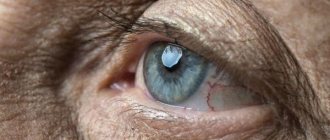
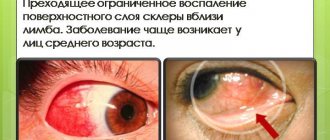
AMD is one of the common causes of irreversible vision loss among people over 50 years of age. Since people in this age group make up the majority of the population, vision loss due to macular degeneration poses a challenge to ophthalmologists.
According to WHO, the elderly population in developed countries accounts for approximately 20 percent, and by 2050 these figures are expected to increase to 33 percent. With increasing life expectancy, a steady increase in atherosclerosis and associated pathologies, the problem of AMD seems to be the most pressing.
The reason for decreased vision in AMD is degeneration of the macula, the area of the retina that is responsible for the acuity and sharpness of central vision; peripheral vision does not suffer. Central vision is necessary for a person to read, work and drive a car, therefore the social significance of this disease is explained by the loss of general performance of people who are not yet old. At the same time, the severity of the process accompanying the loss of central vision is closely related to the form of macular degeneration.
Forms of AMD
Intense metabolic processes in the retina of the eye lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species, including free radicals, which contribute to the development of degenerative phenomena in tissues in case of insufficient functioning of the antioxidant system (AOS). This leads to the formation in the macular and paramacular areas of the retina of non-cleavable polymer structures - drusen, the basis of which is lipofuscin.
When drusen are deposited, atrophy occurs in the adjacent layers of the retina, and the growth of newly formed pathological vessels in its pigment epithelium is also noted. Then there are scarring processes, which are accompanied by the loss of retinal photoreceptors.
In ophthalmology, it is customary to distinguish between two forms of AMD – dry (non-exudative, atrophic) and wet (exudative, neovascular).
The dry form of AMD is much more widespread than the wet form and is found in 85% of cases. With it, yellowish spots - drusen - are revealed in the macular area. The gradual loss of central vision significantly limits the ability of patients to recognize small details, however, this form of the disease is not as severe as the wet form. The dry form of AMD can gradually progress over several years to the stage of late geographic atrophy (GA), with slow degradation of retinal cells and lead to vision loss.
There is no radical treatment for dry AMD, although some drugs are already in clinical trials. Scientific research shows that certain nutrients, such as vitamins A, C and E, can, if not prevent, then significantly slow down the progression of the disease. Regular intake of certain nutritional supplements - eye vitamins - reduces the risk of developing AMD by almost 25%. Protecting your eyes from UV rays with sunglasses will help reduce the risk of developing AMD or slow its progression in the dry form of the disease.
The wet form of AMD is diagnosed in approximately 15% of cases of age-related macular degeneration. The disease progresses rapidly, leading to significant loss of central vision. In the wet form of macular degeneration, rapid neovascularization occurs with the growth of new blood vessels. These vessels are defective and have fragile walls that allow blood cells and lymph to pass through, which flow out and accumulate under the retina. This condition causes damage to the photoreceptors in the retina, which die, forming blind spots (scotomas) in central vision.
The process of growth of newly formed vessels in wet AMD is called choroidal neovascularization (CNV). Moreover, abnormal vascular growth is a mistake by the body in an attempt to create a new network of blood vessels to provide nutrients and oxygen to the retina. Instead, scars form in place of the ruptured vessels, leading to loss of central vision.
Types of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
There are “dry” and “wet” forms of this disease, which depend on the stage of the disease.
“Dry” AMD, or non-exudative, accounts for about 90% of cases and is characterized by slow progression. The “wet” or exudative form occurs in 10% of cases and is accompanied by the development of choroidal neovascularization and rapid loss of vision.
In the development of AMD, the ischemic factor (trophic disorders) is of decisive importance. The disease can develop in two ways:
- The first option is characterized by drusen formation. Drusen are defined symmetrically in both eyes as yellowish thickenings located under the retinal pigment epithelium. Their size, shape and number, as well as the degree of prominence and combination with other changes in the pigment epithelium vary. With significant sizes and an increase in the number of drusen, choroidal neovascularization develops. Characterized by active production of vascular endothelial growth factor, which is a powerful stimulator of angiogenesis. Newly formed vessels can spread under the pigment epithelium, causing retinal detachment. Next, perforation of the pigment epithelium and detachment of the neuroepithelium occurs. A choroidal neovascular membrane is formed, followed by a fibrous scar.
- The second variant is characterized by extensive geographic atrophy of the macular pigment epithelium, with choroidal neovascularization developing only in late stages.
Causes of AMD development
The causes of the disease still remain unclear. But scientists suggest that the following factors may lead to its development:
- Age is the main reason. The incidence increases rapidly with age. Signs of AMD occur in 2% of middle-aged people, in 20% of elderly people aged 65-75 years, and in every third person after 75-80 years.
- Genetic predisposition to the development of the disease, but there are factors that contribute to either the occurrence of the disease or its prevention.
- Race - the prevalence of macular degeneration is more common among Caucasians.
- Heredity (family predisposition) is one of the risk factors in almost 20% of patients with age-related macular degeneration. The risk of AMD increases threefold when the disease occurs in close relatives.
- Cardiovascular disease is one of the main risks for the development of AMD. With atherosclerosis, the risk of the disease increases three times, and with hypertension – seven times.
- Cigarette smoking is the only risk factor confirmed in all studies. Quitting this habit reduces the risk of developing the disease.
- Impact of UV rays on the retina of the eye.
- Poor diet - The risk of AMD is significantly higher in people who eat a lot of saturated fat and have increased body weight.
- Light iris. People with light irises (blue, gray, green eyes) suffer from AMD more often.
- Cataract, especially nuclear. Cataract surgery often contributes to the progression of the disease in people with existing changes in the macula.
How to treat macular degeneration of the retina - I see super
Many people wonder how to treat macular degeneration of the retina, especially in old age. It is after 50 years that this pathology is detected in most patients. However, it can also bother young people and even children. They usually develop Stargardt macular degeneration.
What is macular degeneration
The macula is the layer in the center of the retina that is sensitive to light. It provides excellent vision of objects that are directly in front of a person. But if it is damaged, the patient loses the ability to do basic things: move in space, read, watch movies.
Some patients simultaneously develop color blindness. This is exactly what happens with macular degeneration. Sensitive cells change and can no longer perceive the picture. A person sees a blurry dark spot in the center of the field of vision. Only peripheral vision works without failures.
Over time, complete blindness occurs.
Stargardt's macular degeneration
This disease occurs in adolescents and children. It is transmitted exclusively by inheritance, and has no other reasons. At the same time, children whose parents suffer from macular degeneration have a low chance of getting sick. For every 10,000 healthy children and schoolchildren, there is one sick person.
Dry macular degeneration - what is it?
90% of macular degeneration diagnoses are due to this form of the disease. It represents the initial stage, during which the extra vessels have not yet had time to rejoice. Dry macular degeneration is characterized by thinning of the retina and the presence of yellow pigment in it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nJbs89TFFYQ
Dry macular degeneration occurs in three stages:
- Early. Asymptomatic, small drusen may be present;
- Intermediate. Drusen merge into one large spot or several small ones. Spots begin to appear before the eyes;
- Expressed. The spots before the eyes become larger and darker, which indicates the death of light-sensitive cells.
If dry macular degeneration is not treated, it develops into wet macular degeneration. At this stage, abnormal blood vessels grow and vision deteriorates significantly. Everyone should understand what the diagnosis of “dry macular degeneration” means, what it is, and what its causes are. If risk factors are addressed, the early development of this disease can be delayed and even prevented.
Reasons for the development of macular degeneration
Among the risk factors, doctors most often identify several at once.
- Poor nutrition. If the body does not receive the necessary microelements and vitamins, any disease progresses faster.
- Sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation damages the retina.
- Frequent eye strain. The risk is aggravated by working at a computer, regularly watching TV for long periods of time, and reading in a poorly lit room.
- Smoking. Nicotine causes pathologies of blood vessels, which also nourish the retina.
- Pathologies of the circulatory system. Here, too, the risk lies in the insufficient supply of blood and nutrients to the retina.
- Advanced retinal diseases. Macular degeneration develops in the absence of timely treatment of other ophthalmological pathologies
How to treat retinal macular degeneration
Modern medicine does not have a way to completely eliminate this disease. Treatment is mainly aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and stopping the development of pathology. Surgeries or drug therapy are prescribed according to indications. Sometimes these methods are combined with each other. The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of development of macular degeneration.
Age-related macular degeneration of the retina - treatment and prognosis
With this diagnosis, the disease progresses slowly and painlessly, but is practically untreatable. However, this does not mean that treatment in this case is useless - it can significantly slow down vision loss and enable a person to maintain independence longer.
Macular degeneration, dry form, treatment and nutrition
If the patient is obese, it is urgent to normalize body weight by reducing the calorie content of the daily diet. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fat, especially animal fat, cholesterol, and fast carbohydrates.
The patient's menu should include:
- fish high in omega-3, such as salmon;
- fresh vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins;
- greens containing lutein.
Blood sugar levels need careful monitoring. The reason for this is the high risk of significant deterioration of the condition if diabetes develops.
Therefore, it is better to limit sweets and, if possible, replace them with honey. It is also better not to drink lemonade and natural juices, preferring green tea.
A healthy diet is also necessary to control blood pressure. The eyes are one of the first to suffer from hypertension.
Complications include bleeding and retinal detachment.
Lifestyle during treatment for macular degeneration
When deciding how to treat macular degeneration of the retina, doctors recommend an active lifestyle to all patients. Intense exercise is unacceptable, but physical exercise and walks in the fresh air are still necessary. This helps strengthen the vascular system and improve oxygen supply to organs, including the eyes.
It is enough to exercise in the morning and walk for an hour every day. When walking outside in the morning and during the day, you need to wear good sunglasses. This is true not only for summer, but also for the cold season. The negative influence of ultraviolet radiation on the visual organs should not be allowed. For the same reason, visiting the solarium is strictly prohibited.
It is imperative to give up bad habits.
Specific treatment of macular degeneration of the eye
The treatment method is chosen based on the stage of the pathology and its type. At an early stage, treatment is rarely prescribed due to the fact that diagnosis at this time is difficult. But even when diagnosed at an early stage, developing a treatment concept is difficult and sometimes impossible.
Macular degeneration, dry form - treatment
The main recommendation for patients with early macular degeneration is to eliminate risk factors. Drug therapy in this case consists of prescribing vitamins E, A, B, and antioxidants.
All people diagnosed with early stage macular degeneration are advised to visit an ophthalmologist at least once every six months to monitor the condition.
This is especially true for patients over fifty years of age.
If you have age-related macular degeneration of the retina, treatment and monitoring should be systematic. In the transitional and severe stage, as with the diagnosis of “macular degeneration, dry form,” treatment also very rarely gives a positive result.
Most often, such patients are prescribed laser correction. Overgrown drusen are removed, resulting in slightly improved vision.
Despite this, it is completely impossible to restore it, since photoreceptor cells are not restored under any circumstances.
Macular degeneration, wet form - treatment
The therapy is carried out in a similar way, although its effectiveness is slightly higher. However, even with this type of disease, you can only slow down the process, but not stop it. If the doctor's recommendations are followed correctly, the patient may never lose vision completely.
Analgesic injections
One of the most modern methods of treating this disease is biological therapy. Substances are injected into the eyeball to block the formation of new blood vessels.
Their effect on tissue makes it possible to slow down degradation and prolong the relatively normal functioning of the eyes for many years.
For patients diagnosed with macular degeneration, especially the wet form, treatment takes several weeks.
Photodynamic therapy
The course of treatment includes intravenous injections of verteporfin followed by exposure of the affected vessels to a laser beam. The drug begins to actively affect tissue, destroying new vascular beds.
Laser coagulation
The procedure is carried out with the preliminary administration of local anesthetics. The doctor directs the laser at the abnormal vessels, which, under the influence of high temperatures, are sealed and evaporated.
The radiation frequency allows healthy tissues not to be affected even if the laser beam hits them. However, this rarely happens, since the beam is very thin, which allows for almost one hundred percent accuracy.
The laser can only be used to eliminate newly grown vessels located in a limited area.
Adaptive devices for the treatment of macular degeneration
Palliative methods of vision correction provide a certain effect when blindness has not yet occurred, but vision has already seriously deteriorated. Because macular degeneration does not impair peripheral vision, patients can use it more effectively than healthy people.
To adapt patients to the disease, the following are used:
- glasses with special lenses;
- special devices for reading text and viewing screens;
- e functions in computers (the ability to listen to printed text).
Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina with folk remedies
For hypertension, herbs that have a hypotensive effect are recommended: valerian, motherwort, calendula. At the same time, they will alleviate stress. If you are prone to diabetes, it is recommended to consume:
- vitamin-containing products (jerusalem artichoke, chicory); zinc-containing (sage, bird knotweed, Canadian goldenrod, corn silk);
- chromium-containing (Siberian fir, ginger);
- adaptogens (rhodiola rosea, ginseng, Chinese lemongrass);
- diuretics (birch, horsetail);
- stimulants (walnuts, blueberries, licorice, burdock). Blueberries are useful not only as a stimulant, but also as a means for overall improvement of eye health. It is also worth taking it for prevention after the age of 40-50 years.
Thus, the answer to the question of how to treat macular degeneration of the retina is one - it cannot be cured at all. At the first signs of pathology, you need to contact an ophthalmologist to slow down the onset of blindness.
Premature ejaculation - if this phenomenon occurs in your life - do not despair! There is a way to solve this problem easily and quickly - stud prolongator spray. This lidocaine-based product has become the undisputed leader among similar sprays.
Source: https://vizhusuper.ru/kak-lechit-makulodistrofiyu-setchatki-glaza/
Symptoms of AMD
Age-related macular degeneration is a disease that develops slowly and painlessly, with gradual loss of vision. In rare cases, the onset of vision loss occurs suddenly.
Early signs of gradual vision loss in AMD:
The appearance of dark spots in the central vision. Blurry images. Distortion of the boundaries of objects. Deterioration of color perception. Weakened vision in the dark and in low light.
A simple way to determine AMD is the Amsler test. The lattice or Amsler grid depicts intersecting straight lines with a black dot in the central part. In the presence of AMD, the lines of the pattern may appear blurred or wavy, and some of the grille fragments may appear as darkened, opaque spots.
After conducting the test, an ophthalmologist is able to identify manifestations of the disease long before the development of serious changes in the patient’s vision and recommend additional examination.
Treatment with folk remedies
For this disease, the recipes of traditional healers are designed to support the body, strengthening and toning it.
- Infusion of mumiyo with aloe: dissolve 5 g of mumiyo in 0.1 kg of fresh aloe juice. Keep the product in a cool place and warm to room temperature before use. Apply eye drops twice a day for 2 weeks. It is advisable to repeat after 10 days.
- Vitamin composition 1: mix 35 g of sea buckthorn, blueberry, rowan fruits and 1 tsp. honey Use 2 tbsp. l. before meals three times a day, a month and a half.
- Vitamin composition 2: mix 2 chopped carrots, 2 walnuts and 1 tsp. honey No norm.
- Oatmeal broth: soak 0.5 liters of oat grains for 4 hours, then place the grains in clean water - 3 liters, and boil for half an hour, filter. Keep refrigerated. The daily norm is up to 5 glasses. If desired, you can add berries and honey.
- Calendula infusion: 1 tbsp. l. place the flowers in 0.2 liters of boiled water for 15 minutes. Use 3 times a day – 50 ml orally and instill 2 drops.
- Caraway decoction: 1 tbsp. l. Boil the caraway seeds in 0.2 liters of water for a few minutes. Add 1 tsp. cornflower blue. Apply 2 drops in the morning and evening.
- You can also put goat milk in your eyes, diluting it half and half with water.
- Celandine decoction: 1 tbsp. l. Boil the herbs in 0.1 liters of water for a couple of minutes. Apply eye drops three times a day, a month.
- Herbal decoction: mix onion peels, rose hips and pine needles in a ratio of 2:2:5. Boil 1 tbsp in a liter of water. l. collection Drink 0.5 liters of decoction per day.
- Herbal compress: mix a third of a glass of nettle, 1 tsp. lilies of the valley, 0.5 tsp. soda and 0.2 liters of water. Let it brew for 9 hours in the dark. Apply the compress twice a day.
Diagnosis of AMD
To diagnose age-related macular degeneration, an accurate history, assessment of visual functions and examination of the patient’s retina using various methods are sufficient. Fluorescein angiography of the ocular fundus (FAGD) is considered one of the informative methods for detecting pathology. FAGD involves the use of contrast agents - fluorescein or indocyanine green, which are injected into the patient's vein, then a series of photographs of the fundus is taken.
The obtained stereoscopic images can be used in the same way as the original ones during dynamic monitoring of a patient with severe dry form of AMD or to evaluate the results of treatment.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used to accurately assess changes in the macula, which makes it possible to detect structural changes even in the early stages of retinal dystrophy.
Intraocular injections
However, few doctors convey to their patients the information of the International Congress of Ophthalmologists, which, based on the results of clinical observations, adopted the following procedure for working with the drug: if three consecutive injections of Lucentis do not have an effect, the drug is discontinued.
The fourth and any subsequent injections of Lucentis, even in patients with a positive reaction to the drug, are considered ineffective.
Regenerative therapy
The greatest effect in the treatment of macular degeneration of the retina is shown by the method of regenerative therapy. Clinics in Israel, Germany and Vietnam are conducting their research in the field of tissue technologies; doctors in Kyiv and Minsk are following a similar path, but have not yet proposed an effective technique.
Despite all the effectiveness of the method, you will not hear stories from our patients “how I cured macular degeneration” or “how I got rid of macular degeneration.” It is necessary to clearly understand that macular degeneration is a serious, steadily progressing disease.
For this reason, in order to maintain the achieved result, the procedure must be repeated regularly - approximately once a year. Violation of the treatment regimen leads to a natural decrease in vision.
Treatment of different forms of AMD
Despite advances in improving diagnostic techniques for AMD, its treatment remains a challenge. In dry forms of AMD or a high risk of its development, in order to normalize metabolic processes in the retina, it is recommended to carry out a course of antioxidant therapy.
According to scientific research, the beneficial effect of taking antioxidants was noted in participants with intermediate or late stage AMD. Combination therapy with antioxidants, copper and zinc for 5 years reduces the incidence of advanced AMD by 25% and by 19%, and the risk of a decrease in visual acuity by three or more lines.
The use of replacement therapy for the treatment of the dry form of age-related macular degeneration is carried out constantly. It should be used in persons over 50 years of age or at any age in the presence of risk factors (overweight, hypertension, smoking, cataract extraction, family history).
Therapy for wet AMD is aimed at suppressing the growth of newly formed abnormal vessels. There are a number of techniques and medications registered in Russia that stop and reduce the manifestations of neovascularization, which can improve the vision of patients with wet AMD.
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration
There are enough treatment options, for example, in case of dry degeneration, drusen are removed with a laser; in case of wet AMD, a special drug is injected intravenously, accumulating in the new vessels of the macula; a photodynamic effect is applied to them, as a result of which the lumen of the vessel is closed. Photodynamic therapy is a good alternative to laser treatment, there are fewer complications and the result is good.
Surgical techniques have not yet become widespread in AMD due to their high complexity and possible complications, but in some cases they have a place.
Today, monthly injections of a special drug into the vitreous body - inside the eye, are quite effective, which also helps to block the lumen of blood vessels with good results.
What is dystrophy?
The retina is the most important structure of the eye, which has a complex structure that allows it to perceive light impulses. The retina is responsible for the interaction between the optical system of the eye and the visual parts of the brain: it receives and transmits information.
Retinal dystrophy is usually caused by disorders in the vascular system of the eye. It mainly affects older people, whose vision gradually deteriorates. With retinal dystrophy, the photoreceptor cells responsible for distance vision and color perception are affected.
At first, retinal dystrophy can be asymptomatic and often a person does not even suspect that he has such an insidious disease. Retinal dystrophies can be divided into:
- Central and peripheral. Peripheral retinal dystrophy is most often present in myopic people. Reduced blood circulation in the eye with myopia leads to a deterioration in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the retina, which is the cause of various peripheral retinal dystrophies.
- Congenital (genetically determined) and acquired.
- “Senile” dystrophy develops most often after 60 years. This type of retinal dystrophy can be combined with the development of senile cataracts caused by the aging of the body.
- Retinal pigmentary dystrophy is associated with disruption of the photoreceptors responsible for twilight vision. This type of retinal dystrophy is quite rare and is a hereditary disease.
- White dot retinal dystrophy - usually occurs in childhood and progresses with age. This type of dystrophy is hereditary.
In order to confirm or refute the diagnosis of retinal dystrophy, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination of the visual system. Diagnostics are performed using a complex of modern computerized equipment and allow you to get a complete picture of the patient’s vision.
Examination of patients with suspected retinal dystrophy includes:
- determination of visual acuity;
- study of visual fields (perimetry) in order to assess the condition of the retina in its periphery;
- optical coherence tomography;
- electrophysiological study - determination of the viability of nerve cells of the retina and optic nerve;
- ultrasound examination of the internal structures of the eye - A-scan, B-scan;
- measurement of intraocular pressure (tonometry);
- fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy).
Very often, degenerative changes in the retina accompany moderate and high degrees of myopia. The fact is that usually in this case the size of the eyeball increases, and the retina lining its inner surface stretches, which leads to dystrophy.
The laser is a unique surgical instrument that has given ophthalmic surgeons completely new opportunities. The principle of treatment is based on the fact that laser exposure leads to a sharp increase in temperature, which causes coagulation (clotting) of the tissue. Thanks to this, the operation is bloodless.
The laser is very precise and is used to create fusions between the retina and uvea of the eye (i.e., strengthening the retina) to prevent retinal detachment. To perform the operation, a special lens with an anti-reflective coating is placed on the patient's eye.
It allows radiation to completely penetrate the eye. Laser radiation is supplied through special light guides, and the surgeon has the ability to control the progress of the operation through a stereomicroscope, direct and focus the laser beam.
The main goal of PPLC (peripheral preventive laser coagulation) is precisely prevention - reducing the risk of retinal detachment, and not improving vision. What kind of vision will be after surgery largely depends on whether there are any concomitant eye diseases that affect the ability to see well. The main thing is not to delay solving the problem.
Diagnosis of AMD in ophthalmology: what kind of disease is it?
Aging is caused by many factors, which may have a genetic, hormonal or social background. Lifestyle and ecology also contribute to this process.
The condition of the eyes is affected by stress, large visual loads, the action of free radicals (these are unstable atoms and compounds that act as aggressive oxidants and, as a result, damage the vital structures of the body), excessive insolation, and environmental pollution.
Sometimes these external factors account for up to 80% of the responsibility for premature aging and eye damage.
Let's take the sun for example. We understand perfectly well that without him there would be no life. People have heard since childhood that the sun's rays in reasonable doses have a healing effect on the body.
On the other hand, the blue part of the spectrum and ultraviolet literally burn our retina, especially its central part. Light exposure to human eyes in the modern world is incomparably greater than it was many years ago.
Computers, televisions, and a decrease in the thickness of the Earth's ozone layer have a harmful effect on the retina. Bright light destroys macula cells, provoking the formation of free radicals in them.
An incurable disease such as age-related central retinal dystrophy or age-related macular degeneration (AMD) develops.
The macula (macula) is the central part of the retina. Its diameter is about 5 mm, and it consists of the most highly sensitive cells - cones, the number of which in this zone reaches 7 million.
It is this zone that gives us the ability to see objects, their shape, color. The rest of the retina perceives only light and shadow. In the center of the macula there is a depression - the central fossa with a diameter of about 1.5 mm.
This is the most light-sensitive area of the retina. Due to the high content of special substances - carotenoids, in particular lutein, the macula has a yellow color, especially pronounced in the central region with a diameter of about 3 mm.
Lutein is a powerful protective light filter and neutralizes free radicals in the retina. However, it is not produced in the body; we receive it from the outside through food. Lutein deficiency causes the macula to lack light protection.
According to statistics, in Russia, 15 out of 1,000 people suffer from age-related macular degeneration. According to the World Health Organization, 161 million people in the world have some kind of eye disease, including 25-30 million diagnosed with AMD.
Over time, the number of people with this disease will increase, as human life expectancy increases, and, consequently, there are more elderly people. The age of patients with AMD varies and ranges from 55 to 80 years.
According to the National Eye Institute (USA), among the causes of blindness, age-related macular degeneration ranks second, second only to diabetic retinopathy.