Sympathetic ophthalmia
It is necessary to distinguish between the terms sympathetic inflammation and sympathetic irritation.
In the second case, we are also talking about a concomitant lesion of a paired organ, but this does not manifest itself as signs of an inflammatory reaction, but in neurotic symptoms and reflex reactions caused by inflammation or an attack of intraocular hypertension in glaucoma.
With sympathetic irritation, it is not possible to identify any objective signs of an inflammatory reaction, but the patient's condition is unsatisfactory and causes a large number of complaints.
Immediately after eliminating the cause of sympathetic irritation, the normal operation of the optical apparatus is completely restored. This is the fundamental difference between sympathetic irritation and sympathetic inflammation. Moreover, in a number of cases there is a certain sequence when sympathetic irritation first occurs, and then sympathetic inflammation develops against this background.
Risk group
OM can appear at any age. Some evidence suggests that children and people over 60 have a higher risk of developing the disease. This occurs due to frequent injuries to the organs of vision in children and due to ophthalmological operations in the elderly. Individuals of different racial and ethnic backgrounds may be affected.
Sympathetic ophthalmia is a very rare disease. Prevalence: 1 case per 3.5 million population.
Complications
Untreated or delayed treatment of sympathetic ophthalmia can lead to serious visual impairment:
- Choroidal neovascularization is the abnormal development of blood vessels in the choroid, which, if left untreated, can lead to permanent vision loss;
- macular edema (fluid in the macula) and papillary edema (papilledema);
- glaucoma is a condition that can cause blindness due to high intraocular pressure;
- cataract - the lens of the eye becomes clouded and causes loss of vision;
- Retinal detachment occurs in most cases - this is an eye condition in which the retina separates from the eye structures that hold the layers of the retina together;
- poliosis is a condition that causes a decrease in melanin pigment in the eyebrows and eyelashes;
- severe inflammation causing complete loss of visual perception.
If left untreated, uveoneuroretinitis can lead to permanent blindness.
Forecast
The prognosis for sympathetic ophthalmia is good if the patient begins timely treatment. With the correct therapy technique, complete restoration of visual functions is possible. Depends on severity of signs/symptoms and response to treatment.
In 35% of cases people become blind
Prompt detection and treatment is essential to prevent permanent eye damage resulting in vision loss
Prevention
Sympathetic ophthalmia is difficult to prevent. Some doctors insist on removing the victim's eye using a procedure known as ocular enucleation.
Patients with bilateral uveitis should be closely monitored by their attending physician.
There is no specific prevention of uveoneuroretinitis. All measures are limited to timely treatment of diseases and compliance with safety precautions.
Poor vision significantly impairs the quality of life and makes it impossible to see the world as it is.
In Israel, non-surgical vision restoration up to 93% has been practiced for several years... Read more Was the article helpful?
Pathogenesis
Ultraviolet waves are mostly absorbed by the cornea.
However, the short-wave spectrum of ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the corneal tissue, causing burns. Long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eye can lead to the appearance of superficial punctate keratopathy, pinguecula and pterygium (benign growth of the conjunctiva caused by prolonged photochemical irritation), and squamous metaplasia. Ultraviolet radiation has an irritating effect on the surface epithelial cells of the cornea, which leads to thinning of the corneal layer. In most cases, swelling of the mucous membrane, inflammation and superficial punctate keratitis occurs. With severe damage, complete desquamation of corneal epithelial cells may occur. Complete restoration (epithelialization) of damaged areas of the cornea takes from 36 to 72 hours.
Treatment of electroophthalmia
What to do first if you have an eye burn from welding and how to treat it? Treatment of damage to the cornea of the eye due to electroophthalmia should begin with first aid, which consists of providing the victim with complete visual rest, which is achieved by transferring him to a darkened room or, if this is not possible, by applying a dark, opaque bandage to the eyes. Apply a compress (a clean cloth soaked in cold water) to the eyelids of the affected eyes for 10-15 minutes. During the treatment period, visual load is limited.
Drug treatment of a corneal burn from welding is aimed at relieving the symptoms of keratoconjunctivitis, pain, preventing possible infection and stimulating the processes of epithelization of corneal defects.
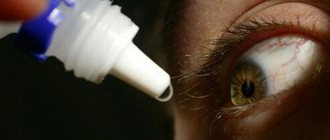
To do this, disinfectant drops (Sulfacetamide) and artificial tears are instilled into the conjunctival sac. To reduce pain, solutions of anesthetics (Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Alcaine, Dicaine) are instilled, and in case of severe pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesil, Nimid, etc.).
To reduce swelling, relieve inflammation, itching and redness, eye drops with a vasoconstrictor effect (Vizin, Proculin, Visoptin) are prescribed. To prevent infection, drops/ointments with antibiotics are instilled (Tsipromed, Signicef, L-Optic Rompharm, Levofloxacin, Erythromycin). Further treatment of damage to the cornea of the eye is aimed at improving corneal regeneration, for which Solcoseryl, Korneregel, Balarpan are prescribed. When providing first aid and treatment, it is strictly forbidden to rinse your eyes with tap water, as well as use independently purchased drops when treating a burn to the cornea of the eye.
The doctors
specialization: Oculist (ophthalmologist)
Guryanova Olga Vladimirovna
4 reviewsSign up
Find a doctor and make an appointment
- Anesthetics: Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Alcaine, Dicaine.
- Vasoconstrictor drugs: Visin, Visoptin, Proculin.
- NSAIDs: Diclofenac, Nimesil, Nimid.
- Disinfectants: Sulfacetamide.
- Local antibiotics: Tsipromed, Signicef, L-Optic Rompharm, Levofloxacin, Erythromycin.
- Preparations to improve tissue regeneration: Solcoseryl, Korneregel, Balarpan.
Classification
Experts distinguish several degrees of eye damage in pathologies such as electroophthalmia:
- Easy degree. With this pathological condition of the eye, the transparency of the corneal layer is significantly reduced, and the conjunctival membrane turns red. In addition, there is severe discomfort in the eyes, itching and burning sensations in the eyes.
- Average degree. the cornea becomes quite sensitive to light. The conjunctival membrane becomes covered with a film and causes pain.
- Severe degree. The patient experiences a decrease in visual acuity and swelling with a constant feeling of discomfort.
- Too heavy form. With this pathological condition of the eye, the process of tissue death begins, followed by rejection of the conjunctival membrane. The patient has to constantly close his eyes due to severe pain. In the absence of effective therapy, the inflammatory process ends in partial or complete blindness.
The main reason for the progression of the pathological process is damage to the epithelial cells of the corneal layer, which stimulates eye inflammation.
Drug therapy
- To relieve swelling and eliminate inflammation, glucocorticoids are prescribed, which have an immunosuppressive effect (inhibit the immune system). Glucocorticoids are administered, including retrobulbar, behind the eye.
- If thyroid hormone levels are too high, drugs that suppress the production of thyroid hormones (thyreostatics), such as Mercazolil, are prescribed.
- Actovegin is widely used, which improves blood circulation and activates metabolism. This drug is prescribed in the form of tablets, injections, and also as an eye gel.
- Vitamins of group A and E may be prescribed.
Forecast
The first thing to do in case of such eye damage is to visit an ophthalmologist. In the case of a lesion of moderate severity, the ophthalmologist can predict the effectiveness of treatment provided that all recommendations are followed. If exposure to ultraviolet radiation continues further, acute and chronic forms of inflammation develop.
The acute form is considered to be electroophthalmia (photoophthalmia), which is accompanied by the development of conjunctivitis. The chronic form of the disease is the development of blepharitis and conjunctivitis.
First aid for electroophthalmia (ultraviolet eye damage)
When performing electric gas welding work without a mask, a worker may catch “bunnies” and complain of severe pain in the eyes.
This feeling is familiar to artists, explorers of the north and south poles, climbers and ordinary people who relax in sunny resorts. Their discomfort is caused by bright sun or light reflected from snow.
As a result, electroophthalmia develops - this is damage to the cornea and the entire eyeball under the influence of an arc or ultraviolet radiation. The visual organs can be damaged in solariums and when quartzing hospital premises. There is also a risk of corneal damage for those who observe welding from the outside.
How to treat eyes damaged by welding
Drug treatment of electroophthalmia is among the delayed measures for corneal restoration. It consists of several points:
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Clodifen drops; Nise, Prenacid, Ibuprofen or Diclofenac in the form of capsules, suppositories, tablets, injection solutions).
- Instillation of the eyes with agents with metabolic effects (Taufon - drops for electroophthalmia, restore damaged tissue and eye performance in 2 - 3 days).
- Treatment of eyeballs with wound-healing gels (Actovegin, Solcoseryl).
- The use of antibiotics to prevent infection (drops Tobrex, Tsiprolet, Gentamicin, Oftaquix).
What folk remedies can be used after eye injury from welding, and when is the best time to do this, the doctor will tell you. During the first 24 hours, non-drug treatment is not performed.
Subsequently, in agreement with a specialist, a solution of aloe juice and bottled water (1:5) or a honey solution (1 part honey to 10 parts bottled water) is used to restore the cornea and conjunctiva. The beekeeping product reduces swelling of the tissues of the eyeball and prevents persistent clouding of the cornea.
PS Do not put off visiting your doctor if you have picked up “bunnies”. Electroophthalmia is dangerous due to the development of chronic keratitis, erosive and ulcerative changes in the cornea and a decrease in the quality of vision.
What not to do with pathology
In case of severe blinding by light and the development of the disease, experts strictly prohibit doing the following:
As a first aid, if you cannot see a doctor right away, you can gently rinse your eyes with bottled water. It can slightly slow down the inflammatory process.
If you have vasoconstrictor drops on hand in your first aid kit, like Visine or Proculin, you can use them. One drop of one of the drugs should be placed in each eye.
Causes
The main part of the ultraviolet rays affecting the eyes is absorbed by the corneal layer. The mechanism of the effect of light on the cornea is the same as on the skin during burns. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the organ of vision can cause the appearance of climatic punctate keratopathy, pterygium, carcinoma and pinguecula. Under the influence of radiation, the surface of the epithelial cells of the corneal layer is greatly irritated and the result is its thinning.
The main cause of pathology is an object emitting ultraviolet radiation. If safety precautions are violated and there are no protective equipment due to the negative impact of rays on the corneal layer, an inflammatory process develops.
Ultraviolet radiation affects human eyes when:
- solar eclipse;
- carrying out welding work;
- visiting a solarium;
- use of quartz lamps;
- bright flashes in the sun;
- contact of the organ of vision with the sun's rays when near a body of water;
- visiting snow-covered places with increased reflectivity.
Prevention
For light burns, the best prevention is to follow these recommendations:
- observe safety precautions;
- use welding only with a shield;
- In very bright sunshine, avoid direct contact with the retina and wear dark glasses.
At the first symptoms of the development of a pathological process, you should seek medical help and not self-medicate.
Electroophthalmia is an inflammatory pathology of the organ of vision, the development of which is caused by the negative effects of ultraviolet rays. The unpleasant consequences of this disease are increased lacrimation and pain.
With timely treatment, it is possible to cope with electroophthalmia and prevent the development of dangerous consequences. If the patient neglects treatment, there is a high probability of complete blindness.
A pathology such as electroophthalmia is often detected in welders, climbers and skiers, and is considered their occupational disease. If the organ of vision is damaged no more than moderately, the prognosis is quite favorable. You need to visit a doctor when the first signs of pathology appear and choose timely therapy.
Symptoms of the disease
The first signs of ophthalmia do not appear immediately, but most often several hours after damage to the organs of vision. Snow blindness is manifested by the following symptoms:
We recommend!
To treat eyes without surgery, our readers successfully use a proven method. Having carefully studied it, we decided to offer it to your attention. Read more…
- Discomfort in the eyeball area, an unpleasant sensation reminiscent of “sand” in the eyes.
- The appearance of photophobia - in this case, the eyes react painfully not only to bright, but also to weak light.
- Sharp painful spasms in the eyeballs.
- Increased lacrimation, swelling, redness of the eyes.
As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, and a person may experience complete loss of vision - fortunately, it is reversible. As a rule, it lasts 4-5 days, after which vision is gradually restored.
What medications will help relieve the symptoms of a burn?
The use of medications to treat various diseases is very popular. Each person decides for himself how to deal with the disease. For electroophthalmia, it is best to consult an ophthalmologist, and the doctor will prescribe the necessary medications. The main goal of treatment is to relieve pain, but you cannot stop there and you need to continue treatment. You cannot use painkillers such as Novocaine and Lidocaine. Homemade cold compresses or special herbal solutions are often used along with pain relievers.
Incompetent people should not get too involved in home pharmacy!
Eye moisturizers are often used and are often called artificial tears. Gels are also applied to the cornea of the eye, which promote rapid healing and accelerate the epithelization of the ocular cornea. For example:
- Actovegin gel;
- Solcoseryl gel;
- Korneregel;
- Retinol;
- 5% thiamine ointment.
All pharmacy methods for treating electroophthalmia can be grouped into 3 categories:
- Eye drops to relieve puffiness can only be purchased after consultation with a specialist. The ophthalmologist will determine the degree of the burn and prescribe the necessary individual remedies. The main function of such drops is to relieve swelling. Most often, Visoptin, Proculin, Visin are suitable for this. They eliminate pain, which is manifested by itching and burning, and at the same time fight the burn, rather than mask it.
- Drops that relieve pain - Alcaine and Tetracaine.
- Antibiotics for the eyes - vitalize the cornea and reduce crippling pain. A good remedy for disease prevention. Gentamicin, Tobramycin, Levofloxacin should be highlighted. And tablets: Indomethacin, Diclofenac. Dust-like agent - Nimesil. In the form of eye drops – Clodifene.
Ophthalmoplegia: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment
Ophthalmoplegia is the name given to paralysis of the eye muscles resulting from damage to the oculomotor nerves.
Causes
Most often, the cause of direct damage to the eye muscles is myasthenia gravis, ocular myopathy, ophthalmopathy of an endocrine nature, or orbital tumor.
Ophthalmoplegia can be neurogenic in nature in the case of an aneurysm of the vessels of the arterial circle of the cerebrum, basal brain tumors, hernial protrusions of the brain into the foramen of the cerebellar tentorium with increased intracranial pressure, ischemic neuropathies of the oculomotor nerves, with damage to the brain stem (in the case of a tumor, stroke, alcoholic encephalopathy, encephalitis ), botulism, multiple sclerosis, meningitis, septic thrombosis and other lesions of the cavernous sinus.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ophthalmoplegia are double vision, often ptosis (otherwise known as drooping eyelid), and limited mobility of the eyeball. If autonomic fibers are involved in the process, pupillary reactions are impaired, and mydriasis (dilation of pupil diameter) is noted.
Aneurysm of the vessels of the circle of Willis is characterized by ophthalmoplegia in combination with damage to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve (the presence of piercing pain in the eye, as well as part of the frontal region).
Cavernous sinus syndrome is a combination of partial or complete external and internal ophthalmoplegia with damage to the first and second branches of the trigeminal nerve (characterized by the presence of pain in the eye, frontal region, upper jaw, cheek). This set of symptoms is often caused by the presence of a tumor located near the sella turcica.
In case of thrombosis of septic etiology, symptoms of a general infectious nature can be traced.
In the case of a carotid-cavernous fistula, pulsating exophthalmos, redness of the conjunctiva, and a detectable vascular noise during auscultation of the eye join ophthalmoplegia.
A variant of damage to the oculomotor nerves (Tholos-Hunt syndrome or painful ophthalmoplegia) is a disease that is caused by arteritis of the carotid artery in the cavernous sinus and belongs to the group of collagen diseases.
It must be taken into account that the occurrence of a symptom complex of painful ophthalmoplegia is also possible in the case of other diseases: ophthalmoplegic migraine, aneurysm, temporal arteritis, periostitis of the superior orbital fissure, ethmoidal sinusitis, as well as in the ocular form of herpes zoster.
The cause of damage directly to the external muscles of the eye is most often myasthenia gravis, which, as a rule, is accompanied by the development of bilateral ophthalmoplegia without involvement of the pupils.
Exophthalmic ophthalmoplegia (endocrine orbitopathy) develops with excessive secretion of the exophthalmogenic factor of the pituitary gland and a special substance of thyroid hormone.
Isolated internal ophthalmoplegia is usually defined as part of Eydie syndrome.
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnosis is a neurological examination with a complete collection of complaints and anamnesis and clarification of the probable causes of ophthalmoplegia.
Paraclinical studies can also be used for diagnosis: computed tomography, craniography, angiography, echo-orbitography (verification of intraorbital processes). It is worth noting that improvement in eye mobility during injection of proserin indicates the myasthenic genesis of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment directly depends on the disease that led to ophthalmoplegia. For myasthenia gravis, anticholinesterase drugs are used; a cerebral aneurysm, which led to ophthalmoplegia, must be operated on (more often they resort to clipping).
Forecast
The prognosis also depends on the cause that led to ophthalmoplegia. As a rule, the prognosis is favorable for life and doubtful for full recovery.
Alexey Borisov (neurologist)
Practicing neurologist. Graduated from Irkutsk State Medical University. Works in the faculty clinic of nervous diseases. Read more…
Diagnostics
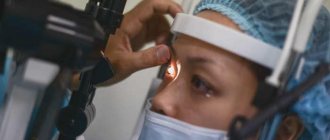
An ophthalmologist conducts an initial examination with a mandatory full diagnosis, establishes the cause of the pathological process and differentiates the pathology from similar ailments. Research is carried out using special equipment. By examining the fundus, retina, and cornea, the degree of inflammation is determined and a final diagnosis is made.
The main research methods are:
- visometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- a fluorescein sample is taken.
Visometry
After confirming the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed therapeutic measures.
Symptoms of exophthalmos
This ophthalmological disease belongs to a group of diseases that manifest themselves not only in the form of physiological disorders, but also have an aesthetic impact. The main symptom of exophthalmos is protrusion of the eyeball, the motor activity of which may remain at the original level or be limited. Usually the disease is accompanied by swelling of the eyelid and conjunctiva, and their redness. Often, when the eye bulges, there is a lateral displacement of the eye, resulting in reduced mobility. Low activity of the eyeball or its complete absence indicates the intensity of the tumor or inflammatory process in the orbit.
Often exophthalmos is accompanied by decreased vision. In this case, retinal hemorrhages, neuritis, congestive disc, and optic nerve atrophy may be observed. Bulging eyes are characterized by lacrimation, pain in the eyes, and photophobia. As a result of incomplete closure of the eyelids and drying of the eye, keratitis and dystrophy of the cornea of the eye can develop. In the presence of exophthalmos, the refraction of the eye can be changed towards hypermetropia. This occurs due to the pressure that forms the pathological focus. In some cases, diplopia (double vision) is observed.
Hypothalamic-pituitary exophthalmos
is formed as a result of irritation of the hypothalamic centers and an increase in the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland. As a result, inflammatory phenomena begin in the hypothalamic region, and hormonal balance is disrupted. With this form of bulging eyes, sudden, rapidly progressing swelling of the eyelids occurs, paresis of the oculomotor nerves and chemosis of the conjunctiva occurs, and in some cases, increased intraocular pressure. The body's thermoregulation, carbohydrate metabolism, water-salt balance, sleep, sexual function, and psyche are disrupted.
If exophthalmos forms against the background of diffuse toxic goiter, it develops gradually. The bulging eyes are bilateral and not pronounced; the eyeballs retain normal mobility. Pain within the orbit, inflammation of the cornea and diplopia are not observed. The palpebral fissure widens not only as a result of an increase in the size of the eyeball, but also due to retraction of the upper eyelid. Possible manifestations of Graefe's symptom (delay of the upper eyelid when looking down), Stellwag's (decreased frequency of involuntary blinks), Dalrymple's (appearance of a white strip of sclera above the cornea when looking down), Moebius (absence or weakening of ocular convergence of the eyes while looking at nearby objects) and others. In advanced cases, hypopyon and corneal ulcer develop.
Pulsating exophthalmos
manifests itself in the form of pulsation of a protruding eyeball in time with the pulse. It can occur either immediately after an injury or much later. Easily determined by palpation and phonendoscope. During hardware examination, a babbling systolic murmur is heard, which disappears when the carotid artery is compressed. The characteristic symptoms that accompany this form of bulging eyes are severe headache and tinnitus. Sometimes there is an expansion of the veins on the forehead, cheeks, temples, and neck. There may be congestion in the veins of the iris, sclera, conjunctiva or retina, as well as swelling of the optic nerve head, which often leads to its atrophy. In some cases, paralysis of the eye muscles occurs.
Intermittent exophthalmos
manifests itself during bending of the head or torso, during physical activity. The symptoms are similar to the pulsating form of bulging eyes, but the manifestations are less pronounced.
Basic Physics
Ultraviolet radiation is a wave whose length ranges from 10 to 400 nm. Visible light has a wavelength above 380 nm, X-rays emit a wavelength less than 10 nm. The effect of radiation on the human body depends on the length of its waves. The longer, the weaker the impact. People practically do not feel UV A rays. With prolonged exposure, UV B rays can cause burns to the mucous membrane or skin. UV rays shorter than 280 nm have a very aggressive effect. They easily penetrate all layers of the eye and destroy the retina.
Welding is used in construction. Products and blocks are connected using a welding arc. An arc is an electrical charge that has great power and lasts for a long time. In a welding arc, waves have a length of 100 to 300 nm. The most common sources of UV rays are electric arcs and autogen. These are the so-called temperature emitters. Also, medical personnel are exposed to UV exposure when working in physiotherapy rooms, who are engaged in photocopying and water sterilization.
With constant exposure to UV radiation, acute and chronic eye diseases occur. Acute pathology is electroophthalmia or photoophthalmia. Conjunctivitis develops. In case of chronic damage - conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
Occupational eye injuries have a very wide spectrum. Numerous injuries and burns are not all the charms. There are chemical and toxic effects on the organs of vision. Harmful effects occur in industrial enterprises. Cement, coal, sawmills. Especially the chemical industry, where people work with acids and alkalis. Vapors of benzene, phosphorus, lead, iodine compounds at high concentrations cause a burn of the conjunctiva, as a result of which pathological changes begin in the eye.
As a result of toxic effects, the retina and optic nerve are affected. And there are frequent cases of toxic glaucoma and cataracts. And in all cases of changes in the organ of vision, special attention is paid to the effects of various types of radiant energy: infrared, ultraviolet, ultrasound, x-rays, radio waves, microwaves. Contact with these rays causes the disease – electroophthalmia.
You may be interested in Hemeralopia or night blindness: treatment, causes, symptoms
— Infrared irradiation causes cataracts in steelworkers, glassblowers, and, in general, in hot shop workers. May lead to hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous body.
— X-ray radiation can also lead to the development of cataracts. It all depends on the radiation dose.
— Hard gamma radiation causes the development of cataracts, similar in nature to x-rays.
— Excess microwave radiation leads to clouding of the lens of the eye.