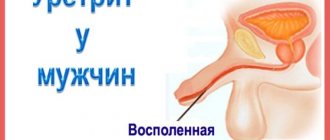
The urethra (urethra) is part of a woman's urinary system and a man's urinary and reproductive systems.
In men, the 20 cm long urethra is located both in the pelvis and inside the penis, and opens into an external opening on the glans. Anatomically, the following sections of the male urethra are distinguished: (1) external opening; (2) scaphoid fossa; (3) penile; (4) bulbous; (5) membranous; (6) prostatic (proximal and distal areas).
Figure taken from www.urologyhealth.org
The prostatic urethra passes through the prostate and is divided into proximal and distal parts at the level of the seminal tubercle. In the proximal part of the prostatic urethra, the excretory ducts of the prostatic glands open at the orifices along the posterolateral surfaces. On the sides of the seminal tubercle are the mouths of the right and left ejaculatory ducts, through which sperm enters the lumen of the urethra from the seminal vesicles and vas deferens. In the distal part of the prostatic part and in the membranous part of the urethra there are elements of the urethral sphincter. Starting from the bulbar region, the urethra passes inside the corpus spongiosum of the penis. The bulbar region is located inside the bulb of the corpus spongiosum. In the membranous and bulbar sections, the urethra bends anteriorly upward. In the penile region, the urethra is located medially along the ventral surface of the penis downward from the cavernous bodies. The capitate part of the urethra is located inside the head of the penis. The inner surface of the male and female urethra is covered with mucous membrane (transitional epithelium, with the exception of a short area near the external opening, where there is flat non-keratinizing epithelium).
Reasons and what it could be
If tickling in the urethra is not associated with injuries, as well as an allergic reaction of the human body, then it can be a symptom of various diseases. In order to make a diagnosis as quickly and correctly as possible, it is recommended to immediately contact a medical facility with qualified and experienced medical professionals. This will allow you to make a correct diagnosis and, if necessary, begin timely treatment.
Very often, a feeling of tickling in the urethra is a symptom of various sexually transmitted diseases that can be transmitted sexually. This is very important, and it is necessary to pay special attention to it.
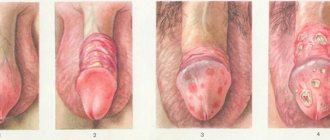
Gonorrhea is considered one of the most common diseases, which can be accompanied by a feeling of itching in the urethra, as well as various green discharge. In some certain cases, this disease is accompanied by a slight increase in the person’s body temperature.
After a short time, these symptoms may disappear and appear again over a certain period of time. In some cases, such a disease can cause various kinds of complications, so a timely diagnosis is very important.
Treatment methods
From the depths of the Middle Ages, such a method of treatment as bougienage has reached our days. This is a manipulation in which metal rods with a smooth surface or bougies of successively increasing diameter are inserted into the urethra. The expansion of the lumen occurs due to stretching, and in some places, micro-tearing of tissue. At the same time, ointments are used to reduce inevitable scarring. Such manipulation brings only temporary relief, since the pathological conditions leading to narrowing remain unchanged - impaired blood flow in the mucous membrane, degenerative changes in the corpus spongiosum, chronic infection. Practice shows that usually each subsequent bougienage increases the length of the narrowing, making the scars rougher and more extensive.
For a long time, internal optical urethrotomy remains the main surgical treatment. This intervention is done under visual control through a cystoscope and consists of dissecting the narrowed area. Today, such an intervention is recommended only in cases where the narrowing is located in the bulbous department, and its length does not exceed 0.5 cm. If the narrowing affects other departments, then such an operation is contraindicated, because it only aggravates the patient’s condition, leading to the formation of more and more extensive scars. Each subsequent such operation in this case is less successful than the previous one.
Some clinics used the installation of a urethral stent (a spring that widens the lumen), but due to the movement of the device inside the organ, this technique was considered ineffective.
Symptoms of the disease
The signs and symptoms of stricture are similar to those of prostate adenoma and chronic prostatitis, urethritis; it is impossible to distinguish them based on complaints and visual examination alone. The person is concerned about:
- weak urine stream pressure;
- jet spray;
- urine continues to flow after urination is completed;
- urination begins after a long wait, with straining;
- the amount of urine gradually decreases, and emptying is accompanied by severe discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen;
- there is an admixture of blood in the urine, and discharge from the urethra.
The situation is complicated by repeated cases of urine excretion by a catheter, when additional trauma occurs. If the urethra completely loses its patency, catheterization becomes impossible. To save lives, an epicystostomy is urgently applied - a percutaneous puncture of the bladder is performed with the installation of a permanent drainage drainage.
Diagnostics
If the feeling of tickling in the urethral area is associated with inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system, then medical workers will initially check for the presence of prostatitis or urethritis . Very often, inflammation of the gland occurs with a variety of diseases of the genitourinary system. Frequent hypothermia of the body can be the main reason why this disease is detected in people.
Many people who do not pay attention to the tickling sensation or itching in the urethral area are in a situation where the disease can become chronic and cause serious complications. The treatment of this disease must be taken very seriously and responsibly. With a timely diagnosis and proper treatment, this disease can be easily eliminated and the patient can feel comfortable.
Current approach in the treatment of urethral structure
Modern effective and reliable treatment for strictures longer than 1 cm - urethroplasty with replacement of the narrowed area with your own healthy tissue. The location of the narrowing in the perineal and hanging (penile) region and its length of more than 2 cm are direct indications for plastic surgery. Replacement is made with tissue taken from the foreskin and the inner surface of the cheek.
Urethroplasty is a very complex surgical procedure. The main difficulty is to create conditions for optimal blood circulation and innervation of the transplanted mucosal area. The essence of urethroplasty is a longitudinal dissection of the narrowing zone and sewing in one’s own tissue as a patch or flap. Depending on the specific circumstances, the “patch” is sometimes sewn onto the vascular pedicle, which speeds up survival.
There are two mandatory conditions for the successful performance of such operations - the highest qualification of the urological surgeon and the impeccable technical condition of the operating room, as well as its absolute sterility.
To treat urethral stricture, you must first make an appointment with one of the urological specialists at the CELT clinic. Our doctors inform the patient in detail about his condition. Our specialists have extensive experience, the necessary equipment and a sincere desire to help everyone who needs it.
Complications
Urethritis is a serious disease; do not hesitate to consult a doctor with this problem, since untimely or incorrect treatment can lead to the development of serious complications.
The infection may spread to other organs; patients may develop cystitis, pyelonephritis, and the inflammatory process may affect the testicles and their appendages. The most severe complication of urethritis in men is prostatitis, which can lead to incurable infertility and sexual dysfunction.
Why is it dangerous?
If you feel itching in the urethral area, in some cases the doctor may suspect a disease such as chlamydia , which can occur without obvious symptoms. At the same time, the causative agents of chlamydia multiply very quickly and over time, a person begins to experience a feeling of tickling or itching in the urethral area.
If the necessary treatment is not carried out, then this disease can pose a danger to the patient's health. An advanced disease can lead to impotence, therefore, if these symptoms are present, it is necessary to promptly seek medical help.
Specific and nonspecific diseases
Among the inflammations of the urinary tract, those caused by a sexually transmitted infection are distinguished: trichomonas, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gonococcus, mycoplasma.
These specific diseases are considered sexually transmitted, and in case of infection, both partners are treated:
- With urethritis , the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, pain appears, regular or only when urinating, and discharge from the urethra with purulent contents. The cause of infection is pathogens of urogenital infection that can rise up and cover the genitourinary organs. Each case of urethritis requires individual treatment, including antibiotics, drugs that strengthen the immune system, and vitamins.
- Chlamydia is caused by chlamydia, which has a detrimental effect on the urinary tract. The consequences of the disease are infertility.
- Gonorrhea is a consequence of casual sexual intercourse. Gonococci destroy the epithelium of the cervix, urethra, and lower rectum. For gonorrhea, antibacterial therapy is indicated under the supervision of a physician; self-medication is unacceptable.
Pathogens: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, anaerobic infection - become the source of such types of nonspecific urethritis as:
- Chronic, resulting from trauma to the urethra during childbirth, sexual intercourse, or masturbation. This disease is characterized by discomfort in the area of the urethra, incessant pain in the back, sacrum, groin, frequent urination, and sometimes urinary incontinence.
- Granular occurs due to inflammation of the genital organs. Methods of therapy: quenching the canal mucosa with a silver solution, electrocoagulation. Relapses are possible, so observation by a urologist is necessary.
- Senile occurs during the postmenopausal period. Symptoms are similar to those of chronic urethritis, but the disease lasts longer, the vaginal mucosa atrophies, and there is hyperemia on the outer integument.
- Premenstrual occurs before menstruation. Usually the symptoms do not last long and disappear completely during menstruation.
- Allergies are triggered by allergens. There is pressure and itching in the urethra. The urinary tract swells, the outflow of urine is disrupted. The method of treatment is bougienage of the urethra, that is, expansion of the narrowed duct to a normal state.
Treatment of urethritis in men
Effective treatment of urethritis will help avoid possible complications. It is carried out with the help of various medications - antibiotics, antiseptics, antioxidants, immunotherapy agents, vitamins, immunomodulators, and topical agents. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor. It is important to maintain proper nutrition and give up alcohol and cigarettes.
Antibacterial drugs are the basis of therapy for urethritis of any etiology. The range of antibiotics used in the treatment of this disease is quite wide. Drugs from the group of cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones are used, and penicillin drugs are used less frequently. Candidal urethritis requires the use of antifungal drugs. In many cases, two antibacterial drugs are prescribed at once.
Drugs for the treatment of specific urethritis:
- Olethetrin;
- Cephodisim;
- Erythromycin;
- Cefotaxime;
- Spectinomycin;
- Rifampicin;
- Cefoxitin;
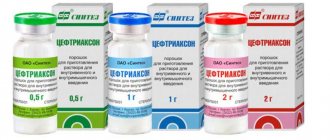
- Ceftriaxone;
- Doxycycline;
- Spiramycin.
For nonspecific urethritis, the following drugs are indicated:
- Doxycycline;
- Erythromycin;
- fluoroquinolones;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Clarithromycin;
- Tetracycline;
- sulfonamides.
Candidal urethritis requires the following medications:
- Amphotericin;
- Nystatin;
- Natamycin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Levorin.
Urethritis in men caused by gonorrhea is treated with the following medications:
- Miramistin;
- Nitazol;
- Tinidazole;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Natamycin;
- Furazolildone;
- Metronidazole;
- Tsidipol.
The course of treatment lasts on average 10 days. It is necessary to strictly follow the regimen of taking antibacterial drugs. You cannot stop treatment on your own; this can lead to the disease becoming chronic.
Urethritis caused by chlamydia is treated by prescribing Doxycycline, Levomycetin, and fluoroquinolones. If mycoplasma is detected in a smear, a man is prescribed representatives from the Tetracycline group. Herpesvirus urethritis involves treatment with Acyclovir, Ribavirin, Ganciclovir, Penciclovir.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Descending cystography | 2 200 |
| Uroflowmetry | 3 000 |
| Ascending cystography | 3 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions