Provoking pathologies
Various factors can provoke the appearance of pain in the eyeball area when moving. In addition to the effects of external stimuli, pathological conditions developing in the main and adjacent tissues of the organ of vision can cause pain.
Conventionally, they are divided into the following main groups:
- Ophthalmological pathologies.
- Diseases not related to the eyes.
Ophthalmological causes of painful sideways eye movement
Most often, pain is caused by pathological processes occurring in the structure of the eye. The main eye diseases that cause pain include:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane. They are provoked by various ophthalmological diseases and manifest themselves in the form of conjunctivitis of various forms and severity of the disease.
- Uveitis. It is characterized by inflammatory processes that affect the vessels of the mucous membrane of the eyes. It is accompanied by pain not only when moving, but also when at rest.
- Iritis. A disease in which the membrane of the organ of vision becomes inflamed under the influence of internal and external factors. The intensity of pain depends on the stage of development of the pathology.
- Glaucoma. Irreversible damage to the structure of the lens, which leads to constant overstrain of the eye muscles.
- Optic nerve neuritis. This is a stem lesion of the peripheral nerve caused by bacterial or viral infections. The pathology can also be caused by injury or compression of the nerve during surgery.
- Myositis. Accompanied by inflammation of the muscle tissue in the eyeball area. Painful sensations provoke not only movements, but also eye strain.
- Blephoritis. It is characterized by inflammation of the eyelid tissues in the area of the ciliary bulbs. With improper therapy, the pain quickly spreads and is felt not only when the eyeball moves, but also when the eyes are closed.
- Dry eye syndrome. It develops as a result of dehydration of the mucous membrane of the organ, which is provoked by prolonged exposure to conditions with dry air and bright lighting.
Diseases not related to the eye apparatus
The manifestation of pain can be a characteristic symptom of pathology of various etiologies. Most often, this symptom manifests itself with the development of such diseases:
- Hypertension. Accompanied by severe pressing headaches that rapidly spread to the visual area.
- Intracranial hypertension. The pain is caused by increased fluid accumulation, putting pressure on brain cells. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies and radiates to the eyeballs.
- Migraine. Pain provokes a sharp change in pressure in the blood vessels, which provokes the appearance of spasms.
- Flu. Inflammation in the respiratory tract, increased intracranial pressure due to difficulty breathing due to a runny nose. This causes variable pain in different parts of the body, including the eyes.
- Sinusitis or sinusitis. Pain in the eyes causes inflammation in the frontal or nasal sinuses.
- Infectious diseases. Damage to the body by pathogenic microorganisms provokes the development of inflammation in the eye tissues and causes a change in intraocular pressure. This leads to eye pain.
Not only the severity of its manifestation, but also its nature depends on the cause of pain when moving the eye.
It hurts to look up and your head hurts – causes, treatment, prevention – About the eyes
Tell VKontakte in Odnoklassniki in
Cephalgia, or headache, is a pathological condition that has various causes and is often a symptom of serious diseases. If it is temporary, you can limit yourself to taking analgesics to get rid of suffering. Pain that occurs constantly indicates the presence of pathology and requires treatment.
What is a headache
This pathological condition, familiar to every person, arises as a reaction of the body to physiological or psychophysiological changes occurring in it. The pathological condition is associated with one of three physiological disorders:
- irritation of nerve fibers in bone tissue and skull;
- disturbance of the tone of the cerebral vessels of the head caused by changes in blood pressure;
- damage to the muscles of the skull and neck.
Signs
Any signs of cephalalgia are behavioral characteristics of a person suffering from this condition. Infants, deaf-mutes, and sick elderly people are unable to explain what is bothering them. Signs of cephalalgia are:
- crying, moaning;
- frequent blinking, squinting of eyes;
- pressing with palms, fingers on the bridge of the nose, back of the head, crown, eyebrows, temples;
- unreasonable rotation of the head or neck;
- unusual facial expressions.
Symptoms
Cephalgia can be clearly localized (when a person is able to say exactly where he has unpleasant sensations), or it can “radiate” to other parts of the body, and then the patient says that his “eyes hurt”, “his temples ache”, “ puts pressure on the neck,” etc. The following symptoms of cephalalgia are distinguished:
- a feeling of tightness in the head and neck area;
- painful reaction to light;
- temperature increase;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- visual disturbances, attacks of blurred vision;
- nausea, vomiting.
Causes of headaches
Head pain occurs for the following reasons:
- excessive consumption of alcohol, coffee or smoking - caffeine and nicotine cause vascular spasms and impaired blood circulation in the brain;
- chronic stress, depression and psychosomatic disorders (phobias, nervousness);
- infections of the respiratory tract, internal organs;
- poisoning with chemicals, harmful gases;
- excessive physical activity, head and neck injuries;
- damage or curvature of the spine;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, previous strokes;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, radiculitis.
Severe headaches
Often severe sharp pains, accompanied by nausea, fever and a feeling of “pressure” on the eyes, often indicate the onset of meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain. Periodically occurring radial pain radiating to the temples is a common symptom of migraine.
The disease is accompanied by dizziness, vomiting, and temporary loss of vision. The nature of the pain is unilateral and intensifies with sudden movements. The pathology of migraine is unknown, but young women are most susceptible to this disease.
Headache often
Hypotension, a disease characterized by low pressure in the arterial vessels, is almost always accompanied by periodic cephalgia, which occurs early in the morning or in the evenings after a working day. The pain is localized temporally, has a pulsating or aching character and goes away after eating, a cup of black tea, rest, and healthy sleep.
It is necessary to conduct laboratory tests and examinations if cephalgia occurs during the day, does not go away for a long time, affects vision, or is dull and permanent. These symptoms may indicate:
- hormonal disorders;
- metabolic problems;
- inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- development of malignant intracranial tumors.
Aching headache
With increased pressure, a long-lasting aching pain occurs in the back of the head. To relieve discomfort, it is recommended to take a pain reliever, go out into the fresh air or open a window.
Aching frontal cephalgia can be the result of complications of tonsillitis, otitis, sinusitis (see video at the end of the article).
In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe antibiotics to prevent meningitis.
Bursting pain
The feeling when the head “splits”, as if something is bursting from the inside in both directions, occurs in the following pathological conditions:
- Depression, nervousness. Mental imbalance affects the functioning of absolutely all body systems, including the nervous system. Cephalgia is caused by a disruption of blood flow to the brain and its normal circulation.
- Severe emotional stress. In this case, pain does not appear immediately, but after a certain time after the disorder has been experienced as a protective reaction of the body - a signal for immediate rest.
- Hormonal imbalances cause disturbances in blood circulation and normal regeneration. Cephalgia appears as a result of these changes.
- Increased intracranial pressure, which occurs as a result of injuries, taking an uncomfortable position during sleep, squeezing the neck muscles, wearing heavy hair clips, hoops, and uncomfortable hats.
- Brain tumors. Cephalgia in cancer is in most cases sharp, pulsating, but bursting pain can also occur.
- Infectious diseases, intoxication as a result of inhalation of harmful substances, food poisoning, drinking alcohol (hangover).
Classification
Based on the degree and nature of pain, the following types of pain are distinguished:
- “Pain of tension” – has a compressive, aching character, appears after heavy physical and mental stress.
- Cluster - very strong unilateral acute cephalgia. With cluster headaches, lacrimation occurs, a runny nose, the eyes turn red, and it is very difficult to tolerate this condition. Men suffer from these pains more often than women.
- Migraine is also intense pain on one side of the head, but migraine, unlike cluster cephalgia, is pulsating in nature.
- Burning – affects the entire area of the head, appears at the onset of multiple sclerosis, osteochondrosis. Non-localized burning may be the result of mental disorders.
What examination should you undergo for headaches?
You should start the examination by contacting a therapist, who, after listening to your complaints, will refer you to a neurologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedist, osteopath or ophthalmologist. After a general examination, a diagnosis is prescribed, the methods of which depend on the specific symptoms. The patient is prescribed:
- blood test for antibodies: provides information about the presence of inflammation;
- ophthalmoscopy: allows you to determine whether there are changes in the fundus;
- encephalogram: performed if osteochondrosis or hypertension is suspected;
- angiography: helps to track changes in the functioning of cerebral vessels;
- Lumbar puncture - sampling of fluid from bone tissue: prescribed if meningitis is suspected.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical examination method used to identify diseases of the central nervous, musculoskeletal, and circulatory systems.
Using MRI, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image of an organ or part of the body (in this case, the brain), which helps to see any changes in its functioning.
The MRI procedure almost completely eliminates the possibility of an erroneous diagnosis.
The MRI is preceded by a consultation with a doctor, during which the doctor will find out whether the patient has had head injuries, what the severity of the injury was, whether there have been surgeries, and whether he has dental implants.
In some cases, additional tests are prescribed.
Immediately before the procedure, you need to remove all metal objects from yourself, put coins out of your pocket, remove brooches, pins, cufflinks, and remove devices that transmit data: phones, tablets, players.
Progress of the procedure:
- The patient lies down, the doctor fixes his head with a special pillow.
- The couch on which the patient lies is rolled into the MRI room, where the tomograph is located.
- An MRI takes only 15-30 minutes. The diagnosis is painless, but for people suffering from hypersensitivity or claustrophobia, the doctor gives a sedative injection.
First aid
For cluster cephalgia and migraine, it is necessary to take pain medication. A sudden attack of pain in the head, especially if it is caused by overwork and stress, can be relieved without the use of medications:
- open the window, ventilate the room;
- relax, take a comfortable position (it is better to sit in a chair or lie down);
- close your eyes;
- Lightly massage your temples and eyes;
- drink herbal tincture (for example, chamomile), green tea.
Medications
The use of any strong painkiller is contraindicated for liver and kidney diseases, serious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and heart disease. Most analgesics are prohibited during pregnancy and lactation. The table below presents a list of medications that effectively relieve an attack of cephalgia:
| Name of medicine | Purpose |
| Painkillers | |
| Citramon | General pain reliever |
| Sumatriptan | Exclusively for the fight against migraines |
| Tempalgin | For any acute pain |
| Anti-inflammatory | |
| Analgin | Sharp throbbing symptomatic pain |
| Aspirin | Aching or impulsive pain |
| Paracetamol | Pain accompanied by increased body temperature |
| Solpadeine | Paroxysmal pain |
Home Remedies
If you have a headache, a cup of coffee, cocoa or tea, or a piece of dark chocolate will not hurt people with low blood pressure. Those who suffer from hypertension need to go out into the fresh air and do breathing exercises. However, it should be remembered that if attacks of cephalalgia recur regularly, you should consult a doctor.
You can treat a headache at home only when it is symptomatic and the cause is well known. Among the traditional methods they offer:
- Relaxation: take a warm bath, turn on relaxing music, try to meditate.
- Do an eye massage: lightly press your fingers on the area of the eyeballs, perform rotational movements, first in one direction, then in the other direction.
- Do breathing exercises: go out into the fresh air, take a deep breath, hold your breath for a few seconds, exhale slowly.
Prevention
As methods of preventing cephalalgia it is necessary:
- limit the consumption of fried, fatty, salty foods;
- exercise: run in the morning, walk 45 minutes a day;
- drink up to 2 liters of fluid per day;
- avoid stress, practice home meditation;
- limit consumption of alcohol, caffeine, quit smoking.
Headache: types, causes, how to cure
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Source:
Why does it hurt to look up? What could cause the symptom?
- In some diseases, patients do not feel any painful symptoms as long as the organs of vision are in a relatively calm position.
- But as soon as you raise your eyes up or squint to the side, pain occurs .
- Most often, this is a clear sign of tiredness and eye strain , but it can also indicate the development of serious diseases, including those that may not be related to ophthalmology.
- blepharitis;
- colds;
- glaucoma;
- migraine;
- myositis;
- disorders of the oculomotor nerve;
- swelling that occurs in the eye area due to inflammation in the tissues of the eyeball.
Discomfort in the eyes when looking upward often occurs with viral diseases of the respiratory tract .
- As a result, pain occurs, which intensifies when looking up or to the sides.
- Another common reason is partial atrophy of the eye muscles after prolonged work at the computer , when a person’s gaze is focused on a relatively small area for several hours.
- But in these cases, the unpleasant sensations are short-term, and with timely rest and performing eye exercises, they do not even arise.
- It is extremely rare that this condition occurs against the background of neuritis of the oculomotor nerve, but this is a rare disorder.
Pain in the head when raising the eyes
- If you complain of pain in the head that occurs when you lift your eyes up, you should first be checked for frontal sinusitis.
- This is an inflammation of the frontal sinuses, which can be diagnosed during examination by an ENT specialist.
- Other reasons for such symptoms may include:
- flu;
- stroke;
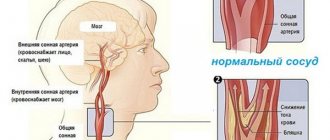
- Horton's disease (inflammation of the carotid artery);
- increased arterial and intracranial pressure;
- neoplasms in the brain;
- myopia;
- trigeminal neuralgia.
Source: https://4hospital.ru/diagnostika/bolno-smotret-vverh-i-bolit-golova-prichiny-lechenie-profilaktika.html
What do accompanying symptoms indicate?
The manifestation of pain during eye movement may be accompanied by other uncomfortable sensations. They are usually caused by the development of various pathological processes in the body, which are manifested by the following accompanying symptoms:
- Dry eyes. As a result of blockage of the lacrimal glands, hormonal dysfunction, constant wearing of contact lenses and laser vision correction.
- Tears. Indicates eye strain and the development of dysfunction of the lacrimal glands, as well as metabolic disorders in the tissues of the visual organ. It also manifests itself with mechanical damage to the eye and exposure of its mucous membrane to aggressive substances of any form.
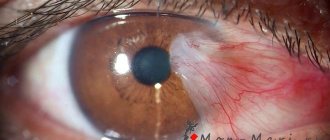
- Redness of the eyes. Develops against the background of inflammation of the eyeball or upper and lower eyelids, increased blood and intracranial pressure. Also indicates the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
- Swelling. Infection of the nasopharynx or ciliary follicles, inflammation of the meibomian glands. It may also indicate the development of an allergic reaction.
- It hurts in the eyes. Foreign objects entering the eyeball area, exposure to external irritants. Indicates the development of inflammatory processes in the eyes, neuralgia of the ternary nerve and demodicosis.
- Temperature. It manifests itself in acute respiratory infections, influenza, inflammatory diseases, intoxication with heavy metals and harmful chemical compounds.
- Pain when turning your head. It is a characteristic sign of intoxication of the body, infectious ophthalmological pathologies, brain damage, increased intraocular pressure and eye injury.
- Loss of vision. Indicates the development of a strong inflammatory process in the internal structure of the eye, which is accompanied by the accumulation of purulent exudate. It may also be a sign of the development of certain ophthalmological pathologies.
Often, characteristic symptoms can appear in the area of both eyes. But, there are cases in which it hurts to turn only the left or only the right eye. This usually happens when:
- Development of astigmatism.
- Ingress of a foreign body or mechanical damage.
- Consequences of surgery.
- Infection or fungal infection of one eye.
Concomitant symptoms of pain when moving the eye can appear singly or complexly. They help to correctly determine the etiology of pain in the eye area.
Headache when looking up
Headache that prevents you from moving your eyes due to increasing intensity is a common problem.
It can be very acute, causing discomfort and limiting quality of life by reducing visual acuity. There are different types of headaches that get worse in situations where you have to move both eyes or one, since it can be caused by different diseases with different causes, consequences and severity.
If a headache occurs or increases when there is a need to move the eyes (how could we not do this!), a rather unpleasant sensation arises. The main causes include glaucoma, stye, conjunctivitis. Given the importance of vision, no symptom should be underestimated.
Glaucoma
A common disease, it occurs mainly in adults, but glaucoma in newborns also occurs.
This is an ophthalmic disease associated with high pressure inside the eye, which, by pressing on the ocular structures, leads to their damage.
With glaucoma, there is a progressive loss of vision, in particular, a narrowing of the field of vision, when the eye sees only what is immediately in front of it, but not in its surroundings, as is the case with a healthy eye.
Symptoms of glaucoma include a sudden increase in pressure in the eye, severe headache on the affected side (the headache is worse when a person has to move the eyes), pain directly in the eye, vomiting, blurred vision, and photophobia may be present. These symptoms should be addressed as soon as possible because... the disease can cause permanent vision damage.
Hordeolum (barley)
Hordeolum or stye (inflammation of the eyelid gland), surprisingly, can also cause headaches, which are localized on the side of the affected eye. Anyone who has suffered from this problem knows how painful it can be to move the eye. These sensations often occur in the area of the temples or, directly, the eyes.
Treatment is based on local application of antibiotics in the form of ointments or eye drops. Other inflammations of the eyelids can manifest in a similar way, which can cause situations where it is painful to move the eye/eyes. If they do not go away on their own or complications arise, you need to visit an ophthalmologist.
Neuritis
Typical pain behind the eye is inflammation of the optic nerve, which transmits image information from the eye to the brain. This is a serious disease, manifested by a sudden loss of visual function and pain behind the eye, especially when it moves.
Often, when you move your eyes, you also get a headache. Although most often it results in restoration of visual function, the disease can lead to nerve damage and thus to one-sided blindness.
The cause is viruses and bacteria, but the disease is also often the first symptom of multiple sclerosis.
The head often hurts during eye movements due to other diseases, for example, inflammation of the teeth, migraines, sinusitis.
Conjunctivitis
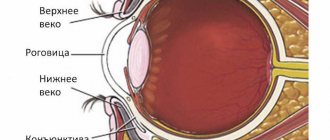
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the transparent membrane that covers both the eye itself and the inside of the eyelids. The conjunctiva has many functions, in particular protective (the cells of the protective system are located here, it is a certain form of a protective barrier).
It also contains glands that produce valuable substances that form the components of tears. The most common infections can be divided into viral and bacterial, according to trigger factors. There are also inflammations caused by parasites, fungi, etc.
, but they are not that common.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized, in addition to eye pain, by thick yellowish mucopurulent discharge, especially after waking up, redness of the eye, and headache.
This disease requires treatment with antibiotics, which are most often administered in the form of drops or ointments directly into the eye; in case of severe inflammation, which also causes a headache in the area of the affected eye, the drugs are usually taken in tablets.
Viral conjunctivitis is characterized by an acute form of the disease, headache, a feeling of sand in the eyes and their redness, as with bacterial inflammation, swelling of the eyelids may be present.
Treatment primarily involves the use of drops with disinfectant properties and ointments at night. Antibiotics are not effective for viral infections.
Often these infections, after visual impairment in one eye, move to the second, as a result of which it becomes painful to move both eyes; In this case, headaches localized in the eye area and spreading to the forehead and temples are not uncommon.
Conjunctivitis can occur even without the involvement of germs. Potential causes include UV rays, vapors of irritating gases, and cases of allergic inflammation are common.
Regardless of the cause, these infections are similar in their manifestations: pain in the eyes, tingling, burning, redness, lacrimation, photophobia, headache; it is unpleasant for a person to move from a dark room to a well-lit space.
First of all, it is necessary to avoid risk factors (substances that cause allergies, gases, cigarette smoke, etc.). UV rays penetrate a little deeper into the eye, affecting the cornea, which is the most innervated tissue in the body. Therefore, its damage is very painful.
It occurs mainly due to the failure to use safety glasses or sunglasses when welding - on a bright sunny day in the mountains, but also in the city if there is snow. The result is so-called snow blindness.
Both injuries cause very severe eye pain, accompanied by a headache, usually occurring several hours after the injury - most often at night.
Refractive errors (farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism)
Other causes include refractive errors, i.e. farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism, for which unsuitable glasses are used; many people do not know about these defects at all. Along with eye pain, headache also occurs, usually aggravated by eye movement.
Ophthalmic migraine
Ophthalmic migraine is a temporary or permanent disorder of one eye that either accompanies a migraine attack or occurs independently in patients with a history of migraine.
Ophthalmic migraine occurs due to circulatory disorders in the retina. Patients complain of temporary loss of vision in one eye. Most patients under 40 years of age experience vision loss in one eye ranging from a few seconds to several hours.
Repeated attacks can cause permanent damage to the visual field. Ophthalmic migraine is not always accompanied by headache. Ophthalmic migraine is not always accompanied by headache.
If it is present, it is localized above or in the immediate vicinity of the affected eye and intensifies with eye movement.
Vision loss or disturbance may occur before, during, or after a headache attack. Ocular migraine is rare and therefore diagnosis is made by differentiation. It is necessary to exclude transient blindness, which is a secondary disease during microembolization of reticular arteries.
Source: //novosibmemorial.ru/golovnaja-bol-pri-vzgljade-vverh/
Diagnosis and treatment
A consultative examination by an ophthalmologist will help determine the exact cause of pain in the eyes when moving. At an appointment with a specialist, a physical examination is performed and a comprehensive examination is prescribed. It includes laboratory and hardware diagnostics, which consists of:
- General analyses.
- Blood biochemistry.
- Analysis for the presence of a fungal infection of the eye mucosa.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye media.
- Measurement of pressure inside the eye.
- Determination of the boundaries of the field of view.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball
- Confocal microscopy
Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the etiology of the development of pain in the eyes during movement is determined and appropriate treatment is selected.
If minor pain suddenly appears, first aid at home is allowed. For this it is recommended:
- Limit or completely eliminate eye strain.
- Make a light head massage in the direction from the temples to the back of the head, and from the back of the head to the forehead.
- Massage the muscles of the collar area.
- Rinse the eyeballs with tea leaves or a light solution of chamomile.
- If pain increases, painkillers may be taken.
If the pain does not stop and its intensity increases, methods of official medicine are used to relieve it. The most effective complex treatment includes taking medications from the following groups:
- Painkillers.
- Antispasmodics.
- Antihypertensive.
- Vasodilators.
- Antibacterial.
- Antifungal.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Preparations for moisturizing the mucous membrane.
- Immunomodulators.
- Antiviral.
- Vitamin complexes for the eyes.
- Diuretics.
- Antihistamines.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When treating pain in the eyes of any etiology, topical medications are predominantly used. Also, as prescribed by a doctor, general medications are taken.
Traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary treatment. The most effective natural medicines are infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs.
- A decoction of mint leaves. It is used to relieve increased muscle tone, reduce visual tension, stabilize blood pressure and restore the psycho-emotional state, strengthens the body's protective functions.
- Infusion of chamomile. Allows you to quickly get rid of inflammatory processes when applied topically, reduces the severity of symptoms, and alleviates burning and stinging sensations in the eyes.
- Compresses and lotions made from aloe juice, honey and yogurt are also effective. Dandelion root juice and mature honey are used as drops. Ice cubes made from brown algae quickly relieve inflammation and pain in the eyes.
The use of traditional medicine should only be done after consultation with the attending physician. Self-medication in this case threatens to deteriorate the health of not only the eyes, but also chronic pathologies in general.
Treatment of pain in the eyes when moving is prescribed by an ophthalmologist, taking into account their etiology. The selection of drugs, the regimen for their administration and the duration of the therapeutic course are made in each case individually and depend on the physiological parameters of the patient.