Indications for use
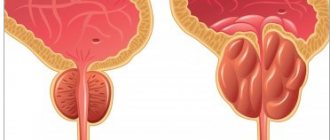
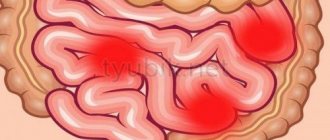
Norfloxacin is prescribed for bacterial infections of the urinary system ( urethritis , cystitis , pyelonephritis ), genitals ( endometritis , cervicitis , prostatitis ), gastrointestinal tract (shigellosis, salmonellosis ), uncomplicated gonorrhea, and traveler's diarrhea . Used to prevent infectious diseases in patients suffering from granulocytopenia .
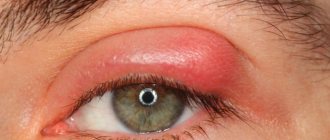
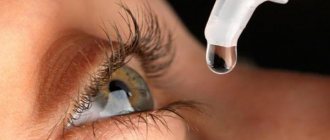
Locally, Norfloxacin is prescribed for conjunctivitis , keratitis , keratoconjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, blepharitis , blepharoconjunctivitis, meibomitis, dacryocystitis . The drug is used to prevent eye infections after extraction of a foreign body or conjunctiva from the cornea, before and after eye surgery, after damage by chemicals.
Norfloxacin is effective for external otitis, acute otitis media, chronic otitis media, and is prescribed for the prevention of infectious complications during surgical interventions on the organ of hearing.
Contraindications
Norfloxacin is not prescribed for intolerance to fluoroquinolones, pregnancy, breastfeeding, lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, childhood and adolescence (up to 18 years).
Use with caution for atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, epileptic syndrome, renal failure, hepatic system, epilepsy .
Side effects
Digestive system: nausea, bitterness in the mouth , diarrhea, loss of appetite, epigastric pain, increased activity of “liver” transaminases, vomiting, dyspeptic disorders; , pseudomembranous enterocolitis develops
Urinary system: glomerulonephritis , albuminuria, crystalluria, polyuria, dysuria, hypercreatininemia, urethral bleeding.
Nervous system: dizziness, headache, fainting, hallucinations , insomnia. Cardiovascular system: arrhythmia, vasculitis , drop in blood pressure, tachycardia.
Sense organs (for local use): photophobia, chemosis, conjunctival hyperemia, pain and burning in the eye, blurred vision.
Musculoskeletal system: tendon ruptures, tendinitis , arthralgia .
Hematopoietic organs: decreased hematocrit , decreased leukocyte count, eosinophilia.
Allergic reactions are possible: swelling, itching , Stevens-Johnson syndrome (exudative erythema of a malignant nature), urticaria . On other organs and systems – candidiasis .
Side effects of the drug Norfloxacin
Norfloxacin is generally well tolerated. The overall incidence of side effects is approximately 5%. With long-term use or administration of the drug at the maximum daily dose, gastrointestinal disorders (bitterness in the mouth, nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, pseudomembranous enterocolitis), increased activity of hepatic transaminases, disorders of the cardiovascular system (tachycardia, arrhythmia, decreased blood pressure, fainting), central nervous system disorders (headache, dizziness, insomnia or drowsiness), urinary system disorders (crystalluria, glomerulonephritis, dysuria, polyuria, albuminuria, urethral bleeding, hypercreatinemia), musculoskeletal disorders (myalgia , arthralgia, tendinitis), hematopoietic organs (leukopenia, eosinophilia, decreased hematocrit, thrombocytopenia), photosensitivity (UV irradiation should not be used when treating patients with Norfloxacin), allergic reactions (skin itching, urticaria, swelling, erythema malignant exudative syndrome/syndrome) Stevens-Johnson), with long-term use - candidiasis.
Instructions for use of Norfloxacin (Method and dosage)
Norfloxacin tablets, instructions for use
Orally: for cystitis without complications - 400 mg twice a day for 7 - 10 days; for infectious diseases of the urinary tract - within 3-7 days; for chronic recurrent urinary tract infections - up to 12 weeks.
For acute bacterial gastroenteritis – 5 days; for pharyngitis , cervicitis, proctitis, acute gonococcal urethritis - 800 mg once; for typhoid fever - 400 mg of the drug three times a day for 14 days.
As a prophylactic agent: against sepsis – 400 mg twice a day; against bacterial gastroenteritis – 400 mg once a day; against travelers' diarrhea - 400 mg of the drug the day before departure and throughout the trip (no more than 21 days); against relapses of infectious diseases of the urinary system - 200 mg of Norfloxacin per day.
In patients with impaired renal function with CC greater than 20 ml per minute, no dosage adjustment is required.
Patients on hemodialysis, as well as those with CC less than 20 ml per minute (or serum creatinine above 5 mg per 100 ml), are prescribed half the therapeutic dose twice a day or the full dose once a day.
Norfloxacin drops, instructions for use
Locally: 1 or 2 drops into the affected ear or eye 4 times a day. Depending on the level of infection, the first dose may be increased to 2 drops every two hours.
Norfloxacin
Norfloxanic is an antibacterial drug from the quinolone group with a bactericidal effect. It suppresses the key enzyme for the synthesis of bacterial DNA and proteins - DNA gyrase, which has the most detrimental effect on the health of microorganisms - they die without any chance of salvation. The spectrum of action of norfloxacin is impressive in its breadth. If we talk about internal infections, then it is better not to get in the way of norfloxacin, for example, gram-positive aerobes such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis. Among aerobic gram-negative microorganisms, norfloxacin is most strongly opposed to Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus vulgaris. Norfloxacin is slightly less hostile, but with pronounced antipathy, towards gram-negative bacteria of the strains Haemophilus influenzae, Yersinia enterocolitica, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp.
For eye infections, norfloxacin is used to combat gram-negative Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Aeromonas hydrophila, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and gram-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus warneri, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc. At the same time, nor floxacin is ineffective against infections caused by obligate anaerobes and Treponema pallidum.
Resistance to norfloxacin develops relatively rarely, occurring in less than 1% of cases treated with this drug. A tendency to develop resistance to the drug to a greater extent than other microorganisms was observed in Enterococcus spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp. But the so-called cross-resistance between norfloxacin and other antimicrobial agents has not yet been observed, so this drug can also be used in cases where other agents can no longer cope with the invasion of pathogens. Norfloxacin can successfully replace tetracyclines, macrolides, penicillins, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, etc.
Under the trade name “norfloxacin” the drug is produced only in Russia (there are also foreign products Nolitsin, Normax, Norilet and Loxon-400). Dosage form: film-coated tablets. In the absence of special instructions from the attending physician, the drug is taken 400 mg twice a day 1 hour before a meal or 2 hours after it. The standard duration of the therapeutic course is 7-10 days, but other options are possible. An important nuance: during treatment with norfloxacin, the patient must ensure sufficient fluid intake into his body. And one more recommendation: because. norfloxacin increases the body's vulnerability to sunlight; direct sunlight should be avoided.
Interaction
of theophylline by 25% . Increases the concentration of cyclosporine and indirect anticoagulants in the blood serum. Reduces the effect of nitrofurans .
The simultaneous use of antacids with magnesium and aluminum hydroxide , as well as drugs with sucralfate , negatively affects the absorption of Norfloxacin - there should be an interval of at least 4 hours between taking these drugs.
Simultaneous use of Norfloxacin with drugs that lower the epileptic threshold can provoke the development of epileptic seizures.
The simultaneous use of Norfloxacin and drugs that are potentially capable of lowering blood pressure can lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Therefore, in such cases, as well as with the simultaneous use of barbiturate-containing and other drugs for general anesthesia, it is necessary to monitor the pulse, blood pressure level, and heart function.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Norfloxacin
Norfloxacin (1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid) is an antibacterial agent of the fluoroquinolone group. It has a bactericidal effect, inhibiting DNA gyrase and disrupting the process of DNA supercoiling. Active against most gram-negative bacteria - Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Proteus spp., Morganella morganii, Klebsiella spp . (including Klebsiella pneumoniae ), Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Citrobacter spp., Yersinia spp., Providencia spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas spp . (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa ), Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Brucella spp., Vibrio spp . Active against gram-positive microorganisms ( Staphylococcus spp., Staphylococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus), resistant to methicillin, Enterococcus faecalis . Norfloxacin is active against bacteria that produce β-lactamases. Anaerobic bacteria are insensitive to norfloxacin; Enterococcus spp. is insensitive. Eating reduces the rate of absorption; when taken orally, about 30–40% of norfloxacin is absorbed. Plasma protein binding is 14%. The maximum concentration in the blood is achieved 1–3 hours after taking the drug, depending on the prescribed dose. Norfloxacin accumulates in peripheral tissues; penetrates well into the tissues of the gallbladder, bile ducts, liver, kidneys, prostate gland, and female genital organs. High concentrations of the drug are also detected in the bronchial mucosa, bronchial secretions and pleural fluid. Penetrates through the placenta. Does not penetrate the BBB. The half-life is 3–6 hours. Norfloxacin undergoes biotransformation in the liver with the formation of metabolites, which are excreted in the urine in unconjugated form; Some metabolites have microbiological activity (less pronounced than that of norfloxacin). Metabolites are not determined in blood serum and are detected in bile, feces and urine (in approximately the same proportion). Urinary excretion of norfloxacin metabolites is less than 10% of the dose taken. About 30% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
special instructions
During treatment with Norfloxacin, direct exposure to sunlight should be avoided and it is recommended to take plenty of fluids. Particular care should be taken when driving vehicles, operating complex mechanisms, and performing work that requires high concentration and rapid psychomotor reactions (especially in the case of simultaneous intake of ethanol).
During therapy, an increase in the prothrombin index ; During surgery, it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of blood clotting.
Drug interactions Norfloxacin
Concomitant use of antacids containing calcium, aluminum or magnesium, preparations containing iron or zinc, as well as sucralfate may lead to a significant decrease in the absorption of Norfloxacin. The interval between the use of these drugs and Norfloxacin should be at least 2 hours. The simultaneous use of theophylline or cyclosporine may lead to an increase in their concentration in the blood, therefore, when taken simultaneously, the dose of these drugs should be reduced and their levels in the blood plasma should be monitored. With the simultaneous use of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin or its derivatives), an increase in their effect may be observed; therefore, regular monitoring of prothrombin levels is necessary. With simultaneous use of probenecid, the excretion of Norfloxacin in the urine is reduced. Concomitant use of nitrofurantoin may be accompanied by a decrease in the antimicrobial effect of Norfloxacin. The simultaneous administration of Norfloxacin with drugs that have the potential to lower blood pressure can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure. In this regard, in such cases, as well as with the simultaneous administration of barbiturates and anesthetics, heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG indicators should be monitored. Concomitant use with drugs that lower the seizure threshold can lead to the development of epileptiform seizures. Synergism has been noted between Norfloxacin and antifungal agents (for example, amphotericin B, ketoconazole, miconazole, flucytosine and nystatin).
Norfloxacin price, where to buy
The price of Norfloxacin in 400 mg tablets is approximately 115-140 rubles per package No. 10.
5 ml eye drops cost 175 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Norfloxacin tablets p.p.o.
400 mg 10 pcs. JSC Obolenskoe farm. enterprise 159 rub. order - Norfloxacin tablets p.p.o. 400 mg 20 pcs. JSC Obolenskoe farm. company
RUB 287 order
- Norfloxacin tab. p/o captivity. 400 mg No. 10Ozon LLC
RUB 168 order
- Norfloxacin tab. p/o captivity. 400 mg No. 20Ozon LLC
RUB 298 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Norfloxacin (tab.p/vol. 400 mg No. 10) Obolenskoye pharmaceutical representative.
150 rub. order
- Norfloxacin tablets 400 mg No. 20 Obolenskoe pharmaceutical company.
RUB 273 order
show more