NEUROFIBROMATOSIS
(
neurofibromatosis
; Greek neuron nerve + lat. fibroma, fibromatis fibroma + -osis; synonym:
Recklinghausen's disease, multiple neurinomatosis, neuroma falsum
) - a tumor disease characterized by the formation of multiple neurofibromas and age spots Ch. arr. on the skin and mucous membranes, accompanied by neurological, mental, hormonal and bone disorders.
It was first described as an independent disease in 1882 by F. Recklinghausen.
Rice. 1. A patient with neurofibromatosis: multiple tumor nodes and pigment spots are visible on the skin of the trunk and limbs.
With Neurofibromatosis, all tissues and organs can be affected, but more often the skin, subcutaneous tissue, nerve plexuses, including intermuscular (Meissner's) and submucosal (Auerbach's), nerve trunks and roots. Typically, Neurofibromatosis nodes are located on the trunk, neck and limbs (Fig. 1), rarely on the soles and palms, or the oral mucosa; bones and endocrine glands are even less commonly affected. Men get the disease about twice as often as women. Sometimes the disease is hereditary or familial in nature and affects members of the same family in 3-5 generations. Quite often, N. is diagnosed with various congenital malformations, dementia, acromegaly, visual and hearing impairment, spinal curvature, etc.
The etiology is not clear. Most authors adhere to the theory of dysontogenetic origin of P., others associate N. with dysfunction of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, etc.
Pathological anatomy
Rice.
2. Macropreparation of a plexiformia neuroma in neurofibromatosis: multiple tumor nodes (some of them are indicated by arrows) of a large nerve and its branches. Rice. 3. A patient with an elephant-like form of neurofibromatosis: proliferation of neurofibromatous tissue in the area of the left upper limb with spread to the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the chest. With N., multiple, sometimes up to 5-7 thousand, various forms of neurofibromas (see) or, less often, neuromas (see) from 2 mm to several centimeters in diameter are found; Sometimes tumors weighing up to 15 kg are found. Often multiple nodes are located along the nerve and its branches, which creates a picture of the so-called. plexiform neuroma (Fig. 2). Its variety is the elephant-like form of N. (Fig. 3), characterized by pronounced hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the dermis.
When gistol, examination of remote nodes reveals a picture of encapsulated or diffuse neurofibroma. Encapsulated neurofibromas usually form in large nerve trunks, while diffuse neurofibromas occur in smaller (dermal) nerve branches. Growing nodes of N. are formed by proliferating peri- and endoneural connective tissue cells, folding into loose, soft-fibrous bundles, which are stained pink with magenta. Stable (mature) N. nodes are characterized by a decrease in the number of Schwann syncytium, the collagen skeleton of the nerve bundles becomes denser and hyalinized - the tumor becomes histologically indistinguishable from fibroma (see Fibroma, fibromatosis) or desmoid (see). In nodes localized on the skin, structures resembling tactile corpuscles (Meissner) or lamellar corpuscles (Vater-Pacini) may appear.
Pigment spots from light beige to dark brown are usually found on the skin of the trunk and limbs, less often on the face, neck, and oral mucosa. They have a smooth surface and do not protrude above the skin level. When gistol, the study of age spots reveals a diffuse accumulation in the papillary layer of the dermis of melanoblasts, melanocytes with inclusions of melanin in the cytoplasm.
With N., atrophic and destructive changes in bones are often noted, and in some cases bone exostoses occur. Bone changes in N. are associated with general trophic disorders, as well as with pressure on the bone of tumor nodes.
Optic tract glioma
Gliomas are benign tumors of the optic nerve and other parts of the visual analyzer. The location can be any (orbital, intracanal, intracranial - the latter is sometimes divided into pre-, post-chiasmatic and chiasmatic), multiple lesions are possible, symmetrical location of tumors is uncharacteristic. A significant dependence of tumor growth on the tumor environment, which is represented mainly by neuroglial cells, has been shown. The latter influence the proliferation of tumor cells by secreting cytokines, as well as neurotoxins, which damage the axons of the optic nerve, leading to impaired visual acuity. This gives hope that in the future, targeted therapies targeting the tumor environment may be able to slow the growth of optic nerve gliomas. This neoplasm rarely causes death, but significantly affects the quality of life of patients. Girls get sick 5–10 times more often than boys.
In addition, other types of brain tumors (astrocytomas, gliomas) occur more often in patients with NF1 than the average population.
Clinical picture
The first wedge, symptoms of the disease are detected immediately after birth or in childhood, but can occur for the first time in adults. They are associated mainly with the appearance of tumor nodes on the skin, in the subcutaneous tissue and along the nerve trunks. In some cases, zones of anesthesia or hyperalgesia may appear in the affected area; convulsions, paresis, and paralysis are rarely observed. Patients often have an uncritical attitude towards themselves and others. Children with N. lag behind in physical and mental development.
When the spinal cord and its roots are damaged in the wedge, the picture is dominated by symptoms of spinal cord compression with early paralysis and paresis, respectively, of the affected segments. Compression of vital organs (for example, when nodes are localized in the neck and mediastinum) can cause disturbances in their function: compression of the respiratory tract is accompanied by increasing difficulty breathing, compression of blood and lymph vessels leads to local circulatory disorders, edema, etc. Multiple tumors nodes, especially on the lower extremities, can create a picture of neurofibromatous elephantiasis as a result of impaired lymphatic drainage.
Based on the predominant localization of the lesion, focal, peripheral and central forms of N are distinguished. In the focal form, one area of the body is affected, for example, the torso, or one organ, for example, the stomach. The peripheral form is characterized by damage to several areas of the body. The central form of N. occurs as a result of primary brain damage.
With malignancy, one of the N.'s nodes progressively increases in size, a large-loop network of dilated veins is visible under the skin, and the displacement of the tumor during palpation is limited. In the future, ulceration of the node may occur with decay and bleeding.
Diagnosis
establish on the basis of anamnesis, wedge, pictures, data from rentgenol, morphology, studies.
Roentgenol, the study was directed to Ch. arr. to identify skeletal lesions and is used mainly for a more complete assessment of the prevalence and severity of the process. Severe N. is characterized by deformation of the spine in the form of scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis of the thoracic region, possible marginal defects of the vertebral bodies, their articular and transverse processes, expansion of the intervertebral foramina and erosion of their edges, abnormalities of the lower edges of the posterior ribs caused by pressure from neurofibromatous nodes.
Rice. 4. Direct radiograph of the distal leg of a patient with neurofibromatosis: curvature of the bones of the leg, thickening of the fibula.
Long tubular bones can be atrophic, curved, and sometimes, on the contrary, hypertrophied, thickened (Fig. 4).
The compact substance in the hypertrophied bone is thickened. Periosteal ridges are visible on the surface of the bone; sometimes paraosteal ossifications are also found, running parallel to the bone surfaces. Intraosseous neurofibromatous nodes that are sometimes found in long bones look like limited swellings and cystic formations.
When involved in patol, the process of the skull bones reveals its asymmetry, especially on the face. In the bones of the cranial vault, defects and abnormalities, areas of bone atrophy or hyperostosis are possible. The eye sockets are asymmetrical, and defects may also be found in their bone walls.
In case of damage to the cranial nerves, their bone canals expand, for example, the internal auditory canal of the temporal bones or the opening of the optic nerve. In some cases, the sella turcica increases. Sometimes isolated damage to the joints is observed, such as deforming arthrosis.
Differential diagnosis
carried out mainly with Dercum's disease (see Dercum's disease) and cysticercosis (see).
Skeletal abnormalities
Normal functioning of bone tissue requires a coordinated interaction between resorbing (osteoclasts) and bone-forming (osteoblasts) cells. The use of a mouse model showed impaired osteoblast function (increased pyrophosphate production, decreased bone morphogenetic protein 2, which promotes osteoblast differentiation) in mice mutant for the NF1 gene. As a result, patients experience impaired bone mineralization, arched deformities of the tibia, kyphotic and scoliotic deformities, chest deformities, pseudarthrosis of large joints, and dysplasia of the sphenoid bones.
Treatment
Treatment is surgical. Indications for it are severe pain or ulceration of the tumor, difficulty moving, compression or displacement of vital organs. In some cases, surgical treatment is resorted to for cosmetic purposes. Since the lesions are multiple, removal of all altered tissues is usually not possible.
With surgical treatment of the elephant-like form of N., there is a need for subsequent skin grafting (see). Neurofibromatous tissue is abundantly supplied with blood vessels; their ligation during surgery must be especially careful. When the node is located in a large nerve trunk, the tumor is enucleated, a transverse resection of the nerve with the application of a nerve suture (see) or its marginal resection with the application of a partial nerve suture. Surgical removal of one of the nodes in some cases can lead to progression of the process with a sharp increase in the size of other nodes.
Other manifestations
Tumor diseases include pheochromocytoma and iris hamartomas (Lisch nodules).
Mental retardation is common.
The cumulative risk of cancer by age 50 in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1 is increased by 20–39%, with a lifetime risk of developing cancer of ~60%.
In addition, people with neurofibromatosis type 1 have an exceptionally high risk of developing malignant brain tumors (approximately 40 times the risk of developing high-grade glioma), endocrine cancer (more than 74 times the risk of developing adrenal cancer), peripheral nerve malignancies (>1000 times increased risk of developing) and breast cancer.
Children with neurofibromatosis type 1 have an increased risk of leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
In addition, some studies confirm an increased risk of developing multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, macrocephaly, and hydrocephalus. .
Figure 3 |
Lisch nodules.
Figure 4 | Manifestations of symptoms of neurofibromatosis type 1 depending on the patient’s age.
The criterion for diagnosing NF type 1 is the presence of two or more signs (according to the National Institutes of Health conference on neurofibromatosis, USA, 1988):
- ≥ 6 café-au-lait spots > 5 mm in diameter prepubertally or 15 mm in diameter postpuberty;
- ≥ 2 neurofibromas of any type or one plexiform neurofibroma;
- Small pigmented spots in the armpits and groin areas, resembling freckles (Crove's symptom);
- Optic nerve glioma;
- ≥ 2 Lisch nodules (iris hamartoma);
- Bone changes: dysplasia of the wing of the sphenoid bone, thinning of the cortical layer of the tubular bones with or without pseudarthrosis;
- Presence of NF type I in first-degree relatives.
Focal areas of hyperintensity (FASI)
Found in approximately 80% of patients with NF1, they are areas of hyperintense MR signal on T2WI and FLAIR located in the basal ganglia, thalamus, brainstem, cerebellum and subcortical white matter. Morphologically they represent areas of myelinopathy with enlarged vacuoles. The correlation of these changes with the clinic is not fully understood. .
Figure 8 | Asymmetric areas of hyperintense MR signal in T2 are detected in the basal ganglia on both sides. Also noteworthy is the hyperintense formation on the left surface of the neck and head - plexiform neurofibroma.
Why is neurofibromatosis treated at the Assuta Medical Center?
Reviews about the treatment of neurofibromatosis in Israel left by grateful patients of the clinic highlight its key advantages:
- Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by highly specialized doctors of the highest category, based on the latest advances in medicine and medical technology.
- The hospital's material and technical support is at the highest level.
- An examination for suspected neurofibromatosis is carried out within a matter of days, guaranteeing high reliability of the data obtained.
- For surgical removal of tumor tumors, gentle techniques and the latest equipment are used.
- When drawing up a medical program, an individual approach is always used, taking into account the characteristics of a particular patient and his case.
- The clinic has an International Department that helps patients from other countries organize the treatment process.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Other manifestations from the central nervous system, head and neck area
Figure 9 |
STIR of the cervical spine in sagittal projection. A hyperintense intramedullary formation with indistinct edges is identified—spinal cord astrocytoma. Patients with NF1 have an increased risk of CNS malignancies. .
Figure 10 | Axial T2Fs (a) and coronal T2WI (b) in a patient with NF1. Uneven expansion and hyperintensity of the MR signal from the spinal nerves, caused by intraneural neurofibromas, are determined. .
Figure 11 |
Sagittal T2VI of the lumbar spine. Ectasia (expansion) of the dural sac is determined. .
Figure 12 |
Axial CT scan of the orbits. Dysplasia of the left wing of the sphenoid bone (circle) is determined; The superior orbital fissure is enlarged. Neurofibromas often arise in this area, leading to proptosis on the affected side. .
Figure 13 | 3D reconstruction of CT scan of the skull bones. Dysplasia of the left wing of the sphenoid bone is observed. Also noteworthy is the enlargement of the brain skull.
How is neurofibromatosis diagnosed in Israel?
It is not difficult to recognize neurofibromatosis due to its characteristic external manifestations. But in order to find out the nature of the lesion and its severity and prescribe the most effective treatment, the patient is sent for a comprehensive examination. The Assuta clinic uses the most modern laboratory and instrumental diagnostic techniques, which allow us to obtain the most accurate and reliable data in a short time. All diagnostic measures take no more than three working days, giving doctors the opportunity to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Day 1. Visual inspection
Thanks to the advance preparation of a diagnostic program and an appointment with the necessary specialists, a foreign patient immediately upon arrival in Israel goes to the hospital to see a doctor. The attending physician, whom he has the opportunity to choose independently, listens to complaints, studies the medical history and conducts a thorough examination, identifying neurofibromatosis by characteristic signs. The doctor pays attention to the presence of light brown spots and specific rashes on the body, subcutaneous nodes and other neoplasms, checks visual and hearing acuity, and notes possible changes in bone structures. It also evaluates motor coordination and muscle tone.
After this, to confirm the diagnosis and identify possible damage to internal organs and systems, the doctor sends the patient for additional examinations.
Day 2. Diagnostic procedures
The next day is devoted to completing all the examinations prescribed by the doctor. The diagnostic program may include:
- genetic tests - to determine the region of the chromosome in which the damaged gene is located and to determine the type of neurofibromatosis.
- X-ray examination of organs and structures affected by the pathological process, including the spine and skull bones;
- ophthalmoscopy , which is an examination of the fundus of the eye using special instruments. Allows you to detect abnormalities in the eye structures;
- audiometry to determine hearing sensitivity;
- consultation with a neurologist to identify neurological symptoms;
- computer and magnetic resonance therapy of affected organs;
- biopsy , which consists in taking samples of tumor tissue for further histological examination. Performed to exclude the malignant nature of neurofibromas.
Day 3. Clarification of the diagnosis and determination of the treatment regimen
It usually takes no more than one day to process the results of all studies, after which they are reviewed by a group of experts consisting of specialists in various fields: neurologists, ophthalmologists, otorhinolaryngologists, orthopedists, surgeons and others. Together they study and scrupulously analyze the data obtained, make an accurate diagnosis and develop an optimal treatment program, taking into account the specifics of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
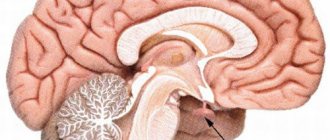
Brain stem gliomas
They make up approximately 8–10% of the total number of CNS neoplasms in NF1. The average age of patients is 8 years. The cerebellum is most often affected, followed by the pons and diencephalon. Concomitant hydrocephalus and brain herniation should be noted. Tumors appear hyperintense on T2WI and usually exhibit contrast enhancement heterogeneously. To avoid missing low-intensity contrast enhancement, subtraction may be used. .
Figure 7 | Brain stem glioma. In the area of the cerebellum, a hyperintense formation is detected on T2WI (a), which on post-contrast T1WI (b) demonstrates weak inhomogeneous accumulation of contrast.