as a root or leaf extract. Due to its immunosuppressive and antibiotic properties, the plant is prescribed for inflammatory diseases - acne, dermatoses, eczema, furunculosis, skin infections, itching, insect bites, psoriasis and mouth wounds. Burdock roots are traditionally used to treat gastrointestinal disorders.
It is important to know! In South Korea and China, burdock is considered an anti-inflammatory and diuretic plant. However, its positive effect on PBP and diuretic effects have not been confirmed in scientific studies.
Main active ingredients:
- polyacetylene compounds (in roots) – sulfur-containing heterocyclic acetylene substances;
- essential oil (in roots) with derivatives of benzaldehyde, acetaldehyde and pyrazine;
- inulin (in roots);
- triterpenes (in roots);
- bitter sesquiterpene lactone (in leaves) of the germacranolide type - artciopicrin;
- lignan.
Burdock ingredients inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators. The antimicrobial effect of the herbal remedy has also been proven. The root is part of various medicinal preparations (powders, tablets and tinctures) that are offered against skin diseases and rheumatism.
Methods of application:
- Tea: mix 2-6 g of root with hot water, strain and drink three times a day.
- Decoction: mix 2.5 g of finely chopped root with water, let it brew for several hours, then boil for up to 60 minutes and strain.
- Liquid extract (1:1 with 25% alcohol): take 2-8 ml, three times a day.
- Tincture (1:10 in 45% alcohol): take 8-12 ml three times a day.
Walnuts
Walnut leaves contain tannins, ellagic acid and gallic acid. There is also a hydroangle in the epi- and mesocarp. The seeds contain up to 50% omega fatty acids, sucrose, dextrose, dextrin, starch, pentosans, lecithin and inositopentaphosphoric acid.
Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids provide an anti-inflammatory effect. The 85 patients in the study were divided into two groups: one received ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10) and omega-3 fatty acids, and the other received pure olive oil. Scientists studied the effect of administered substances on cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney inflammation. The study results were published in the Clinical Nutrition Journal.
Researchers were able to demonstrate a reduction in inflammation based on 3 parameters:
- Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) activity decreased by 90%. Protein plays a significant role in the occurrence of inflammatory mechanisms.
- The concentration of lipid mediators was significantly increased. These endogenous, hormonal agents suppress inflammation. They are similar to fatty acids and are likely produced in the body from omega-3 fatty acids.
- C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations decreased. CRP promotes the immune response and the inflammatory cascade. The protein serves as an orientation signal for phagocytes.
Advice! The use of polyunsaturated fatty acids in combination with vitamins and some amino acids is recommended. This is especially true for the initial stage of the disease when treated with a relatively mild course. Omega-3 fatty acids may also help improve chronic kidney inflammation.
Echinacea
Echinacea ingredients have anti-inflammatory effects even in very low concentrations. In experiments on animals (rats and mice), it was found that the plant extract improves wound healing. This may be due to inhibition of tissue-soluble enzymes (hyaluronidases). In addition, the intensity of inflammatory signals decreases: the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase is inhibited. This, in turn, reduces the formation of certain mediators (pro-inflammatory prostaglandins), resulting in the suppression of inflammation, fatigue, loss of appetite and pain.
Echinacea extracts increase the nonspecific immune response: blood cells produce more signaling substances (IL-1, IL-10, TNF-α, interferon-β), so the efficiency of phagocytes increases. Some studies also observed an increase in specific immunity - the formation of antibodies (IgM, IgG). Even if the immune system is artificially suppressed by drugs (hydrocortisone), an echinacea product can reverse this effect.
The plant contains a number of antioxidant ingredients (cichoric acid, echinacoside, caffeic acid, cynarine). They bind radicals and thus protect against UV damage and other oxidative stress. Laboratory experiments with various Echinacea preparations have shown direct antiviral activity (HSV-1, HSV-2, influenza A2, genital herpes and shingles). However, this effect was not confirmed in all studies.
Some echinacea extracts also had an effect on yeast: N-hexane extracts were active against Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. The frequency of relapses of fungal infection Candida (Candida mycoses) decreased by 5-10 times.
Mullein
The main indication for use is inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. Saponins are known to indirectly facilitate mucus removal. It soothes the inflamed mucous membrane and thus relieves the excruciating pain of PBP. Hot tea has a diaphoretic effect.
The flowers have a diuretic effect because they contain flavonoids. In traditional medicine, mullein is also used for bladder and kidney diseases. The clinical effectiveness of this use has not been proven in any study.
Aloe
Some studies in laboratory animals suggest that the extracts have significant hypoglycemic effects and may be useful in the treatment of type II diabetes, but these have not been confirmed in humans.
The gel found in the leaves is used to soothe minor burns, wounds and various skin conditions such as eczema and ringworm. The anesthetic effect occurs immediately after application to the affected area. Aloe does not affect patients with PPD.
Lingonberry leaves
Lingonberry leaves are used for urinary tract infections. Experiments have shown that antioxidants can effectively prevent the initial reaction of arteriosclerosis: oxidation of LDL. They also relieve inflammatory processes in the renal parenchyma. Therefore, lingonberry leaves are often used in the prevention of cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
Laboratory tests have shown that isolated lingonberry products reduce plaque formation and harmful bacteria. They can also help treat periodontitis. In in vitro experiments, the substances reduce the incidence of carcinogenesis. No studies have been conducted on humans, so firm conclusions cannot be drawn.