Calcium oxalate monohydrate wewellite than dissolve. My diet for oxalate stones
What is allowed with oxalates
Cauliflower and white cabbage, lingonberries, carrots, apricots, eggplants (in moderation), bananas, pears, grapes, pumpkin, cucumbers, prunes, cherries, barberries, soaked herring, cilantro, potatoes (boiled only), cucumbers, peeled, turnips, apples, apricots, watermelons, melon, peaches, quince, dogwood and other berries and fruits, birch sap, rowan, prune juice, dried apricots, pears, squash and eggplant caviar.
Wheat bread, made from 2 grade flour, gray, rye, vegetable oil, walnut, hazelnut, pine nut
Consume dairy products only in the first half of the day! Fermented milk drinks, kefir, sour cream in small quantities, cottage cheese (up to 400 grams per day), fresh yogurt, butter and Provencal oil no more than 60 grams. per day, 1 egg per day, vegetable soups without adding peas, beans, mushrooms, lentils, beans, sorrel, spinach, parsley and without frying and sauteing flour and vegetables (the best option is dietary cabbage soup from fresh cabbage), fruit soups .
Weak tea, coffee (preferably surrogate) with milk (no more than 50 grams per day). Boiled, fried and baked meat, poultry and low-fat fish (boil first) – eat 150-200 grams each. in a day.
For those who are susceptible to urolithiasis, urologists advise eating less foods containing animal proteins. Dairy, dietary types of boiled sausages, unsalted lard in small quantities.
Pasta and cereal dishes. Add pasta only to soups in small quantities. A lot of vegetables, fruits and berries, in addition to the above, in raw, boiled, baked form, except for sour varieties (cranberries, Antonov apples, gooseberries, red currants), mild tomato paste, sweet tomatoes, sour sauerkraut, no more than 30 grams. on the day of sugar, jelly, compotes, white sauces that do not contain vinegar. Salt no more than 2 grams. per day.
Wewellite food. Diet for oxalates in urine
The reasons for the appearance of oxalates in the urine and the basis of the concept of “diet for oxaluria”
Oxalates found in urine are salts of oxalic acid, which are brown crements with sharp edges. A disease accompanied by increased secretion of oxalates in the body is called oxaluria. This disease can develop for several reasons, which can be either hereditary or acquired due to the following factors:
- Intake of vitamin C in large quantities from food and foods enriched with oxalic acid;
- The presence of chronic diseases that increase the content of oxalates in the urine, for example, pyelonephritis or diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and other inflammatory bowel processes;
- Insufficient intake of vitamin B6;
- Consequences of surgical interventions performed on the intestines, which can also increase oxalates in the urine.
Treatment of symptoms that provoke the appearance of oxalates in the urine above normal values is based on a diet that excludes or reduces to a minimum all foods high in oxalic acid, as well as its salts.
Foods prohibited for consumption if there are oxalates in the urine
A diet for oxalates in the urine excludes from the diet such foods as:
- Potatoes, eggplants and tomatoes.
- Soy and beans.
- Celery, chard and beets.
- Chili pepper and green pepper.
- Parsley and leeks.
- Spinach and sorrel;
- Rhubarb.
- Asparagus.
- Parsnip.
In the category of foods that should be limited in intake, many nutritionists include coffee and tea, chocolate and cocoa, pine nuts and walnuts, almonds, peanuts, sesame seeds and sunflower seeds.
A diet with oxalates in the urine gives patients the opportunity to consume the required amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats in the diet and ensures a sufficient supply of calories to the body. Excluding the products listed above from the menu will help avoid the development of calcium oxalate crystalluria, and as a result, the appearance of stones in the bladder and kidneys.
Foods allowed in small quantities for oxalates
Fruits and berries enriched with oxalic acid salts, which should be consumed with caution and in minimal quantities, include:
- apples and grapes;
- plums and oranges;
- gooseberries and cranberries;
- blackberries and raspberries;
- Red Ribes;
- kiwi;
- figs and dates.
Please note that eating fruits that are not fully ripe can increase the excretion of oxalates in the urine, as they contain glyoxylic acid.
Recommended list of foods for oxalates
If oxalates are detected in the urine, you must adhere to a certain diet, which includes the following foods:
- cauliflower and white cabbage;
- from vegetables: carrots, eggplant in small quantities, pumpkin, cucumber, cilantro, boiled potatoes;
- berries and fruits: apricot, pear, banana, lingonberry, prune, dried apricot, cherry, watermelon, melon, peach, quince, dogwood, rowan, black currant, sea buckthorn;
- wheat bread made from second-grade flour, gray and yesterday's rye bread;
- dairy products: sour milk, kefir, a little sour cream and cottage cheese;
- chicken egg no more than 1 piece per day;
- soup: vegetable or with the addition of cereals, lean meat and fish;
- from drinks: weak tea and coffee with milk, jelly and compote;
- pasta and cereals.
Preparations for dissolving oxalate kidney stones. Methods for dissolving stones
It is difficult to cure the disease. There are no principles for dissolving oxalate stones in the kidneys yet. You can only crush them, but this is not always possible, since their density does not allow this. Large elements can be removed surgically. If large oxalate forms, experts recommend one of the following surgical interventions:
- endoscopic surgery;
- classical open intervention.
A small stone can be crushed using ultrasound. All formed fragments are removed using the same method. In the presence of microliths and sand, conservative methods of therapy are usually used. It is important to completely clean the urinary tract and prevent recurrence of the pathology. How to remove oxalate stones from the kidneys? Conservative treatment includes several stages. Among them:
- the necessary water load to cleanse organs and systems of excessive amounts of salts (you need to drink 2 liters of liquid daily);
- moderate physical activity is an important way to remove sand and microliths from the body (jumping and running are best);
- compliance with medical recommendations: medications to remove oxalates and normalize metabolism are used according to certain regimens.
Often all medications are selected in a comprehensive manner. Most of them at the same time:
- have an antimicrobial effect;
- relieve inflammatory processes;
- dissolve oxalates and remove them from the body.
Infection can often occur in the presence of stones. In such cases, antibacterial agents are necessarily prescribed. Most often these are sulfonamides, but other drugs can also be used. It is possible to use antispasmodics that relieve pain, facilitating the removal of oxalates without damage.
Basic principles of the diet
Snacking on the go with achalasia cardia is unacceptable. Achalasia cardia can progress, leading to not the most pleasant consequences, for example, inflammation of the esophageal wall. To protect yourself from complications and alleviate the condition, the patient must follow the recommendations of the attending physician on proper nutrition. In this case, we are talking not only about specific foods that can or cannot be consumed, but also about the rules of eating themselves.
- Firstly, food must be chewed thoroughly, since small pieces will pass from the esophagus into the stomach much more easily. At the same time, you should not be distracted or rush while eating. It is best to drink liquid with your meals as this will put extra pressure on the esophageal sphincter, allowing it to relax.
- Secondly, you need to eat frequently (4-5 times a day) in small portions. Overeating will cause food particles to accumulate in the esophagus, making the situation worse. At the same time, foods should not be irritating, namely too hot or cold, since this also negatively affects the digestion process.
- Thirdly, after eating, you should not do physical activity for some time, especially bending your body. You should also not lie down, as this position will obstruct the passage of food into the stomach. As for sleep, during it the head should be slightly elevated above the level of the body, which will allow food to pass freely through the esophagus without accumulating. To do this, it will be enough to place another pillow under the main one.
Vewellite diet. Wewellite calcium oxalate monohydrate
Vitamin therapy for oxalic acid diathesis should ensure that the body is saturated with vitamins A, B2, D and phytin. These vitamins are found in carrots, raspberries, sea buckthorn, black currants, and apples. As a last resort, carrying out vitamin therapy, but take: renitol, riboflavin, calciferol, phytin. As herbal medicine, preference should be given to low-component collections that include medicinal raw materials with bactericidal and antihypoxic properties, as well as components that normalize the colloidal structure of urine.
The leaves and buds of birch, black elderberry flowers, lingonberry leaves and fruits, cranberry fruits, peppermint herb, kidney tea, bearberry leaves, rose hips, sage herb, and fragrant violet roots have an oxalatolytic effect, that is, the ability to increase the solubility of oxalate stones.
Diet for oxalate stones.
Extracts from these plants should be taken after meals. Antihypoxant plants: nettle leaves, linden leaves, cudweed grass and some others help reduce the formation of oxalic acid in the human body.
For oxalate diathesis and the formation of oxalate stones, the choice of herbs and individual plants is relatively small. During periods of exacerbations and for preventive purposes during remission, the following fees can be used. Grass drop cap - 2 parts.
Diet for oxalates in urine
Cornflower flowers - 3 parts. Veronica grass - 3 parts. Take warm with honey instead of tea. Prepare a new infusion and drink it at night.
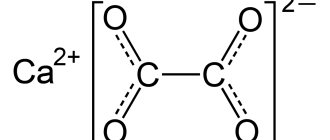
Terms: months Cost of products: rub. The main predisposing factor for the formation of calcium oxalate stones is hyperoxaluria, which means high urinary excretion of more than 40 mg per day of oxalic acid. The oxalic acid anion combines with a calcium cation to form a soluble salt calcium oxalate, most often in the form of a monohydrate - wewellite calcium oxalate-monohydrate and a dihydrate - weddelite calcium oxalate dihydrate. One of the reasons for the formation of oxalate stones in the kidneys is excessive intake of oxalates from food or increased intestinal permeability, which increases the penetration of oxalic acetic acid through the intestinal mucosa and its entry through the kidneys into the urine.
It is important to monitor the pH of urine, given that a pH in the range of 5.5-6.5 is optimal for the precipitation of oxalic acid salts. There are no special requirements for culinary processing of products, but at the same time it is preferable to boil or stew the products. Vegetables and fruits in the diet include cauliflower and white cabbage, boiled potatoes, eggplant and squash caviar, carrots, eggplants in moderation, pumpkin, cucumbers, apricots, bananas, grapes, pears, prunes, apricots, cilantro, sour apples, watermelons, melon, peaches, dogwood, quince, rowan.
Drinks include juice from dried apricots, pears, prunes, birch, cucumber juice, compotes, jelly, slightly alkaline mineral waters. The diet completely excludes foods rich in oxalic acid, such as strong tea, sorrel, spinach, kidney by-products, tongue, brains, liver, fatty meats and fish, bread kvass, jelly, gelatin-containing dishes, cocoa, coffee, chocolate, rhubarb, mushrooms , pickled vegetables.
During the period of exacerbation, the consumption of potatoes, beets, tomatoes, onions, and carrots is also limited. Salted cheeses, canned food, smoked meats, fish caviar, as well as soups prepared in strong meat, fish and mushroom broths and containing legumes, spinach, sorrel, and vegetable caviar are excluded. The diet is limited to foods containing a lot of vitamin C - lemon, grapefruit, oranges, currants, rose hips, rowan berries, Antonov apples, strawberries, gooseberries, cranberries, tangerines, sweet peppers, horseradish, dill, wild garlic.
Calcium oxalate monohydrate and calcium oxalate dihydrate are calcium salts that form kidney stones. The similarities between the two far outweigh the minimal differences.
If you are prone to oxalate stones, treatment and prevention are the same no matter what type of oxalate stones you form. Chemically, calcium oxalate dihydrate and calcium oxalate monohydrate are almost identical. The molecules of both substances have two carbon atoms and one calcium atom. The only difference is that calcium oxalate dihydrate is weakly bound to two water molecules, whereas calcium oxalate dihydrate is weakly bound to one water molecule. For this reason, the molecular weight of the dihydrate is Kidney stones are pieces of solid matter that become wedged into the ureters, the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
Stones are classified by the type of material from which they are composed, such as struvite, calcium oxalate, uric acid or cysteine. Calcium oxalate stones can be made from calcium oxalate monohydrate or calcium oxalate dihydrate. If you get kidney stones once, you are at risk of getting them again.
The study found that patients treated with monohydrate stones tend to be older. Men and women were equally able to pass any type of stone.
Diet for urate stones (urates)
Limit:
concentrated meat and fish broths, offal, sorrel, spinach, peas, beans, beans, red wine, beer, pickles, smoked meats, marinades, coffee, cocoa, chocolate.
Recommended:
tea with lemon, citrus juice in between meals (prevents the formation of urates); eat meat, fish and poultry only in boiled form, no more than three times a week; milk and all dairy dishes, eggs, rice and oatmeal, vegetables, fruits, day-old bread, black and red caviar, honey, marmalade, marshmallows, walnuts.
Calcium oxalate monohydrate. Calcium containing
The appearance of calcium salts in the urine is associated with three factors:
- The hardness of the water used.
- The nature of calcium metabolism in the body.
- Kidney performance.
Calcium oxalates account for a total of 80% of cases. Below are two minerals from the mentioned category.
Veddelit
The reason for the deposition of weddelite is the abundance of magnesium and calcium salts. There is a correlation between the fluid consumed and the presence of the disease. People in areas with hard water live at increased risk. In areas with soft water, the risk of cardiovascular disease is increased.
Weddelite deposition
The chemical formula of weddelite is described as calcium oxalate dihydrate. The resulting rock is light, yellowish, and loose. Shows weak birefringence. Considered insoluble.
Wevelite
Calcium oxalate monohydrate. Formed when there is an excess of oxalic acid in the urine. According to scientific data, these products contain the named component in descending order of concentration:
- Star-shaped carambola fruits.
- Black pepper.
- Parsley herb.
- Poppy seed.
- Amaranth genus.
- Spinach.
- Chard and regular beets.
- Cocoa beans.
- Nuts.
- Berries.
- Kariota.
- Beans.
Excess oxalic acid is found in regular tea. From plants: sorrel, white pigweed and sorrel, roots and leaves of rhubarb and buckwheat.
The shape of the crystals resembles the oval shape of red blood cells. They are constantly formed in microscopic sizes and are removed in the urine. Light brown with a well-defined birefringence effect. Extremely hard, difficult to dissolve.
Oxalic acid
Let's say a little more about oxalic acid. Small crystals of hydrates constantly form in the bladder and are excreted. The substance is the basis of diseases:
- Gout.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Vulvular pain.
People with these symptoms should beware of foods high in oxalic acid. Scientists estimate that magnesium oxalate is 567 times more soluble than the similar calcium compound—an additional reason to consider the latter of the two elements.
The role of iron in the development of gout can be traced. Doctors attribute the highest percentage of disease development to this element. You should be careful with dark beer, yoghurt and liver. Smokers should think about cadmium, which acts as a catalyst for the conversion of ordinary ascorbic acid into oxalic acid. In parallel with foods rich in oxalic acid, it is recommended to use calcium compounds. This paradoxical regime causes precipitation of oxalates directly in the intestines (97% of the total).
Patients are strictly not recommended to drink cold black tea. It has been shown that by drinking about 3 liters, you can earn stones extremely quickly. A separate line specifies grazing of livestock on land planted with grass with an excess of oxalic acid. In such cases, even poisoning has been reported.
Let us add that the bacterium Oxalobacter formigenes lives in the colon, which is responsible for the utilization of oxalates. If this population is killed by antibiotics, harmful products are absorbed into the blood, leading to the described consequences. A diet for stones is definitely indicated. Removed from the diet:
- Spicy dishes and smoked meats.
- Alcohol.
- Spices.
- Seasonings.
The consumption of eggs, sour cream, mushrooms and vegetables is reduced.
Phosphates
Calcium phosphates account for 10% of cases. Struvite is a combination of carbonate apatite and magnesium ammonium phosphate. The development of dysbiosis leads to the spread of harmful bacteria throughout organ systems. Some reach the genitourinary:
- Klebsiella.
- Proteas.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The mentioned representatives of the facultative microflora are waiting for an opportunity to cause harm, mastering the intestines in small quantities and being ignored by the immune system. A distinctive feature of struvite is rapid growth with possible relapse. More common in women.
The crystals are opaque rectangular prisms that exhibit a concentric laminar structure. The stones take on the appearance of corals.
Brushite is calcium hydrogen phosphate. They begin to grow in an acidic environment. Solid, complex shape. It is almost impossible to remove without surgery. Phosphate stones are formed for the following reasons:
- Lack of vitamins A, D and E.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Excess cocoa and coffee in food.
- Phosphaturia.
- High concentration of salt in urine.
Carbonate apatite grows in an alkaline environment when the concentration of citric acid decreases. Small crystals of off-white color, rough with an uneven surface.
Diet for phosphate stones (phosphates)
Limit:
foods rich in calcium: milk and dairy products, including yogurt, cheese, feta cheese; spices, sauces, savory snacks and seasonings.
Recommended:
meat and fish in all types, including mild fish snacks, soaked herring; weak tea and coffee without milk, bread, eggs and egg dishes (1 - 2 times a week), butter and vegetable oil; peas, pumpkin, Brussels sprouts, red currants, sour apples.
The general law for all patients with urolithiasis, regardless of the type of stones, is to drink plenty of fluids . Drink at least 1.5-2.0 liters of fluid per day (including tea and soups). The urine should be “like water”, because with a low concentration of salts, they will not fall out in the form of crystals and lead to the formation of stones!
However, there are often cases when the exact composition of the stones cannot be determined (for example, it was not possible to catch a loose stone, the examination did not reveal biochemical abnormalities). In such cases, it remains to adhere to general recommendations, of which the main one is drinking plenty of fluids. The diet should be varied, balanced, with enough vegetables and fruits. Avoid coffee and chocolate. And do not forget to periodically monitor the condition of your kidneys using ultrasound and urine tests.
Wewellite (calcium oxalate dihydrate). Determination of the composition of urinary stones
The only direct and 100% reliable way to determine the composition of urinary stones is a chemical analysis of the passed urinary calculus (or its fragments). This is why it is so important, after an attack of renal colic or undergoing a procedure for crushing stones, to urinate in a transparent jar and carefully check the excreted urine for the presence of solid inclusions (they can be very small, in the form of sand). In case it is impossible to carry out a chemical analysis (for example, the stone is located in the kidney, or it was not possible to catch it), indirect signs are used that make it possible to judge with greater or less certainty the composition of urinary stones. These signs include:
- changes in the biochemical blood test (increased levels of calcium, phosphorus, uric acid);
- changes in general urine analysis (presence of salts in sediment);
- changes in daily biochemical urine analysis (increased excretion of calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, oxalates)
In addition, X-ray examination can provide important information on the composition of kidney stones. Stones containing calcium (such as oxalates and phosphates) are clearly visible on X-rays, while urate stones (which do not contain calcium) do not block X-rays and therefore are not visible on X-rays (so-called X-ray negative stones). , in most cases, the doctor is able to determine the chemical composition of the stones, which is crucial both in selecting the optimal treatment and in preventing the re-formation of stones (see).
Classification of stones
Stones removed from the kidneys come in different types, colors, and sizes. Depending on the causes of formation, stones are divided into:
1. Non-infectious stones
- Calcium oxalates
. This is the most common type of kidney stones. First, calcium oxalates are found in crystalline form in the urine. Doctors attribute this to a violation of oxalic acid metabolism, constant stress and insufficient water consumption. Transforming into kidney stones, calcium oxalates, if natural removal of stones is not possible, require surgical removal (in the presence of large stones/staghorn stones) or remote crushing. Treatment of inflammatory complications of kidney stones is carried out with the help of vitamins, antispasmodics and antibiotics. Surgeries are required in the presence of oxalate stones, if their size exceeds 1.5 cm. In other cases, they resort to remote crushing or drug therapy. - Calcium phosphates
. Phosphates are divided into two types; only brushite is non-infectious. It appears in the kidneys when there is a high concentration of calcium and phosphates in the urine. Calcium phosphate stones grow quite quickly, but due to the predominance of alkalis in the composition, they are easily crushed and dissolved. Most often, phosphate stones are removed with the help of properly selected therapy and diet. If the disease is advanced or can lead to complications, then the formations are removed by crushing. If the cause of stone formation is an infection, then antibacterial treatment is first carried out. - Uric acid
. Such stones form when the urine pH is low and the content of uric acid and blood in the urine is high. Most often, those who suffer from uric acid stones consume a lot of protein, suffer from impaired production of ammonium excretion and even simple diarrhea. Another reason for the formation of such stones is the high acidity of urine. Uric acid stones are removed surgically in less than 5% of cases. Most often, drug treatment is sufficient to dissolve the stones and remove them naturally. Patients with this type of urolithiasis must adhere to a strict diet until the problem is completely eliminated.