Treatment of bladder stones must be timely, as they can be complicated by cystitis and pyelonephritis. In some cases, stones end up in a very narrow ureter, where acute urinary retention can easily occur. The danger of the disease is also that stones often enter the bladder from the kidneys, and this indicates the prevalence of the process and problems in the functioning of several organs at once.
Why stones may appear
Among men, bladder stones are common if there are diagnoses such as hyperplasia, adenoma or prostate cancer. Because of them, the lower urinary tract becomes clogged. In this case, an obstruction occurs in the neck of the bladder or urethra, preventing the free flow of urine. This most often occurs in men over 50 years of age.
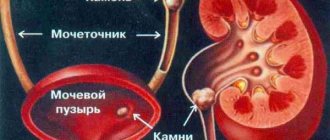
Stones can form if you are unable to empty your bladder completely. Urine remains and stagnates in it, which provokes the loss of salt crystals. Deposits are also caused by foreign bodies: ligatures, stents, catheters, etc.
Other causes of bladder stones:
- hereditary predisposition;
- injury or stenosis of the bladder;
- abuse of sweet and spicy foods;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- neurogenic bladder;
- living in hot regions.
Blood in urine
A characteristic symptom of stones that have filled the bladder is hematuria - blood entering the urine. Occurs when there are injuries and scratches from the sharp edges of stones that injure the mucous membrane. When a stone is displaced, it injures the passage to the urethra. In this case, blood may appear only when the bladder has finished emptying.
If traces of blood in urine are visible, this is macrohematuria.
In contrast to the manifestations of macrohematuria, the processes of microhematuria occur hidden, blood can only be detected in the picture of an increase in red blood cells, under the glass of a laboratory microscope.
Main symptoms
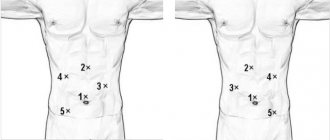
Signs of the appearance of stones in the bladder are associated with the fact that they irritate the bladder mucosa or block the outflow of urine. Symptoms are very varied and depend on the size and composition of the stones. Most often, pain is felt in the lower abdomen.
There are other symptoms of bladder stones:
- intermittent urination;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- severe burning sensation when urinating;
- feeling of pain in the lower back (if the stone moves into the kidney from the ureter);
- false urge to urinate.
Complications
Urolithiasis, if the patient is not treated in time, can lead to more serious consequences:
- penetration, development and spread of infections in the urinary tract;
- pyelonephritis and other kidney diseases;
- nephrosclerosis. These are transformations of kidney tissue that are associated with degenerative processes;
- problems with the intestines - in particular, paresis;
- accumulation of purulent formations;
- renal failure and bacterial shock.
If the stone is not removed, then as the disease develops the kidney may even die - this is extremely dangerous and risky, so the disease requires effective and thorough treatment.
Types of stones according to different criteria
Different patients may develop one or more stones (multiple). They are small (microlites) and large (macrolites). If stones are formed in the bladder, then they are called primary. Stones that enter the organ from the kidneys are considered secondary. They are characterized by an increase over time.
According to their chemical composition, stones are divided into:
- to oxalate,
- phosphate,
- cystine,
- urate,
- struvite,
- mixed.
How are stones classified?
The stones differ from each other, given their chemical composition.
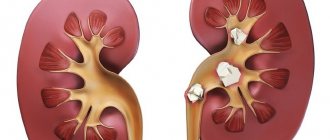
- Oxalates. This stone contains calcium salts of oxalic acid. They are distinguished by their dense structure, dark color, and spiky, uneven surface.
- Phosphates. Such stones consist of calcium salts of phosphoric acid. They have a soft and crumbly consistency. Their surface is smooth and slightly rough, the color is white-gray. They are characterized by intensive growth, especially if there is an infection in the body.
- Urats. These crystals of uric acid salts are distinguished by a dense structure, light yellow or brick color, and a smooth or finely dotted surface.
- Carbonates. The formation of such stones occurs when calcium salts of carbonic acid settle. They have a soft structure, light shade, smooth surface. Can be of various shapes.
- Cystine. They consist of the sulfur compound of the amino acid cysteine. Such stones are distinguished by their soft consistency, smooth surface, round shape, and white-yellow color.
- Cholesterol. They can be found quite rarely. These stones contain cholesterol. They are distinguished by a soft crumbly consistency and black color.
In some cases, the stone may be not homogeneous, but mixed.
Methods for diagnosing bladder stones
First of all, in making a diagnosis, an analysis of the patient’s medical history and complaints is important. The doctor needs to know the nature of the pain, cases of sand and stones, the presence of acute or chronic diseases, including recent ones. The size of the stones can be determined by rectal or vaginal examination. The first method is used to palpate the prostate gland in men.
Instrumental and laboratory diagnosis of bladder stones includes a number of examinations:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Cystoscopy to determine the size, color, surface and mobility of the stone.
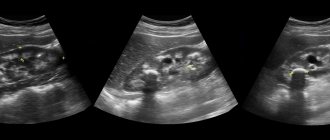
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the urinary organs.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI and CT).
- Urography and uroflowmetry.
- X-ray diagnostics to assess the condition of the urinary tract.
Causes of urolithiasis
The appearance of stones indicates metabolic disorders, as a result of which insoluble salts begin to accumulate in the body. It is believed that the tendency to urolithiasis is congenital, but stones will not appear without the influence of one of the additional factors, including:
- hot climate, provoking active sweating;
- composition of drinking water (hard water promotes stone formation);
- addiction to spicy, salty and sour foods, excess calcium and animal protein in food;
- lack of vitamins (A and group B), ultraviolet radiation (life “without the sun”);
- severe dehydration, for example as a result of infectious diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle, including forced inactivity as a result of injuries;
- chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines (gastritis, colitis, peptic ulcer);
- diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostate adenoma, prostatitis);
- metabolic diseases (for example, gout).
What should be the correct treatment?
Conservative treatment of stones brings good results for small stones. In this case, measures are taken to alkalize the urine. For this purpose, a special diet and medications are prescribed to maintain the desired alkaline balance.
For large stones, minimally invasive surgical interventions are used. The most effective and safe methods for removing bladder stones:
- Transurethral cystolitholapaxy - crushing the stone using ultrasound, laser or other type of energy, and its subsequent removal through a cystoscope.
- Percutaneous suprapubic litholapaxy (treatment method in childhood) – fast and safe stone crushing.
- Open suprapubic cystolithotomy. It is prescribed only for very large stones, if they cannot be crushed by other methods.
Treatment for bladder stones may differ between men and women, as they are sometimes caused by pathologies unique to one sex. In men, these are diseases of the prostate, and in women, often a neurogenic bladder. In this case, it is additionally necessary to treat the underlying disease that caused the stones, otherwise they may form again in the future.
The many causes and possible complications make kidney stones a serious disease that requires prompt medical attention. At the State Urology Center you can make an appointment with a urologist and get to him even on the day of your visit, and if necessary, get emergency help. All services in the clinic are provided within the framework of compulsory medical insurance, so you do not have to worry about the cost of diagnosis and treatment.
On weekdays you can get an appointment with a urologist on the day of your visit
Removing stones from the kidneys, urinary and gall bladder with oils and herbs
The main reasons for the formation of stones are poor diet and sedentary lifestyle. The role of a hereditary factor, especially through the female line, cannot be ruled out. Stones form in the kidneys, bladder, ureters, gallbladder , urethra, liver... The process of stone formation is enhanced by chronic infections, injuries to the spine, urethra, gout, obesity, lack of vitamins A, B and D in food, and a sedentary lifestyle.
What types of stones are there? The chemical composition of stones is different. Stones can be urate (in acidic urine, consisting of uric acid salts), phosphate (in alkaline urine), oxalates (the hardest stones, found in both acidic and alkaline urine).
What are the symptoms of gallstones and kidney stones ? The patient may not even suspect the presence of stones until an attack occurs, which manifests itself in renal or biliary colic.
Biliary colic is expressed by pain in the right hypochondrium and spreads throughout the abdomen. The attack is preceded by nausea and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The attack can last from several minutes to several days, during which it either stops or resumes.
Renal colic is expressed by acute pain in the kidney area, which radiates along the ureter to the genitals. During an attack, frequent painful urination, nausea, vomiting are observed, intestinal paresis may even occur, the patient is restless, pale, and has rapid breathing. Blood pressure often increases.
In 15% of cases, 2-3 days after the attack, the stones pass into the intestines and can be found in the stool.
If you have stones in your kidneys, bladder, or gall bladder , don't panic! Official medicine in most cases offers surgical treatment (laser crushing of stones or removal) . Don't rush to go under the knife! Stones can be dissolved and excreted from the body as sand in urine by following the instructions below.
- Drink medicinal mineral water to thin the bile and facilitate its outflow from the gallbladder;
- Eat moderately, regularly and often, this is necessary for the proper functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract and monitor the quality of food on your plate;
- Periodically use thermal procedures: heating pads, compresses, hot bath, sauna;
- During the period of exacerbation, ensure yourself peace; on normal days, lead a more active lifestyle;
- To dissolve and remove stones use folk remedies , use not only medicinal herbs, but also various oils, which will be discussed below.
To remove kidney stones , I recommend following two proven regimens, including taking herbs and oils. Each scheme is designed for approximately a three-month course - this course is usually sufficient if the stones are of medium size.
So, this complex should include:
Watermelon Oil Balm
.
prepare
it, you need to mix 100 ml of watermelon oil, 50 ml of pumpkin oil, 30 ml of flaxseed oil. Drink Watermelon Oil Balm for 2 weeks, 1 dessert spoon 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day. The balm will first cleanse the intestines, soften the stones, and prepare the kidneys and ureters for a more intensive process of dissolving and removing stones.
After two weeks of taking oil balm, start taking herbs
, dissolving stones in the kidneys and bladder and a decoction of madder root - in parallel. The special collection purposefully acts to eliminate existing stones and prevent the formation of stones, gently dissolves stones without causing discomfort, reduces the absorption of salts in the intestines and regulates the colloidal composition of urine due to the silicon-containing components of the collection. The collection has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, sedative and antimicrobial effect.
Collection composition:
bearberry leaf, nettle, mint, horsetail grass, knotweed, mullein, shepherd's purse, elderberry flowers, linden, rosehip fruits and roots, thuja needles, parsley grass and roots, hazelnut bark, thorn roots - 2 parts each, licorice roots, tansy, caraway fruits – 1 part each. Mix.
How to prepare the decoction:
Brew a tablespoon of herbs with a glass of boiling water. Boil for 5-7 minutes. Leave for 30 minutes. Strain. Drink half a glass in the morning and evening before meals.
Madder
- a well-known unique plant, the main effect of which is
the ability to loosen oxalate stones
, phosphate, oxalate salts of calcium and magnesium, uretes formed in the kidneys and bladder, cholelithiasis.
Madder has the property of gradually loosening and destroying kidney, urinary and gall bladder stones and does not have a significant effect on blood pressure and respiration. In addition, it causes a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the renal pelvis and ureter, while at the same time enhancing peristaltic contractions of muscle fibers, which contributes to the painless movement of stones. Has a diuretic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect in pyelonephritis, nephritis, cystitis. To prepare a decoction
1 teaspoon of crushed
madder roots
to 1 glass of water and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. Cool, strain. Drink 100 ml of decoction in the morning and evening before meals.
The course of treatment with a collection of herbs and a decoction of madder root is 2 months. At the end of taking the herbal collection and madder decoction, resume taking the Oil Balm with the same two-week course to complete the cleansing of stones .
After about 2-4 weeks you can undergo an examination (ultrasound). If the stones have not completely come out, then continue treatment according to the same scheme, but use sunflower madder root
. The fact is that madder, despite its undeniable advantages in loosening and removing stones, has some hepatotoxic effects and taking its decoction for more than 2 months in a row is not recommended. But don't worry, because... Watermelon oil balm perfectly protects the liver during treatment.
So, sunflower root
– an equally effective remedy for loosening and removing salts and stones from the urinary system, and indeed from the entire body, in particular this root is successfully used for the deposition of salts in joints and vertebrae (arthritis, polyarthritis, osteochondrosis, etc.), gallstone disease. The salt-removing effect can be seen by the “rusty” color of urine when taking a decoction of the root. In the fall, it is necessary to prepare thick parts of sunflower roots, cut off small hairy roots, wash and dry thoroughly. To prepare a decoction for 3 liters of water, you need to take 1 glass of roots, boil for about 1-2 minutes, leave for 30 minutes. Strain. The tea must be drunk 2-3 days in advance and stored in the refrigerator. Then these same roots can be used again, but boiled for 5 minutes in the same volume of water, and also drunk within 2-3 days. Having finished drinking tea from the first portion, proceed to the next one, etc. This tea should be drunk in large doses half an hour after meals.
Salts begin to come out only after 2-3 weeks of taking the decoction. Drink until the urine turns from rusty to clear, like water. This is approximately 2 months.
During the course of removing stones with herbs you must adhere to a “light” salt-free diet , limit the consumption of meat, fried, smoked and fatty foods. Fruits, vegetables and grains will help! And fresh berries or fruit drinks made from them - cranberries and lingonberries - will also help the kidneys. In the fall, of course, watermelon.
If you refused surgical intervention in favor of herbal medicine to remove stones, then you made the right choice!
author of the article Veselova M.V.
Hakobyan Gagik Nersesovich – professor, doctor of medical sciences, oncologist, urologist in Moscow
The appointment is conducted by a doctor of the highest category, urologist, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor. Author of more than 100 scientific papers.
Urological oncology experience – more than 15 years. Helps men and women solve urological and oncourological problems.
Conducts diagnostics, treatment and complex operations for such diagnoses as:
- tumors of the kidneys and upper urinary tract;
- prostate and bladder cancer;
- urolithiasis disease;
- BPH;
- hydronephrosis, ureteral stricture, etc.
Treatment
The treatment regimen for urolithiasis is influenced by the parameters of the cystolithiasis stone: composition, location, and impact on the general condition of the patient. The characteristics of the course of the disease are also taken into account. The main task in the treatment of cystolithiasis is to remove stones from the urinary system. They are either dissolved or removed through surgery.
Thus, treatment of urolithiasis comes down to several points:
- taking certain medications;
- physiotherapy;
- diet;
- operation.
To restore the patient’s quality of life, pain is relieved and antispasmodics are prescribed. In some cases, very strong painkillers are required.
The process of dissolving stones is not fast, some methods do not give results immediately - the program is selected according to the situation and is constantly monitored by doctors.
Diet for urolithiasis is important: high-quality drinking regimen, limiting fatty, spicy, spices, coffee, tea, chocolate. Legumes, citrus fruits, dairy products and many other types of food are also not recommended - each patient is given a detailed reminder.
As for surgical intervention, the types of operations are also different - there are more than five techniques that are selected based on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the stone(s).
Various herbal mixtures are used as folk remedies. But under no circumstances should you drink them on your own, without consulting a doctor - first get the doctor’s permission.
During your consultation, the urologist will answer all your questions in detail.
If you are bothered by difficulty or frequent urination, pain in the lumbar region, blood in the urine, as well as other symptoms (read about what else should alert you here), seek help from a urologist.
Admission includes:
- familiarization of the doctor with the patient’s medical history;
- inspection;
- making a preliminary diagnosis, prescribing tests and necessary procedures.
*If you plan to get tested immediately after your appointment with your doctor, go to the clinic with a full bladder.
Do not delay your visit to the clinic - come for a consultation with a urologist at the State Urology Center in Moscow - the R. M. Fronshtein Urology Clinic of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov. Entrust your health to a competent specialist!
Treatment methods for urolithiasis
Treatment of urolithiasis is mainly surgical - an operation is performed to remove the stones. If the stones are formed by uric acid salts, their dissolution is possible. In this case, a course of special medications is prescribed.
However, if the conditions that caused the stone formation remain the same, then the stones may appear again after they are removed. To avoid this, a course of preventive treatment is carried out, including adherence to a special diet, medication, maintaining the necessary water balance, and physical therapy.
By contacting JSC “Family Doctor” with complaints about a disease of the urinary organs, you will receive advice from qualified urologists. Their experience, as well as equipping the Family Doctor clinics with modern equipment, including its own laboratory, will allow you to quickly and accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Stone removal is carried out in the Hospital.
Removing Stones
Currently, stone removal is usually done using minimally invasive methods. Laparoscopy and open surgery should be resorted to only in extreme cases. First of all, methods such as pyelolithotripsy are used (stones are destroyed as a result of mechanical, ultrasound or laser action using instruments placed along the natural urinary tract) and percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy (removal is performed through an incision in the lumbar region. This is how large and coral-shaped stones are removed).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.