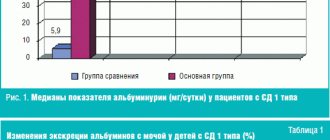
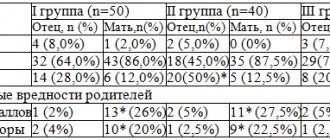
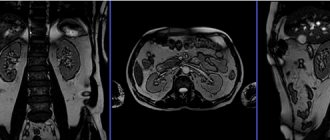
The renal apparatus is a complex mechanism responsible for the two-stage formation of urine, the final product of metabolic processes in the body. At the first stage, the renal glomeruli filter (purify) the blood plasma from protein compounds, forming primary urine.
At the second stage, reabsorption occurs (reabsorption of nutrients and water) and the formation of final (secondary) urine containing metabolic products. The filtration function is to excrete fluid and harmful substances from the body and preserve beneficial substances.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a measure of the volume of blood that the kidneys can clear within one minute. GFR in a blood test is calculated using special laboratory formulas, which take into account biochemical blood parameters, anthropometric data, age category, gender and race of the patient.
Reference! The renal glomerulus (corpuscle) is a network of capillary loops collected in a single bundle. The corpuscle is the primary filtration zone in the nephron, the main functional unit of the kidneys. To produce the average daily urine volume (≈1.5 liters), one and a half million glomeruli process about 180 liters of blood in 24 hours.
Factors affecting glomerular filtration rate
GFR is one of the key indicators of the functionality of the renal apparatus. The rate of plasma purification for the formation of primary urine depends on several factors:
- filtration blood pressure in the kidneys (normally, when plasma enters, the pressure should be higher than at the exit of the final metabolite);
- blood flow in the glomeruli (reflects the volume of processed plasma, the level of which according to the standard is 600 ml/min);
- filtration surface area (depends on the number of nephrons capable of filtration);
- the number of functional nephrons (when some nephrons die, GFR slows down);
- permeability of the filtration membrane;
- age (as the body ages, metabolic processes and biochemical reactions slow down and, accordingly, GFR objectively decreases);
- physical activity (affects muscle contractions and, as a consequence, creatinine levels);
- peculiarities of eating habits (speed may be impaired due to urinary retention due to the abuse of salty foods);
- taking medications that affect creatinine levels;
- body weight (the presence of extra pounds can slightly slow down glomerular filtration);
- the presence of chronic diseases of the urinary system;
- gender (men have a higher GFR than women).
In women, filtration rate is affected by pregnancy.
Features of the kidney structure
In a biochemical blood test, parameters that correlate with GFR are:
- Creatinine is a metabolite of protein and amino acid metabolism. The energy resource for the muscular system is adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP). The source of its formation is creatine phosphate, synthesized by the liver. After production, creatine phosphate moves to muscle tissue, where during the fermentation process under the influence of creatine phosphokinase, creatinine is formed and energy is produced. From muscle tissue, creatinine enters the systemic circulation, is filtered and excreted by the kidneys. In a blood test it is measured in µmol/l. The normal level for children is 27-62, for men – 80-115, for women – 53-97.
- Urea is the final product of protein breakdown, formed by the liver and intended for the safe evacuation of nitrogen from the body. After entering the blood, it is filtered and excreted by the renal apparatus. Measured in mmol/l. Reference values for men are 3.0-9.2, for women – 2.6-7.2.
- Albumin is a protein produced by hepatocytes (liver cells). Responsible for oncotic pressure (redistribution of fluid between blood and tissues), delivery and distribution of adrenal and thyroid hormones, organic compounds, acids, vitamins and minerals. Laboratory measurement value is grams/liter. The norm for adults is considered to be from 40 to 50. Children's indicators depend on the age group: up to 5 years - 33.6-43.0; up to 11 years – 37.0-47.1; up to 21 years old – 40.6-45.6.
In chronic renal pathologies and acute renal failure, the amount of albumin decreases and the concentration of urea and creatinine increases, which affects the filtration rate.
Classification of chronic kidney disease by GFR
There are 3 main types of diseases that reduce or increase the filtration rate. Using this indicator, you can get a preliminary diagnosis, and additional tests will give a clearer picture.
The class of diseases that cause a decrease in the GFR rate include:
- Chronic kidney disease (see stages of CKD in the table). This disease leads to increased concentrations of urea and creatinine. In this case, the kidneys cannot cope with the load normally, which leads to the gradual death of nephrons, and then to a decrease in the filtration rate.
- About the same thing happens with pyelonephritis. This disease is infectious in nature. Pyelonephritis is characterized by inflammatory processes that necessarily affect the nephron tubules. This inevitably leads to a decrease in glomerular filtration rate.
- One of the most dangerous conditions can be considered hypotension. In this case, the disease is associated with very low blood pressure. All this can lead to heart failure and a decrease in GFR levels to critical levels.
The class of diseases that provoke increased kidney function includes:
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure (hypertension);
- lupus erythematosus, which also leads to increased stress on the kidneys.
Filtration process
The kidneys are supplied with blood through the renal artery, which divides into arterioles (smaller vessels) and then into microvessels - the capillaries of the renal glomeruli. Plasma is supplied to the glomeruli under pressure created by cardiac activity. The body is surrounded by a two-layer capsule. The inner layer is a membrane that acts as a glomerular filter.
Proteins and large molecules of other compounds do not leak through the membrane, remaining in the nephrons. The purified liquid or primary urine consists of water and nutrients. It is filtered into the nephron tubules, where reverse resorption (absorption) of water, glucose, electrolytes (potassium and sodium) and other substances into the systemic circulation occurs.
Waste products, urea, uric acid and creatinine form secondary urine, which enters the ureters, then stored in the bladder for further excretion through the urethra. The filtration rate reflects the cleaning ability of the renal apparatus. A decrease in GFR is a sign of impaired renal function and a decrease in the number of functional nephrons.
Accepted laboratory norm of GFR
The rate at which the glomeruli filter has variable normative values (from the lower to the upper limit), which is explained by age, gender, race, and weight. A slight deviation from the norm in older patients is not a pathology.
Since one of the main parameters involved in calculating filtration rate is creatinine produced in muscles, men with normal muscle mass have a higher GFR than women. The normal range for men and women of fertile age is 90-120 ml/min.
More detailed gradation of indicators by age
| Age | 20-30 years | up to 40 years old | up to 50 years | up to 60 years old | up to 70 years old | 70+ |
| Average value in ml/l | 116 | 107 | 99-100 | 94 | 86 | 76 |
Children's GFR values change with age. In newborn babies, the filtration rate is low because the body is in the adaptation stage. During the first year of life, indicators gradually rise.
Table of values for a child of the first year of life
| Age | 1-7 days | up to a month | up to 3 months | up to six months | 6-12 months | from year |
| Average value in ml/l | 39-60 | 47-68 | 58-86 | 77-114 | 103-157 | 127-165 |
If the patient's indicators do not fall within the reference interval, this means a violation of glomerular filtration. Changes in GFR are a clinical sign of renal dysfunction. The cause of the failure is determined using additional kidney tests.
Methods for calculating GFR
There are several methods for determining the filtration capacity of nephrons. Carrying out a clearance test or determining the purification coefficient includes:
- analysis of creatinine in plasma and urine collected during the day;
- assessment of the relationship between the obtained values.
Blood sampling and urine collection are carried out in accordance with accepted rules of laboratory diagnostics. Before the study, the patient must reduce physical activity, eliminate strong tea, alcoholic drinks and coffee from the diet, and stop taking medications and dietary supplements.
Rehberg's test
The amount of creatinine in a blood sample is determined from the patient. Next, the person independently collects daily urine. The initial morning portion of urine is skipped. The countdown starts from the second urination.
The urine excreted during each emptying is collected into one pharmaceutical container with a capacity of 2.7 liters or a sterilized and dried three-liter container. On a special form, you must note the volume and time of each urination. The container should be stored in the refrigerator under an airtight lid.
After 24 hours, the urine should be mixed. Separate a 50 ml portion of urine from the total amount, pour it into a small sterile container, accompany it with a completed form and deliver it to the place of analysis. The average clearance rate in adult patients is 125 ml/min.
Cockcroft-Gold test
The Cockcroft-Gold test differs from the Rehberg test in that you need to drink 2 glasses of unsweetened liquid and empty the bladder after 20 minutes. The next time you urinate, the volume of urine, the time and duration of the act of emptying are noted.
A blood test is taken between urine collection procedures. Clearance is determined by the formula: GFR = Km/Kk×V (Km – creatinine in urine, Kk – creatinine in blood, V – volume of urine excreted in one minute).
MDRD (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) technique
A modified version of determining GFR, assessing not only the rate itself, but also its change in connection with age and the development of renal pathologies, taking into account all the patient’s personal data.
Option for calculating GFR without taking into account albumin in the blood
Calculation option taking into account albumin in the blood
CKD-EPI equation
This calculation of GFR is considered the most informative if there are doubts about the results of previous studies.
GFR according to filtration clearance formula
By calculating the volume of filtered plasma, it is possible to identify abnormalities in kidney function. As a rule, all formulas for calculating GFR come down to the ratio between a substance in urine (which is selected by a specialist) and blood.
For example, inulin is often used as a control substance. Using measurements, the level of another substance, insulin, is determined. The dependence is determined as follows: the more inulin in the urine relative to inulin in the blood, the faster urine is formed. This characteristic is called inulin clearance.
The formula for calculating filtration clearance of inulin is as follows:
GFR=(Min*Vur)/Pin
- Min – inulin in final urine
- Vurine – volume of urine (final)
- Pin - inulin in the blood
Calculation using the MDRD formula
The MDRD formula has become widespread in European countries. However, some scientists believe that this test is low-informative and cannot be used to make a final diagnosis. However, it is commonly used to test kidney function in pregnant women.
The purpose of the MDRD is to determine GFR according to the patient's age, sex, and serum creatinine level.
MDRD calculation method:
GFR = 11.33*GFR – 1.154*Age – 0.203*P
- CCC = blood creatinine concentration
- Age – patient’s age
- P – gender indicator (for women it is 0.742)
This formula is usually used when a reduced GFR is suspected, since an increased GFR may result in incorrect calculation results. However, the good thing about the formula is that it can be used to track age-related changes and their impact on kidney function.
Indications for a clearance test
The study is prescribed for suspected renal pathologies, according to the symptom complex presented by the patient:
- consistently elevated blood pressure (blood pressure) and heart rate (heart rate);
- pain in the lumbar region;
- swelling of the upper and lower extremities, face or periorbital area;
- cloudy urine.
The study is indicated for patients with chronic diseases of the kidneys, heart, endocrine system, pregnant women, and professional athletes.
Important! An abnormal glomerular filtration rate (high or low) is not a diagnosis, but a consequence of the underlying disease. Based on the combination of symptoms, the patient should be prescribed an extensive examination of the kidneys, heart, and endocrine system organs.
Why is the Rehberg test performed?
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) reflects how well the kidneys perform their function. In various kidney diseases, the glomerular filtration rate changes and is significantly reduced in renal failure. GFR is also used to classify the severity of chronic kidney disease.
GFR can be measured using formulas using only the serum creatinine concentration. GFR depends on many factors, for example, a person’s gender, age, race, diet, height, weight (therefore, the formula includes a value of 1.7 m2 - the average value of a standard body surface area), etc.
Determination of creatinine clearance, or GFR, should be periodically carried out for people who are at risk of developing chronic kidney disease, for example, those diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, gout, etc.
Deviations in GFR indicators
The root causes of pathological changes in glomerular filtration rate are:
- diseases and acute conditions not related to the urinary system: dehydration (dehydration), sudden nervous shock, chronic purulent-inflammatory processes, hypertension and hypotension, abnormal oncotic pressure, etc.;
- pathologies of the renal apparatus itself.
Consistently low GFR is characteristic of chronic renal failure (CKF). Based on the rate of glomerular plasma clearance, five stages of chronic renal failure severity are distinguished.
Deciphering the stages of chronic renal failure according to GFR
| 1 – close to normal | 2 – light | 3-A – moderate | 3-B – pronounced | 4 – heavy | 5 – terminal |
| 90 | 60-89 | 49-59 | 30-40 | 15-30 | |
| observation, changing eating habits, quitting alcohol | strict control, diet | diet, nephrotic drugs | constant use of medications | hospital treatment | hemodialysis |
The presence of chronic renal failure is indicated by low GFR, which does not change over 3 months. A decrease in filtration rate is a sign of problems with the formation of primary urine, characteristic of the following diseases:
- atherosclerotic stenosis (narrowing) of the renal vessels. The pressure in the glomeruli drops due to a lack of blood supply to the kidneys;
- hypotension and cardiac decompensation. In pathologies, the stability of intrarenal pressure is disrupted;
- kidney stones (nephrolithiasis);
- inflammation of the stroma and tubules of the kidneys (interstitial nephritis);
- death of the kidney parenchyma, its replacement by connective tissue (nephrosclerosis);
- mechanical damage to the glomerular filter (membrane) due to injury;
- high oncotic pressure, due to which water is retained in the bloodstream.
GFR is influenced by malignant and benign parenchymal neoplasms of the kidneys. Elevated GFR values accompany hypertension, adrenaline imbalance in the blood, diabetes mellitus, and low oncotic pressure as a result of dehydration of the body. Glomerular filtration rate changes in some autoimmune pathologies.
What is it, what does it show and in what units of measurement?
The main problem of the kidney is that under the influence of heavy stress, nephrons die.
As a result, it works worse and worse as a filter, since new elements will no longer be formed. As a result, a lot of different diseases and complications arise. People who drink alcohol, eat a lot of salty foods and have bad heredity are especially prone to this.
If, based on any symptoms, the doctor determines that the patient’s complaints are related to the kidneys, he may be prescribed a diagnostic method such as GFR, that is, determining the glomerular filtrate rate .
Read our article about how the human kidneys work.
This method determines how quickly the filters in the body cope with the task , that is, they cleanse the blood of harmful substances. This is fundamental in determining some diseases, including chronic ones.
In order to determine GFR, special formulas are used. There are several of them, and they differ in information content. But everywhere they use one term, namely clearance. This is an indicator by which you can determine how much blood plasma will be processed in one minute.
Correction
First of all, it is necessary to find out the root cause of the violation of the cleansing ability of the renal apparatus. Treatment is prescribed based on the main diagnosis. If there are minor deviations in GFR values, the patient is prescribed nutritional therapy. The diet includes:
- maximum reduction in the amount of salt and salty foods consumed;
- exclusion of hot sauces, seasonings and spices from the menu;
- restriction of protein in the diet;
- compliance with the drinking regime.
If kidney function is impaired, you must completely abstain from alcoholic beverages.