What is cauda equina syndrome?
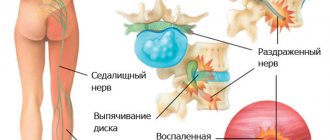
The “cauda equina” is a group of motor, tactile, and autonomic nerve nodes. It is located below the lower back and is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses to the pelvic organs, as well as to the lower extremities. When an inflammatory process occurs in the cauda equina area (due to the development of any other disease), traumatic injury, or compression of nerve endings, a person begins to feel pain below the lower back. This condition is called cauda equina syndrome. In this case, we are often talking about severe, unbearable pain, as well as a disruption in the functioning of nerve endings, which can later lead to paralysis.
Clinical manifestations (symptoms) of the disease
Since the cauda equina innervates the lower extremities and pelvic organs, accordingly, symptoms of damage to it will manifest themselves from these structures. May be observed:
- pain;
- sensitivity disorders;
- muscle weakness;
- bladder dysfunction;
- dysfunction of the rectum;
- vegetative-trophic disorders in the lower extremities;
- sexual function disorders.
Let's take a closer look at each of the symptoms that make up this syndrome.
The pain can be local and radicular. Radicular pain often appears first and is associated with direct irritation of the roots. They represent sharp, sometimes shooting sensations along the nerve roots, that is, the pain itself spreads down one or both legs, radiating to the area of the buttocks, perineum, and sacrum. Such pain intensifies with movement and walking. Local pain is felt in the spine and is more dull and chronic. These pains are associated with irritation of the soft tissues and structures of the spine. The same patient may experience only one type of pain.
Sensory disorders
Sensory disturbances are a feeling of numbness in the sacrum, perineum, buttocks (so-called “saddle anesthesia”) and in the legs along the radicular type (in the form of vertical stripes from top to bottom). Sensitivity disorders are asymmetrical (mosaic) in nature.
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness develops in the legs and worsens when walking. In combination with pain, this sometimes forces the patient to stop and rest before continuing to move. Sometimes patients have difficulty even standing upright.
Bladder dysfunction
Bladder dysfunction develops later than pain, sensory disturbances and muscle weakness, although there are exceptions. Impaired urinary function can be in the form of difficulty starting urination, urinary retention, lack of urge to urinate, and a feeling of bladder fullness. At an advanced stage of the process, urinary incontinence may develop.
To study "Diprospan" injections: reviews for osteochondrosis
Dysfunction of the rectum
Dysfunction of the rectum, as well as disorders of the bladder, is observed later than pain in the specified area. They manifest themselves as a lack of urge to defecate, impaired passage of gas, constipation, and in advanced cases (rarely) - fecal incontinence.
Vegetative-trophic disorders
Vegetative-trophic disorders are observed much less frequently. This may include dryness and thinning of the skin on the legs, peeling, impaired sweating, redness or bluishness of the skin, and impaired hair growth.
Sexual function disorders
Sexual function disorders consist of erectile dysfunction, but are rarely the first symptom of damage to the cauda equina.
Causes of pathology
There are many reasons for the development of cauda equina pathology:
- the nerve endings can be compressed by the resulting intervertebral hernia;
- progressive osteochondrosis;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the spinal column;
- tumors and metastases;
- mechanical damage to the spine;
- infectious diseases (for example, epidural abscess);
- spondylolisthesis (a pathology in which one vertebra slips off another).
When performing various types of operations in medicine, epidural anesthesia is practiced, that is, when an anesthetic substance is injected through a catheter into the epidural space of the spine. If the technology for performing such a procedure is violated and nerve endings are damaged, cauda equina syndrome may occur in humans.
Treatment process
Treatment of the pathology is complex and etiotropic, including conservative and surgical techniques. To restore the function of the affected nerve bundles, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of their damage.
Patients are prescribed medications:
- Analgesics – “Baralgin”, “Ketorol”,
- NSAIDs - Diclofenac, Movalis, Ketoprofen,
- Glucocorticosteroids – “Kenalog”, “Diprospan”,
- Muscle relaxants – “Mydocalm”, “Baclofen”,
- Chondroprotectors – “Alflutop”, “Chondroitin sulfate”,
- Antioxidant drugs - Actovegin, Piracetam,
- Vascular agents – “Trental”, “Cinnarizine”, “Vinpocetine”,
- Antibiotics in the presence of an infectious process.
In some cases, therapeutic novocaine or lidocaine blockades are performed with the introduction of anesthetics or hormones. In case of bladder dysfunction, catheterization is performed, and in case of constipation, cleansing enemas are given.
We advise you to study - Spinal fracture: first aid, symptoms, treatment
Surgical treatment is indicated for patients in whom the disease rapidly progresses and significantly impairs the quality of life. If there is no effect from conservative therapy, neurosurgeons begin surgery.
- In case of osteochondrosis, a damaged intervertebral disc is replaced with a silicone implant, which increases the distance between the vertebrae and reduces pressure on the nerve roots.
- Neoplasms, hematomas, and hernias are surgically removed.
- Emergency operations are performed in case of severe dysfunction of the pelvic organs, acute injury with compression of the nerve roots and increasing lower paraparesis.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the spine can only be eliminated through surgery.
surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia
The outcome of the operation depends on the time it is performed. The sooner the compression is removed, the higher the patient's chances of recovery.
Experts recommend that patients eat well during treatment and rehabilitation, eliminating all harmful foods from the diet: fried, smoked, spicy, fatty, salty, sweet. Nutrition should be rational and balanced in terms of the amount of basic nutrients - proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It is useful to enrich the diet with fresh herbs, vegetables and fruits. It is advisable to drink clean water, herbal teas, vegetable and fruit juices, fruit drinks, and fortified cocktails. It is necessary to completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages and fight tobacco smoking.
Symptoms
There are many symptoms of cauda equina syndrome in humans, and it is almost impossible not to notice them.
Pain
The main symptom of cauda equina syndrome is pain. Its intensity directly depends on how severely the nerve endings are compressed or damaged. The pain may appear gradually and progress slowly. At first, a person may only experience short-term attacks, such as at the end of the work day. Over time, attacks of pain may intensify, and the intervals between them may decrease. The pain can be acute, occur suddenly, and shoot through the lower back. In this case, the person’s general condition worsens, performance decreases, and even after a long rest, relief does not occur.
Muscle weakness
Another symptom of a pinched cauda equina can be muscle weakness. As a result of compression of the nerve bundles, the muscles stop receiving the amount of nerve impulses they need. Accordingly, their tone is disturbed, movements of the lower extremities are difficult, although the person may not feel pain as such. It becomes difficult for a person to walk, stand for a long time, and we are not talking about running, jumping and other physical activities at all.
Numbness in the groin area, tailbone area
Loss of sensation, or numbness, is another symptom that may indicate cauda equina syndrome. Numbness is localized in the groin area, in the buttocks, thighs, and also in the tailbone area.
Problems with the bladder and bowels
Compression of the nerve endings of the cauda equina can negatively affect the intestines and urinary system. A person may be worried about: excessive gas formation in the intestines, constipation, urinary incontinence, or, conversely, urinary retention. If you experience one or more of the listed symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. In the early stages of the disease, the situation can still be corrected. In cases where the nerve bundles of the cauda equina are severely suppressed, it is almost impossible to restore their function.
Causal factors
The main reason for the development of almost any disease of the spine is its congestion, which occurs when lifting heavy objects, prolonged sitting or incorrect posture.
There are a number of reasons that cause compression and damage to the terminal nerve bundle, as well as diseases that lead to the development of the syndrome.
Ossification of the cartilage of the intervertebral disc and loss of its shock-absorbing properties are observed in osteochondrosis. The nerve endings are compressed by a rigid connection and become pinched, which results in pain. If left untreated, degenerative and dystrophic processes in the intervertebral discs lead to their prolapse and the development of a serious complication of the disease - intervertebral hernia, which further compresses the nerve fibers. This pathology is the most common cause of the syndrome.
- Subluxations of the vertebrae, fractures of the sacrum and coccyx are usually accompanied by damage to the nerve trunks. Hematomas formed after injury cause compression. This group of causes also includes iatrogenic injury, which is a complication of epidural anesthesia, neurosurgical operation or spinal diagnostic puncture.
- Benign tumors compress nerve roots, and malignant tumors grow into nerve bundles, causing their destruction. Metastases from malignant tumors of other organs can also provoke the syndrome.
- Congenital narrowing of the lower segments of the spinal column is the cause of compression of the nerve bundles.
- Spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis are acquired deformities of the spine caused by age-related changes in the human body.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes - neuroinfections, osteomyelitis and epidural abscess. The source of infection is chronic foci in the human body: caries, otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, furunculosis.
- Spondylolisthesis is the slippage of one vertebra from another.
- Demyelination of nerve fibers is a consequence of multiple sclerosis.
- Pathology of the vessels that supply the spinal cord and bleed under some circumstances can cause compression of the nerves.
Damage to the spinal nerves first causes their irritation and hyperexcitability, which is accompanied by pain. Gradually, the function of the nerve trunks weakens. Under the continuous influence of the causative factor, it completely fades away, which leads to motor and sensory disorders in the innervation zone.
Risk factors contributing to the development of pathology:
- Floor. Men are at higher risk of developing the syndrome than women. This is due to faster wear of cartilage and bone tissue.
- Injuries. The occurrence of pathology is facilitated by operations on the spine, injuries, sharp turns and falls on the back.
- Obesity. Fat deposits increase the load on the back, which negatively affects the condition of the intervertebral discs. In obese individuals, muscle tone decreases, and the spine gradually loses its flexibility.
- Smoking. Toxins disrupt the blood supply to the intervertebral discs and increase the risk of developing the disease many times over.
- Passive lifestyle. Office workers, drivers and salespeople are much more likely to develop the syndrome than people in other professions.
- Hereditary predisposition is the presence of diseases of the spine and peripheral nervous system in close relatives.
- Heavy lifting and vibration have a negative impact on the spine.
To study Extrusion of spinal discs
Diagnostics
The success of treating cauda equina entrapment syndrome in humans and eliminating the symptoms of this disease directly depend on the diagnosis. Like many other diseases of the nervous system, cauda equina syndrome is quite difficult to diagnose. The following studies can be used to identify pathology:
- Radiography
. Most often, patients with fractures in the lumbar region are referred for x-rays. X-rays help assess the degree of complexity of the fracture, the integrity of the spine, the degree of displacement of the vertebrae and the location of bone fragments. X-rays also help evaluate the condition of spinal segments in the presence of a hernia. - MRI
. This study helps to identify foci of inflammation, areas of calcification, fractures and cracks in bones, and the structure of soft tissues. - Blood tests and other routine tests.
Treatment of cauda equina syndrome is usually carried out by a neurologist
. At the initial appointment, he examines the patient, conducts special tests for sensitivity and mobility of the lower extremities, determines the exact location of the pain, and finds out what specific symptoms are bothering the patient. For diagnosis and treatment of such a complex neurological disease, you should contact experienced, qualified doctors. In particular, in St. Petersburg you can contact the Energo clinic. Our team consists of doctors of various specializations; the clinic is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment and the necessary medications for effective and quick care for patients. You can make an appointment by phone; you don’t have to wait long for an appointment in a “live queue”.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment will be effective only if the diagnosis is made in a timely manner. The longer you wait to see a doctor, the more serious the consequences may be. If you feel one of the signs described above, you need to immediately be examined and determine the cause of the ailment.
Diagnostic methods
The specialist palpates problem areas, checks tactile sensitivity and the presence of reflex contractions, and motor functions. Based on the examination and complaints of the patient, a preliminary diagnosis is established.
X-ray examination allows us to identify injuries and possible destructive changes in the intervertebral discs and spinal canal.
The patient is irradiated with electromagnetic waves, which makes it possible to obtain a detailed, very clear image of the spine and internal organs, and to identify the slightest deviations from the norm.
We advise you to study - Spinal traction at home
The patient's cerebrospinal fluid is taken for analysis by inserting a needle into a certain point in the spinal column. The study allows you to determine the presence of infection and check the patency of the nerve canals.
Treatment of cauda equina syndrome
Treatment of cauda equina syndrome can take three directions:
- A surgical operation when surgeons during an intervention weaken or completely eliminate compression (pinching) of the nerve roots. The operation can be aimed at removing a hernia (which was compressing the nerves), a tumor, or restoring the position of bone segments disturbed as a result of a fracture.
- Drug treatment. Patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers and others.
- Physiotherapy, exercise therapy, special gymnastics. Such procedures are aimed at increasing muscle tone, strengthening them, activating metabolism and improving the general condition of the patient.
The latter method of treatment is not independent; it is rather used to accelerate the effect of drug treatment or recovery after surgery.