Indications
The indication for eye tonography is the need to measure the pressure inside the eye and is necessary in the following cases:
- if your eyes get tired very quickly;
- there is a feeling of heaviness in the eyes, and pain in the superciliary areas and eye sockets;
- after prolonged visual stress, the head begins to hurt;
- vision decreases;
- if, when looking at very strongly lit objects, rainbow circles appear.
These are the first signs of the disease. If you detect the disease in its early stages and start treatment on time, you can avoid complete blindness. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is used. If the disease is not treated, you can eventually lose your vision completely.
Also, signs of glaucoma can be small scotomas (dark spots) in front of the eyes, blanching of the optic nerve head, and asymmetry of the eyes.
Sometimes the cause of eye pain is trigeminal neuralgia.
With glaucoma, the eyes hurt when the intraocular pressure is very high. This is possible during an acute attack. Tonography is carried out in the following cases:
- the patient has diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems that impede the outflow of fluid;
- if the patient has relatives with glaucoma and is over 40 years old;
- The patient has neurological pathologies that can cause eye function.
Features of the procedure or what is important to know
As for the early diagnosis of primary type glaucoma, no matter what anyone says, it is important. If the disease is not identified immediately, the disease will turn into a pathological process that can be stopped with the help of medications, and if not, then surgery or laser treatment will have to be used.
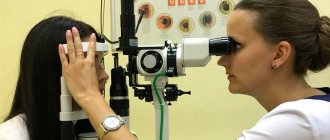
Using the procedure, an eye examination takes place in several stages when identifying the presence of pathology:
- IOP is measured using tonometry or elastotonometry;
- examine the indicators of outflow of aqueous humor in the eye (AH) - tonography;
- examine the fields of visual vision - use different perimetry techniques.
At the same time, in clinics the procedure for each eye is carried out separately using impression and applanation devices. Impression-type electrotonographs of Nesterov and Sakharov remain quite common. Less commonly used is a Schiotz tonometer with perilimbal suction cups if necessary. A simplified procedure is carried out thanks to the Maklakov apparatus.
Contraindications
Eye tonography is contraindicated in cases where:
- there are injuries to the cornea;
- inflammatory or infectious process in the membrane of the eye;
- the cornea has pathologies that can change the readings;
- individual allergic reaction to anesthesia, which is used at the beginning of the procedure.
Also, tonography of the eye is not performed if the patient has consumed alcohol or drugs. If the patient has mental disorders that do not allow his behavior to be predicted during the procedure, then tonography is not performed.
After signs of inflammation are eliminated, tonography can be performed. If antiseptics are used during the procedure, the patient will not have side effects or discomfort after the examination.
How is the procedure done?
As mentioned earlier, the procedure for computed tomography of the retina takes no more than one minute (without the use of contrast) and about 15 minutes if an iodine-containing substance is required (in which case it is performed on an empty stomach). Before starting the diagnosis, the doctor talks about how the whole process will go. It is worth noting that patients have no reason to worry - the study is not only short-term, but also painless. The examination process itself is as follows: after the patient has removed all metal objects, he is asked to lie down on a special table, which will subsequently be advanced into the tomograph so that the patient’s head falls into the scanning area. As with other types of tomography, the patient must remain motionless.
3D visualization
A black-and-white three-dimensional image is displayed on the radiologist’s computer, which allows you to examine the eyeballs, retina, and optic nerve from all sides. The image can be enlarged to view fine details. All results are saved on the computer of the clinic where the retinal CT scan is performed.
Preparation for tonography
Before starting the study, the doctor must calibrate the device in order to ensure the greatest accuracy of individual parameters. If a tonograph is used for the study, which is not connected to a computer, then the calculations must be carried out manually.
In order to reduce the sensitivity of the cornea, drops with an anesthetic effect are dripped into the eye.
A special ring is used to widen the eyelids. A saline solution should also be used to moisten the mucous membrane. The following actions may affect tonography results:
- Physical activity. After active movements, the pressure drops by 4.3 mm and is restored within an hour.
- One cup of coffee raises intraocular pressure by 4 mm. The recovery period is 90 minutes.
- Alcohol increases the readings by 3.7 mm. The effect lasts for an hour.
- Water. After the patient drinks 1 liter of water, the pressure rises by 4.4 mm, and is restored after 2.5 hours.
What diseases can EPI detect?
Electrophysiological examination of the eyes helps to identify a variety of ophthalmological pathologies:
- Myopia, hypermetropia of varying degrees.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Cataracts.
- Glaucoma.
- Amblyopia.
- Congenital hemeralopia.
- Retinal detachment, retinal rupture.
- Injuries to the eyeball, atrophy of its tissues.
The method is effective in diagnosing damage, dystrophic changes in the optic nerve, cancerous tumors or cystic formations formed in the organ of vision. The procedure facilitates high-quality diagnosis of increased eye fatigue. It is carried out to determine the intoxication of the body by harmful industrial emissions, poisons, etc.
Method of eye tonography
The procedure for conducting simplified tonography of the eye is as follows:
- The patient lies down on the couch, and the cornea is numbed with special drops. In order to relieve a spasm of accommodation, the patient is advised to look at one object. The eye is immobilized using a dilation ring.
- A weight weighing 15 g is placed on the cornea. The procedure lasts 5 seconds.
- After half a minute, using the colored side of the weight, IOP is measured.
- The cylinder is positioned for another 4 minutes and the IOP results are recorded.
- The last procedure is carried out two more times with an interval of 5 seconds.
Based on the tonography results, an elastotonometric curve is drawn and analyzed. The nature of the curve determines the individual reaction of the eye to the impact of loads of various masses, taking into account the scope and bend of the curve.
The technique of conducting electronic tonography is generally similar to the simplified one, only the diagnosis is carried out using a special electronic tonograph, and the eyelids are parted with a plastic ring and a special sensor is installed on the eye. When performing tonography using an electronic tonograph, it is possible to automatically obtain the indicators of interest for the outflow of moisture from the anterior chamber of the eyeball.
To ensure that the procedure does not cause complications other than anesthesia, the doctor must instill an anesthetic. Usually a solution of sodium sulfacyl (30%) is used.
Briefly and the procedure: tomography and glaucoma
Tonography is a technique for studying the ongoing process related to the outflow of aqueous humor. It also includes graphical recording of the IOP level, which stands for intraocular pressure. The peculiarity of the technique is extended tonometry (examination time is about 4 minutes) with subsequent calculation of the main indicators of hydrodynamics in the visual apparatus.
Thanks to a procedure such as eye tonography, you can find out the level of two indicators:
- “F” – 60-second volume of intraocular fluid;
- “C” is the coefficient of “ease” of aqueous humor outflow.
The last indicator will demonstrate the value, namely, it will determine the specific volume of moisture (in mm 2) flowing from the organs of visual vision in 60 seconds during the compression pressure - “mm. Hg st./mm3". But 60 seconds of liquid in this regard should be equal to proportional to the numerical indicator of the pressure that is filtered.
Important! An electronic type of tonograph is used in diagnosing the disease. In addition, in practice they also use a simplified procedure method thanks to the simple Maklakov apparatus.
Normal eye tonography
During tonography, the normal pressure inside the eye is 15-17 mm Hg. If these indicators are equal to 20 mm, then the likelihood of glaucoma increases, and an indicator at the level of 24 mm indicates the presence of glaucoma.
The CLO indicator should be from 0.11 to 0.6 mm3 per minute. The average value is 0.3 mm3 per minute. If glaucoma is at an early stage of development, then these indicators are closer to the lower limit of normal - from 0.12 mm3 to 0.2 mm3 per minute. If such results are obtained as a result of the study, then it is necessary to undergo a more thorough examination and be constantly monitored by a doctor. If there is glaucoma, then the CLO indicator will be 0.1 mm3/min or lower.
The rate of formation of intraocular fluid is another tonography indicator. It varies from person to person, but on average it ranges from 1.5-4.5 mm3/min. It is very important that the indicators in the right and left eyes differ from each other. If they exceed 0.8 mm3, then this can also be considered a sign of glaucoma.
The Berker coefficient (KB) is the ratio of the initial indicator to the maximum result obtained during tonography. Its norm should not exceed 100, but with glaucoma, especially in the early stages, this figure is much higher.
KB varies depending on age. At the age of up to 30 years, it does not exceed 90; from 30 to 39 years, the indicator is 100; for the next two decades, 5 units are added. At the age of 60 years and older, normal BC levels are 135 units.
If intraocular pressure readings exceed 27 mm, then to eliminate errors, a re-diagnosis is carried out after 30 minutes. This will help avoid measurement errors.
The highest intraocular pressure is observed in infants. Also, women, compared to men, have slightly higher rates. Also, pressure is slightly affected by weather changes, as well as body position.
Video about how to treat glaucoma and why a comprehensive examination is necessary
The video explains that glaucoma is a disease that leads to blindness. So, in order to identify the disease at the initial stage, it is better to go to the clinic. Also, it is treated in a complex way, and if the stage is advanced, then only with laser or surgery. I advise you to prevent the progression of the disease and immediately contact an ophthalmologist if you have the first signs.
Varieties
There are several options for measuring intraocular pressure - from a simple finger method to modern non-contact ones. Indications obtained by different methods cannot be compared with each other, since they are focused on different values of norm and pathology.
Using your fingers
Finger tonometry is the simplest way to measure IOP and does not require complex diagnostic instruments.
Compression is performed through closed eyelids with your fingers:
- The patient relaxes and looks down.
- The diagnostician places his palms on his forehead, and with his index fingers presses on the eyelids just below the brow ridge or at the outer corner of the eye.
- Pressure is applied in small bursts alternately on the right and left eyes. This allows you to feel the fluctuation wave and assess the degree of density of the eyeball.
The method gives an approximate idea of the degree of IOP and is applicable in cases where instrumental diagnostics cannot be carried out (for example, after eye surgery).
Contactless
With non-contact computer tonometry, compression on the cornea is carried out by an air flow. The study evaluates the degree and rate of change in the cornea in response to exposure to the jet.
The procedure is carried out in a sitting position:
- The patient's head is placed and fixed on a special stand. A person should look at one point, eyes wide open and gaze fixed.
- Within a few seconds, the device delivers an intermittent flow of air, changing the shape of the cornea.
- The degree of deformation of the cornea is assessed by a computer program, producing diagnostic results in the form of a numerical IOP value.
Despite all its technological advantages, the non-contact method is inferior in accuracy to contact methods. Therefore, the technique is used only for the initial detection of glaucoma and for preventive examinations. It is impossible to monitor the treatment of patients with glaucoma using air tonometry.
Contact
Most often, applanation contact tonometry according to Maklakov is used to measure ocular pressure. Maklakov's tonometer is the simplest equipment, consisting of a set of metal weights with a lead rod. The ends of the weights are made in the form of flat plates coated with glass with a diameter of 1 cm.
How is tonometry performed:
- The patient takes a lying position and anesthetic drops are instilled into his eyes.
- The ophthalmologist applies a diagnostic dye solution made from collargol to the base of the weight and stands at the patient’s head.
- With one hand, the doctor expands the patient’s eyelid, and with the other, strictly vertically lowers the cylinder onto the cornea. As a result of compression, the paint transfers from the weight to the cornea.
- The remaining traces of the tonometer dye are transferred to the paper in the form of an imprint.
- The procedure is repeated for the second eye to obtain another print.
- The prints are measured using a special transparent ruler. The smaller its diameter, the denser the eye and the higher the IOP, and vice versa. The results are compared with normative tables for different genders and ages.
At the end of the study, another drops are instilled into the eyes - this time antibacterial to prevent the development of infectious complications.