Urinary incontinence is involuntary urination when a person cannot control this process of his own free will. This urological pathology is called incontinence. It can appear due to various reasons, depending on them there are several types of incontinence:
- stressful,
- urgent,
- mixed,
- paradoxical,
- temporary.
A urologist will help identify the specific cause by performing the necessary diagnostic procedures and examining the patient’s genitourinary system. Diagnostics allows you to identify the exact cause of urinary incontinence and choose effective treatment tactics.
Disease statistics
Incontinence occurs in 20% of the world's population. The difficulty of studying and disseminating pathology is complicated by the fact that only a few people approach medical institutions with it. According to medical statistics, in Russia 12-70% of children and 15-40% of adults suffer from incontinence. The problem occurs in both women and men, but under the age of 40 the female half of the population is more susceptible to it. But in men, incontinence manifests itself at a later age - this is due to age-related changes in the prostate.
Urinary incontinence brings not only physical inconvenience, but also psychological one. Patients complain of a significant deterioration in the quality of life, the manifestation of psycho-emotional disorders, and disruption of adaptation in everyday, family and professional spheres of life. Urinary incontinence is not an independent disease, but a symptom of other pathological processes in the body. A urologist necessarily prescribes an examination and identifies the underlying disease, which allows this consequence to be eliminated.
Classification of urinary incontinence
Doctors divide the disease into 2 main types: false and true urinary incontinence.
False urinary incontinence
This is the inability to control urination due to congenital or acquired pathologies of the urinary system (urethra, ureter, bladder).
True urinary incontinence
If the doctor has not identified the above reasons, serious damage to the urinary system and pathologies of its development, then incontinence is called true.
Causes of urinary incontinence
- 1.
Anatomical pathologies, sensory impairment - Anatomical pathologies can be not only congenital, but also acquired. For example, the normal location of the pelvic organs and the normal functioning of the nerve endings may be disrupted due to difficult childbirth, excess weight, chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, due to weightlifting and other sports. As a result, changes occur in the urethra, bladder, and pelvic ligaments, resulting in the development of incontinence.
- 2. Hormonal imbalance.
- Most often, this cause occurs in women during menopause, when there is a deficiency of estrogen in the body. The lack of production of female sex hormones entails atrophy of the membranes of the genitourinary organs, decreased tone of the ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor, which leads to incontinence.
- 3. Injuries and diseases of the nervous system.
- Incontinence can be caused by:
- inflammatory diseases,
- circulatory disorders,
- injuries of the urinary system,
- tumors
- diabetes,
- multiple sclerosis,
- malformations of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
Urological pads for women: how to choose?
Krivoguz Igor Mikhailovich - family doctor, infectious disease specialist
Urological pads are used for urinary incontinence, regardless of the cause. In women, the problem is widespread and tends to appear at a younger age. To avoid discomfort, it is important to be able to choose the right urological pads, which have certain differences.
Causes of urinary incontinence in women
Urinary incontinence is a polyetiological pathological condition that develops due to several different causes:
· Having suffered a difficult birth with injuries, in particular perineal ruptures.
· Overweight woman.
· Previous gynecological operations that affected the structures of the urinary tract to varying degrees.
· Features of the anatomy of the urinary tract - the length of the urethra (urethra) of a woman is several times less than that of men, which in turn increases the likelihood of developing urinary incontinence.
· Changes in hormonal levels, in particular those associated with menopause - a decrease in the level of female sex hormones estrogen leads to a decrease in the tone of the bladder sphincter.
· The development of a functional disorder associated with the peculiarities of the nervous system and called urge incontinence - a woman, even with an incomplete bladder, suddenly develops an imperative urge to urinate, against the background of which urination begins almost immediately, which is very difficult to stop. The pathological condition brings significant discomfort to a woman’s life.
All causes require therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating their influence. In order for a woman to continue an active lifestyle during the treatment period, special urological pads were developed.
Differences from gynecological pads
Most women associate the word sanitary pad with menstruation. Urological products are similar in shape and size, but also have several of the following fundamental differences:
· Different shape and thickness.
· Ability to quickly absorb large volumes of liquid.
· Material of manufacture – urological pads are made of large-porous material.
· Rate of absorption – menstrual hygiene products can absorb a small volume of liquid over a longer period of time.
· Duration of use – the period of time during which pad replacement is required for gynecological pads.
For mild incontinence in women, gynecological pads can cope with the function, but there remains a high risk of “leaking” and discomfort at the most inopportune moment.
Requirements for urological pads
Products significantly facilitate a woman’s socialization and improve the quality of life. Modern industry produces a large number of urological pads, which must meet the following several requirements:
· Sufficient elasticity of the material from which the product is made.
· Softness of the surface adjacent to the skin of the perineum.
· No irritating effect on the skin when used.
· Relatively small thickness and dimensions, which make it possible to wear tight-fitting clothes.
· Deodorizing properties, which consist in neutralizing unpleasant odors.
When choosing a product, you should be guided by the listed requirements, since the absence of one of them will negatively affect the quality of urine absorption during incontinence.
How to choose
Urological pads have certain specifics, so they cannot be replaced with personal hygiene products during menstruation, despite their external similarity. First of all, to select a product, you should know the severity of urinary incontinence:
· 1 (drip) degree – up to 50 ml of urine is released.
· 2 (mild) degree – incontinence is characterized by uncontrolled release of 100 ml of urine,
· 3 (medium) degree – up to 200 ml is released.
· 4 (severe) degree – up to 500 ml of urine is released.
For each degree of severity of urinary incontinence, appropriate urological pads are allocated, as indicated on the packaging.
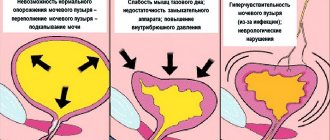
Types of Urinary Incontinence
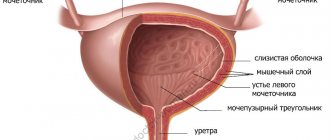
Normally, the process of urination begins with the production of urine by the kidneys. It accumulates in the bladder, causing its walls to stretch. While urine flows into the bladder and it fills, the muscle responsible for contracting and emptying the bladder, the detrusor muscle, is relaxed. There are pressure receptors in the walls of the bladder, at a certain degree of fullness they are triggered, we feel the urge to urinate. The detrusor muscle tenses, and the bladder sphincter, a muscle that prevents the free flow of urine, on the contrary, relaxes. If the detrusor pressure is higher than the urethra, urination will occur. This is a controlled process and a person can tense or relax the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles to control urination.
Stressful
It occurs without urge when intra-abdominal pressure increases, for example, during physical activity, coughing, laughter. The presence of stress urinary incontinence indicates a decrease in the tone of the pelvic floor muscles and a lack of collagen in the ligaments. Reduced collagen content can be congenital, and also occurs in women during and after menopause. Women who smoke are more susceptible to stress urinary incontinence. The fact is that a smoker’s body decreases the level of vitamin C, a substance that ensures the strength of collagen structures.
The second cause of stress urinary incontinence is excessive mobility of the bladder neck or incomplete contraction of the sphincter (urologists then talk about sphincter incompetence). Due to the stretched or displaced location of the cervix, the sphincter does not fully contract, which means that with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the resistance of this muscle will be insufficient to hold urine.
The third reason is sphincter injury. It can be a consequence of a pelvic fracture, surgery, etc.
Urgentnoe
Accompanied by an imperative (difficult to restrain, imperative, sharp) urge to urinate, which cannot be postponed even for a short period. However, in some cases this pathology is not accompanied by an urge or it is weakly expressed. Patients with urge incontinence are characterized by an overactive bladder, that is, the detrusor is tense even in the process of filling the bladder with urine. This condition of the bladder is a consequence of pathology of the nervous system. Urge incontinence can be provoked by various external factors: a change in temperature (for example, when leaving a warm apartment on the street), the sound of pouring water, drinking alcohol, a state of excitement. People with an overactive bladder sometimes experience a nervous connection between their incontinence and a specific event.
Mixed
This type combines the symptoms of the two above types of incontinence.
Paradoxical (overflow incontinence)
It affects older people with a history of diseases of the genitourinary organs (prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, urethral stricture, etc.). A prolonged obstruction to the outflow of urine leads to overflow and overstretching of the bladder.
Temporary (transient)
The reason for such urinary incontinence lies in the influence of external factors and disappears after they are eliminated. Factors may include constipation, acute cystitis, high blood alcohol content, etc.
Cystitis after sex
Review from the site prodoctorov.ru
Good afternoon Exactly a year has passed since I found my savior - Oganes Eduardovich. How did I find him? In another attack of despair due to an exacerbation of cystitis after sexual intercourse, I was looking for a doctor who would understand what was happening to me and offer at least one real and adequate reason for my condition. If we go back a little, I have suffered from cystitis since 2010, it has always been associated with sexual intercourse. Then I was still a student at a medical university, I already understood something, of course, I didn’t self-medicate, I went to doctors, the answers were mostly of a superficial nature: it happens, women often have cystitis, you are predisposed, you have a cold, etc. But all these reasons were unconvincing, incorrect and unprofessional. Tons of antibiotics, furagin, like vitamins, and constant fear. When exacerbations occurred, I could neither sit, nor lie, nor stand, nor eat, nor drink, in general it was very bad! Repeated attacks were accompanied by hospitalization in the hospital, because the urine was bloody, antibiotics were injected, and cystoscopy was performed live. During my last hospitalization, already as a doctor, reading specialized literature on urology, I understood that exacerbation of cystitis after each sexual intercourse could not be in the category of “it happens,” that there was a clear reason, and asked to do a cystoscopy itself in order to see — do I have polyps, do I have a normal structure, etc., to which the doctors, to my great regret, laughed it off (with very unprofessional, vulgar jokes). And so in July 2021, being in an extremely depressing state, thinking that I would never have a family life, or children either (but there was such a fear of cystitis, a fear of even just urinating that I preferred no sex, just not to suffer) , I came to see Oganes Eduardovich. I don’t remember what I said, I think I even cried, but I remember the serious and reliable image of my doctor, he calmed me down and asked clear questions (questions necessary for a differential diagnosis), no jokes, laughter, indifference, he then treated treat me like your daughter! Naturally, the matter cannot be resolved without an examination, which was done (although I asked other doctors more than once), the diagnosis was made on the same day: Dystopia of the urethra - that is, it is located lower than it should be + adhesions. Drawings, diagrams are drawn, everything is explained in detail. A clear action plan was given and the only possible solution was urethral transposition surgery according to Komyakov. Of course, I couldn’t believe that the solution was so real and that everything could disappear without a trace, I was worried, but the suffering that I experienced forced me to agree to the operation without hesitation. The date for the operation was set. But before it was carried out, a cystoscopy was necessary, which for the first time in my life was performed under anesthesia (in a dream), where I did not experience the pain of this examination, and it was much easier. The diagnosis was confirmed. The day of the operation arrived. The department where I was hospitalized is clean and comfortable, the nurses are the best, and the doctors are talented! Oganes Eduardovich explained everything again, drew it, the operation was carried out successfully (which I had no doubt about). There was both general anesthesia and epidural anesthesia - and all for a better postoperative period, so that there was no pain. The postoperative period also went great, very attentive and kind nurses, Oganes Eduardovich and Nikita Mikhailovich (my second savior) - they made daily rounds, closely monitored my condition, the food was very tasty, the rooms were clean. In general, everything was great, but I just couldn’t believe it, had I really gotten rid of my illness? Well, dear and respected Oganes Eduardovich, almost a year has passed since the date of my operation (from September 22, 2021) and I can say that there was not only an exacerbation of cystitis, but not even a hint of any discomfort in the area urethra! I am happy and now enjoying life and love (in every sense) with my husband! I ride a bike, swim, run, lead an active lifestyle, work quietly as a pediatrician, and every day I remember you, thank you, and thank God for meeting such a talented, smart, professional doctor like you! My gratitude cannot be expressed in words! I love and adore you! My husband rejoices with me! And separately I would like to convey words of enormous gratitude to you from my mother, who is endlessly happy to see her daughter healthy! PS It was a great happiness when, a month after the operation, I passed a urine culture for flora and it was sterile for the first time! Finally, when I go to the toilet I am not afraid of burning, stinging, etc. Thank you! And to your entire magical team!
Diagnosis of urinary incontinence
In order to determine the causes and severity of urinary incontinence, the doctor interviews the patient, pays attention to his complaints, and collects an anamnesis of the development of the pathology. The patient is asked to keep notes for some time, where he records the volume and frequency of urination. Diagnosis of urinary incontinence in women is accompanied by an examination by a gynecologist to determine the condition of the muscles of the uterus and vagina, and the location of the bladder. Cough and pouch tests are performed.
A more accurate picture of the condition of the pelvic floor, its anatomical structure and the functionality of the bladder is provided by ultrasound of the bladder and urethrocystography. The doctor prescribes a general analysis and urine culture to identify inflammatory processes.
Chronic cystitis
Treatment of chronic cystitis
First of all, it is worth noting that if you are diagnosed with chronic cystitis, how to treat the disease can only be determined by a qualified doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Self-medication is unacceptable and can lead to irreversible consequences. The choice of treatment tactics directly depends on what factors caused the development of the pathology, on the individual characteristics of the patient and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The basis of treatment for chronic cystitis is antibiotic therapy. The doctor selects antibiotics individually, depending on what microorganisms caused the inflammation. If it is not possible to make an antibiogram, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The duration of such therapy is also very individual, and ranges from 7-10 days to 2-4 weeks.
In parallel, general therapy is carried out, which is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the immune system, restoring hormonal balance and eliminating other factors contributing to the development of pathology. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed immunomodulators (if there are no contraindications), antihistamines, drugs that improve local blood circulation, antihypoxants and other drugs. Only correction of the general condition gives the patient a chance for successful treatment of the disease and a full life.
Symptomatic therapy is also used, which is aimed at eliminating pain. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. If the patient has concomitant diseases of the bladder (urolithiasis, bladder polyps, etc.), then treatment of these diseases is necessary, including surgical treatment.
In some cases, doctors may consider it appropriate to flush the bladder with anti-inflammatory drugs. The patient should also regularly attend physiotherapeutic procedures that help normalize blood circulation and strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
In the interstitial form of the disease, chronic cystitis, the symptoms, treatment and signs of which are very different from the manifestations of other forms of pathology, quite often requires surgical treatment. Preference is given to organ-preserving operations. Procedures such as laser therapy, electrophoresis using various medications, electrical stimulation, etc. are also effective.
Treatment of urinary incontinence
To treat incontinence, both conservative and surgical treatment can be prescribed. Procedures and medications are selected by a urologist after a complete examination of the patient and identification of the cause of urinary incontinence. If therapeutic treatment measures show ineffectiveness, surgical treatment is resorted to.
Non-drug therapy
Includes bladder training and exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles. The doctor also gives recommendations on controlling the patient’s weight, nutrition, and physical activity.
Bladder training is a 3-step exercise. First, the patient is taught the principles of controlling the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, then a urination plan is drawn up and, at the last stage, its implementation is monitored. Because of the fear of uncontrollable urination, patients with incontinence tend to empty their bladder early, at the first weak urge. The training is designed to increase the interval between urinations, allowing them only at a certain time according to the plan. The rest of the time, the patient must restrain the urge by controlling the sphincter muscles. At first the intervals are minimal, then they increase, reaching more than 3 hours. During the training period, the patient also takes medications prescribed by the urologist. As a result, the person’s urinary pattern changes, and discontinuation of drug therapy does not lead to worsening.
Drug therapy for urinary incontinence
There are medications to treat any type of urinary incontinence. Drug therapy works best for the urgent type. The drugs reduce the contractile function of the bladder, increasing its functional capacity. Antispasmodics and antidepressants are used for these purposes. The dosage and duration of the course are prescribed by the doctor individually. If necessary, the course of treatment is adjusted and repeated.
Surgical treatment of urinary incontinence
It is used when there is proven ineffectiveness using conservative methods. The form of incontinence and the results of previous treatment influence the tactics of surgical intervention. Stress and paradoxical urinary incontinence are effectively treated surgically. Stress incontinence is effectively treated using minimally invasive methods - collagen injections and similar drugs. Contraindications to injections are neurogenic bladder, prolapse of the bladder, prolapse of the vaginal walls.
Surgical treatment for urinary incontinence consists of performing loop operations.
Delicate problem (urinary incontinence)
Some topics in our society are considered awkward to discuss even with a doctor. One of these health problems that women, especially older women, often face is urinary incontinence. Every fifth woman suffers from this pathology during reproductive age, every third woman suffers from perimenopausal and early menopausal age, and every second woman suffers from this pathology in the elderly (after 70 years). Urinary incontinence is not just a hygiene problem
, it very seriously affects a woman’s quality of life, since it is accompanied by a forced decrease in physical activity, neuroses, depression, and sexual dysfunction. We talked with EuroMed Blades urologist Anna Sergeevna PROSHKINA about the reasons that lead to this condition, as well as about methods of treating the disease.
— Anna Sergeevna, please tell us in more detail what this condition is.
— Urinary incontinence is understood as the involuntary and uncontrolled release of urine from the urethra, caused by violations of various mechanisms regulating bladder emptying.
The following types of urinary incontinence occur in women:
• Stressful
– involuntary loss of urine associated with incompetence of the urethral sphincter or weakness of the pelvic floor muscles. Prerequisites for stress urinary incontinence in women can include obesity, constipation, sudden weight loss, heavy physical labor, and radiation therapy. The disease most often affects women who have given birth, and the number of births is not so important as their course. The birth of a large fetus, a narrow pelvis, ruptures of the soft tissues of the perineum and overstretching of the pelvic floor muscles.
• Imperative
(urgent, overactive bladder) - unbearable, uncontrollable urges caused by increased reactivity of the bladder. Most often this is due to age-related deficiency of estrogen and other sex steroids and the resulting atrophic changes in the organs of the genitourinary system. Surgeries on the pelvic organs (removal of cysts and tumors of the appendages, uterus), prolapse and prolapse of the uterus, chronic cystitis and urethritis contribute.
• Mixed
– combining signs of stress and urge incontinence. A sudden, uncontrollable need to urinate occurs during physical exertion, followed by uncontrollable urination. The immediate provoking factor of stress incontinence is any tension that leads to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure: coughing, sneezing, fast walking, running, sudden movements, heavy lifting and other physical effort. The prerequisites for the occurrence of urgency are the same as for stress incontinence, and various external stimuli (sharp sound, bright light, water pouring from the tap) can be provoking factors. The mechanism of stress urinary incontinence in women is associated with insufficiency of the urethral or vesical sphincters and/or weakness of the pelvic floor structures. An important role in the regulation of urination is given to the state of the sphincter apparatus - with changes in the architectonics (the ratio of muscle and connective tissue components), the contractility and extensibility of the sphincters is impaired, as a result of which the latter become unable to regulate urine output.
Normal urinary continence is ensured by a positive urethral pressure gradient (i.e., pressure in the urethra is higher than in the bladder). Involuntary urine leakage occurs if this gradient changes to negative.
Pathogenesis of urge urinary incontinence
associated with impaired neuromuscular transmission in the detrusor, leading to bladder overactivity. In this case, when even a small amount of urine accumulates, a strong, unbearable urge to urinate occurs.
— What symptoms should you pay attention to? — Patients who have a stressful form of the disease begin to notice involuntary, without a prior urge to urinate, urine leakage, which occurs during any physical stress. As the pathology progresses, the amount of urine lost increases (from a few drops to almost the entire volume of the bladder), and exercise tolerance decreases.
Urge incontinence
may be accompanied by a number of other symptoms: increased frequency of urination more than 8 times during the day, urination at night, and difficult urge to control. If urination disturbance is combined with bladder prolapse, discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of incomplete emptying, a sensation of a foreign body in the vagina, and pain during intercourse may be experienced. — What consequences does this pathology have? “The woman experiences not only hygienic problems, but also serious psychological discomfort. The patient is forced to give up her usual lifestyle, limit her physical activity, avoid appearing in public places and in companies, and refuse sex.
Constant leakage of urine is fraught with the development of dermatitis in the groin area, recurrent genitourinary infections (vulvovaginitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis), as well as neuropsychic disorders - neuroses and depression. However, due to shyness or the false idea of urinary incontinence as an “inevitable accompaniment of age,” women extremely rarely seek medical help with this problem, preferring to put up with the obvious inconveniences. A patient facing the problem of urinary incontinence should be examined by a urologist and gynecologist. This will allow not only to establish the causes and form of urinary incontinence, but also to choose the optimal ways of correction. An important stage of diagnosis is a urination diary, which records the frequency of trips to the toilet, the volume of each excreted portion of urine, the number of episodes of incontinence, the number of pads used, and the volume of fluid consumed per day. — What methods exist to treat this problem? - First, we determine the causes of incontinence - these can be not only hormonal imbalances or complications after childbirth, but also banal urinary tract infections or tumor diseases. It is clear that in this case, exercise for the pelvic floor muscles will not give much effect.
Non-drug treatments for incontinence include:
- bladder training; - exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor; — physiotherapy; - diet: - sharp limitation of foods and drinks that irritate the mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder; — fight against extra pounds and further weight control.
The training consists of creating a urination plan and executing it. You still need to learn how to carry out the plan and train better under the guidance of a doctor. The intervals between urinations should gradually increase. The fact is that women suffering from incontinence develop over time a certain stereotype of going to the toilet: they strive to go there, even if the urge is weak, as if “for prevention” or “in reserve”, so that in no case will there be any embarrassment . While carrying out the plan, a woman must restrain her urges. The interval between urination should be increased by half an hour every week until its duration reaches 3-3.5 hours. Thus, the woman changes the old stereotype of behavior and develops a new one. Usually the training is supported by drug therapy, which lasts for 3 months, just like the training program. No less attention should be paid to training the pelvic floor muscles. For most women, trained pelvic floor muscles are the key to success in the treatment and prevention of urinary incontinence. Unfortunately, only a few people consciously work on their pelvic muscles. This is the best prevention of female incontinence. For example, “Kegel exercises” are included in the list of physical therapy exercises for incontinence.
In addition to these exercises and training, one should not forget about physical therapy. It can strengthen muscles and make ligaments more elastic by improving blood supply to the pelvis. For this purpose, physiotherapeutic methods such as microcurrents and electromagnetic pulses are usually used.
Medications have proven themselves to be especially effective for the urgent type of urinary incontinence. For treatment, m-anticholinergics are prescribed first (they have a relaxing effect on the muscles of the bladder; they dampen urge impulses from the nervous system) and antidepressants (central-acting drugs). Thus, under the influence of drug therapy, the bladder relaxes and increases in volume, the imperative urges that the woman could not cope with disappear, and accordingly, she begins to go to the toilet less often.
Surgical intervention
Typically, surgery is used for stress incontinence. The issue of surgical intervention is decided if drug treatment is ineffective. At the present stage of development of surgery, doctors use about 250 different methods of surgical interventions to eliminate stress urinary incontinence in women. Many of these methods are used in our country, including minimally invasive methods, for example, throwing a loop of synthetic fabric. After such operations, a woman can go home the next day after the intervention.
The method of treatment, the choice of medications and their dosages, as well as the duration are selected by the doctor individually depending on the severity of the pathology, the severity of urinary incontinence, and the age of the patient.
Many women are embarrassed by their problem and put off visiting a doctor.
, “quietly” using urological pads. This attitude towards one’s health is unreasonable, because modern medicine makes it possible to solve this delicate problem and enable patients to return to a full life.
Problems of treatment and prevention of urinary incontinence
Despite the fact that the pathology is widespread, very few people go to the doctor for a solution to the problem. This problem is considered intimate, very personal, sensitive and people, succumbing to prejudice, feel shame, this is a serious obstacle to solving incontinence problems. If a person encounters this pathology in old age, he often takes this condition as a natural sign of aging. The life of a person with urinary incontinence loses its original quality, and the longer he lives with this disorder, the higher the risk of developing psycho-emotional disorders, concomitant physical diseases and other complications, including disability.
In this regard, I would like to inform all people who have this problem - regardless of the reasons, urinary incontinence is a pathology, and not a natural manifestation of the body's characteristics! Urinary incontinence is highly treatable and the sooner you see a doctor, the higher the chances that the problem will be solved and your quality of life will remain the same, without any temporary, psychological or physical limitations!