Reasons for the appearance of e. coli in urine, smear in women
There are several reasons for the development of pathology. It is possible to determine and establish the exact nature of the origin of the disease only after consultation with a specialist and passing all the necessary examinations.
Physiological
The disease develops against the background of violation of personal hygiene rules, during sexual intercourse, as well as through infection from a carrier or potentially dangerous household items.
Causes:
- insufficient treatment (washing) of the genitals or the use of low-quality personal hygiene products to care for the genitals;
- violation of genital care techniques;
- use of uncomfortable or low-quality underwear;
- touching the genital area with dirty hands;
- specific types of sexual intercourse - anal sex;
- sexual transmission of infection;
- a large number of sexual partners;
- lack of protection during sexual intercourse.
In this case, women are mostly affected by the disease. The number of infection carriers among women is 4-5 times higher than the number of infected among men.
Pathological
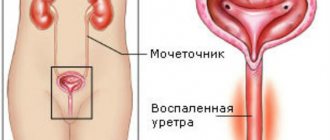
The main provoking factor in the development of the disease is the structural feature of the urinary system in women. The anus is located close to the urethra, which greatly increases the risk of penetration (migration) of pathogenic microflora.
Causes:
- concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system of an inflammatory nature - inflammation of the walls of the bladder, kidneys, urethra;
- weakened immunity, including local;
- dysbacterial damage to the intestines, disturbed microflora;
- abnormalities in the structure of the urinary system.
Often the disease develops during pregnancy. Pathology occurs in more than 30% of cases. This is due to hormonal changes and disorders in the immune system.
What does increased E. coli bacteria mean?
Any microorganism found in urine is a symptom of some disease. Sometimes it is not entirely clear how and where E. coli enters the urine; the causes of the phenomenon are very diverse.
Physiological reasons
To a greater extent, the physiology of women is to blame for the penetration of the insidious bacillus into the urinary system. The wide, but short, urethra, its proximity to the anus, is the reason for the penetration of the stick into the urethra from the feces. This is facilitated by constant violations of hygiene rules - infrequent washing, irregular change of bed and underwear.
Inflammation of the genitourinary organs
- vesiculitis affecting the seminal vesicles;
- pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys;
- prostatitis - pathology in the prostate gland;
- urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- Cystitis is a disease of the bladder.
Intestinal bacteria also signal other problems in the urogenital area. This is adnexitis, colpitis, orchitis or endometritis.
Chronic diseases
E. coli in the urine of men, women, and children can become more active against the background of sluggish chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, due to which the immune system is significantly weakened. Then the stick spreads unhindered throughout the body, deprived of protection from infections.
Unprotected sex
Sexual contacts without contraceptives and anal sex increase the risk of a rod in a urine test. At the same time, you can become infected with many other, no less unpleasant bacteria - streptococcus, staphylococcus.
Other reasons
A rod in the urine of women is a common occurrence during pregnancy, when almost any infection has access to the body. A pathogenic strain enters a new environment due to:
- close contacts with its carrier;
- insufficiently thermally processed products;
- contaminated unboiled water;
- hormonal imbalances, diabetes.
Often a rod is detected in the analysis due to the fact that the urine container was not sterile.
Symptoms of Escherichia coli in urine
Escherichia coli in urine culture in women is accompanied by symptoms associated with the disease. Signs of the development of the pathological process vary depending on the period of formation of the disease. The incubation period lasts from 6 hours to 3 days.
The following symptoms are observed:
- a sharp increase in temperature, up to 39 0C;
- development of nausea with frequent vomiting;
- headache;
- sharp pain when urinating;
- general weakness of the body;
- pain in the muscles and joints;
- persistent diarrhea syndrome - visiting the toilet can be up to 10 times a day;
- the presence of foreign impurities in the stool - most often accompanied by the formation of mucus, in rare cases - a small amount of blood is noted.
After the incubation period, the patient's condition normalizes. The enterotoxigenic form of the disease is accompanied by severe vomiting, a slight increase in temperature, and the development of loose, watery stools.
Routes of transmission
The main route of infection is fecal-oral. With it, the pathogen can be transmitted through food, running water, and even juices. Infection occurs by eating fruits picked directly from trees or garden beds, ignoring hygiene rules, or drinking unboiled milk or water. It is possible to become infected with Escherichia through contact and household contact - through dirty hands and dishes. This route of transmission is dangerous because it can cause a large spread of infection in groups, kindergartens or schools. A newborn baby can become infected from the mother during passage through the birth canal if microbial bodies are present in the vagina. The incubation period lasts up to 6 days. In severe cases, the disease is accompanied by a temperature of up to 39 degrees and sepsis. Only bacteriological examination can confirm the presence of any pathology.
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract occurs when diarrheagenic Escherichia enters the flora. In most cases, patients are young children and infants. The incubation period lasts up to 3 days.
The main signs of infection include:
- stomach upset,
- nausea,
- drowsiness,
- weakness,
- complete or partial refusal to eat.
At the age of up to 1 year, the disease is accompanied by flatulence and a false urge to defecate. The main diseases associated with infection of the gastrointestinal tract with Escherichia are colitis, dysbacteriosis, and enteritis.
Pathogenesis of damage to the reproductive system
A completely healthy person should not have E.coli in their urine. If bacteria are detected in a laboratory analysis, the doctor carries out emergency treatment and prescribes a set of medications, including antibiotics.
If no symptoms of infection are observed, and the number of E. coli in the microbiological analysis is increased, this indicates errors in urine sampling.
Often, microbes are detected in women during pregnancy during a gynecological examination and taking a smear for bacterial culture. This phenomenon has a negative effect on the fetus and can lead to the development of cerebral palsy.
If Escherichia coli is detected in a flora culture, this can cause the following pathological processes:
- acute or chronic prostatitis (a stick in the prostate secretion, urethra and ejaculate when such a diagnosis is made is found in 70% of men),
- inflammation of the appendages in women,
- cystitis,
- urethritis,
- vaginitis,
- pyelonephritis,
- colpitis
If examinations in the field of gynecology showed the presence of a uropathogenic bacillus in the vaginal flora, then we are talking about epididymitis, i.e. inflammation of the epididymis. This can cause dangerous complications. A pathogenic microorganism can lower a woman’s immunity, disrupt the menstrual cycle, and increase the possibility of contracting gonorrhea and chlamydia.
Treatment is usually carried out using such agents as bacteriophages, suppositories, the drug ciprofloxacin, or a broad-spectrum antibiotic - monural.
In men, Escherichia can be detected in semen; this is checked using a spermogram. The danger is that bacteria attach to sperm, thereby reducing the enzymatic activity of germ cells, which ultimately leads to infertility.
How the infection is transmitted
At the moment, there are several ways of transmission or infection with an infectious pathogen. In this case, the disease is classified depending on the method of infection.
| Distribution routes | Peculiarities |
| Fecal-oral | Localized in the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Domestic | Occurs upon contact with contaminated things and household items. |
| Food | It develops against the background of eating contaminated food - unwashed vegetables, fruits, dairy products, kvass, compote. |
| Contact and household | The main reason is non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. This type of pathology also occurs during sexual intercourse. |
| Water | Pathology occurs when contaminated liquid is consumed. |
Escherichiosis often develops against the background of moving from one country to another due to climate change, diet and other stressful situations.
Prevention
Hemolytic anemia
To prevent infection, control measures must be followed at all stages of the food chain, from agricultural production on farms to food processing, processing and preparation in both commercial establishments and at home.
In industrial settings
The incidence of disease can be reduced through the implementation of a variety of risk reduction strategies for ground meat (e.g. screening of animals prior to slaughter to prevent the introduction of large numbers of pathogens into slaughter areas). Good slaughter practices and hygiene reduce fecal contamination of carcasses, but do not guarantee that products are free of STEC bacteria
To minimize microbiological contamination, it is essential to provide food hygiene training to workers in farms, slaughterhouses and food processing plants. The only effective way to kill STEC bacteria in food is through a bactericidal treatment such as heat (such as cooking or pasteurization) or irradiation
At home
Measures to prevent E. coli O157:H7 infection are similar to those recommended for the prevention of other foodborne illnesses. The basic good food hygiene practices outlined in the WHO Five Principles for Making Food Safer can help prevent the transmission of pathogens that cause many foodborne illnesses, as well as protect against foodborne illnesses caused by STEC.
The five essential principles for achieving safer food are:
Five Essential Principles of Safe Food
These recommendations must be followed in all cases, especially the recommendation regarding “proper cooking of food”, whereby the core temperature of the food reaches at least 70°C. It is necessary to wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, especially if they are eaten raw. If possible, vegetables and fruits should be peeled. Vulnerable populations (such as children and the elderly) should avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat products, raw milk, and products made with raw milk.
Regular hand washing is strongly recommended, particularly before preparing food, eating and after using the toilet, especially for people caring for young children, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems, as the bacteria can be transmitted not only through food, water and direct contact with animals, but also from person to person.
Some STEC infections result from contact with recreational waters
Therefore, it is also important to protect such bodies of water, as well as sources of drinking water, from the ingress of animal excrement.
Diseases caused by Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli in urine culture in women can lead to additional complications and cause other disorders in the body.
In severe cases, the following conditions and diseases may occur:
- development of infectious-toxic shock;
- septic lesion;
- pneumonia;
- meningococcal infection;
- encephalitis;
- hemolytic-uremic disease – enterohemorrhagic form;
- formation of thrombocytopenic purpura;
- acute form of renal failure;
- “travelers” syndrome is an enterotoxigenic form;
- enterocolitis.
In rare cases, the disease can lead to coma.
Diagnostics
To identify the disease, various instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used. Before prescribing research, a general consultation with a specialist, a survey and anamnesis are carried out.
Urinalysis as a way to detect bacteria in the urine of women
This research method allows you to determine the level of pathogenic microflora in the urinary fluid. In this case, both the quantitative content of bacteria and the nature of their origin are determined. The norm is the complete absence of E. coli in the urine. A low content of pathogenic microflora may indicate the onset of the development of a pathological process.
Urine culture for sterility, antibiogram
The procedure is aimed at determining the sensitivity of bacterial strains to a particular group of antibiotics. The study is mandatory and helps to correctly determine the further drug treatment regimen.
It was found that the pathogens are immune to amoxicillin, streptomycin, and kanamycin. High efficiency has been proven for dekasan and miramistin. The study is carried out over 7 days .
Rapid test for bacteriuria
Diagnostics allows you to almost instantly determine the presence of pathogens in the body. However, the method has a significant drawback - the number and nature of the origin of microorganisms are not established.
Express test methods:
- Saline. Testing is carried out using a special salt, which turns blue in the presence of bacterial damage.
- Nitrites. In the presence of microorganisms, nitrites are converted to nitrates. Used for adults only.
- Determination using glucose. The presence of pathogenic flora contributes to the lack of glucose.
The specific method is selected by the attending physician.
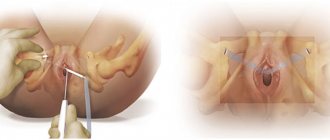
Vaginal microflora smear
The research method is carried out directly in the specialist’s office. Using special instruments, biological material is collected from the walls of the vagina.
This smear is sent to the laboratory for further study. Diagnostics allows you to determine the quantitative content of bacteria, as well as their etiology.
Prevention
Escherichia coli
It is advisable to talk about prevention when we are talking about the possible development of a disease caused by pathogenic microflora. In this case, we should talk about the relationship between opportunistic flora and the possibility of its activation. Therefore, it is quite enough to follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle:
This will help avoid an increase in the number of hemolytic E. coli and prevent possible disease.
In tests for dysbacteriosis, a 5-year-old child was found to have E. coli hemolytic 10 in 8, while the norm was zero. Is it worth treating her? How effective is the treatment? If left untreated, what consequences might there be?
E. coli is an Escherichia coli, a causative agent of intestinal diseases, it is opportunistic, it has several varieties. Hemolytic E. coli is more pathogenic.
An increase in its titer does not always indicate a disease. It is not necessary to treat an increased amount of the pathogen, but to take measures depending on the existing symptoms, if there is a general picture, when making a diagnosis. It is not possible to draw any conclusions without knowing the overall picture. It is not clear for what reason the analysis was done, what the clinical manifestations were, after which and for how long intestinal disorders or other signs were observed.
In general, the treatment of diseases caused by microorganisms, that is, infections, is carried out according to indications with antimicrobial drugs - antibiotics, phages, as well as drugs aimed at eliminating dysbiosis if it is present. To prescribe a suitable antibiotic for the treatment of a specific disease, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis to identify the sensitivity of the intestinal microflora to antibiotics in order to prescribe etiotropic (“causal”) treatment as accurately as possible. There are a lot of medications; they should be selected individually. These include phages, antibiotics, as well as drugs for the treatment of dysbiosis containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Should elevated bacteria counts in test results be treated? – you should strive for the disappearance of general pathological symptoms, improvement of general well-being and not pay attention to tests. The analysis itself, without a clinical picture and complaints, has no definite meaning
Also important is the content of other microflora that is normal for the intestines, this should also have been in the analysis results, that is, the number of beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli
Typically, E. coli is present in parts of the large intestine, as a competitor to beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
For probiotics, you can use Hilak Forte.
Immunomodulators can also be used.
You can ask your doctor questions in more detail on the website.
What to do if bacteria are detected during pregnancy?
The period of bearing a child in most cases is accompanied by disruptions in the hormonal system, decreased immunity, which results in risks of developing infections or other pathological processes.
In this case, infection is dangerous for the formation and development of the fetus, which is why immediate consultation with a doctor is required if the diagnosis is suspected.
The disease can lead to early discharge of water, and occasionally termination of pregnancy can occur. When pathogens penetrate through the placenta into the fetus, the pathology can subsequently lead to abnormalities in the development of the unborn child or birth defects. Often the disease leads to the development of meningococcal infection and septic lesions.
Treatment with antibiotics in the early stages is prohibited due to the high toxicity of the drugs and the risk of complications during pregnancy. During this period, adherence to a diet that is specially selected in each case separately is indicated.
Drug treatment
Escherichia coli is often detected in urine cultures in women in the last stages of the disease. In this case, the condition requires surgical medical treatment. Therapy with medical means is selected in accordance with the severity, nature of the course and established form of the disease.
First of all, antibacterial drugs are prescribed - polymyxin M, nifuroxazide, nilidixic acid (for 5 days). Additionally, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
At the end of antibiotic therapy, probiotics are prescribed. To restore and improve digestive functions, enzyme-based medications are used - Mezim, Pancreatin, Festal.
After antibacterial drugs have dealt with the Escherichia coli bacterium, you need to use probiotics to restore the microflora.
For fighting sensations and high temperature, painkillers and antipyretics are prescribed - Analgin, Ibuprofen.
Diarrheal syndrome is accompanied by a large loss of fluid, which is why drugs are prescribed that restore the water and electrolyte balance in the body.
Treatment of infection
E. coli in urine and bladder
Many factors are taken into account when drawing up a treatment protocol. In particular: the child’s age, severity of the disease, current symptoms, the body’s response to medications.
In order to suppress the activity of the pathogen, antibiotics are prescribed. Medicines from the line of fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, Levofloxacin), which have a wide spectrum of action and a small number of side effects, are often used. Pathogen addiction syndrome develops slowly.
For mild cases of the disease, oral rehydration is recommended for the child. He should drink as much fluid as possible throughout the day. This helps restore the disturbed water-salt balance, and also compensates for the fluid lost by the body. You can purchase the drugs at any pharmacy. They are available in powder form for preparing an aqueous solution.
In severe cases of the disease, saline solutions are used for intravenous administration. Infusion detoxification is carried out in a hospital setting and is implemented in order to remove toxins accumulated in the body. The child receives a large volume of fluid intravenously (drip). The most commonly used solutions are salts and glucose.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at improving general well-being. The patient may be prescribed:
- sorbents – drugs that help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract;
- antidiarrheal medications - Immodium, Enterofuril, Loperamide and others;
- antispasmodics - drugs that eliminate pain - No-Shpa, Spazmalgon, Plantex, etc.;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process - Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen and others;
- eubiotics, probiotics, prebiotics - drugs that restore the imbalance of microflora - Laktovit, Bifidumbacterin, Linex, etc.;
- vitamin complexes.
During the entire period of treatment, the child must adhere to the principles of dietary nutrition and maintain a water regime. In the acute period (with severe diarrhea), table No. 4 is recommended, which involves reducing the intake of fats and carbohydrates, limiting salt, and frequent split meals.
After improvement of the condition and stabilization of the stool, the patient is transferred to diet No. 2. It provides the healing body with all the necessary substances.
Modern medicine has made great strides forward and the presence of hemolyzing E. coli in a child’s body does not pose a significant danger to him. Timely initiation of therapy allows you to get rid of the infection and eliminates the formation of any complications.
Treatment with mumiyo
Shilajit is a biologically active substance taken orally.
Properties of the product:
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect;
- improvement and normalization of material metabolism;
- has a general strengthening effect due to the macro- and microelements included in the composition;
- strengthening the nervous system;
- no contraindications - approved for use by children from 3 months, prescribed during pregnancy.
To eliminate signs of the disease, it is recommended to use the following recipe: 1 g of the product must be completely dissolved in boiled water. Using the resulting solution, daily douching is carried out. It is recommended to carry out such procedures at least 2-3 times a day.
For oral use, you need to take 0.5 g of the product and dissolve it in 0.2 liters of distilled water. This solution should be taken 3 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals. The duration of such treatment should be 21 days. Then you need to take a 7-day break.
If necessary, and only after preliminary consultation with the attending physician, therapy can be extended for 1 or more additional courses.
Treatment with fermented milk products
In women, escherichia coli, detected during urine culture studies, leads to disruption of the intestinal microflora and provokes the development of dysbiosis.
A proven remedy in the treatment of escherichiosis is curd whey. In this case, you can make the delicacy yourself. To do this, use kefir, infused until creamy, and cottage cheese, cooked in a water bath.
Another fermented milk product that helps normalize digestion is yogurt. To prepare the product, you need to take 1 liter of milk, then boil and cool. Then add 1 small white bread cracker. The resulting mixture must be fermented for 24 hours.
After 24 hours, small white bread crackers must first be rubbed with garlic and added to the drink. It is recommended to take the product 3-4 times a day.
Traditional methods of combating intestinal infections
Traditional medicine in this case is complemented by folk remedies. There are many recipes for combating intestinal illness, preserved from grandmothers:
- 300 g of earthen pear (Jerusalem artichoke), cut into cubes, are dipped in boiling milk diluted with water in a 50/50 ratio. Remove the softened Jerusalem artichoke, add 20 g of flour and 40 g of butter to the milk and cook until it thickens. Pour the mixture over the previously removed Jerusalem artichoke and add greens. A unique sauce can serve as an addition to rice.
- Brew 20 grams of cinquefoil in 250 milliliters of boiling water. Steam for 15 minutes and leave overnight. Drink 80 ml three times a day.
- Pour a tablespoon of string into a glass of cold boiled water and keep in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Take 20 ml of the decoction three times a day.
- Mix coltsfoot, medicinal clover and centaury in equal parts to make a total of 20 grams. Pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. Drink once a day from 20 to 50 ml.
- Herbs with antimicrobial effects are also recommended by traditional medicine. In addition to the already mentioned coltsfoot, string and chamomile, infusions of calamus root, calendula and St. John's wort are recommended. Decoctions and jelly are prepared from rose hips, cranberries and blueberries. Oak bark and horse sorrel seeds have a fixing effect on diarrhea. Pomegranate peels boiled with raisins are useful. Ordinary honey kills “bad” rods and restores microflora; many do not even suspect the healing effect this product has in the treatment of diarrhea and dysbiosis.
Treatment with Jerusalem artichoke
Jerusalem artichoke or “earthen pear” is an effective folk remedy that helps restore digestive functions and improve intestinal function. To prepare, you need to take 0.3 kg of plant roots and peel them. Then you should cut the earthen pear into small cubes and place it in a container.
On top add 0.25 liters of fresh natural milk, 2 tbsp. butter and 1 tbsp. wheat flour. The product (separately from the plant) is put on fire and boiled until creamy. After cooking, pour the Jerusalem artichoke with milk and sprinkle with herbs on top.
Treatment with Potentilla anserina
The plant helps prevent the pathogenic effects of dangerous microorganisms, has an antimicrobial effect, and relieves inflammation.
To prepare the medicine you need to take 1 tbsp. plants and pour 0.25 liters of boiled water. Place the mixture on the fire, bring to a full boil and cook for 15 minutes. Leave the decoction overnight, then filter and take throughout the day, dividing the portion into 3 equal parts.
Treatment of infection
Once you are familiar with the symptoms and treatment, E. coli prevention involves preventing the bacteria from entering the body. You should be guided by the rules of personal hygiene, do not drink water from unknown sources, vegetables and fruits should be consumed clean, and heat treatment of products should be carried out correctly.
Many factors are taken into account when drawing up a treatment protocol. In particular: the child’s age, severity of the disease, current symptoms, the body’s response to medications.
In order to suppress the activity of the pathogen, antibiotics are prescribed. Medicines from the line of fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, Levofloxacin), which have a wide spectrum of action and a small number of side effects, are often used. Pathogen addiction syndrome develops slowly.
For mild cases of the disease, oral rehydration is recommended for the child. He should drink as much fluid as possible throughout the day. This helps restore the disturbed water-salt balance, and also compensates for the fluid lost by the body. You can purchase the drugs at any pharmacy. They are available in powder form for preparing an aqueous solution.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at improving general well-being. The patient may be prescribed:
- sorbents – drugs that help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract;
- antidiarrheal medications - Immodium, Enterofuril, Loperamide and others;
- antispasmodics - drugs that eliminate pain - No-Shpa, Spazmalgon, Plantex, etc.;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process - Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen and others;
- eubiotics, probiotics, prebiotics - drugs that restore the imbalance of microflora - Laktovit, Bifidumbacterin, Linex, etc.;
- vitamin complexes.
During the entire period of treatment, the child must adhere to the principles of dietary nutrition and maintain a water regime. In the acute period (with severe diarrhea), table No. 4 is recommended, which involves reducing the intake of fats and carbohydrates, limiting salt, and frequent split meals.
After improvement of the condition and stabilization of the stool, the patient is transferred to diet No. 2. It provides the healing body with all the necessary substances.
Modern medicine has made great strides forward and the presence of hemolyzing E. coli in a child’s body does not pose a significant danger to him. Timely initiation of therapy allows you to get rid of the infection and eliminates the formation of any complications.
This will help avoid an increase in the number of hemolytic E. coli and prevent possible disease.
All preventive measures for Escherichia coli boil down to the following recommendations:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly;
- follow the rules of heat treatment of meat;
- do not drink raw milk;
- purchase meat and dairy products only from trusted sellers with a quality certificate for the product;
- strengthen immunity;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning in the house.
Intestinal infection is common among adults and children. Not only is it accompanied by severe symptoms, but it can also lead to severe dehydration, disruption of important body functions, and death of the patient.
It is important to follow preventive measures and treat E. coli at the first manifestations
By following simple tips, you can protect your child from E. coli
The main reason for the increase in the number of E Coli bacteria in a child’s stool is low immune defense. Most pediatricians recommend not to stop breastfeeding your baby for at least a year, because, as you know, with mother’s milk the baby receives lactose and all the necessary components to combat the effects of negative microflora.
If breastfeeding is not possible, infant formula containing prebiotics should be used. Naturally, basic hygiene of a nursing mother will minimize the occurrence of diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract in the child and hemolytic E-Coli will not appear in the feces of the baby.
Treatment with infusion of medicinal herbs
Escherichia coli in urine culture in women can cause the development of other diseases, which is why it is recommended to use a collection of several medicinal plants when treating pathology.
This infusion helps eliminate signs of inflammation, relieve swelling, and relieve pain. The product allows you to get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and has a pronounced antimicrobial effect. To prepare the infusion, various plants are used that exhibit antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
It is recommended to use St. John's wort, chamomile, and calendula. Take one part each of agrimony and St. John's wort and 2 parts each of mint, plantain, and chamomile. Then everything is thoroughly mixed. Take 1 tbsp from the prepared mixture. product and pour in 0.5 liters of boiled water. It is recommended to use a half-liter jar, which is then wrapped in a towel and set aside for 30 minutes.
Take the infusion instead of tea. The product helps normalize stool, eliminates signs of bloating and flatulence, and reduces pain.
Prognosis and complications
Diseases with untimely treatment lead to the development of various complications, expressed in damage to internal organs and the formation of other pathological processes in the body. The prognosis for escherichiosis is favorable in most cases, but if left untreated, the disease can ultimately lead to death.
To avoid the development of pathology, it is recommended to follow special preventive measures:
- food processing before consumption;
- monitoring and performing daily hygiene procedures;
- compliance with personal hygiene techniques and rules;
- limiting contact with a carrier of an infectious disease;
- compliance with other sanitary and hygienic rules and regulations at enterprises;
- annual examination by a specialist.
If prescribed therapy, dietary nutrition, and preventive measures are followed, the disease can be completely clinically cured. At the first signs of escherichia coli infection in women, it is necessary to consult a doctor for advice and undergo all types of diagnostics, including urine culture, to prescribe adequate therapy.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky