Structure of the hearing organ
Sounds surround a person from birth. There are 3 sections of the hearing organ:
- outer ear;
- middle ear;
- inner ear.
The outer ear is the visible part of the organ. It is represented by the auricle and the external auditory canal. The concha is a funnel-shaped cartilage covered with skin. On its surface there are various formations: pits, curls, hills. They help improve sound quality, make it louder and direct it into the ear canal.
The fibers of the ear muscles are attached to the concha. In the process of evolution, man has lost the ability to “move his ears” in order to more accurately localize sounds; these muscles work in rare “lucky” people. The skin of the shell has sebaceous and sweat glands.
The external auditory canal is a winding canal, the length of which is slightly more than 2 cm, and the diameter is up to 0.7 cm. In it, the sound signal continues to be amplified and transmitted to the middle ear. The passage is lined with skin containing sebaceous and sulfur glands. Earwax is a yellowish substance that provides hydration to the canal and protection against infectious agents. When accumulated and compacted, it forms plugs that disrupt the movement of the eardrum. This can lead to conductive hearing loss.
Describing the structure of the hearing organ, anatomists indicate that the outer part of the canal has cartilaginous walls, and the part in contact with the middle ear has bone walls. The structures of the middle and inner ear are located in the body of the temporal bone.
The eardrum is a thin membrane covered on the outside with skin and on the inside with mucous membrane. In young children, it has an opening that exposes the middle ear to the outside environment and is more vulnerable to infection. It closes by 3 years.
The middle ear is a cavity whose volume is slightly more than 1 cubic centimeter. It contains three small auditory ossicles, which are connected to each other in a chain:
- hammer;
- anvil;
- stapes.
They are named so because of their resemblance to everyday objects. The stapes connects to the window of the vestibule. The middle ear is also connected to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian tube.
The inner ear is the most bizarre formation of the human hearing organ. It consists of:
- vestibule (vestibulum);
- snails;
- semicircular canals.
The organ of hearing includes only the cochlea. It contains lymphatic fluid and stretches fibers (the main membrane). Each of the fibers is like a small string and “responds” (resonates) to a sound of a certain frequency. There are about 25 thousand of these fibers. On the wall of the cochlear canal there is a receptor field, which consists of nerve (hair) cells - the organ of Corti. The death of hair cells can lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
Pelvic organs
Located in a space limited by the small pelvis. There is a difference between male and female pelvic organs, which is determined by gender.
The small pelvis includes:
- part of the intestine is the rectum, which is about 15 cm;
- the bladder, which has a different location in men and women. In women it is in contact with the walls of the vagina and uterus, in men it is adjacent to the flows and seminal vesicles, as well as the rectum;
- female genital organs: vagina, uterus, ovaries;
- male genital organs: seminal vesicle; prostate.
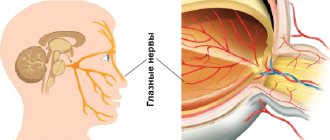
What is the organ of hearing and balance?
The human ear is responsible not only for the perception and further transmission of sound information. The inner ear is the organ of hearing and balance. This is a complex formation in which a wave of mechanical vibrations, like sea surf, spreads through the lymphatic fluid and sways the processes of nerve cells, forming an electrical impulse. This signal carries information about the volume, duration, and pitch of sound to the brain.
Another part of the inner ear is the organ of balance (vestibular apparatus). It consists of: the vestibule, the three semicircular canals located in it, the utricle and the sac. The vestibule is a round-shaped cavity with a diameter of about 5 mm. It is located between the canals and the cochlea. The canals are mutually perpendicular and at the junction with the vestibule they have expansions - ampoules. The channels are filled with endolymphatic fluid.
The utricle and saccule are fields of nerve cells that perceive various irritations. A change in body position is registered by the receptors of the uterus and causes a reflex reaction of the muscles, helping a person maintain balance. The vibration is picked up by the ends of the sac.
The vestibulocochlear nerve runs from the organ to the brain.
quiz
1. In which body cavity are the liver, spleen and gall bladder located? A. Abdominal cavity B. Dorsal cavity C. Pelvic cavity
Answer to question #1
right. These organs, along with most of the body's organs, are found in the abdominal cavity. The pelvic cavity contains mainly the reproductive organs and bladder, and the spinal cavity contains the brain and spinal cord.
2. Which of the following is NOT found in the thoracic cavity? A. Heart B. Lungs C. Brain
Answer to question No. 2
C is correct. The brain is located in the dorsal cavity. The abdominal cavity of the body, which contains the thoracic cavity, contains most of the body's organs. The thoracic cavity is further divided into the left and right pleural cavities, which contain the lungs, and the mediastinum, which houses the heart in its own pericardial cavity.
3. A scientist studying body cavities and the sizes of various organisms comes to the conclusion that large organisms need body cavities to facilitate their movement. Which of the following statements supports this idea? A. The smallest organisms have body cavities, while some of the largest do not. B. As organisms increase in size and complexity, they tend to have more body cavities. C. All organisms have body cavities, and the fastest ones have the fewest.
Answer to question number 3
B is correct. This is true. Flatworms have no layers, while more complex segmented worms have entire coeloms. Thus, segmented worms can grow much larger. Although the theory is not fully developed, it is clear that larger organisms tend to have more body cavities. This may be to support their complex movements, or it may simply be a by-product of the development of the third germ layer.
Functions of the hearing organ
When talking about the functions of the hearing organ, physiologists describe them in accordance with their anatomical structures. So, each department has its own specific tasks:
- catches sounds and directs them further (outer ear);
- transmits sound waves (outer and middle ear);
- protects against infections, loud sounds, damage to internal parts (outer ear, eardrum);
- transforms sound energy into electrical energy (inner ear).
The functions of hearing are evolutionarily closely related to danger notification and communication in the community. In order to maintain your ability to hear for a long time, you must follow simple rules for preventing hearing loss.
What organs are hidden in the abdominal cavity?
The abdominal cavity contains parts of the body that enter the digestive system. These include:
- stomach;
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- duodenum;
- small intestine;
- colon;
- rectum;
- anus.
Stomach
The main part of the digestive system. It is a continuation of the esophagus, which is separated from it by a valve covering the entrance. The stomach is shaped like a pouch, fills with food and produces juice (a specific liquid) rich in enzymes that break down food.
Intestines
The intestine is the longest part of the digestive tract. It begins after the gastric outlet. It is shaped like a loop and ends with an outlet hole. The intestine consists of:
- small intestine;
- colon;
- rectum.
The small intestine consists of the duodenum and ileum, which pass into the large intestine, and the large intestine into the rectum. The main function of the intestines is to digest food and remove its remains from the body.
Liver
The largest gland in the human body. Also involved in the digestion process. The main task is to ensure metabolism and participate in the process of hematopoiesis. It is located immediately below the diaphragm and is divided into two parts called lobes. It connects to the duodenum, is closely connected with the portal vein, communicates and functions with the gallbladder.
Spleen
Located under the diaphragm. The main functions are:
- in the formation of blood elements;
- protection of the body.
The spleen changes in size depending on the amount of accumulated blood.
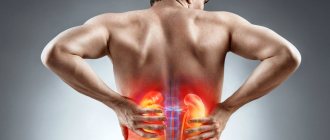
Kidneys
The kidneys are also located in the abdominal cavity, despite the fact that they are not related to the digestive tract. Kidneys - consist of paired parts that perform an important function: regulation of homeostasis. They have the shape of beans and are involved in the process of urination. The ureters are located directly above the kidneys.
Bladder
It is a specific container - a bag designed to collect urine.
Features of the hearing organ
Human hearing organs are paired. What does this mean? A person can listen with both the right and left ear at the same time. Binaural hearing gives more information about the sound and amplifies it under certain conditions.
If the source of mechanical vibrations is at the same distance from the right and left ears, the signal volume increases by 50%. This means that in case of unilateral impairment, compensation with the help of a hearing aid of even low power significantly improves the quality of life.
Perceiving with two ears is better for determining the localization of sound. Binaural hearing gives:
- surround sound sensation;
- idea of the location of the source.
This helps you avoid danger (such as an approaching car) and isolate useful sounds from all the background noise when talking to one person in a noisy room.
Read more about hearing characteristics in this article.
If you experience any hearing problems, you must urgently undergo a hearing test using professional equipment. If you seek help in time, you have a chance to fully restore your hearing.
Location of human organs
They are found in several specific cavities.
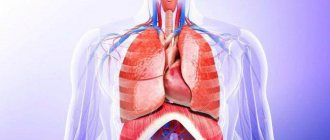
So, in the chest, located within the boundaries of the chest and upper diaphragm, there are three others. This is a pelicard with a heart and two pleurals on either side with lungs.
The abdominal cavity contains the kidneys, stomach, most of the intestines, liver, pancreas and other organs. It is the torso located below the diaphragm. It includes the abdominal and pelvic cavities themselves.
The abdominal cavity is divided into the retroperitoneal space and the peritoneal cavity. The pelvic region contains the excretory and reproductive systems.
To understand in even more detail the location of human organs, the photo below serves as an addition to the above. It shows cavities on one side, and the main organs that are located in them on the other.