Why can’t you choose antiallergic eye drops without a doctor?
The task of immunity is to protect a person from various factors hazardous to health. When they enter the body, the immune system begins to produce antibodies that resist viruses, bacteria, and cancer cells, which are also called antigens. Due to this, a person can not get sick for a long time even when exposed to harmful agents.
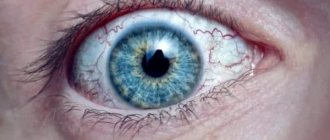
If the immune system is not working properly, it may see antigens in substances that do not pose a health risk. Considering them to be harmful agents, the body begins to produce antibodies to destroy them. In other words, he is fighting a disease that actually does not exist. This increased sensitivity to certain substances is an allergy. It can manifest itself in different ways, including before the eyes.
The direct causative agents of an allergic reaction can be external and internal factors. The former include pollen, dust, and cosmetics; the latter include food and medicine. Any substance can act as an allergen. Sometimes it takes a lot of research to identify it. Allergies are often caused by the following factors:
- plant pollen;
- pet hair;
- cosmetical tools;
- contact lenses or solution for their care;
- various chemical compounds;
- medications, including eye drops.
In rare cases, allergies are caused by ultraviolet radiation, low air temperature, unfavorable sanitary and hygienic conditions in the work area, infections, etc. Thus, there are quite a lot of factors that can provoke an allergic reaction.
You yourself will not be able to determine the type of allergen, so it is not recommended to buy and use medications without a prescription.
Many people use folk remedies and various drugs that are in their home medicine cabinet for treatment, without knowing exactly the cause of the disease. At best, they will be useless. At worst, self-medication will cause complications. We'll tell you about them later. First, let's list the typical symptoms of eye allergies.
How does eye allergies manifest?
Conjunctivitis usually occurs, since this part of the eyeball is primarily affected. But there are many types of such diseases. Each of them has its own distinctive features. Here is a list of common symptoms of all allergic reactions to the eyes:
- itching, burning, pain, stinging, feeling of “sand” under the eyelids;
- dryness, which leads to the development of severe lacrimation;
- swelling and redness of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- photophobia;
- mucous and sometimes purulent discharge;
- rashes on the eyelids, peeling of the skin around the eyes;
- blurred vision.
The number and intensity of symptoms depend on immunity, the type of allergy causative agent, and the duration of exposure to the allergen. The very first symptom of almost any allergic inflammation in the eyes is unbearable itching, which cannot be relieved without the use of medications.
Instructions for use
Regardless of the composition, before use it is recommended to rinse the nasal cavity and remove crusts. Apply 2-3 drops into each nasal passage, slightly throwing your head back to allow it to be absorbed into the mucous membrane. When treating children, you can use a glass rod to add eye ointment. As many drops as recommended by the doctor are applied to the spatula-shaped tip and applied to the nasal mucosa. Thanks to the gel consistency, the medicine does not spread, but is quickly and evenly absorbed. For increased fragility of capillaries in the nose from the Markov group of drugs, the first version of drops No. 5 is used.
Method of administration
Each type of drop has its own instructions for use. Some are administered over a limited course with a constant dosage, but there are also formulations in which the amount of the substance must be gradually increased and then reduced in the same sequence (for example, drops No. 4 with an antibiotic).
The daily frequency of administration is 3-4 times, after an equal amount of time, but not less than 4 hours. If the medicine contains galazolin, the therapeutic course is limited to 5-6 days due to possible addiction.
Contraindications and side effects
Each component of the composition has individual restrictions on use. But since the patients’ allergic reactions are taken into account when prescribing, the risk of side effects is minimal. But the patient’s individual reaction to the joint administration of the ingredients cannot be predicted. Negative symptoms may develop.
If signs of intolerance or worsening of the condition appear, you must notify your doctor. It is he who makes the decision to cancel or correct the therapeutic regimen or composition, to use drops No. 4 with cefazolin or gentamicin.
Features of use
Drops should not be purchased for future use, since the shelf life is limited. After the bottle is opened, the medicine should be put in the refrigerator (preferably on a shelf in the door). The contents of the bottle retain their properties for 10 days, during which time the drug is recommended to be used. If treatment is extended, you will have to purchase another package.
What types of eye allergies are there?
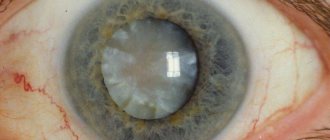
Based on the localization of the process, the causes of the disease and other factors, eye allergies are divided into types such as papillary conjunctivitis, contact dermatitis, chronic conjunctivitis, allergic keratoconjunctivitis, hay fever, or seasonal allergies. All of them are characterized by: itching, burning, lacrimation and redness of the conjunctiva. There are other specific signs.
Papillary conjunctivitis often develops as a result of an allergy to a medicine or as a reaction to mechanical damage to the eyeball.
This disease also occurs due to contact lens solutions. In the first days, the patient's eyes are very itchy and painful sensations arise when moving them. Swelling is also observed. Subsequently, red dots appear on the cornea, indicating erosion. On the upper eyelid, rashes form in the form of oval tubercles - follicles in which blood or lymph accumulates.
Seasonal allergies, which most often occur due to pollen, are called hay fever, or allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
This disease is accompanied by symptoms of rhinitis and conjunctivitis:
- runny nose and frequent sneezing;
- attacks of suffocation;
- debilitating itching;
- hyperemia of the tunica albuginea;
- photophobia;
- secretion of sticky secretion;
- profuse lacrimation.
Typically, allergy sufferers know that they have seasonal allergies and try to prevent its development with eye drops.
Contact dermatitis, as a rule, occurs due to exposure to cosmetic products on the connective membrane, especially if they are of poor quality. A distinctive sign of the disease is small rashes around the eyes.
The eyelids are constantly itching. The patient rubs them with his hands, which leads to peeling of the skin. Allergic keratoconjunctivitis most often occurs in children aged 5-12 years, and mainly in boys, who experience changes in hormonal levels during these years. Inflammation in this pathology covers not only the conjunctiva, but also the cornea, which is accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity. This disease is also diagnosed in adults. Often it is a complication of ordinary allergic lesions of the conjunctiva.
Chronic conjunctivitis occurs when the eyes are hypersensitive to several substances - pollen, cosmetics, wool, etc. Some people get used to itching in the eyes and no longer notice the symptoms of the disease, which lasts for months or years. This is the only type of eye allergy that does not occur in an acute form.
Description of nasal drops
The first sign of the onset of ARVI is most often a runny nose. The pathogenic flora first penetrates the nasal mucosa, then descends into the oropharynx and is activated. If treatment is started when rhinitis appears, it is possible to stop the spread of pathogenic agents from the very beginning and stop the disease.
Goal drops have a vasoconstrictor effect, normalize the production of nasal secretions, stop the inflammatory process and inhibit the activity of viruses and bacteria. Even if rhinitis cannot be stopped, ARVI proceeds without complications.
Professor Markov proposed 10 developments, but in practice 7 are used. The complex products contain certified pharmacological drugs:
- Zinc sulfate. Refers to antiparasitic and antimicrobial agents, stops the production of nasal mucus, dries, stimulates the work of macrophages. Has a drying effect.
- Streptocide (sulfonamide). A broad-spectrum antibacterial agent with the greatest activity against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci.
- Galazolin, the active ingredient is xylometazoline hydrochloride. Adrenergic agonist, alpha adrenergic stimulant. Narrows the capillaries localized in the mucous membrane lining the cavity and passages of the nose, making breathing easier. It acts for a short time, quickly becomes addictive, which is why the dosage has to be increased.
- Diphenhydramine. Blocks the body's immune response caused by the introduction of allergens, reduces capillary permeability, and has a sedative effect. When applied topically, it has mild anesthetic properties.
- Thymogen. Artificially synthesized polypeptide. Accelerates metabolic processes at the cellular level, stimulates the immune system and the regenerative ability of the mucous membrane, and has an antimicrobial effect.
- Sulfacyl sodium (albucid). An antimicrobial agent, originally developed for use in ophthalmic practice, with a wide spectrum of action.
- Gentamicin. An antibacterial component from the group of aminoglycosides, relieves inflammation during purulent processes. Rapidly absorbed, highly active against aerobic gram-negative bacteria. It is quickly absorbed and distributed throughout all tissues of the body, even when applied topically.
- Hydrocortisone. A hormonal agent from the group of glucocorticosteroids that enhances the regenerative properties of the body at the cellular level and reduces allergic manifestations. Suppresses the activity of leukocytes, reduces capillary permeability.
- Dioxidine, active substance - hydroxymethylquinoxaline dioxide. An artificially synthesized antiseptic with antimicrobial action is effective against pathogenic flora that have developed resistance to antibiotics.
- Aminocaproic acid. Hemostatic agent, reduces capillary permeability, accelerates blood clotting and stimulates fibrin production.
The composition is balanced, each drug has a targeted effect. When prescribing, the cause of rhinitis, the physiological status of the patient and concomitant anamnesis are taken into account. If there are contraindications, components can be replaced.
The complex of ingredients is different, but all types of the drug have a gel base, thanks to which they are evenly distributed throughout the mucous membrane, forming a film, and do not leak out. They are easy to use and, if you follow the recommended dosage, the likelihood of side effects is low.