Retinorm capsules are a complex of vitamins necessary to maintain good visual acuity. They are taken when there is increased load on the visual organ and exposure to high doses of ultraviolet radiation. They may also be indicated in the complex treatment of age-related retinal degeneration and after eye surgery.
OftaPlus.ru suggests reading the full instructions for use of Retinorm eye vitamins, as well as reviews about this dietary supplement. Also at the end of the article you can find a list of analogues.
Pharmacological properties
Since the biological active components included in Retinorm capsules are not synthesized in the human body, they must be delivered from the outside.
- Vitamins C and E, lutein, zeaxanthin and other trace elements activate metabolic processes in the tissues of the eyeball. This reduces the risk of age-related degenerative changes in the retina.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin are plant carotenoids. They accumulate in the macula and block the retina from being exposed to harmful ultraviolet rays. They have the properties of strong antioxidants and prevent a decrease in visual function.
- Vitamins C and E are strong antioxidants, enhance and complement the action of the complex, and protect eye tissue from damage. Restores visual pigment, which is responsible for color perception. Strengthen vascular walls, increase the elasticity of intraocular vessels, including vessels in the fundus. These are obligatory participants in tissue respiration and other processes of cellular metabolism. They are reliable neuroprotectors, strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the eyes.
- Zinc, copper, selenium - maintain visual acuity and protect against the adverse effects of the external environment. Strengthen the nutrition of the fundus of the eye, including the normal functioning of the optic nerve. Their deficiency leads to increased eye fatigue, decreased vision, and the development of degenerative processes.
Lutein and zeaxanthin
Lutein and zeaxanthin , essentially related substances, belong to the class of hydroxylated (oxygen-containing) carotenoids. Both of them are found in small quantities in the blood plasma, but their greater concentration is observed in the retina: lutein accumulates in the periphery, and zeaxanthin in the center. Both pigments are equally necessary to strengthen the retina, improve color perception and the ability to adapt to different light conditions. Both of these elements must enter the human body in sufficient quantities, so it is better to take them simultaneously.
Indications for use
Prescribed as a dietary supplement to food - a source of lutein, zeaxanthin, zinc, copper, selenium, vitamins C and E.
It is also recommended to take Retinorm eye vitamins to restore metabolic processes in the eye tissues and improve the functional state of the retina, the disruption of which is caused by the following factors:
- visual fatigue (when working at a computer, reading, driving, activity in low light conditions);
- the impact of increased UV radiation (including occupational risk factors);
- wearing contact lenses and glasses;
- age-related changes in the retina.
Vitamins are prescribed during the recovery period after disorders of the organ of vision associated with damage to the integrity of the eye tissue.
Description
The biologically active components of RETINORM are not synthesized in the human body, therefore they must be supplied externally with food or as part of dietary supplements.
Lutein, zeaxanthin, vitamins C, E and microelements included in RETINORM help normalize metabolic processes in eye tissues and reduce the risk of developing age-related changes in the retina.
LUTHEIN and ZEAXANTHIN
Our vision directly depends on the degree of density of the macula (macula) - the central part of the retina. Plant carotenoids (lutein and zeaxanthin) accumulate in the macula and block the harmful effects of ultraviolet light. They act as strong antioxidants, blocking the action of free radicals that damage eye tissue and contribute to vision loss.
VITAMINS C and E
They are the most common antioxidants that enhance and complement each other’s action, protecting eye tissue from damage. Helps restore visual pigments (rhodopsin, etc.) of rods and cones, which are responsible for normal light and color perception. Helps strengthen the walls and increase the elasticity of blood vessels, including the vessels of the fundus. Participate in tissue respiration and other processes of cellular metabolism. They have a neuroprotective effect. Helps strengthen the eye muscles and ligaments.
ZINC, COPPER, SELENIUM
Necessary microelements for maintaining vision function, have an antioxidant effect, and also compensate for the adverse effects of the environment. Helps improve the nutrition of the fundus of the eye and maintain the functional state of the optic nerves. Insufficient consumption of these microelements can lead to deterioration of vision, increased eye fatigue and the development of optic nerve dystrophy.
As a biologically active food supplement - a source of lutein, zeaxanthin, an additional source of vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, copper and selenium.
The components that make up RETINORM: lutein, zeaxanthin, vitamins C, E and trace elements help improve the functional state of the retina and normalize metabolic processes in the tissues of the eye, which can be disrupted by:
- visual fatigue (working at a computer, reading, driving, activity in low light conditions)
- exposure to increased ultraviolet radiation (in summer, at high altitudes, occupational risk factors, etc.)
- wearing contact lenses and glasses
- age-related changes in the retina
- during the recovery period after disturbances in the functions of the organ of vision associated with damage to the integrity of the eye tissues
Reviews of vitamins Retinorm
Pros that people point out in reviews:
- good composition;
- ease of use;
- adequate price;
- helps with visual stress.
Minuses:
- unpleasant aftertaste;
- taking 3 times a day;
- doesn't help everyone.
Opinion No. 1 (+):
Opinion No. 2 (+):
Opinion No. 3 (-):
Beneficial features
Zeaxanthin promotes:
- Prevention of complications of diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes.
- Neutralizes free radicals that can destroy cellular structures.
- Reducing the risk of developing cancer processes.
- Improving skin health (increasing tone, preventing early aging).
- Maintaining normal brain function and improving cognitive functions.
- Minimizing the risk of stroke, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Increasing the sharpness, clarity, contrast sensitivity of vision, accelerating the processing of visual information.
- Strengthening the protection of eye tissues from age-related pathologies and the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation.
- Maintaining optimal density of the eye lens and retina.
- Reduce eye fatigue, reduce light hypersensitivity.
- Prevention of macular degeneration, blindness, cataracts, uveitis, diabetic retinopathy.
The effect of Astaxanthin on the human body
Since Astaxanthin quenches inflammation and dissolves in every part of our body, it is easy to understand that it provides many benefits to the body.
Some of its benefits include:
- Cardiovascular Protection:
Numerous studies show that astaxanthin helps protect the heart, and its mode of action appears to lower C-reactive protein. This protein is a marker of inflammation in the body, and lower levels are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and other diseases. Additionally, astaxanthin appears to integrate with the mitochondrial membranes of heart muscle cells, helping to protect them. - Nervous system protection:
Several studies point to astaxanthin's ability to protect nerve cells and therefore slow down cognitive decline and other nerve-related diseases. This makes astaxanthin very useful in preventing loss of brain function. - Eye Health:
We know that eating foods rich in carotenoids can be beneficial for protecting your vision. The most notable carotenoids for the eyes are lutein and zeaxanthin, which are often recommended for preventing age-related macular degeneration. However, astaxanthin is in a different league when comparing its antioxidant properties to other carotenoids. Research shows that astaxanthin prevents damage to most eye tissues and structures and may be beneficial in preventing age-related eye problems such as retinopathy, glaucoma and neuropathy. - Skin Health:
Astaxanthin has demonstrated benefits for skin health, helping to protect against ultraviolet radiation, improving elasticity, firmness and reducing wrinkles. Astaxanthin has been shown to prevent UV damage to cells. What's even more interesting is that it doesn't block UVB rays; these are the rays that help in the production of vitamin D from the sun. - Astaxanthin has been found
valuable for preventing many other problems, including supporting the immune system, protecting gum health, and improving reproductive health.
What are lutein and zeaxanthin?
In ordinary life, we don’t even think about how important vision is for us. It happens that we are completely negligent about our health. And when the first alarming symptoms arise, we begin to panic and look for a way out. Then, perhaps, it is better not to let the situation arise before a problem arises, but to warn it in advance?
The substances lutein and zeaxanthin belong to the group of carotenoids. These pigments are capable of coloring in red, yellow and orange shades. In the plant world there are many berries, flowers and fruits that contain carotenes.
They are also found in regular leaves. In autumn, during the period of destruction of chlorophyll, the foliage on the trees becomes a characteristic shade. This is how the presence of xanthophylls, a component of yellow pigments, is expressed.
All plants, like all living organisms, need protection from UV radiation. Zeaxanthin and lutein are natural light filters. Their action is to absorb aggressive ultraviolet rays and neutralize their harmful effects. These elements are also present in the human body.
Lutein is found in our blood and almost all tissues. The largest amount is concentrated in the retina and in the macula area. Zeaxanthin is an isomer of lutein. The quality and acuity of our vision directly depends on the required content of these substances. If there are too few of them, vision will begin to decline over time.
The importance of carotenoids for the eyes
They play a very important role in the functioning of the entire visual system, namely:
- protect the eye lens from oxidation;
- filter out the dangerous part of the light spectrum before it penetrates the photoreceptors;
- perform the function of photoprotection - reduce the flow of blue-violet rays;
- protect from free radicals formed in direct light;
- preserve the health of eye cells and maintain visual acuity.
What does shortage lead to?
The consequences of a lack of lutein and zeaxanthin include the following:
- loss of vision;
- deterioration in the ability to see clearly at night;
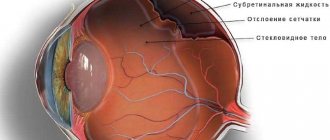
- retinal dystrophy;
- change in the shape of the lens;
- development of cataracts
- thinning of the macula;
- narrowing of the field of view.
Our body is not able to produce lutein and zeaxanthin on its own. So we need additional sources of these elements, which include:
- Food;
- dietary supplements;
- medicines.
It is recommended to take at least 5 milligrams of lutein per day. If a person has just started drinking a dietary supplement, then it takes some time for carotenoids to accumulate. Only after this you will be able to notice the result.
Vitamin complexes with lutein and zeaxanthin
Vitamins are also found in food products
Many who want to maintain the health of their eyes at the proper level have almost certainly heard about eye vitamins with lutein and zeaxanthin.
Due to the fact that the name of these substances is not familiar to the general public, our resource decided to devote a separate paragraph to them in today’s article.
First of all, it should be noted that lutein and zeaxanthin are common antioxidants. The direction of their action is to neutralize oxidative processes in the human body, thereby improving the absorption of nutrients and neutralizing the risks of developing various diseases.
Of course, lutein and zeaxanthin act similarly in relation to eye health, but their presence in vitamin complexes for the visual system is due to a slightly different reason.
The fact is that these substances are found in the retina, lens, and cornea of the human eye and play an important role in their functioning. More significant for the visual system is zeaxanthin, which forms a large part of the central region of the retina and is involved in the process of light refraction.
Over time, both lutein and zeaxanthin gradually “evaporate” from the human body, which negatively affects visual function.
It is almost impossible to completely compensate for the lack of these substances by taking plant foods (greens, broccoli, etc.) rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, therefore specialized complexes with them are widespread on the pharmacological market.
Eye vitamins with lutein and zeaxanthin are used to:
- slowing down the natural processes of blinding that develop in people with age;
- prevention of pathologies of the retina, lens and cornea;
- maintaining visual function at a consistently high level.
Specialized prescriptions for taking such vitamin complexes are not required, so if desired, absolutely anyone can organize an appropriate course. It will definitely be useful for both the eyes and the entire body.