Surgery to eliminate testicular hydrocele is an effective method of therapy. The pathology can be either congenital or acquired as a result of inflammatory processes, bruises or testicular torsion. Depending on the age of the patients and the stage of the hydrocele, the doctor decides on surgery. The State Institute of Urology performs the Winkelmann operation - this is the standard of treatment accepted throughout the world. Drug therapy does not bring stable results, but surgical intervention for small-sized dropsy shows high success and a low relapse rate.
Preoperative period
Hydrocele is asymptomatic; patients seek medical help even with severe scrotal asymmetry. Upon palpation, a compaction is detected. To diagnose the disease, diaphanoscopy is used. In addition, the doctor prescribes a blood test, urine test, and a bacterial smear from the urethra. Before surgery, it is necessary to exclude an inguinal hernia and testicular tumor.
The Winkelmann-Bergmann operation is indicated for small formations (up to 150-200 ml). In preparation for surgery, the patient will need:
- take a biochemical blood test;
- check clotting factor;
- check your blood sugar levels.
Progress of the operation
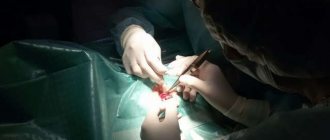
Surgery is performed under general or local anesthesia. The choice depends on the patient’s age and the nature of the pathology. The intervention consists of the following stages:
- surgical incision in the skin of the scrotum (varies from 3 to 7 cm);
- layer-by-layer dissection of the testicular membranes;
- isolation of the testicle along with the membrane;
- pumping out liquid;
- revision of the membranes and palpation examination, returning them to the place of localization;
- revision of the family cord;
- installation of drainage and stitching of tissues;
- applying a bandage to the surgical area.
Bergmann's operation for testicular hydrocele differs from Winkelmann's method in the nature of manipulations with the membranes. In the first case, the testicular membranes are excised, and in the second, they are turned inside out.
The average duration of the operation is about 30-60 minutes. If during its course an inguinal hernia or communicating dropsy is detected, the doctor decides to change the course of the intervention.
The tissue is sutured along the back surface of the testicle; after the operation, 2-3 sutures are placed on the skin; visually they will be almost invisible. If recovery is successful, the sutures are removed after a few days, and absorbable suture material can be used.
2.Indications and preparation
Direct indications for surgical intervention for hydrocele are a rapid increase in the volume of the testicle (or an existing giant dropsy), severe pain in the scrotum, a comorbid combination with some other diseases and anomalies of the urogenital system, a sharp decrease in the overall quality of life and, in particular, a limitation in the ability to carry out the usual types of activities (physical labor, sports). In addition, in some cases, the presence of hydrocele has the most detrimental effect on the psychosexual sphere and can, especially in the bilateral version, result in infertility.
Advantages and disadvantages
Excess serous fluid in the dilated membrane can be easily drained by puncture under local anesthesia - which is practiced in some cases. However, the likelihood of relapse is very high, since in this case the cause of dropsy is not eliminated. Surgical correction does not have this drawback; it allows you to get rid of hydrocele once and for all. In addition, such an operation is usually quite simple in technical terms.
On the other hand, this is still an open surgical intervention with all its risks, and the clinical complexity of each specific case also varies widely: sometimes the operation lasts up to 2 hours.
Preparation
The operation (no matter what method is used) does not require any special preparation. If general anesthesia is chosen as anesthesia, which is not always advisable, the intervention is performed on an empty stomach.
However, a thorough preoperative examination and planning of the operation, taking into account all individual factors, is strictly mandatory.
Visit our Urology page
Postoperative recovery
The Winkelmann operation for testicular hydrocele is minimally invasive, and there is no long-term rehabilitation after it. Immediately after suturing, ice is applied to the wound surface for 2-3 hours. Then the testicles are placed in a suspensor, which supports the testicles and relieves the load on the spermatic cord, which prevents injury and possible complications.
Additionally, painkillers and antibacterial therapy are prescribed. It is recommended to get out of bed the next day; a day later the drainage element is removed. If the intervention was successful and the patient feels well, discharge from the hospital is possible within a few days.
Bed rest is recommended for men; they can return to their usual lifestyle no earlier than after 8-10 days. Physical activity, active sports and sex are available only after 2 months. It is important to observe these restrictions, since excess load on the spermatic cord and its additional trauma can lead to infertility.
Hydrocele
Hydrocele of testicular membranes
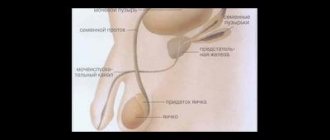
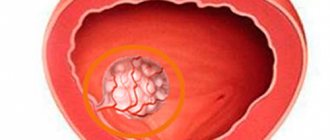
Hydrocele of the testicular membranes (dropsy of the testicle, hydrocele - from the ancient Greek ὕδωρ - water and κήλη - swelling) is an accumulation of serous fluid between the proper membranes of the testicle, during which it increases in size.
Often found in children. Occurs in 1% of men. In most cases, a hydrocele is not very bothersome. Classification
In adults, the disease is often acquired; in children, it is usually congenital. Hydrocele of the testicular membranes is classified according to its genesis or severity of the disease.
By genesis: congenital and acquired. The congenital form can be communicating or non-communicating. Acquired form: primary (idiopathic) or secondary (symptomatic). According to the severity of the disease: acute or chronic form. Diagnostics
Inspection and palpation of the genitals. It should be distinguished from inguinal and inguinal-scrotal hernia, cysts, hydrocele of the spermatic cord, testicular tumors and spermatocele. The disease is quite common and is observed in both children and adults.
Congenital hydrocele
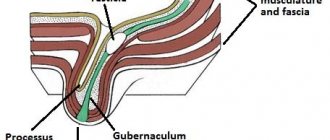
Normally, the laying of a testicle occurs in the abdominal cavity, then the formed testicle migrates to the scrotum under the influence of male hormones with the participation of the “Gunter’s” cord surrounded by the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum. The lumen of this process should be completely closed by the time the child is born. In the case when a violation of the obliteration (closure) processes occurs, a communicating hydrocele of the testicle or an inguinal hernia occurs, depending on the diameter of the process.
In this case, fluid from the abdominal cavity freely enters the testicular membranes through the duct. Sometimes only partial closure of the vaginal process occurs. In this case, the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum is obliterated at different levels of the inguinal canal and testicle. This leads to diseases such as isolated hydrocele of the testicle (testicular cyst), isolated hydrocele of the spermatic cord (spermatic cord cyst) and isolated hydrocele of the spermatic cord and testicle (spermatic cord and testicular cyst).
The tunica vaginalis of the testicle produces a fluid that serves as a lubricant for the testicle and promotes its free movement inside the scrotum. Normally, a balance is maintained between the production of this fluid and its reabsorption.
The so-called physiological dropsy is associated with a violation of this mechanism. It occurs in approximately 10% of newborns and in more than half of the cases disappears on its own by the end of the child’s first year of life. The reason for its development lies in the imperfection of the lymphatic system of the groin area in newborns and infants, which leads to slow resorption (absorption) of the resulting serous fluid between the membranes of the testicle. As the child grows, obliteration of the vaginal process and an increase in the absorption properties of its membranes are possible, which in a significant proportion of children leads to independent healing of dropsy.
Acquired hydrocele
Acquired dropsy occurs with acute or chronic inflammation of the testicle, with testicular trauma, with cardiovascular failure, with neoplasm of the scrotal organs. Surgery on the genitals can also lead to hydrocele. This is the so-called reactive “symptomatic” dropsy, which goes away as the underlying disease is treated.
The development mechanism is associated with compaction of the testicular membranes, which disrupts lymph flow with inhibition of microcirculation (impaired blood circulation). As a result, fluid accumulates between the shells. Hydrocele of the testicular membranes develops without pain and without any disorders. The accumulation of fluid occurs slowly and imperceptibly, sometimes spasmodically. The enlargement of the scrotum may be small, but sometimes it reaches the size of a goose egg and even the head of a child. With dropsy of the testicular membranes of very large sizes, difficulties arise during urination and sexual intercourse. Hydrocele has a smooth surface and a dense elastic consistency, painless on palpation, fluctuation is determined. The skin of the scrotum is loosely folded. The testicle usually cannot be felt, and only with slight dropsy can it be determined at the bottom of the swelling. During diaphanoscopy, transillumination of the entire formation is noted. The symptom of transillumination is negative only in cases where the testicular membranes are sharply thickened, there is a hematocele or pyocele (blood or pus in the testicular membranes), or a testicular tumor. Hematocele is a hemorrhage into the hydrocele cavity of the testicular membranes, which can occur as a result of injury, with hemorrhagic diathesis, after unsuccessful puncture of the hydrocele. Purulent hydrocele of the testicle occurs more often with orchitis and epididymitis as a result of infection during an abscess of the testicle or epididymis.
Diaphanoscopy and ultrasound examination
The diagnosis of hydrocele is established using ultrasound examination of the testicles and diaphanoscopy. Ultrasound examination reveals the accumulation of fluid between the membranes of the testicles and the unchanged testicle, and evaluates the volume of fluid and its liquor structure. Diaphanoscopy (from ancient Greek διαφανής “transparent” and σκοπέω “I observe”) is a method based on transillumination. With a hydrocele, the entire formation is evenly translucent. However, the method is not always informative. After suffering inflammation of the testicular membranes or hematocele, transillumination may be uneven. Diaphanoscopy also allows for differential diagnosis with hernias (intestine, omentum strand), when a violation of the passage of light through the swelling is detected.
Pathogenesis
The causes of congenital hydrocele are as follows. During the prenatal period, the testicle descends into the scrotum through the inguinal canal; along with the testicle, part of the peritoneum moves, which is called the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum. Then the lumen of the vaginal process of the peritoneum becomes overgrown. If this lumen does not close, fluid collects in it from the abdominal cavity. In addition, the cells of the inner lining of the peritoneum, which covers the process of the peritoneum from the inside, are themselves capable of producing fluid. The processus vaginalis may communicate with the peritoneum or be blind. If it communicates with the peritoneum, fluid can sometimes circulate from the hydrocele into the abdominal cavity. If a hydrocele is detected in a newborn child, treatment is not started. Such hydrocele of the testicle can disappear on its own when the process of the peritoneum heals and the fluid from the hydrocele cavity is absorbed.
Acquired hydrocele of the testicle occurs with inflammatory diseases of the scrotal organs, injuries of the scrotum and perineum, and impaired lymphatic drainage from the scrotum. Sometimes hydrocele of the testicular membranes can be reactive due to inflammatory processes in the testicles or epididymis or testicular torsion. This type of hydrocele disappears when the underlying disease disappears.
Treatment
Treatment of testicular hydrocele in inflammatory diseases of the testicle and its epididymis consists of treating the underlying disease: prescribing antibacterial therapy, rest and wearing a suspensor. To remove fluid from the hydrocele cavity, a puncture of the hydrocele is performed. The liquid is removed, and sclerosing drugs are injected into the cavity. This treatment method may have complications. If the puncture is unsuccessful, the testicular membranes may be damaged, hemorrhage occurs and blood accumulates in the hydrocele cavity. Sometimes an infection can enter the hydrocele cavity and an inflammatory process occurs. Surgery is considered a radical treatment method. For hydrocele of the testicular membranes, three types of surgical interventions are performed.
Winkelmann operation. During this surgical intervention, one of the layers of the testicular membrane is cut along the anterior surface, turned inside out and sutured behind the testicle. In this case, fluid accumulation no longer occurs.
Bergman's operation. Part of the inner layer of the testicular membrane is removed, the remaining part is stitched. In the postoperative period, antibacterial drugs are prescribed and a suspension is worn for some time.
Operation Lord. During this operation, the membranes of the testicle are dissected, the hydrocele is released, and the so-called corrugation of the vaginal membrane around the testicle is performed. In this case, the testicle itself is not freed from the surrounding tissues and does not dislocate into the wound. This allows you to reduce trauma to adjacent tissues and feeding vessels of the testicle.
However, there is no fundamental difference between the proposed operations (Winkelmann, Bergmann or Lord). So, in most cases, the surgeon determines the type of plastic surgery of the testicular membranes already during the operation. So, for example, it is irrational to perform a Winkelmann or Lord operation for large-sized dropsy, when there is an excess of membranes. Lord's operation is also not suitable for chronic dropsy, when the membranes become hard and their corrugation will lead to a poor result from an aesthetic point of view.
According to the course, acute and chronic hydrocele of the testicle are distinguished. Usually, dropsy of the testicular membranes is not accompanied by pain. Fluid in the membranes of the testicle can accumulate very slowly, in some cases the accumulation of fluid can occur intermittently. With hydrocele of the testicular membranes in the scrotum, you can palpate a pear-shaped formation, the base of which is at the bottom, and the narrowed apex is directed towards the inguinal canal. Sometimes fluid can get into the inguinal canal. Then the hydrocele of the testicle may have the appearance of an hourglass with a constriction in the area of the external inguinal ring. The size of a hydrocele can vary: from small increases in the size of the scrotum to a spherical formation the size of a football. Most often there is no pain when palpating. The skin on the scrotum remains unchanged and is easily displaced. Hydrocele of the testicle can be felt as a dense elastic formation. If the hydrocele is large, it can become an obstacle to sexual intercourse, and sometimes difficulty urinating.
Complications
As a rule, Winkelmann's operation for testicular hydrocele is well tolerated by patients, but the success of surgical intervention is largely determined by the qualifications of the doctor. That is why you need to undergo treatment in a specialized medical center. The State Institute of Urology employs highly qualified urologists with extensive practical experience.
Possible complications of the operation:
- orchitis;
- bleeding;
- scrotal hematomas;
- suppuration of the scrotum;
- spermatic cord injury.
Causes of hydrocele
Understanding why fluid began to accumulate in the lining of the testicle, and this led to hydrocele, is not always easy.
Most often, the cause of the development of testicular hydrocele is an imbalance in the production and reabsorption of fluid by the vaginal tunic of the testicle. This fluid allows the testicle to move freely in the scrotum. A “lag” between absorption and production leads to the accumulation of excess fluid and enlargement of the testicle.
There are other reasons that lead to testicular hydrocele. Often testicular hydrocele originates from a small cyst.
Among the most common causes of the development of testicular hydrocele in men are the following: trauma to the scrotum, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin and pelvis (filariasis), inflammation of the testicle and/or its epididymis (orchiepididymitis). In the latter case, a purulent hydrocele may develop.
Contraindications
Winkelmann's operation for hydrocele is contraindicated if the patient has:
- urological diseases in the acute stage (pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, cystitis);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system during exacerbation;
- severe form of diabetes mellitus;
- large infectious foci;
- ARVI or other respiratory diseases;
- angina;
- exacerbation of diseases of the respiratory system.
If you are looking for where to have surgery for hydrocele, the State Institute of Urology is ready to offer its services.
We employ the best doctors, the center is equipped with the necessary modern equipment, and provides attentive postoperative care for patients. September 7, 2020
Akopyan Gagik Nersesovich - urologist, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, professor of the department of urology of the Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov
Clinic of Urology named after R. M. Fronshtein of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov invites you to an appointment with experienced urologists. To get an appointment with a qualified specialist, just fill out a short online application. Be sure to fill out all the fields, including a brief description of the symptoms (the “Information” column), specify whether you are interested in a secondary or primary appointment.
Pay attention to the “Attach file” button - it allows you to immediately send medical documents to the doctor in electronic form. This may include images, tests and other information that will be important to determine the diagnosis.
Still have questions? Call us by phone or! On a weekday, you can come for a consultation with a doctor within a few hours after filling out the online application. Do not delay visiting a specialist if you are concerned about your genitourinary health!
Price and cost of surgery for hydrocele in children
| Service | price, rub. |
| Surgical treatment of hydrocele of 1st category of complexity | 37000 |
| Surgical treatment of hydrocele of 2nd category of complexity | 49000 |
| Surgical treatment of hydrocele of 3rd category of complexity | 63000 |
The cost of the operation includes (no additional payment for services is necessary!):
- inpatient accommodation 1 day double room with all amenities
- preoperative tests
- disposable suture material Vicryl, PDS
- application of intradermal cosmetic suture
- disposable surgical consumables
- surgical instruments Ceatec GmbH Germany
- microsurgical instruments and equipment
- constant telephone communication with the attending physician
- examination any day in the clinic within 14 days after surgery
The cost of the operation does not include: anesthesia, additional diagnostics and treatment of concomitant diseases and their complications.
Anesthesiological support: anesthesiological apparatus Drager Fabius Plus (Germany), combined general anesthesia (inhalation anesthesia, caudal/local anesthesia).
** This is not a public offer agreement. Check the cost of services on the day of your request.
Don't waste your precious time - call!
Our specialists will be happy to answer all your questions
+7
Our advantages
Experienced surgeons
Individual approach
Without pain and fear
Comfortable conditions