5 Terminal chronic renal failure Gender Blood creatinine, mg/100 ml Formula Female≤0.7144*(0.993) age * creatinine/0.7) -0.328 Female>0.7144*(0.993) age * creatinine/0.7) -1.21 Male≤0.9141*(0.993) age * creatinine/ 0.9) -0.412Male>0.9141*(0.993) age * creatinine/0.9) -1.21
Division of stages of chronic kidney disease by GFR level
Department of Internal Medicine No. 3
“The best traditions, innovative technologies”
Tag cloud WP Cumulus 1.23 Rus requires Flash Player to work
Cockcroft-Gault glomerular filtration rate calculator
Glomerular filtration rate calculator MDRD
Chronic kidney disease
According to large population registries, the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is at least 10%, reaching 20% or more in certain categories of people (elderly, type 2 diabetes). For comparison: chronic heart failure occurs in 1% of the population, bronchial asthma in 5% of the adult population, diabetes mellitus in 4-10%, arterial hypertension in 20-25%.
Until recently, there was no generally accepted classification of chronic kidney failure (CKF). For example, in Russia the classifications of Ratner (creatinine level), Tareev (GFR value), and urologists Ryabov and Kuchinsky (complex) were used. But the modern world requires unification of approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases; so that the doctor, regardless of his place of work and residence, can understand his colleagues.
CKD) is now widely accepted
, CKD – chronic kidney disease), proposed by American nephrologists (K/DOQI, 2002).
Definition, criteria, classification
Chronic kidney disease is defined as kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three months or more, regardless of diagnosis.
Current criteria for CKD (K/DOQI, 2006)
Kidney damage for 3 months or more, defined as structural or functional impairment (according to laboratory and instrumental research methods) with or without a decrease in GFR or
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) = 3 months. with or without a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR), manifested by one of the following symptoms:
- morphological disorders,
- changes in urine (proteinuria),
- changing visual tests.
2. GFR=3 months with or without signs of kidney damage. Markers of kidney damage
- Laboratory tests: proteinuria, albuminuria (>30 mg/day).
- Ultrasound: change in kidney size (normal: xx cm), increased echogenicity, space-occupying formations, stones, nephrocalcinosis, cysts.
- CT scan: obstruction, tumors, cysts, bladder and ureteral stones, stenosis a. renalis.
- Isotope scintigraphy: asymmetry of function, kidney size.
Etiology
- Diabetes.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Chronic glomerulonephritis (primary, secondary).
- Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis (drug-induced, pyelonephritis).
Diagnosis 1. Assessment of kidney function:
- GFR: inulin or creatinine clearance,
- estimated creatinine clearance: Cockcroft-Gault formula (for drug dosing),
- estimated GFR: CKD-EPI and MDRD formulas (for assessing CKD stages),
- cystatin S.
2. Kidney biopsy. 3. Potassium, sodium. 4. With GFR, Classification of chronic kidney disease (K/DOQI, 2002; RNA, 2011)
| Cockcroft-Gault |
| Cockroft-Gault(norm): |
| Body surface area: |
| Body mass index |
| Stages | Description | GFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | ICD-10 |
| 1* | kidney damage with N or increased GFR | >=90 | N18.1 |
| 2* | kidney damage with mild reduction in GFR | 60-89 | N18.2 |
| 3a | moderate decrease in GFR | 45-59 | N18.3 |
| 3b | significant reduction in GFR | 30-44 | N18.3 |
| 4 | severe decline in GFR | 15-29 | N18.4 |
| 5 | renal failure | N18.5 |
* – in the absence of signs of kidney damage, stages 1-2 are not established. Formulation of diagnosis
| Stages | Action plan |
| 1-2 | Correction of cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, obesity, hyperglycemia, low physical activity) |
| 3 | GFR every 3 months, ACEI or ARB2, avoid nephrotoxic drugs, adjust medication dosage |
| 4 | Consultation with a nephrologist, preparation for dialysis or transplantation |
| 5 | Dialysis or transplant |
CKD management framework (K/DOQI, 2002, 2006; CSN, 2006; UKRA, 2012, as amended) Treatment of renal failure Diet:
reduction in protein to 0.8 g/kg (GFR 15-29 ml/min/1.73 m2) - 0.6 g/kg (GFR) Slowing progression: smoking cessation, control of hypertension, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin 2 receptor blockers, glycemic control.
Syndromic treatment:
hypertension, electrolyte disorders, hyperparathyroidism, anemia, dyslipidemia.
Refusal of nephrotoxic drugs:
aminoglycosides, vancomycin, gold preparations, cyclosporine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Replacement treatment:
hemodialysis (traditional, outpatient / home), peritoneal dialysis , kidney transplantation. Treatment is syndromic
Methods for determining glomerular filtration
Currently, quite a lot of methods and tests have been created to determine the level of glomerular filtration. All of them have a personal name (in honor of the scientist who discovered this or that sample).
The main ways to study glomerular function are the Rehberg-Tareev test and determination of glomerular filtration rate using the Cockroft-Gold formula. These methods are based on changing the level of endogenous creatinine and calculating its clearance. Based on its changes in blood plasma and urine, a certain conclusion is made regarding kidney function.
All people can carry out these tests, since these studies have no contraindications.
The above two samples are the standard in the study of renal filtration. Other techniques are used less frequently and are carried out mainly for specific indications.
How is creatinine level determined and what are these procedures?
What is it, what does it show and in what units of measurement?
The main problem of the kidney is that under the influence of heavy stress, nephrons die.
As a result, it works worse and worse as a filter, since new elements will no longer be formed. As a result, a lot of different diseases and complications arise. People who drink alcohol, eat a lot of salty foods and have bad heredity are especially prone to this.
If, based on any symptoms, the doctor determines that the patient’s complaints are related to the kidneys, he may be prescribed a diagnostic method such as GFR, that is, determining the glomerular filtrate rate.
Read our article about how the human kidneys work.
This method determines how quickly the filters in the body cope with the task, that is, they cleanse the blood of harmful substances. This is fundamental in determining some diseases, including chronic ones.
In order to determine GFR, special formulas are used. There are several of them, and they differ in information content. But everywhere they use one term, namely clearance. This is an indicator by which you can determine how much blood plasma will be processed in one minute.
What formulas are used to calculate GFR?
In medicine, the value associated with creatinine clearance is most often used - this method is considered the simplest and most convenient for medical diagnosis. Since it is excreted through the glomeruli only by 85-90%, and the rest through the proximal tubules, calculations are carried out with an indication of the error.
The lower its value, the correspondingly higher the GFR rate. Direct measurement of insulin filtration rate is too expensive for medical diagnosis and is used mainly for scientific purposes.
The patient's blood and urine are used for analysis.
It is especially important to collect urine strictly within the allotted time period. Today there are 2 options for collecting material:
- Two hourly portions of urine are collected, and in each sample the minute diuresis and the concentration of the end product of protein breakdown are examined. The result is two GFR values.
- Less commonly used is the daily amount of urine, in which the average creatinine clearance is determined.
Standard formula
(up x Vn) / (Ср x Т),
where Vn is the volume of urine over a fixed period of time, Cp is the concentration of creatinine in the blood serum, T is the time during which urine is collected in minutes.
Cockcroft-Gault formula
/ (72 x serum creatinine concentration, mg/dL)
The result of the calculation using this formula is true for an adult man; for women, the result must be multiplied by a coefficient of 0.85.
Criatinine clearance formula
/ serum creatinine concentration, mg/min
For women in this case, you also need to apply a coefficient of 0.9.
Since GFR depends on the rate of clearance of creatinine from blood plasma, it is also calculated manually using the formula:
From the editor: Low blood pressure: what to do?
(urine creatinine concentration x urine volume over time)/(plasma creatinine concentration x urine collection time in minutes)
Cockcroft-Gold test
This technique is somewhat similar in implementation to the Tareev test. In the morning, on an empty stomach, the patient is given a certain amount of liquid to drink (1.5-2 glasses of liquid - tea or water) to stimulate minute diuresis. After 15 minutes, the patient urinates in the toilet (to remove the remaining urine formed during the night from the bladder). The patient is then advised to rest.
After an hour, the first portion of urine is collected and the time of urination is accurately noted. During the second hour, the second portion is collected. Between urinations, 6-8 ml of blood is taken from the patient's vein to determine the level of creatinine in the blood serum.
After minute diuresis and creatinine concentration are determined, its clearance is determined. How to determine the glomerular filtration rate?
The calculation formula for determining it is as follows:
- F = (u : p) ˑ v, where u is the concentration of creatinine in the urine, p is creatinine in the blood plasma, V is minute diuresis, F is clearance.
Based on the F indicator, a conclusion is made about the filtration capacity of the kidneys.
Glomerular filtration is reduced - why and how to treat?
Regardless of how GFR is determined, it must be remembered that this is only a preliminary diagnosis, that is, a direction for further research.
Therefore, it is too early to talk about suitable treatment at this stage. First, you need to make an accurate diagnosis, determine the cause of what is happening in the body, and only then begin to eliminate this problem.
But for emergency cases, when glomerular filtration is critically reduced, diuretics can be used. These include Euphyllin and Theobromine.
If a patient has been diagnosed with a violation of GFR, that is, the indicators will be higher or lower than normal, it is imperative to adhere to the correct drinking regime and a gentle diet that will not overload the kidneys. It is necessary to completely exclude salty, fatty and spicy foods from the diet. For a while, you can switch to boiled and steamed dishes.
Folk remedies for the treatment of GFR problems can only be used with the approval of the attending physician.
Parsley is ideal for improving kidney function. It is useful both fresh and in decoction form. Rosehip is considered a good diuretic. Its fruits are brewed with boiling water, infused, and then drunk three times a day for several days.
Kidney pathologies can be very dangerous, so the entire treatment process must be monitored by a specialist. And it doesn’t matter whether tablets or herbal decoctions are used. Both of these, if used incorrectly, can cause great harm to the kidneys.
Find out how the glomerulus of the kidney works and its functions from the video:
Reberg-Tareev test
It is used in clinical practice somewhat more often than the Cockcroft-Gold test.
Blood serum and urine are used for research. It is imperative to take into account the time of collection of analyzes, since the accuracy of the study depends on this.
There are several options for this test. The most common technique is the following: urine is collected over several hours (usually two-hour portions). In each of them, creatinine clearance and minute diuresis (the amount of urine produced per minute) are determined. The glomerular filtration rate is calculated based on these two indicators.
Somewhat less often, the determination of creatinine clearance in a daily urine sample or the study of two 6-hour samples is carried out.
In parallel, no matter what method the test is carried out, in the morning on an empty stomach blood is taken from a vein to assess the concentration of creatinine.
About this calculator
*This calculator allows you to estimate cretinin clearance using the Cockcroft DW, Gault MH method
Formula
Creatinine clearance using the Cockcroft-Gault formula = (140-age) * (weight in kilograms) * (0.85 if female) / (72 * creatinine mg/dL)
In the US, creatinine is typically measured in mg/dL, while in Canada and Europe it is measured in µmol/L. 1 mg/dL creatinine is equal to 88.4 µmol/L
For this reason, a correction factor is used in the formula: the creatinine level is divided by 0.0884 and multiplied by 1000.
Interpretation
Reference values for creatinine clearance in ml/min
| Age | Men | Women |
| Under 1 year | 65-100 | 65-100 |
| 1-30 years | 88-146 | 81-134 |
| 30-40 years | 82-140 | 75-128 |
| 40-50 years | 61-120 | 58-110 |
| 50-60 years | 82-140 | 75-128 |
| 60-70 years | 82-140 | 75-128 |
| Over 70 years old | 55-113 | 52-105 |
additional information
The above formula allows you to obtain an acceptable estimate of creatinine clearance except in cases where:
- There is a rapid change in plasma creatinine levels (both rise and fall).
- The patient is significantly exhausted.
In these situations, the following assumptions must be made:
- In the case of a rapid rise in plasma creatinine levels (i.e. more than 44.2-61.88 µmol/l per day), it is best to assume that creatinine clearance does not exceed 10 ml/min.
- In malnourished patients, it can be assumed that the actual clearance will be less than the estimate, but its exact value cannot be determined.
When using the calculation formula, it should be remembered that the obtained creatinine clearance value is an estimate and may differ from the actual one either up or down, therefore the resulting estimate should be taken into account only in conjunction with other factors identified during the examination of the patient. Decisions regarding drug therapy and dosage should be based on clinical assessment
Significant changes in creatinine levels can also be caused by other factors (dehydration, use of nephrotoxic drugs, excess creatinine production due to injury or excessive exercise, or decreased creatinine production due to kidney disease or exhaustion).
Particular care should be taken when assessing creatinine clearance in:
- Elderly (over 90 years old)
- Patients with low body weight (less than ideal)
- Patients after liver transplantation
Note: Using actual body weight to calculate clearance in obese patients (and possibly in patients with ascites) may result in creatinine clearance estimates that are significantly higher than actual values.
Some experts prefer in such cases to use an indicator such as “corrected body weight” (it can be calculated, for example, using the following formula: ideal body weight + 0.4 *).
This is especially relevant in cases where estimation of creatinine clearance is necessary for calculating antibiotic doses.
Calculation of parameters
Straight
In order to obtain the GFR value, the following analytes are used:
- inulin;
- 125I-iothalamate;
- 99mTc-diethylenetriaminepentaacetate.
But the use of these substances is limited by the need for continuous intravenous infusion in order to maintain a constant concentration in the blood. In order to calculate the parameter, during the infusion, four portions of urine are collected with an interval of half an hour. This method is technically difficult and quite expensive, which is why it is applicable within the framework of research work, and not in widespread practice.
Indirect
Most often, this parameter is assessed by the level of endogenous creatinine clearance. This substance is the final metabolite of the metabolism of creatine and creatine phosphate.
The rate parameters of creatinine formation and excretion of this substance are constant and determined by muscle volume. Therefore, men, especially those actively involved in sports, produce more of this substance. In addition, the intensity of creatinine formation increases in the case of extensive necrotic changes in skeletal muscles.
The elimination of creatinine is carried out for the most part by glomerular filtration, however, a small percentage of it is secreted by the tubular apparatus. For this reason, the filtration rate, as measured by creatinine clearance, is slightly overestimated.
If the kidneys are functioning physiologically, then the magnitude of this increase ranges from 5 to 10%. If glomerular filtration rate decreases, the percentage of secreted creatinine increases. In case of insufficient renal function, the level of creatinine clearance may be 70% greater than the GFR.
The magnitude of tubular secretion of creatinine cannot be predicted due to its variable nature in the same patient. Another difficulty in estimating GFR is the effect of medications on the level of tubular secretion of creatinine. For example, Trimethoprim and Cimetidine can increase plasma creatinine concentrations and reduce its clearance without changing GFR.
However, the analysis of creatinine clearance is a simple and widely used method for determining the functional state of the kidneys.
The physiological value of daily creatinine excretion in men is 18-21 mg/kg, and in women – 15-18 mg/kg. If lower values are obtained, then one of the following outcome options is assumed: incorrect urine collection, lack of muscle volume, severe renal failure.
Serum creatinine concentrations should be determined before or after urine collection. The resulting value must be recalculated to the body surface area standard (divided by the patient's body surface area and multiplied by 1.73 m²). The acceptable range of values depends on the research methodology, but most often it is within the range of 85-125 ml/min for men and 75-115 ml/min for women).
Mathematically, the level of creatinine clearance is expressed through the equation: C = (Km∗V)Kcr, which reflects the concentrations of creatinine in urine and blood, respectively, as well as the volume of urine excreted per minute (that is, minute diuresis).
Other formulas
In medical practice, GFR is determined based on a number of equations, which include the concentration of creatinine in the blood and a list of individual parameters (age, body weight, height). The calculation is made easier by using special calculators. The Cockroft-Gault, MDRD, and CKD-EPI equations are used. To determine GFR in childhood, the Cunnaghan-Barratt and Schwartz formulas are used.
Cockcroft-Gault
. Characterized by inaccuracy in the case of acceptable or slightly reduced filtration rate parameters. Body weight is taken in kilograms, age in years, creatinine concentration in µmol/l.
MDRD
is now used quite widely. The disadvantage of this calculation method is that it underestimates the GFR value at high values.
- 1.73 m2 is the surface area of the body of an average adult.
- Scr—serum creatinine concentration.
- IDMS is taken as one if the laboratory does not use dilution isotope mass spectrometry to determine creatinine, 0.95 if it does.
This calculator is not used for acute kidney injury. In addition, this formula has not been studied in patients over 70 years of age, so the results of its use in the age group of 70 years and older may not be accurate.
CKD-EPI
You can get a more accurate parameter value if the filtration rate is more than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2.
Where:
- Cr—serum creatinine concentration;
- age — age (year).
Schwartz
Applicable for children and adolescents under 18 years of age. Looks like this: . The coefficient of 36.2 was selected empirically. There are modifications of this formula in which this coefficient has different meanings and is determined by the specific age group of the child and his gender.
Barrat
Also used to assess filtration rate in childhood.
.
Chronic kidney disease
According to large population registries, the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is at least 10%, reaching 20% or more in certain categories of people (elderly, type 2 diabetes). For comparison: chronic heart failure occurs in 1% of the population, bronchial asthma in 5% of the adult population, diabetes mellitus in 4-10%, arterial hypertension in 20-25%.
Until recently, there was no generally accepted classification of chronic kidney failure (CKF). For example, in Russia the classifications of Ratner (creatinine level), Tareev (GFR value), and urologists Ryabov and Kuchinsky (complex) were used. But the modern world requires unification of approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases; so that the doctor, regardless of his place of work and residence, can understand his colleagues.
Currently, the concept of chronic kidney disease (CKD, chronic kidney disease), proposed by American nephrologists (K/DOQI, 2002), has received general recognition.
Decoding the result
To correctly interpret the obtained value, you need to know the norm. The following table shows the indicators for adults and children:
| Age | SCF |
| Children (ml/min/1.73 m2) | |
| 2-8 days | 17-60 |
| 9-28 days | 26-68 |
| 37-95 days | 30-86 |
| 1-6 months | 39-114 |
| 6-12 months | 49-157 |
| 12-19 months | 62-191 |
| 2-12 years | 89-165 |
| Adults ml/min | |
| Men | 90-125 |
| Women | 90-110 |
GFR allows you to determine and predict the development of chronic renal failure (CRF). It has the following stages:
| Stage | Name | GFR in ml/min/1.73 m2 | Blood creatinine, mmol/l |
| I | Tubular | >90 | |
| I | Compensated | 89-60 | 0,105-0,176 |
| II | Subcompensated | 59-30 | 0,177-0,351 |
| III | Decompensated | 29-15 | 0,352-0,440 |
| IV | Terminal (indication for hemodialysis) | >0,440 |
In case of acute kidney injury, minute urine output and blood creatinine are currently analyzed without determining GFR (but not everywhere in the CIS). Diagnosis of a specific kidney disease is carried out only after a comprehensive analysis of all clinical data: anamnesis, complaints, objective symptoms + other laboratory and instrumental studies.
Modern diagnostic methods
Today, medicine is actively developing. And there are already many ways to diagnose a patient’s health condition. For example, until recently, ultrasound examination with an ultrasound machine was considered the most important method. Then new methods began to appear: now this is the well-known computed tomography and other types of modern diagnostics.
From the editor: All symptoms of VSD and neurosis
But the GFR method for clearing creatinine remains indispensable. It is this that allows us to fully assess the performance of a person’s kidneys and identify the first signs of renal failure.
The kidneys are the main filter of the human body, and if its work is disrupted, then we can say that other organs will soon “give up their positions.”
In addition, a complete stop of kidney function leads to the death of a person. He needs constant artificial blood purification, called dialysis, and is therefore tied to a specific place, namely the hospital. At the same time, the patient cannot afford to go somewhere for a visit or on vacation, because he needs to undergo dialysis with some regularity. And it's good if it's free. Otherwise, not everyone has the financial ability to cope with this procedure.
Mechanism of increase in creatinine
Creatinine is formed in human muscles. It is the end product of protein metabolism. Normally functioning kidneys remove it completely from the body in the amount of 1-2 g per day. The content of creatinine in the blood varies among people, and the indicators vary depending on the person’s gender, age, muscle mass, diet, and other factors not related to the state of the urinary system.
But a significant increase in creatinine always indicates renal pathology. The mechanism of the disorder is simple: when nephrons die against the background of one or another kidney disease, the kidneys do not stop coping with urine filtration. Accordingly, decomposition products are excreted in smaller quantities; a significant part of them enters the circulatory system. Including creatinine.
How is the calculation carried out?
Renal clearance in medicine is calculated in two ways:
- A one-time measurement of creatinine levels in the blood, after which the information obtained is entered into one of many special formulas. This method is used much more often due to convenience.
- Measuring the volume of creatinine in urine per day. To do this, you need to urinate in a container during the day and bring it for analysis. To ensure that the process is carried out correctly, you need to ignore the urine that appears during the first morning bowel movement. All further liquid can be collected within 24 hours. The norm of creatinine in men: 18-21 mg/kg, in women: 15-18 mg/kg. The container with the liquid should be stored in a cool place to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Criteria
Glomerular filtration rate is measured using a limited number of criteria, depending on the formula that is used in a particular case.
Types of criteria:
- age (years);
- creatinine (µmol/l, mg/dl);
- gender (male, female);
- race (Caucasian, Negroid, Mongoloid);
- height (cm);
- Weight, kg).
Creatinine with GFR calculation
Thank you very much for your work. The result is a very useful and multifunctional calculator. Maybe there is a version for Android? Using the site in daily work is not always convenient.
For a smartphone, you can use a minimalistic GFR calculator with the same functionality https://boris.bikbov.ru/skf-kalkulyator-dlja-mobilnych-ustroistv.html After you open the link provided, you need to select “Save” in your mobile phone browser, and when you need a calculator, call it from the “Saved Pages” menu.
Good day! Can you clarify the following point: There are 2 methods in use (in the world and here) - Jaffe and enzymatic, the difference in values is 10-15 units. Naturally, the results from calculators are the same. There is no mention or adjustment for the method in any calculator. Please comment if possible.
I really appreciate this calculator. I did the math and calmed down a little, because I’m in the green zone for now and I hope to stay in it for as long as possible. And we will continue to deal with hypertension.
Please tell me, according to the Schwartz formula, my SFR is 83, but according to other formulas it’s more than 120, what does this mean?
The Schwartz formula is only for children. If the patient is over 18 years old, the CKD-EPI formula must be used.
Good afternoon. Cost of purchasing calculators for installation on the site?
Free All site materials, including the GFR calculator, are distributed under the CC-BY-NC license. Those. they may be reproduced and copied for non-commercial purposes, provided that an active link to this site is provided.
Hello! Tell me, is creatinine indicated in blood or urine for calculation?
Blood creatinine. Moreover, for the correct calculation of GFR, it is necessary that laboratory kits for determining creatinine be standardized with a reference laboratory.
Please accept our gratitude for your calculator. Relieved nervous tension.
Hello, very good job. Could you tell me what formula you use to calculate the GFR using the Schwartz formula? No matter how many options I have found on the Internet, the result comes out different from yours.
The Schwartz formula is given in the KDIGO 2012 manual (first link), and the quadratic modification (not officially approved) is given in the fourth link.
In the Russian Federation, blood creatinine is not always calculated using the IDMS method. As I understand it, is this method taken into account by your calculator, or not? For example, the result of blood creatinine in a regular hospital laboratory analyzer is 106 µmol/l (with a reference interval of 53-97 µmol/l ), in another study of the same patient - 85 µmol/l (normal - 44-80 µmol/l). How then to calculate GFR using a calculator?
To calculate the CKD-EPI formula, reagents for measuring creatinine must be standardized to IDMS. Of course, if you use non-standardized whales, then it is incorrect to use creatinine to calculate GFR. Unfortunately, in Russia there is no standardization requirement for IDMS, and most laboratories do not indicate in the analysis results which method of measuring creatinine was used. The only way to find out is to ask the laboratory directly.
source
Using calculators
To determine the glomerular filtration rate at home, you can use special calculators. As of 2018, there are quite a large number of them, but if the patient has knowledge of English, it is better to use English-language calculators. They are more functional and stable.
When working with the calculator, you need to enter data in the appropriate fields, after which the program will calculate the glomerular filtration rate. Based on the results obtained, we can draw a conclusion about the condition of the kidneys.
Recommended topic:
Uremic coma
Attention. Self-medication can be dangerous to health. Under no circumstances should you take medications without the knowledge of your doctor.
What are there
Now you can use the calculator to calculate GFR in any convenient way:
- Online calculators. This type can calculate the glomerular filtration rate using the CKD-EPI, MDRD formulas.
- Calculator for a personal computer. It will need to be installed on a PC, after which it will be possible to find the SCF without access to the Internet.
- Calculator for smartphone. This type is convenient to use for its intended purpose anywhere, even if there is no access to the Internet.
- Paper monograms and specialized rulers. If you don’t have a mobile phone or computer at hand, you can use this method. Its disadvantage is the greater complexity of the calculation.
Normal values for men and women
The final result is influenced by the secretion of the substance by the renal tubular system, which means that creatinine clearance can be significantly higher than the actual GFR values, especially in patients with chronic pathology. Incorrect collection results in a false rejection.
Increased GFR
Increasing filtration capacity in the long term is fraught with depletion of functional reserves, that is, the organ will simply be “exhausted.” In the future, the kidney will simply lose the ability to increase GFR in response to damage (stimulus). This occurs in the following diseases:
- glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome;
- early stage of hypertension;
- focal hyalinosis;
- segmental sclerosis;
- diabetes;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- intense physical activity;
- taking cephalosporins (antibiotics).
The earliest sign of hyperfiltration is microalbuminuria (the appearance of protein in the urine). The “gold standard” for diagnosing renal damage is a biopsy followed by morphological examination.
Decrease in GFR
In clinical practice, cases of deterioration in the filtration capacity of the kidneys are most often encountered, which may be due to the following reasons:
- pyelonephritis;
- bleeding (injuries, surgical interventions);
- dehydration (profuse vomiting, diarrhea, diabetes insipidus, adrenal insufficiency, burns);
- shock of any etiology;
- vasculitis;
- sepsis, anaphylaxis;
- taking medications (diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, etc.);
- malignant hypertension;
- jades;
- urolithiasis disease;
- long-term compartment syndrome;
- tumors;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- decompensated heart or liver failure.
GFR values and stage of chronic renal failure
There are five stages of chronic renal failure. Depending on the stage, test results also change.
Stage 1 – there are signs of kidney damage, but there are no disturbances in the filtration rate or it is slightly increased (more than 90 ml/min).
2 – damage to kidney tissue. The filtration rate is moderately reduced (from 89 to 90). It is necessary to conduct a full examination of the patient, assess whether the pathology is progressing and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Stage 3 – GFR is moderately reduced (from 59 to 30 ml/min), serious treatment is required, including complications.
4 – pronounced decrease in speed (29-25). Mostly, with such indicators, they begin to choose the type of replacement therapy.
5 – last stage, end-stage renal failure, GFR values below 15. Without replacement therapy (hemodialysis, kidney transplantation), the patient dies.
Decoding
A GFR value of less than 60 ml/min is defined as the onset of chronic kidney disease as a result of the death of the majority of nephrons.
The nature of changes in glomerular filtration rate depending on age:
- 20-20 — 116
- 30-39 — 107
- 40-49 — 99
- 50-59 — 93
- 60-69 — 85
- from 70 years old - 75
This calculator's calculations cannot be used in the following cases:
- Pregnancy
- When deciding to initiate renal replacement therapy
- Conditions after kidney transplantation
- Rapid deterioration of renal function (eg, in acute or rapidly progressive nephrotic syndrome)
- When prescribing laboratory tests to determine the dose of nephrotoxic drugs
- Paresis or paralysis of the limbs
- Skeletal muscle pathologies (myodystrophies)
- When the anthropometric indicators and muscle mass of the patient have significant deviations from the norm (for example, patients after amputation of a limb, bodybuilders, etc.)
- Patients on a vegetarian diet
- Obesity (BMI {amp}gt; 40 kg/m2) or wasting (BMI {amp}lt; 15 kg/m2)
From the editor: What to do when your nose bleeds from pressure
Increased creatinine in blood tests. Causes.
Sometimes the creatinine level in the blood changes slightly or greatly. This happens for various reasons:
- When creatinine does not leave the body due to kidney damage (urolithiasis, renal failure, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, uremia), decreased blood supply to the kidneys, severe shock.
- When there is an increased level of creatinine in the blood. There are a lot of factors here - endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus), frequent irradiation of the body, excessive physical activity (weightlifting, bodybuilding, improper diet (large amount of protein consumption), abuse of sports nutrition, with an increased content of growth hormone in the body (gigantism), severe skin injuries and operations, destruction of muscle tissue (compression) due to car accidents, various infectious diseases, loss of large amounts of blood, internal ulcers and tumors, anemia.
Treatment for increased creatinine depends on the degree of the indicator. If this does not particularly affect the general condition of the body and the indicator is within the acceptable norm, doctors recommend a special diet, reduced physical activity, increased consumption of clean drinking water, diuretics, antioxidants to remove waste and toxins, and normalization of sleep.
A low creatinine level is also a pathology and has a negative effect on the body. Its causes are as follows: low muscle mass, severe muscle injuries, a diet with low protein intake, cirrhosis of the liver, pregnancy, amputation of limbs, long-term treatment with allergy medications, a vegetarian diet, blockage of the urinary tract.
In this case, you cannot independently prepare a diet based on diets and hunger strikes, and reduce sports activities to a minimum. Taking medications under the supervision of a doctor.
The higher the clearance, the better the kidneys work, but an increase in the level of creatinine in the blood can occur for two types of reasons - excessive production of the substance in the body, provided the kidneys are healthy, or insufficient excretion due to pathology of the excretory organs. The first ones may be:
- extensive injuries affecting muscle and bone tissue or burns of a large area;
- states of shock;
- dehydration;
- blood loss, anemia;
- hyperthyroidism, accompanied by rapid breakdown of muscle tissue;
- necrotic processes in the body;
- consequences of ionizing radiation;
- heart failure - causes a decrease in blood flow to the kidneys;
- acromegaly is a pathology characterized by excessive production of growth hormone;
- intestinal obstruction.
Physiological reasons for an increase in creatinine can also be intense exercise and pregnancy (which, however, may be accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of this substance in the blood).
The most cause for concern should be renal pathologies, leading to the fact that the breakdown product cannot be adequately excreted from the body, including:
- renal failure;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- intoxication (alcohol or medication);
- inflammatory kidney diseases – glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis;
- circulatory disorders in the renal glomeruli;
- urolithiasis disease;
- extrarenal uremia.
There is a relationship between creatinine levels and diet; the more protein foods on the menu, the higher the level of creatine breakdown product.
The concept of glomerular filtration
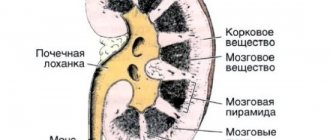
The process of urine formation consists of several stages. At each stage, a failure may occur, leading to dysfunction of the entire organ. The first stage of urine formation is called glomerular filtration.
It is carried out by the renal corpuscle. It consists of a network of small arteries formed in the form of a glomerulus surrounded by a two-layer capsule. The inner layer of the capsule fits tightly to the walls of the arteries, forming a renal membrane (glomerular filter, from the Latin glomerulus - glomerulus).
It consists of the following elements:
- endothelial cells (the inner “lining” of arteries);
- epithelial capsule cells forming its inner layer;
- layer of connective tissue (basal membrane).
It is through the renal membrane that water and various substances are released, and its condition determines how fully the kidneys perform their function.
Through the renal membrane, water is passively filtered from the blood along a pressure gradient, and along with it, substances with small molecular sizes are released along an osmotic gradient. This process is glomerular filtration.
Large (protein) molecules and cellular elements of the blood do not pass through the kidney membrane. In some diseases, they can still pass through it due to its increased permeability and end up in the urine.
The solution of ions and small molecules in the filtered liquid is called primary urine. The content of substances in its composition is very low. It is similar to plasma from which the protein has been removed. The kidneys filter from 150 to 190 liters of primary urine in one day. During the further transformation that primary urine undergoes in the nephron tubules, its final volume decreases by approximately 100 times, to 1.5 liters (secondary urine).
What indicators are taken into account when calculating
As stated above, several factors influence creatinine levels.
- gender – in women the indicator is 5-10 units lower than in men;
- age – for children, the content is 2 times less;
- muscle mass - the larger it is, the higher the level of metabolite;
- physical activity - after it creatinine in the blood increases;
- diet – excessive protein consumption also increases creatinine levels;
- taking medications (NSAIDs, some ACE inhibitors, Cyclosporine);
- dehydration.
When calculating the filtration rate based on creatinine, all these factors must be taken into account, otherwise the results will be incorrect and the diagnosis of “renal failure” will become erroneous. Of course, this analysis alone does not give a final verdict; additional studies are always carried out, but suspicion of a severe pathology will not be good news for the patient.
What is the calculation used for?
Determination of GFR is a diagnostic measure that helps to preliminary assess abnormalities in organ function. A decreased or increased value indicates pathological changes in them. Without an accurate calculation, some diseases cannot be identified. Additional studies will only confirm the diagnosis.
The GFR value is determined by:
- renal circulation rate;
- blood pressure level;
- the number of nephrons involved in filtration;
- the rate of tubular secretion (determined by only one test - the Reberg study).
These indicators help assess the condition of organs and the presence of dangerous pathologies. Some of them, if not identified in time, will require kidney transplantation in the future. To avoid a labor-intensive operation that threatens complications and repeated interventions, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, including the calculation of GFR.
Formulas for calculating GFR
(140 – age) x patient’s weight in kg / (amount of creatinine in mmol/l) x 814.
If calculations are carried out for a woman, the value obtained from the formula is multiplied by 0.85.
11.33 x Crk (serum creatinine) – 1.154 x (number of years) – 0.203.
For women, the result is multiplied by 0.742.
Doctors consider the CKD-EPI formula to be optimal. It is too complex for non-specialists, but you should know that it can be used to more accurately estimate GFR values at low and high values.
In addition to these formulas, a universal calculator can be used to make a preliminary assessment of the filtering capacity of the kidneys; it is easy to find on the Internet. But the readings obtained with its help cannot be considered reliable, without taking into account factors such as lifestyle and nutrition, and taking certain medications.
A nephron is a structural unit of the kidney, which consists of the renal corpuscle and renal tubules. In the renal corpuscle, blood is filtered, and with the help of the tubules, reverse absorption (reabsorption) occurs. Blood passes through this system many times every day, and as a result of the processes described above, primary urine is formed.
Subsequently, it goes through several more stages of purification, dividing into water, which returns back to the blood, and metabolic products, which are excreted into the environment along with urine.
Ultimately, from the 120 liters of glomerular ultrafiltrate that passes through the nephrons daily, about 1-2 liters of secondary urine are formed. If the excretory system is healthy, the formation of primary urine and its filtration occurs without any complications.
Determination of filtration rate using the MDRD formula
In contrast to the main methods for determining the glomerular filtration rate, the MDRD formula is somewhat less widespread in our country. It is widely used by nephrologists in most European countries. In their opinion, the Reberg-Tareev test is low-informative.
The essence of this technique is to determine GFR based on gender, age and serum creatinine level. Often used in determining kidney function in pregnant women.
It looks like this:
- GFR = 11.33 x Crk - 1.154 x age - 0.203 x K, where Crk is the concentration of creatinine in the blood (in mmol/l), K is the sex coefficient (for example, for women it is 0.742).
This formula works well when the filtration rate level decreases, but its main drawback is incorrect results if the glomerular filtration rate increases. The calculation formula (due to this disadvantage) was modernized and supplemented (CKD-EPI).
The advantage of the formula is that it is possible to determine age-related changes in kidney function and monitor them over time.