Normally, control over urination is completely subject to the will of the person. Losing urine without consciously wanting to “go to the toilet” is considered incontinence.
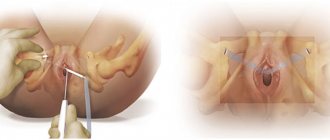
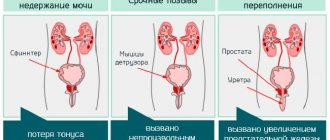
Urinary incontinence in women after childbirth is referred to as stress or stress incontinence.
The mechanism of development of such a violation is as follows:
- The kidneys secrete urine constantly - a few seconds after complete emptying, a portion of urine already appears in the bladder. Leakage of any amount of urine is resisted by a special part of the urethra - the urethral sphincter.
- If the ligaments of this structure are weakened or stretched, then with a sharp increase in pressure from above, from the abdominal cavity, the “lock” of the urethra cannot cope and allows urine to pass through.
- Increased pressure in the abdomen occurs when coughing, lifting heavy objects, during exercise, while laughing, or sneezing.
The main possible causes of burning after urination in women
- The leading cause of burning after urination is occupied by various infections. In women, due to the specific anatomical features - the proximity of the anal passage to the vagina and urethra, allows bacteria to freely penetrate into the urethra, then freely into the bladder and kidneys, because this canal in women is short and wide. A burning sensation can be a consequence of sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, urogenital chlamydia and other diseases. Such diseases are accompanied by purulent or mucopurulent discharge.
- Another equally common reason is unclean sex, poor intimate hygiene and the use of low-quality contraceptives, which destroy the natural microflora of the vagina and can cause contact dermatitis. In this case, opportunistic bacteria begin to multiply very quickly, because the local immunity that restrains them is disrupted.
- Burning after urination occurs with urethritis and cystitis. It is also accompanied by pain in the canal and lower abdomen and a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied.
- Stones formed in the kidneys or bladder, when exiting through the urethra, injure its mucous membrane and provoke not only a burning sensation, but also the release of blood into the urine.
- Often, a burning sensation is caused by hygiene detergents due to an allergic reaction to the substances they contain.
Rare urination
During childbirth, the nerve endings of the bladder are compressed. Because of this, the brain does not receive a signal that it is time to empty the bladder. As a result, the organ grows and its walls become tense. When relaxation comes, pain arises. To avoid this, you should go to the toilet every 2-3 hours, even if you don’t feel like it. Obstetricians always warn about this, but not all young mothers listen to them. But in vain. Medical staff make recommendations for a reason. In addition to pain when urinating, stagnation of urine can lead to inflammation of the urinary tract.
Why does a burning sensation occur after urination in men?
In men, the length of the urethra is much longer than in women, so bacterial inflammation occurs less frequently in them, and among the main causes, in addition to sexually transmitted infections, the following can be identified:
- The consequences of inflammation of the urethra are urethritis.
- Urolithiasis, when sediments of urine, consisting of insoluble salts, irritate the mucous membrane, passing through the urethra.
- Most often, burning sensation after urination in men occurs in the presence of various diseases of the prostate gland (for example, prostatitis), which provoke a violation of the outflow of urine.
Stitches and abrasions
They remain after a cesarean section and natural birth, during which the obstetrician had to make incisions. With large fetuses and malpresentation of the baby, ruptures are possible. Abrasions can also occur if the catheter is installed carelessly. The damage takes time to heal. Recovery time is different for each woman. Until the wounds heal, the urine will irritate them, causing a burning sensation. To reduce discomfort, it is recommended to pee while standing in the shower, legs apart, and directing the stream of water towards your genitals. In some cases, the gynecologist may prescribe special suppositories. If it became painful to write a week after giving birth, and before that everything was fine, the stitches most likely came apart. In this case, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's immune system weakens significantly. At this time and immediately after childbirth, it is difficult for the body to resist infections. Therefore, chronic inflammatory diseases worsen and new ones arise. Here are the most common pathologies that can cause a woman who has recently given birth to have difficulty urinating.
What needs to be done to identify the cause of burning after urination
First of all, you should not delay by self-medicating, but contact a specialist who will prescribe a clinical urine test, the results of which will determine the cause of dysuria. In this case, the presence of protein in the urine, a large number of leukocytes and bacteria will indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the bladder and urethra. If red blood cells and salt crystals are found in the urine, this indicates the initial stage of urolithiasis. If there are no deviations from normal values, but there is a burning sensation after urination, then one can suspect the neurogenic nature of such a symptom. To more accurately identify the causes of burning, doctors prescribe an ultrasound of the kidneys, bacteriological examination of urine, a vaginal smear, and testing for sexually transmitted infections.
Urinary incontinence and loss of orgasm are the fruits of the same problem
Urinary incontinence itself is sometimes perceived as an annoying nuisance that can be hidden. Especially in the initial stages of losing a few drops of urine. Women are in no hurry to solve this problem.
Moreover, more significant things come to the fore.
For example, weakening or absence of orgasm. Sex ceases to be sensual, which does not have the best effect on relationships and psychological comfort. Growing like a snowball, this problem steadily leads to nervous breakdowns and depression, and sometimes to the destruction of the family.
Although the reason for this whole “bouquet” is a relaxed vagina that has not been restored after childbirth.
By carrying out procedures to restore and strengthen the perineal tissue, you can solve the problem of urinary incontinence and restore the joy of sexual life.
Treatment of burning after urination
Treatment methods are chosen only by a specialist after a thorough examination and depend on the cause that causes the burning sensation. Inflammatory processes in the urethra and bladder are treated with antibacterial drugs, to which the bacteria causing the problems are not resistant. With the development of urolithiasis and the presence of salts in the urine, acidic or alkaline drinking is indicated, depending on the type of salts. In cases where stones have formed in the kidneys and ureters, it is recommended to crush them using a special ultrasonic device, and, in extreme cases, to remove them surgically.
Burning after urination is an unpleasant and dangerous symptom, so consultation with an experienced specialist and examination should be prompt.
Return to list
How to speed up recovery of bladder function
- Try to empty your bladder as quickly as possible after giving birth - this will stimulate the uterus to contract and protect the urinary organs from infection.
If you have difficulty getting up, use a bedpan, not a cold one, but a preheated one. Urination can be caused reflexively - by the sound of pouring water. If you are unable to go to the toilet on your own, tell the nurse who will insert the catheter.
- Train your bladder: do not reduce the amount of fluid you consume, especially if you are breastfeeding.
- Force your bladder to work: In the first days after giving birth, go to the toilet every two hours, even if you don’t feel the urge.
- Walk more: this stimulates normal bowel and bladder function.
- Perform special exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles - Kegel exercises.
While lying down or sitting, tighten the muscles of the vagina and anus as if you were holding back urination, hold in this position for a few seconds, and then completely relax the muscles. When performing exercises, do not tense your stomach and buttocks or move your legs together. It is recommended to do Kegel exercises at least 3 times a day, and preferably more often. It is optimal to perform 8–10 muscle contractions in one approach.
- Avoid drinking drinks and foods that irritate the bladder - coffee, spicy seasonings, pickles, smoked meats.
Restoring normal functioning of the bladder can take from several days to one to one and a half months. If incontinence does not go away during this time, you need to inform your gynecologist about this at a routine examination, which usually occurs six weeks after birth.
Endometritis
Inflammation of the endometrium. After the placenta is separated, the inner surface of the uterus is a continuous wound. Incisions after cesarean section are an additional risk factor. Infections easily become infected. The first symptoms appear 5-12 days after birth, in severe cases - on 2-3 days. The woman develops a fever and chills. The contractility of the uterus decreases, and lochia becomes less abundant. The already large organ becomes even larger and puts a lot of pressure on the bladder, making urination difficult. There is pain in the lower abdomen, purulent discharge is possible. Treatment consists of taking antibiotics and drugs that stimulate uterine contractions. Anticoagulants are also prescribed. The contents of the cavity of the reproductive organ are cleaned, the wound is washed. Physiotherapy is also carried out.
Most new mothers find it painful to urinate after giving birth. But this is not always normal. It is important not to be shy about communicating your discomfort to your doctor. Ignoring the problem or self-medicating can lead to disastrous results.
Causes
Not only inflammatory processes resulting from childbirth can cause discomfort, but also the following reasons:
- reflex spasm of the urethra;
- swelling of the genital organs;
- negative effects of drugs or anesthesia;
- emotional depression;
- psychological discomfort caused by reluctance to use a bedpan after childbirth;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- excessive blood loss, which caused a decrease in the body’s protective properties;
- the presence of infection during labor.
If you have a problem with painful urination, then you should pay attention to the type of pain and other additional symptoms that accompany it. So, with an infectious disease of the bladder, a woman feels fullness and a strong desire to urinate, but at the same time the amount of urine released is minimal and contains blood impurities. In this case, pain, burning and tingling sensations can appear regardless of the process of urination and accompany the woman even during rest.
Infection can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- poor clotting;
- lack of vitamins;
- heavy blood loss after childbirth;
- infection caused by a catheter;
- difficult pregnancy;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- remnants of the placenta;
- long and difficult labor.
However, pathogenic microorganisms that are always present in the human body, but manifest themselves during periods of decreased immune resistance, which subsequently provokes the development of inflammation, can also cause problems with urination in a woman in labor.
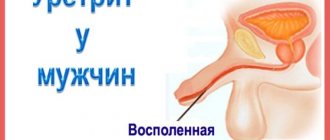
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra. Often occurs due to the penetration of bacteria into damaged mucosa. It is characterized by pain and burning at the beginning of urination, constant itching in the urethra. The urge becomes more frequent, and blood is released in the urine. The labia and vestibule of the vagina become red and swollen. Foamy or purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor is possible. Patients feel discomfort in the perineum. Usually only local treatment is carried out, since most antibiotics are prohibited for nursing mothers. Antiseptic solutions are used for douching and washing the urinary canal. Sitz baths with anti-inflammatory decoctions help. In difficult cases, the doctor may prescribe systemic antibacterial therapy.
Pain when urinating after caesarean section
If writing hurts after childbirth, especially if you had to undergo a caesarean section, then it is likely that the problem is not only psycho-emotional discomfort and fatigue. The pain that appears after a cesarean section can be incessant and accompanied by severe pain, spasms and pulsation. It can be painful to write after a caesarean section in the following cases:
- medications used during surgery;
- unprofessional catheter installation;
- inflammation.
Incorrect installation of a catheter after childbirth is the most common reason that causes pain in women in labor when going to the toilet. After the catheter is removed, the pain may persist for some time, but within a few days it goes away without a trace without additional treatment. If pain prevents you from performing normal daily activities, you can consult a doctor, he will prescribe suitable painkillers.
Inflammation less often causes pain when trying to go to the toilet in small quantities. An infection in the urinary tract leads to the development of the following symptoms:
- cloudy urine;
- temperature increase;
- burning when urinating;
- unpleasant odor;
- aching pain in the lower back;
- tingling in the ovaries.
If the above symptoms are present, a young mother should visit her gynecologist. Often, a woman is prescribed antibiotics and is recommended to perform a small list of exercises that will help get rid of lower back pain and serve as a prevention of further problems with the toilet.
What not to do?
When it is painful for a woman to pee after giving birth, she should under no circumstances do the following:
- drink diuretics;
- sitting on the toilet for a long time, as this can provoke the development of hemorrhoids;
- wash yourself with untested solutions and substances;
- self-prescribe painkillers;
- lift weights;
- be indiscriminate in the selection of personal hygiene products.