Indications Contraindications Crosslinking stages Price Our advantages
Corneal crosslinking is an effective, low-traumatic technique used to treat a number of pathologies of the cornea, in this case, keratoconus, as well as other diseases. This method was developed by prof. T. Seiler in the late 90s. last century and was used to treat patients with keratoconus and postoperative keratoectasia (a complication of laser vision correction). Nowadays, the corneal cross-linking technique is also gaining widespread use in the treatment of various dystrophic lesions of the cornea.
Mechanism of action and indications
The corneal crosslinking method is based on the ability of the stromal collagen fibers of the cornea to undergo certain changes under the influence of certain physical or chemical factors. It was found that the combined effect of ultraviolet rays on the cornea in the presence of riboflavin (vitamin B2) causes a photopolymerization reaction of collagen fibers, which leads to their compaction and increases the biomechanical properties of the cornea.
In addition, riboflavin and ultraviolet rays have an anti-edematous and antibacterial effect. Thanks to these effects, in this period corneal crosslinking is triumphantly used as an effective method for treating keratoconus, as well as various dystrophic pathologies of the cornea (keratopathies, corneal ulcers, Fuchs' dystrophy with pain syndrome, keratomalacia).
Recovery
After surgery, the cornea returns to its normal state in an average of 5-6 days. Over the course of 3-6 months, vision returns to normal or even improves. The rehabilitation period requires wearing soft lenses for therapeutic purposes for 3 days. At this time, it is necessary to instill an antibacterial agent into the eyes. After this period, anti-inflammatory drugs are used for another 3 days. If there are no signs of infection, pain or changes in the eye, there is no need to prolong the use of medications. After surgery, the patient should be periodically examined by a doctor to prevent complications.
Stages of the procedure
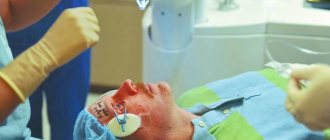
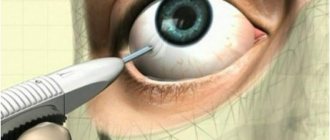
Before the operation begins, the patient is given eye drops containing an anesthetic. After the onset of anesthesia, the doctor applies an eyelid speculum and, using an eye spatula, carefully removes the top layer of the corneal epithelium (this is necessary to improve the penetration of the vitamin B2 solution into the thickness of the cornea). Within 15–20 minutes, a riboflavin solution is instilled into the eye, at the same time the doctor examines the cornea using a slit lamp and evaluates how evenly the vitamin B2 solution penetrates the corneal tissue.
Upon reaching the required degree of saturation with the riboflavin solution, the corneal tissue is treated with low-intensity ultraviolet rays for 30 minutes, which avoids damage to the deeper structures of the eyeball. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, collagen fibers located in the cornea are welded together and form a strong frame that is resistant to stretching.
At the end of the procedure, antibacterial eye drops are instilled into the eye to prevent inflammation, after which the operated surface of the cornea is protected with a special therapeutic soft contact lens. Throughout the entire healing period of the cornea (an average of 3 - 5 days), the patient must wear a treatment lens and instill anti-inflammatory drops.
Treatment of disease using cross-linking
One of the modern methods of treating keratoconus is cross-linking of corneal collagen.
Stages of treatment
Carrying out this procedure allows you to increase the rigidity of the cornea, which, in turn, allows it to resist the process of further deformation. A positive treatment result is achieved by strengthening the chemical bond between the collagen fibers of the cornea.
Crosslinking is a simple and gentle procedure, the practical implementation of which does not cause any possible complications. They begin the procedure only after a thorough diagnostic examination of the visual organs. Crosslinking is a procedure that involves going through the following stages:
- At the first stage, local anesthesia is performed and the top layer of the cornea is removed using a microscope. No further surgical interventions are performed at this stage. A special solution containing vitamin B2 is instilled over a period of 30-40 minutes, and then, simultaneously with its action, a laser effect is carried out on the cornea of the eye.
- The second stage involves placing a special lens on the eye, which the patient wears for 1 to 2 days.
Crosslinking helps to gradually stabilize vision after the lens is removed and special drops are instilled into the eyes over several days. Restoration of the corneal surface is observed 4-5 days after the procedure, and visual acuity can be restored within several months.
Indications and contraindications for
Crosslinking was initially used to treat keratoconus, but gradually the range of its use expanded and today it is successfully used to get rid of various pathologies of the cornea.
However, crosslinking cannot always be used to treat a patient, and the main reason for this is insufficient thickness of the cornea, age under 18 years, and various infectious eye diseases.
Forecast
Corneal cross-linking is one of the safe and at the same time effective procedures, the implementation of which is distinguished by its simplicity and lack of risks. Some patients experienced an improvement in visual acuity of several lines after using this treatment method. In addition, cross-linking can be successfully combined with other correction techniques for changes in refraction that are observed with keratoconus.
Keratoconus is one of the complex and unpleasant pathologies of the visual organs, which today can be successfully treated. One of the safe and effective methods of treating this disease is cross-linking, which can stop further progression of the disease and thereby stop the process of further deterioration of vision.
Contraindications
The corneal cross-linking procedure is not performed on persons under 18 years of age. Contraindications are also small (less than 400 microns) thickness of the cornea in any dimension, inflammatory eye diseases in the acute phase, decompensation of internal diseases (this mainly applies to pathologies of the cardiovascular or respiratory systems), and mental illness. If it is necessary to perform cross-linking on both eyeballs, the minimum interval between operations is 3 months.
Complications of crosslinking
In most cases, the prognosis for cross-linking is favorable. At the same time, like any invasive intervention, the procedure can have a number of complications. Possible complications include:
- temporary visual impairment (recovery of visual acuity is observed within 1 to 4 months after the procedure);
- reversible decrease in corneal transparency that does not affect visual acuity;
- slow (up to 1 month) restoration of the corneal epithelium;
- redness and irritation of the eyes, in rare cases - the development of keratitis;
- activation of herpetic infection with the development of herpetic lesions of the cornea.
Advantages of corneal crosslinking in MGC
A favorable outcome of any medical procedure is determined by a combination of several main factors, which include accurate diagnosis, selection of the most effective treatment method, high qualifications of the attending physician, and high-quality management of the postoperative period. Each patient of the Moscow Eye Clinic is guaranteed to receive all these benefits.
Thanks to the clinic being equipped with the best examples of diagnostic equipment from global manufacturers, a diagnostic examination allows you to detect any eye pathologies, takes a compact period of time and is carried out in comfortable conditions. On the day of the examination, the patient receives the results of the examination with a transcript of the detected abnormalities and the doctor’s recommendations.
The clinic employs some of the best specialists in the capital. The treatment of corneal pathologies at the Moscow City Clinical Hospital is carried out by Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences. Alexey Yurievich Slonimsky is one of the most authoritative domestic specialists in the treatment of patients with various corneal pathologies (cataract, corneal dystrophy, keratitis), a recognized leader in the field of end-to-end corneal transplantation for keratoconus. The corneal crosslinking procedure is performed by an ophthalmologist, Ph.D. Kishkin Yuri Ivanovich.
Our clinic is open seven days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m., seven days a week. For the convenience of patients, there is a day hospital, where each patient can receive the necessary support.
Corneal diseases
Corneal diseases occur in 25% of patients visiting an ophthalmologist. The cornea is the transparent membrane of the eye, 10-12 mm in diameter, which, like a watch glass, covers the colored structure of the eye called the iris.
A decrease in the transparency of the cornea, leading to loss of vision, can be due to many reasons: burns and eye injuries, keratitis and corneal ulcers, primary and secondary corneal dystrophies, keratoconus and keratoglobus. These corneal injuries and diseases require surgical treatment.
DIAGNOSIS OF CORNEA DISEASES
TREATMENT
In the surgical treatment of corneal diseases, two main directions can be distinguished: keratoplasty (corneal transplant), when the damaged cornea is replaced with healthy donor corneal tissue, and keratoprosthesis - transplantation of an artificial cornea.
MNTK "Eye Microsurgery" has the most experience in Russia in performing keratoplasty: over 30 years of work, over 16,500 donor cornea transplants have been performed. The Eye Microsurgery MNTK operates the largest and most modern Eye Bank in Russia with the latest medical and technological support. The complex is the only medical institution in Russia where the keratoprosthesis method is widely used, using its own models of keratoprostheses.
Keratoplasty surgery is performed on patients with keratoconus, corneal dystrophies, corneal opacities, etc.
| Keratoplasty | The total treatment time for one eye is 14-21 days (preoperative examination 2-3 days, on the 4th day - surgery ( the timing of the operation depends on the availability of donor material ), postoperative follow-up treatment - 10 days) |
To treat corneal cataracts, keratoprosthesis surgery is performed.
| Keratoprosthetics | The total treatment time for one eye (one stage) is 5 days (stage 1: strengthening the cataract and implanting support elements, preoperative examination 2 days, surgery on the 2-3rd day, postoperative observation - 1-2 days; 2nd stage implantation of a keratoprosthesis (3-4 months after the 1st stage).The duration of the operation is the same as at the 1st stage. |
Keratoplasty and keratoprosthetic operations are performed on an inpatient basis and usually take from 30 minutes to 1 hour. In the operating room you will be accompanied by a surgeon, his assistant, an operating room nurse, an anesthesiologist and a nurse anesthetist. Modern methods of anesthesia used in the MNTK “Eye Microsurgery” make it possible to completely eliminate pain.
The operations are performed by highly qualified surgeons from the Department of Transplantation and Optical Reconstructive Surgery of the anterior segment of the eyeball using the most modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers.
, new technologies for the surgical treatment of corneal dystrophy and keratoconus have begun to be widely used at the Eye Microsurgery International Scientific and Research Center .
- Deep anterior layer keratoplasty, which allows you to preserve your own healthy endothelium and avoid opening the eyeball (depressurization), reduce surgical and postoperative complications and the risk of graft rejection.
- Posterior lamellar endothelial keratoplasty, intended for the treatment of corneal dystrophy, allows the portion of donor tissue to be minimized, which reduces the risk of rejection and preserves most of the native cornea.
- Reconstruction of the anterior segment of the eyeball with implantation of an artificial iris based on penetrating keratoplasty in cases of severe corneal trauma combined with loss of the lens and iris.
- An alternative to penetrating keratoplasty for initial and advanced stages of keratoconus is introstromal keratoplasty with implantation of segments. The operation is performed in the early stages of keratoconus, has an orthopedic function, strengthens the thinned area, improves visual acuity, and stops the progression of keratoconus.
- Cross-linking of corneal collagen (cross-linking) slows or stops the progression of keratoconus based on biochemical remodeling of the cornea.
Improvements in microsurgical techniques and instruments, the emergence of new advanced equipment, and new approaches to pre- and postoperative therapy have expanded the range of surgical interventions on the cornea and provided a large percentage of favorable outcomes and high results.
MODERN METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF KERATOCONUS
KERATOCONUS
Keratoconus is a progressive dystrophic disease of the cornea, caused by a number of genetic and acquired factors, characterized by progressive thinning of the cornea with protrusion of its central parts, the formation of myopic refraction and irregular astigmatism. The etiology of keratoconus and other types of keratoectasias is currently unknown. Active progression of keratoconus occurs in 20% of cases and, as a rule, begins during puberty. The progression of the disease leads to a significant decrease in visual acuity and the ineffectiveness of methods for its correction. Making a diagnosis, especially in the initial stages of the disease, is very difficult. The most informative study at the moment in diagnosing this terrible disease, along with generally accepted research methods, is the performance of a scanning keratotopograph PENTACAM (OCULUS, Germany), which makes it possible to evaluate both the anterior and, most importantly, the posterior surface of the cornea - since this is where the initial anatomical changes occur. topographic characteristics in the initial stages (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Scanning keratotopograph PENTACAM (OCULUS, Germany).
Treatment of keratoconus
Depending on the stage of the disease and some important anatomical and topographical characteristics, the ophthalmic surgeon, based on many years of experience and the latest scientific developments of the Eye Microsurgery Institute, will offer the optimal treatment method. There are three main treatments for keratoconus:
Crosslinking of corneal collagen (Fig. 2)
The idea of using a conservative method of treating keratoconus was born in Germany by a group of researchers at the Technical University of Dresden. T. Seiler and G. Wollensak took as a basis the principle of photopolymerization, which has long been used in dentistry (“light filling”). As a result of a series of works, the most effective and safe technique for cross-linking corneal collagen was developed, based on the effect of photopolymerization of stromal fibers under the influence of a photomediator (riboflavin solution) and low doses of ultraviolet radiation from a solid-state source. This technique makes it possible to stop the progression of keratoconus and avoid end-to-end corneal transplantation.
Rice. 2. Crosslinking of corneal collagen
Indications:
- Keratoconus stages I-II.
- Keratoectasia after refractive excimer laser interventions.
- Corneal marginal degeneration
- Keratomalacia of various origins - cornea melting, usually during autoimmune processes.
- Keratoglobus.
- Bullous keratopathy stages I-II.
- There is encouraging data on the use of cross-linking in the treatment of keratitis and corneal ulcers.
Contraindications:
- Intolerance to Riboflavin (Vitamin B2).
- If the thickness of the cornea in at least one dimension is less than 400 microns.
- Age less than 15 years
- Low corrected visual acuity in keratoconus, despite sufficient thickness.
- Presence of corneal scars.
- The presence of allergic conjunctivitis.
Implantation of intrastromal corneal segments
In our practice, we use domestic IRS manufactured at Scientific and Experimental Production LLC "Eye Microsurgery" from polymethyl methacrylate, which is a segment with an arc length of 160 ° (90, 120, 160, 210 °), base 0.6 mm, height 150 - 450 µm, internal diameter 5.0 mm and external 6.2 mm, with a hemispherical cross section (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Intrastromal corneal segment
Correction of keratoconus and high-degree complex myopic astigmatism. First, a corneal tunnel is formed in the cornea, through which a corneal segment is inserted, which leads to flattening of the central zone of the cornea. An important aspect of this operation is its reversibility – i.e. the possibility of replacing or removing a segment if vision changes with age. This is possible because the center of the cornea is not damaged and no corneal tissue is removed. The next day after the operation, the patient’s eye is absolutely calm and after a short rehabilitation the patient can resume everyday visual stress (Fig. 4 It should be noted that implantation of intrastromal segments does not affect the patient’s cosmetics and allows him to use soft contact lenses. Depending on the indications, a combination is possible cross-linking and introstromal implantation of corneal segments.
Rice. 4. Patient's eye the day after implantation of the corneal segment
3.Keratoplasty
Recently, the method of choice for surgical treatment of keratectasia in advanced stages of the disease has often become anterior deep lamellar keratoplasty, during which the corneal stroma is peeled off from Descemet's membrane. At the same time, the increase in visual acuity is comparable to that after penetrating keratoplasty. The advantages of anterior deep lamellar keratoplasty over penetrating keratoplasty are: preservation of the endothelium of the recipient's cornea, which reduces the risk of graft rejection; reducing the risk of developing cataracts in the postoperative period due to the administration of a shortened course of steroid therapy; reducing the requirements for the donor graft, since the quality of its endothelium in this case does not play such a significant role as in penetrating keratoplasty.
It should be noted that the best results can be obtained when performing keratoplasty - both penetrating and anterior deep layer-by-layer with the use of femto-laser support, which ensures ideal cutting accuracy and unsurpassed compatibility of the cut donor graft and the recipient bed, leading to a significant increase in the visual functions of patients . Thus, currently, a qualified ophthalmic surgeon has a wide range of surgical methods for treating keratoconus. However, it should be noted that the most effective treatment is considered to be in the early stages of the keratectic process, which is possible with timely correct diagnosis of the keratectasis. The most effective modern methods for early diagnosis of the keratecstatic process are: computer keratotopography, optical coherence tomography, confocal scanning microscopy, immersion confocal microscopy, analysis of elevation maps. Our institute is equipped with the most advanced equipment for the early diagnosis of keratoconus, which allows us to detect keratoconus, even at the earliest stages of development, in 100% of cases. It should also be noted that the abundance of different methods for treating keratoconus poses the task of choosing the most effective method of treatment for each individual patient. The leading specialist of our institute is Doctor of Medical Sciences. Svetlana Borisovna Izmailova, based on a comprehensive analysis of the results of treatment of patients with keratoconus, developed an algorithm for the surgical treatment of keratoconus, which allows systematizing approaches to the treatment of keratoconus and differentially selecting the most optimal and effective method of treatment depending on the stage of the disease. Thus, the MNTK “Eye Microsurgery” presents the entire range of modern therapeutic and diagnostic technologies, allowing pathogenetically oriented treatment for each patient with keratoconus at any stage - from initial to acute. We can help everyone!
Our specialists:
Malyugin B.E. – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor. Performs operations on mechanical and femtolaser implantation of corneal segments, various types of keratoplasty, including layer-by-layer. Proficient in technologies for intraocular correction of residual myopia and astigmatism in patients with stabilized keratoconus.
Izmailova S. B. – Doctor of Medical Sciences Performs implantation of corneal segments, including femto-assisted, UV cross-linking, penetrating and lamellar keratoplasty - mechanical and femto-laser assisted. Proficient in technologies for intraocular correction of residual myopia and astigmatism in patients with stabilized keratoconus.
Kostenev S.V. – Doctor of Medical Sciences Performs implantation of corneal segments with femto-laser assistance and UV crosslinking. Performs PRK to correct residual ametropia.
Kovshun E.V. – Ph.D. He specializes in the treatment of advanced stages of keratoconus using penetrating and lamellar keratoplasty, and performs implantation of corneal segments and UV crosslinking.
Volkova O.S. – Ph.D. Performs implantation of corneal segments, including with femto-laser assistance, and penetrating keratoplasty.
Golovin A.V. – Ph.D. Performs femto-laser implantation of corneal segments.
Pashtaev A.N. – Ph.D. Performs femto-laser implantation of corneal segments.
Moroz O.V. – Performs implantation of corneal segments.
Contact us! We will help you!
YOUR DOCTORS
Crosslinking cost
The cost of the corneal crosslinking procedure at the Moscow Eye Clinic is 30,000 rubles. for one eye. Prices for other medical services at MGK can be found here.
All questions you are interested in can be asked to specialists by calling the MGK hotline 8(800)777-38-81 (toll-free from mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) and the number in Moscow 8(499)322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on website.