ALDOSTEROME
(synonym:
primary aldosteronism, Conn's syndrome
) is a hormone-producing tumor of the adrenal cortex that secretes an increased amount of aldosterone.
Primary aldosteronism was first described by JW Conn in 1955. The term “aldosteroma” was introduced by O. V. Nikolaev (1963) and was an addition to the classification of hormonally active tumors of the adrenal cortex published in 1947. Aldosteroma is localized in one of the adrenal glands; bilateral tumors are observed in approximately 6% of cases.
The disease usually affects young people, more often women. Cases of the development of aldosteroma in children have been described. Malignant aldosteromas are rare.
Some researchers, in particular Gerny (I. S. Gerny, 1970), believe that 5-8% of all patients with hypertension suffer from primary aldosteronism and can be cured surgically.
What is aldosteroma
Aldosteroma
is a tumor of the adrenal cortex that secretes one of the adrenal hormones, the mineralocorticoid aldosterone. The development of aldosteroma is characterized by signs of primary aldosteronism – it is also called Conn’s syndrome. In the vast majority of cases, the tumor process is benign in nature. According to statistical data, the malignant type of aldosteroma is detected only in 3-5% of the total number of cases. The area affected by the tumor is usually small in size and is almost always observed in one of the adrenal glands, while bilateral multiple lesions (multiple aldosteromas) occur only in 5-6% of cases.
Aldosteroma is diagnosed most often in middle-aged people (35-50 years), and the prevalence of the tumor among women is 3 times higher than in men. In medical practice, there have also been cases of the development of aldosteroma in children.
Causes and mechanism of development of aldosteroma
The reasons for the development of aldosteroma, along with other tumors, remain poorly understood today. According to a number of researchers on this problem, heredity plays a certain role in the development of aldosteroma.
The mineralocorticoid hormone - aldosterone, produced in excess quantities, several tens of times higher than normal, by an adenoma of the adrenal cortex - aldosteroma, participates in water-salt metabolism in the body, exerting a number of main effects on it:
- first of all, aldosterone enhances the reabsorption of sodium ions in the renal tubules, as a result of which the sodium concentration in the blood increases, the osmotic pressure and volume of circulating blood increases, and the sensitivity of the arteriolar walls to vasoactive substances increases and, as a result, a persistent increase in blood pressure develops;
- enhances the excretion of potassium, magnesium and hydrogen ions in the urine, which leads to the phenomena of intracellular acidosis and extracellular alkalosis, which entail dysfunctional disorders of organs and systems;
- suppresses the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, resulting in a noticeable decrease in the amount of renin produced and its activity.
An increase in the level of aldosterone in the blood affects the heart muscle, causing hypertrophic changes in the myocardium, damaging blood vessels and kidneys.
Most of the aldosterones (about three quarters) secrete aldosterone independently, completely losing the connection between tumor cells and the renin-angiotensin system of the kidneys. The size of benign aldosteromas usually does not exceed 3 cm. They may be accompanied by atrophic or hyperplastic defects that affect the rest of the adrenal cortex. The malignant form of aldosteroma is characterized by rapid growth to impressive sizes, accompanied by signs of metastasis.
Signs of aldosteroma
Based on the mechanism of influence of increased secretion of aldosterone by adrenal adenoma, the clinical picture of aldosteroma develops. Signs of the disease reflect the syndrome of primary aldosteronism and are manifested by such main syndromes as cardiovascular, neuromuscular and renal. About 10% of aldosteromes are characterized by an asymptomatic course.
The syndrome of damage to the cardiovascular system is caused by sodium retention in the body, which contributes to the development of hypervolemia, swelling of the vascular walls, leading to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and an increase in pressure in them. In this regard, patients with aldosteroma develop a persistent increase in blood pressure, ranging from moderate to severe. Patients usually complain of headaches, pain in the heart, and blurred vision. Fundus ophthalmoscopy reveals sclerotic changes in retinal vessels and neuroretinopathy. Ultrasound examination of the heart reveals thickening of the muscular walls of the heart at the initial stages of the disease, and degenerative processes in the myocardium in later stages.
Due to increased excretion of potassium and magnesium from the body due to increased concentrations of aldosterone, dystrophic changes in nervous and muscle tissue develop. Patients with aldosteroma may complain of fatigue, muscle weakness, pain in the fingers and toes, in the leg muscles, cramps, and blurred vision. With an acute lack of potassium and magnesium, paresthesia, flaccid paralysis, and convulsive attacks may occur, which are subsequently complicated by heart attacks and strokes.
On the part of the kidneys, with aldosterome, the development of nephropathy associated with potassium deficiency is observed. This manifests itself in a constant feeling of thirst, frequent urination, associated with a violation of the concentrating ability of the kidneys. If the aldosteroma is malignant, along with the main symptoms, abdominal pain, hyperthermia, and various signs of intoxication may be noted.
Clinical picture
In clinical symptoms, three main groups of symptoms can be distinguished: cardiovascular, renal, and neuromuscular.
Excessive secretion of aldosterone (see) disrupts the water-electrolyte balance in the body towards hypokalemic alkalosis and sodium retention. Sodium accumulates intracellularly, and therefore patients do not have peripheral edema. The accumulation of sodium in the wall of blood vessels leads to hyperhydration and narrowing of their lumen, which increases vascular tone and peripheral resistance and leads to the development of hypertension. High blood pressure occurs almost all the time. Against the background of constant hypertension, crises can be observed that resemble attacks in pheochromocytoma (see), but, unlike the latter, they are often accompanied by bradycardia.
As a result of hypertension, changes in the fundus of the eye develop from hypertensive vasospasm to severe retinopathy with hemorrhages and swelling of the optic nerve head. In children, changes in the fundus occur especially quickly and often lead to visual impairment, including blindness.
Patients with aldosteroma are characterized by polyuria and nocturia with isosthenuria and alkaline urine. In some patients, daily diuresis reaches 10 liters. Fluid restriction does not improve renal concentrating function.
Almost all patients complain of muscle weakness. Paresthesia, convulsions, and sometimes flaccid paralysis are often observed, which is caused by a deficiency of potassium in the tissues.
ECG changes are characteristic of hypokalemia: a decrease in the S-T interval, often a negative T wave in leads 1.2, V5, V6. Serum potassium and chloride levels are usually reduced, but potassium levels may be normal in some patients. Hypernatremia is rare. More often than not, the sodium level in the blood is normal. Urinary excretion of aldosterone is often increased, sometimes 3-5 times compared with normal levels. Renin activity in blood plasma is low, however, when aldosteroma is combined with primary kidney damage (similar observations are described in the literature), renin activity may be increased.
Diagnostic criteria for aldosteroma
To make a diagnosis of aldosteroma, it is necessary to conduct a series of laboratory and instrumental studies if the patient exhibits signs characteristic of this disease. A couple of weeks before the upcoming examination, in order to obtain more accurate results, the patient should not take medications that lower blood pressure.
When conducting a biochemical blood test in patients with aldosteroma, a disturbance in the potassium-sodium balance is revealed in the direction of increasing sodium concentration, decreasing renin activity, increasing aldosterone levels and decreasing chlorine concentrations, causing alkalosis. A general urine analysis of patients with aldosteroma is characterized by a decrease in relative density, detection of protein and an increase in the daily excretion of potassium and aldosterone.
Primary hyperaldosteronism, which accompanies the course of primary aldosteroma, is confirmed by tests with aldactone, hypothiazide or march test.
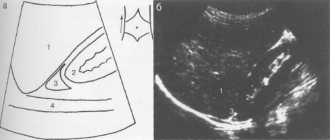
If aldosteroma is suspected, patients are advised to undergo an ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands, which makes it possible to identify the presence of a tumor process and differentiate it from other types of pathological processes of the adrenal glands. To more accurately and reliably identify the location, as well as determine the size of the tumor, a computed tomography scan of the adrenal glands with intravenous administration of a contrast agent is recommended. Most often, computed tomography turns out to be the most justified study in diagnosing aldosteroma, provided it is carried out in a specialized center using high-quality equipment and experienced specialists. Tomography not only makes it possible to clearly determine the presence or absence of aldosteroma in the adrenal gland, but also makes it possible to describe its size, contours, and evaluate the accumulation and washout of contrast by the formation (this makes it possible to obtain information about the benignity or malignancy of aldosteroma).
Until recently, X-ray diagnostics of aldosterone were also carried out using angiography and pneumosuprarenography of the adrenal glands, but the results of these studies turned out to be inaccurate in cases where the tumor was small and had a poor blood supply. Therefore, currently they are resorting to a more complex method of x-ray diagnosis - selective venography of the adrenal glands. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the ratio of aldosterone and cortisol levels, which is sharply increased in patients with aldosteroma.
Since one of the main clinical signs of the disease is persistent arterial hypertension, aldosteroma must be distinguished during the diagnostic process from arterial hypertension associated with other syndromes and secondary hyperaldosteronism.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made based on clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. To diagnose aldosteroma (especially the normokalemic form), a test with hypothiazide (100 mg) is also used, which in case of aldosteroma gives a pronounced decrease in potassium in the blood. For the purpose of topical diagnosis of aldosteroma, suprarenorography, sometimes arteriography and venography (see) of the adrenal glands are most often used. The technique of venography by catheterization of the middle adrenal veins presents certain difficulties, therefore, recently, some researchers have given preference to occlusive venography of the inferior vena cava. For differential diagnosis of aldosteroma with renovascular hypertension, angiography is performed (see) and blood renin is determined. In patients with aldosteroma, plasma renin activity is sharply reduced; in patients with renovascular hypertension, it is usually high.
Treatment tactics and prognosis of patients with aldosteroma
When aldosteromas are detected in patients, they resort to surgical intervention, which consists of adrenalectomy, that is, removal of the tumor along with the affected adrenal gland, or resection of the adrenal gland while preserving part of it. To carry out the operation, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation of the patient, which involves prescribing a special diet a couple of weeks before surgery, which includes limiting the consumption of sodium-containing products. Additionally, potassium supplements and aldosterone antagonists are prescribed - veroshpiron, aldactone. To prevent a possible postoperative complication in the form of acute cortical adrenal insufficiency, patients are prescribed glucocorticoids - cortisone, hydrocortisone, etc. During the postoperative period, the levels of potassium and sodium in the blood and indicators on the electrocardiogram are monitored.
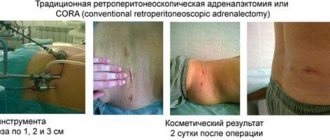
Surgical treatment of aldosteroma can be performed using three main options for accessing the adrenal gland:
1. open access
– the operation is performed through a skin incision up to 15-20 cm long with the intersection of the muscles of the abdominal wall and diaphragm;
2. laparoscopic access
– the operation is performed through punctures on the anterior abdominal wall, and the surgeon performs manipulations on the adrenal gland after preliminary injection of carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity;
3. retroperitoneoscopic approach
– the operation is performed through three punctures or through one access up to 3 cm long, located on the back.
Currently, the retroperitoneoscopic approach, developed in the late 90s in Germany, is the least traumatic and provides the shortest possible time for patient rehabilitation and the best cosmetic result. In the vast majority of cases, after surgery performed using this approach, patients can eat in the evening, and discharge can be made the next day after surgery. The remaining approaches (open and laparoscopic) are characterized by significantly greater trauma.
The North-Western Center for Endocrinology and Endocrine Surgery currently performs the largest number of operations on the adrenal glands in Russia
– more than 100 per year. Operations are performed retroperitoneoscopically, including using a single skin incision (SARA technology - single accessretroperitoneoscopicadrenalectomy). The duration of hospitalization is usually 3-4 days. Patients are accommodated in comfortable rooms equipped with air conditioning, a separate bathroom with shower, telephone, TV, and wireless Internet.
In the vast majority of cases, operations for aldosterome are performed free of charge, within the framework of the federal quota system (high-tech medical care, high-tech medical care) or within the framework of the specialized medical care system.
FAQ
Main symptoms of adrenal tumors
When a mass formation appears, the manifestations depend on the excess secreted hormone, as well as on what tissue is affected by the adrenal tumor. Symptoms in women are sexual dysfunction, changes in the mammary glands and genitals, and other signs of virilization. With an adrenal tumor, symptoms in men can also manifest themselves in feminization: the development of gynecomastia, erectile dysfunction, cessation of facial hair growth, etc. However, an asymptomatic course of the disease is possible when a person learns about the disease during examination. However, as the tumor increases in size, signs characteristic of any pathology of the adrenal glands may appear: the development of persistent hypertension, abdominal or back pain, disturbances in the functioning of the heart, muscle weakness, etc. If left untreated, adrenal tumors in women and men certainly lead to complications : to disruption of the kidneys, reproductive system, diabetes mellitus, etc. Some benign formations have a risk of malignancy.
Diagnosis of an adrenal tumor
Adrenal masses are often detected during ultrasound. In this case, a number of studies are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis, among which the most effective are tomography (MRI and CT), studies of hormonal levels, and kidney examinations. To exclude a malignant process, scintigraphy of bone structures is recommended. In addition, it is possible to prescribe examinations, the purpose of which is to exclude damage to other organs.
Surgery to remove an adrenal tumor - what you need to know
The duration of adrenalectomy is no more than an hour, surgery is performed under general anesthesia. We use modern methods of pain relief in accordance with international protocols, so pain is excluded in the postoperative period. Already from the first day, getting out of bed is allowed, on the second day the patient can take light food, and on the third day he switches to a normal diet. Discharge from the hospital is possible on days 3-4, and after 12-16 days the person returns to their normal lifestyle.
Are there any disadvantages to adrenalectomy?
The organ-preserving technique allows you to preserve the reserve of adrenal tissue, thereby providing the patient with a high quality of life, because even with bilateral damage you can do without hormone replacement therapy. However, when performing an operation, there is a risk of leaving part of the tumor with multiple lesions, which increases the likelihood of a relapse in the future, and the operation itself involves more complex hemostasis in the intervention area. However, in a clinic equipped with innovative equipment and attended by experienced specialists, such a risk is minimized, since the selection of patients at the preoperative stage is carried out using modern and effective diagnostic methods. In addition, the use of the Liga Sure electrosurgical system, ultrasonic scissors for safe tissue resection, PerClot hemostatic agents, etc. during surgery minimizes all possible risks.
Prognosis for adrenal tumors
If treatment for a benign tumor is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. However, in some cases, for example, after removal of androsteroma, hypertension may persist in a third of patients, and tachycardia in case of pheochromocytoma, which, however, respond well to treatment. For malignant tumors, the prognosis is not so favorable and depends on the timeliness of treatment.
Registration for surgery to remove aldosteroma
To sign up for an operation to remove aldosteroma, you need to consult a specialist at the North-Western Endocrinology Center with all the examinations you have. The center specialist will study the available medical documentation and, if necessary, conduct additional research. If the diagnosis of primary hyperaldosteronism is confirmed and there are indications for surgery to remove the aldosterone-producing tumor, you will be hospitalized at the center for surgery using the most modern technologies. Surgeries on the adrenal glands are performed free of charge at the center.
.
Patients with aldosteroma are consulted:
| Sleptsov Ilya Valerievich, Endocrinologist surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Surgery with a course in surgical endocrinology, member of the European Association of Endocrine Surgeons | |
| Rebrova Dina Vladimirovna, Endocrinologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Assistant at the Department of Endocrinology named after Academician V.G. Baranov, North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov. Member of the European Society of Endocrinologists, International Endocrinological Society, St. Petersburg Association of Endocrinologists. | |
| Fedorov Elisey Alexandrovich, Surgeon-endocrinologist of the highest qualification category, Candidate of Medical Sciences, specialist at the North-West Center for Endocrinology. | |
| Chinchuk Igor Konstantinovich , Endocrinologist surgeon, oncologist, candidate of medical sciences, member of the European Thyroid Association (ETA). Performs endoscopic operations on the adrenal glands. Retroperitoneoscopic approach. More than 350 surgical interventions per year, half of which are endoscopic. |
Consultations are carried out in outpatient branches of the North-Western Center for Endocrinology and Endocrine Surgery:
- Petrograd branch
(St. Petersburg, Kronverksky pr., 31, 200 meters from the Gorkovskaya metro station, telephone for appointment, from 7.30 to 20.00, daily);
— Primorsky branch
(St. Petersburg, Savushkina st., 124, building 1, 250 meters to the right from the Begovaya metro station, telephone for appointments from 7.00 to 21.00 on weekdays and from 7.00 to 19.00 on weekends).
For consultation, please bring all available examination results.
Doctor's comment
If you are diagnosed with an adrenal tumor, you should know that the only way to get rid of it is surgery. We always give preference to organ-preserving surgery, of course, in the absence of contraindications. But for this you need to undergo a thorough examination; all diagnostic procedures are performed within the walls of our clinic. You can undergo diagnostics at any time convenient for you - without any queues. As for surgery, we use the most modern techniques, and the clinic’s equipment with innovative equipment allows us to perform surgery without blood loss, quickly and painlessly. Moreover, after healing, there are practically no traces of the intervention left on the skin. You should know that with timely treatment, it is possible to perform surgery while preserving the adrenal tissue reserve; this allows you to do without hormone replacement therapy even with bilateral damage, which significantly affects the quality of life in the future. Therefore, make an appointment without delay, because the price of this is life without special restrictions after recovery!
Head of the surgical service at SwissClinic Konstantin Viktorovich Puchkov
If you are diagnosed with an adrenal tumor, you should know that the only way to get rid of it is surgery. We always give preference to organ-preserving surgery, of course, in the absence of contraindications. But for this you need to undergo a thorough examination; all diagnostic procedures are performed within the walls of our clinic. You can undergo diagnostics at any time convenient for you - without any queues. As for surgery, we use the most modern techniques, and the clinic’s equipment with innovative equipment allows us to perform surgery without blood loss, quickly and painlessly. Moreover, after healing, there are practically no traces of the intervention left on the skin. You should know that with timely treatment, it is possible to perform surgery while preserving the adrenal tissue reserve; this allows you to do without hormone replacement therapy even with bilateral damage, which significantly affects the quality of life in the future. Therefore, make an appointment without delay, because the price of this is life without special restrictions after recovery!
- In our clinic, in the absence of contraindications, preference is given to an organ-preserving technique with maximum preservation of adrenal tissue and its functions.
- The operation to remove an adrenal tumor is carried out using modern equipment and materials produced by well-known European and American companies. Ultrasonic scissors, a dosed electrothermal ligation device “Liga Sure” (USA), hemostatic drugs, modern suture material, the use of a special plastic container for tissue removal, etc. - everything is aimed at a quick, bloodless and safe operation without the use of threads and clips .
- The clinic employs specialists with many years of experience, the highest or first qualification category, many of our doctors are candidates or doctors of medicine.
- We have the opportunity to perform simultaneous operations: during one anesthesia, you can get rid of several diseases that require surgical treatment at once.
- Each patient receives an individual approach! Only the procedures that are necessary for you, the absence of pain both during the operation and in the postoperative period, comfortable rooms, the possibility of staying in a day hospital, etc. - all efforts are aimed at making treatment in the clinic comfortable, effective and short-lived.
ATTENTION PATIENTS!
Currently, the North-Western Endocrinology Center provides free surgical treatment for patients with adrenal tumors
. Treatment is carried out within the framework of the compulsory medical insurance program or the SMP program (specialized medical care).
To obtain free hospitalization for out-of-town patients
you must send copies of documents (passport: page with photo and basic data, page with registration; compulsory health insurance policy, SNILS, results of existing examinations - a detailed list is presented below) to the address
Questions about hospitalization can be asked to the responsible administrator, Valentina Petrovna Kleshnina, by calling +7 900 6291427 (weekdays, from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m.).
Package of necessary examinations
should include the following list (if there are no results from the listed studies, they must be performed in any case):
- CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity, if there is only an ultrasound report, then it is necessary to perform a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast, indicating the native density of the adrenal tumor (if necessary, print this item and show the CT scan to the doctor before the study).
The following laboratory parameters must be determined:
- Aldosterone, renin, potassium in the blood, in case of taking diuretics, they must first be discontinued for three weeks (tests are taken in the morning from 8 to 9 am, sit for 15 minutes before taking the tests), after taking these blood tests, resume taking your previous medications;
- Analysis of 24-hour urine or blood for total metanephrines;
- Performing a test with 1 mg of Dexamethasone (in the evening, at 23:00, take 2 tablets of Dexamethasone, in the morning of the next day - from 8 to 9 in the morning, determining the level of cortisol in the blood), the analysis is taken separately from the others, in the last place.
You must also provide information
about the normal level of blood pressure in the patient (working blood pressure), if the pressure increases, indicate the maximum blood pressure numbers, how long ago the increase has occurred and how often rises in blood pressure occur.
To carry out the above examinations, there is no need to go to the hospital; they can be performed at your place of residence or in the nearest laboratory.
For patients from St. Petersburg
It is advisable to apply for a face-to-face consultation before entering the clinic (make an appointment by phone (812) 565-11-12, Primorsky branch of the center, address: Savushkina St., 124, building 1, make an appointment by phone (812) 498-1030, Petrograd branch of the center, address: Kronverksky pr., 31).