What types does the disease take?
Melanopathy can be physiological or pathological. In the first case, the disease is caused by the natural properties of the body - dark body and hot environment. In pathological cases, excessive pigmentation is caused by unnatural phenomena - the appearance of a substance in the cells of the brain, colon, kidneys, and mucous membrane. During the examination, an endoscopic picture of physical processes is visible. In medical practice, the following common types of melanosis are noted:
- Uremic. This type of disease is the first in prevalence and is skin hyperpigmentation caused by renal failure in Addison's disease. More often, a progressive type of pigmentation appears on the foot and palm, less often on open areas of the body. The cause of the disease is the concentration of melanocyte-stimulating hormone in blood components. The skin takes on a gray, ashy hue, the intensity of which depends on the degree of kidney damage.
- Hepatic. It manifests itself as severe itching, which when scratched leads to increased pigmentation. The cause of the disease is liver disease, cirrhosis, bile stagnation.
- Cachectic. Thickening and darkening of the skin occurs. Mostly pigmentation forms in the neck, genitals, and abdomen. The exact cause of this type of melanosis is not known. Medical scientists suggest that the cachectic form of the disease is a consequence of the influence of toxins on the body or protein breakdown.
- Endocrine. Pigment spots appear due to disruption of the thyroid gland, endocrine pathologies, and surgical intervention.
- Toxic. A type of severe intoxication of the body caused by excessive exposure to hydrocarbons and toxins. People who work with gasoline, oil, and machine oil are susceptible to poisoning.
- Neurodermal. A hereditary disease that is transmitted genetically.
Constant scratching and ignoring the disease lead to complications and increased pigmentation. If you notice age spots on yourself, you should consult your doctor.
Dubreuil's melanosis
In addition to the well-known types of the disease, there are some specific types. Among them, Dubreuil's melanosis is a precancerous type of pigmentation. This is a neoplasm in the form of a pigment spot, mole or subcutaneous nodule, which precedes cancer. Pigment cells accumulate in the dermis or epidermis, creating a reactive acanthotic cord. The spot that appears has clear boundaries, a smooth surface with dark-colored papillomas. The disease mainly affects older people with fair skin. Women acquire precancerous limited melanosis more often than men.
The exact cause of Dubreuil's melanosis is not known. Some researchers classify it as a disease of old age, while others classify it as a nevi. The disease represents the first, initial stage of oncology, which does not penetrate the internal organs of a person. It is recommended to observe emerging moles and spots to rule out a precancerous form of the disease.
Riehl's melanosis
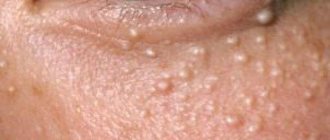
The clinical and histological manifestations of the disease are identical to the toxic type and Becker melanosis. Appears as blue-brown pigmentation on the face, neck, abdomen and chest. Facial skin becomes deformed and becomes rough. The definitive cause for the development of excessive pigmentation is certainly unknown. One of the assumptions is the effect of cosmetic and hygienic body care products on the body.
For diagnosis, samples are taken from drugs and products that the patient regularly uses. The samples taken are examined in a laboratory using microscopic specimens to identify toxic substances. Another assumption is a deficiency of vitamin A in the body. The disease Riehl's melanosis is provoked by direct sunlight, so in the summer you should protect your skin from the aggressive sun and avoid unprotected tanning.
Melanosis of the sclera
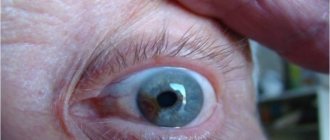
With this disease, the visual organ is affected. Statistics show that melanosis of the sclera is a secondary lesion of the body associated with diseases of the hematopoietic vessels and membranes. The main impact falls on the eyes. Defects, inflammations, and benign neoplasms develop, and conjunctivae appear on the eyeball.
The disease is also accompanied by brittle bones and muscle weakness. This type of pathology develops in a child in the womb or immediately after birth. The described types of disease lead to premature death.
Neurocutaneous melanosis
This type of disease is a genetic disease that is inherited. There is an accumulation of hyperpigmentation, moles, and age spots. Localized on the brain, the formations affect the soft tissue without spreading to other organs. The exact cause of the disease is not fully understood, and treatment methods remain under development.
The nature and course of the disease in a particular person manifests itself differently, which creates difficulties in treatment. Symptomatic therapy is characterized by low effectiveness, making the recovery process difficult. Neurocutaneous melanosis, if treated with timely diagnosis, portends a positive prognosis.
Etiology of the disease
If discomfort occurs in the visual organs, it is necessary to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, since symptoms may arise due to dry eye syndrome, inflammation and conjunctivitis.
Melanosis of the sclera, expressed by excessive accumulation of pigment, can be focal or diffuse in nature. The disease can appear in both children and adults at any age. The table shows the forms of the disease:
| Peculiarities | Pathological | Physiological |
| Increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation | Predisposition in people with dark skin color | |
| Additional skin pigmentation | ||
| May be caused by metastases in the mother during pregnancy | Occurs due to exposure to sunlight |
The disease may be hereditary.
A pigment spot on the sclera of the eye, according to doctors, can be caused by the following reasons:
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- genetic predisposition;
- damage to the adrenal glands with loss of the ability to produce glucocorticoids;
- pathology of the pituitary gland associated with a decrease in the production of melanophore hormones.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease has a standard symptom - the appearance of pigment spots, darkening of areas of the skin, causing inconvenience and anxiety. Darkening affects the cheeks, lips, nose and is located symmetrically on both sides. But melanosis, forming in the body, also has additional symptoms:
- Mixed pigmentation of the skin. Seen in newborn babies.
- Intolerance, hypersensitivity to direct sunlight and ultraviolet radiation.
- The formation of large lesions consisting of connected small spots.
- Disturbed functioning of the intestines and digestive tract.
- Swelling of the extremities not associated with injuries or other diseases.
- Skin deformation, roughness and thickening.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland and nervous system.
- Severe itching of the affected areas.
Melanosis requires medical supervision and treatment, otherwise the disease will lead to complications and the development of other diseases. If you notice signs of pigmentation on the body, the appearance of birthmarks or large moles, you should consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examination.
Diagnosis of the disease
Melanosis in some cases is dangerous due to the onset of the development of cancer, a malignant tumor. Therefore, if you notice darkening of the skin, you should consult your doctor. Diagnosis of melanosis is carried out as follows:
- Visual examination of the skin with a Wood's lamp.
- Conversation with the patient, detailed description of complaints and pain syndromes.
- Palpation of the affected area to exclude neoplasms, lumps and tumors.
- The patient takes a general blood test for laboratory testing. The test result will show the amount of melanin in the blood. If inflammatory processes occur that affect pigmentation, the study will indicate the location.
- Determination of genetic predisposition.
- Examination with a dermatoscope, which magnifies the pigment for a detailed examination.
- Computer diagnostics. Study of skin for comparison with healthy appearance. Carrying out tomography.
- Analysis of the epidermis and dermis by cutting or scraping the affected area for laboratory testing.
- Biopsy. It is used only when oncology is completely excluded.
The study of this disease is carried out by pathological anatomy - a science that studies pathological processes using microscopic examination and the scientific study of analyses. After conducting diagnostics and clinical examinations, the doctor makes a diagnosis. Examination options may vary depending on the age, gender and condition of the patient.
Symptoms of the disease
When scleral pigmentation is disturbed, the following characteristic signs of the disease are observed:
- the appearance of colored areas on the conjunctiva and next to the lacrimal canaliculus;
- spread of hyperpigmentation to the choroid;
- decreased visual acuity;
- blurriness of objects at far and near distances;
- the formation of dark, smooth or raised spots of varying sizes on the skin of the eyelids;
- increased or decreased reaction to light;
- development and rapid progression of myopia;
- spread of pigmentation to the frontal lobe and the area around the brow ridges.
Methods of therapeutic treatment
It is strongly recommended not to determine the type and nature of the disease yourself at home. The disease must be diagnosed by a professional doctor specializing in this area. After a thorough examination of the skin and the resulting spots, studying the symptoms, the doctor prescribes the necessary tests. After this, a diagnosis is made and a treatment method is prescribed.
In the first stages of the disease, the use of local treatment using traditional methods is recommended. You can apply lotions and wipes with a solution of apple cider vinegar, hydrogen peroxide or salicylic acid. These substances have antibacterial properties that can fight bacteria and harmful microorganisms. If melanosis is advanced and has the final stage of development, then the following methods are used to combat it:
- Creams and ointments with photoprotective properties.
- Drugs aimed at strengthening the endocrine system and thyroid gland.
- Medications that relieve intoxication.
- Prescribing a complex of vitamins to maintain and strengthen the immune system.
- Antioxidants that neutralize oxidative processes in the body.
- The use of enterosorbents that eliminate harmful substances and microelements.
- Prescription of drugs that relieve inflammatory processes in the body.
- Peeling is a procedure performed in beauty salons. This involves deep cleansing of the facial skin, removing the top, coarsened, affected layer. The procedure involves different methods of implementation.
- Photorejuvenation. By removing the top layer of skin affected by pigments, a rejuvenation effect is achieved.
- Intravenous injections of medications prescribed by the attending physician.
- Laser resurfacing is a cosmetic procedure performed using ultraviolet irradiation. Formed defects can be removed with a laser.
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor specializing in this field. An individual case of illness requires a special approach. Methods of therapy can be medicinal and cosmetic, depending on the severity and neglect of melanosis. When choosing and prescribing therapy, the age, gender of the patient, stage and nature of the disease, as well as the physical condition of the patient are taken into account. Self-medication leads to the development of complications and serious pathologies.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of melanosis, you should protect your skin from direct sunlight in the summer. Aggressive ultraviolet rays damage the top layer of skin, leading to the development of excessive pigmentation. Therefore, it is important to wear a hat or Panama hat with a wide brim to protect your face. The use of sunscreen will help disperse ultraviolet rays without causing harm to the skin. It is also necessary to regularly undergo a comprehensive medical examination in an effort to prevent the development of dangerous diseases.
Newly appeared moles and age spots should be examined to rule out the development of skin cancer. Proper nutrition and an active lifestyle will strengthen the immune system, protecting the body from viruses and bacteria. Doctors recommend including foods containing vitamins and beneficial microelements in your daily diet.
A sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits will enrich the body with essential substances and improve health. Timely diagnosis and seeking medical advice can identify melanosis at an early stage. With proper systematic treatment prescribed by the doctor, the disease recedes.
Melanoma is a malignant tumor that forms from pigment cells. If diagnosed early, it can be treated and removed. It may resemble a mole in appearance and is often identified in later stages.
Therapeutic and preventive procedures
Melanosis is an incurable disorder, but usually does not cause discomfort and is not harmful to the body. The appearance of negative symptoms may indicate the appearance of a malignant tumor. Consultation with an ophthalmo-oncologist is necessary.
It is impossible to cure a disease that manifests itself as a violation of eye pigmentation. In general, doctors make a favorable prognosis and talk about a low risk of complications. However, to avoid negative symptoms, ophthalmologists recommend adhering to a healthy lifestyle. In strong sunlight, the eyes must be constantly protected with dark sunglasses, since ultraviolet radiation has a detrimental effect on the sclera and retina. Treatment can be aimed at relieving specific individual symptoms and is selected individually.
What is ICD 10
According to ICD 10, cutaneous melanoma is a malignant formation on the epidermis. The process of tumor initiation involves the degeneration of melanocytes, which, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, produce the pigment melanin.
Melanocyte cells are found in moles, which is why many simply do not pay attention to the development of the disease. Foci of formation: open areas of the skin, face, neck, back, feet, other areas of the arms and legs.
Melanoma according to ICD 10 is a disease in which the following are at risk:
- people with white skin, blue and green eyes, red hair;
- beachgoers whose skin gets sunburned by exposure to the sun;
- persons who have suffered severe thermal burns, but continue to tan above normal;
- people whose relatives have suffered or are suffering from skin cancer;
- persons with more than 100 moles under the age of 20;
- patients with Dubreuil's melanosis: precancerous lesions of the skin.
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
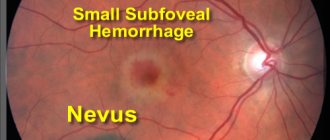
Nevus of the sclera is a unilateral, area of dark pigmentation of the sclera with clear boundaries.
Conjunctival nevus is a unilateral, darkly pigmented area of the conjunctiva with clear boundaries.
The etiology of nevi of the sclera and conjunctiva is not completely clear.
DIAGNOSTICS
An accurate diagnosis of a pigmented neoplasm of the eye is established by histological examination.
CLINICAL SIGNS
- Benign nevi and physiological or racial melanosis (Fig.) do not change over time, while primary acquired melanosis and melanoma change.
- In 87% of cases of histological analysis, the nevus does not change over time.
- With malignancy, the clinical picture is more vivid: ulceration, bleeding, discoloration, and the appearance of new vessels around the tumor.
- Pathologic features of conjunctival melanoma with the highest mortality rate include increased tumor thickness, location on the conjunctiva of the eyelids, fornix, or caruncle, increased mitotic activity, lymphocytic infiltration, and association with primary acquired melanosis.
Physiological (racial) melanosis—flat pigmentation of the conjunctiva, developing bilaterally, starting at the limbus and more pronounced in the interpalpebral zone, is probably racial melanosis in a dark-skinned patient.
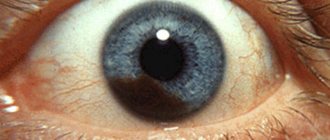
Primary acquired melanosis—multiple unilateral areas of dark pigmentation with uneven contours.
Classification
Classification of skin melanoma according to ICD 10 code includes the following types:
Superficial spreading melanoma appears as a scalloped plaque with a mosaic coloration. After the formation of a node, the tumor stops growing horizontally and develops in a vertical direction.
This is an aggressive type of skin melanoma. Formed on an unchanged area of the epidermis.
Externally it looks like a node or polyp-like growth. The nodular formation develops rapidly: after 2-3 months bleeding and an increase in size are observed. Localized on the scalp, neck, and limbs.
This is a form of malignant type, which, according to medical statistics, occurs in 10-15% of cases. It differs from others in the protracted phase of horizontal formation.
Lentigo tumor is mildly aggressive and forms in most older people in open areas of the dermis: on the neck and face.
A rare type of malignant growth that occurs under the nails. It is often confused with a stain under the nail from dirt or a bruise, which makes timely diagnosis of the disease difficult.
Folk remedies for the treatment of eye melanosis
Melanosis is a congenital abnormality of the anterior surface of the sclera (the whites of the eyeball). Pigmentation appears on it in the form of a speck. These spots are formed due to deposits of a substance called melanin. Pigmentation may be gray or pale purple.
Congenital melanosis is most often unilateral. As a rule, pigmentation of the sclera intensifies in the first year of a child’s life. As a rule, melanosis appears as a result of disturbances in the body's carbohydrate metabolism, galactosemia; the baby's sclera is yellowish and at the same time cataracts (layered) occur.
Acquired anomalies in the color of the sclera can be affected by diseases such as: hepatitis (Botkin's disease), obstructive jaundice, cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholera, chlorosis, jaundice (hemolytic), Addison-Biermer anemia, sarcoidosis.
Melanosis is a consequence of the inflammatory process. There are many folk remedies for the treatment of eye melanosis. Nature itself can help with this. Take 2 tsp. cornflower inflorescence (without baskets) and brew with 1 cup of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours, strain and make lotions for 5 days. This tincture will relieve inflammation of the eyes. 2 tbsp will also help. finely chopped oak bark, pour half a liter of boiling water and boil for 20-30 minutes.
Strain and rinse your eyes with the solution. To treat eye melanosis, a decoction of cumin fruits (1 tbsp) and 1 glass of water will also help. Pour cumin with water and boil for 5-10 minutes. Add 1 tsp to the broth. cornflower inflorescence and filter through cotton wool. This decoction is instilled 2 drops 2 times a day. Chamomile is also a folk remedy for the treatment of eye melanosis. Take 1 tbsp. ordinary pharmaceutical chamomile and fill it with one glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 10-20 minutes. Soak prepared cotton swabs in the broth and apply them to your eyes. Lie quietly for 20 minutes.
An effective remedy for the treatment of melanosis is a decoction of celandine with natural honey. To do this you need to take 1 tbsp. celandine and pour 1 cup of boiling water, boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Strain the solution and add 1 tsp. natural honey. Stir well. Soak cotton swabs in the solution and apply to sore eyes for 10-15 minutes.
For melanosis, a remedy made from fresh cucumber, soda and boiling water will help. Mix all ingredients in equal proportions and apply eye lotions for 10-15 minutes before bed for 3 weeks.
A good remedy for the treatment of melanosis is compresses prepared from 3 parts of birch leaves, 2 parts of red clover (heads) and rose hips, 1 part of strawberry leaves, ½ part of St. John's wort. 1 tsp pour 50 ml of boiling water over the mixture. Wrap it up and leave for 50 minutes. The broth should be filtered and compresses applied to the eyes for 15-20 minutes. Such a compress will not only help cope with the disease, but also restore vision.
One of the most important components for the treatment of eye diseases, including melanosis, is a proper diet. If you have eye diseases, you need to limit yourself to starchy foods, reduce your consumption of sweets, give up white bread, tomatoes, refined cereals, puddings, sweets and jams. You should also avoid salty and fatty foods, including meat. Don't drink strong tea and coffee. Avoid spices and salt. Your diet should include foods such as leafy vegetables, fish, and seafood.
Products necessary to improve vision and treat eye diseases: carrots, parsley, cabbage, citrus fruits, peppers (sweet), apples, onions, nuts, eggs, honey. It is better to cook porridge from whole grains (wheat, rye, corn). You can enjoy a salad that will relieve eye diseases. It is done very quickly and easily. To do this, you need to take cabbage (white cabbage) - 100 g, beets - 40 g, carrots - 60 g, radish - 30 g, parsley - 20 g, fennel - 20 g. Finely chop everything and season with corn or olive oil. Eat this salad at least once or twice a week, and you will forget about the problems associated with eye disease.
It is necessary to massage your eyes daily. It will only take a couple of minutes, but will give an amazing effect. To do this, lightly tap your fingers (nails) in the eye area. The procedure should be done 2-3 times a day. This will give your eyes energy, improve blood circulation, and relieve fatigue and swelling.
But remember that when using folk remedies to treat your eyes, you must consult a doctor. Go to an ophthalmologist and, based on the individual characteristics of your body, he will prescribe treatment for you. Do not abuse natural gifts. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help avoid many complications.
Stages
International ICD codes for melanoma (c97, c44, c43) suggest the following stages of disease formation:
- Zero. The formation of a malignant tumor as a result of cell degeneration processes.
- First. Foreign formation begins to develop in a horizontal direction. The first stage is diagnosed when the formation reaches 1 mm in thickness.
- Second. Subsequent tumor growth. The growth has already reached more than 2 mm in size.
- Third. Spread of melanoma to regional lymph nodes.
- Fourth. A critical stage of a malignant tumor that spreads beyond the affected lymph nodes and destroys distant organs and tissues of the body.
Forecast
The risk of melanoblastoma exists in adults and children. There is a high probability of growth of a malignant tumor in the mediastinum - the lower scalp of the body, the oral mucosa due to genetic predisposition. The presence of melanoma in relatives is a direct threat for most patients.
The prognosis of skin melanoma depends on the stage. This determines how many organs are affected by the metastatic process. With critical damage to one organ, the patient lives from six months to a year; if three or more are destroyed, the life span is reduced to 2 months.
You can protect yourself from a tumor by isolating the affected area. This gives a chance to localize the spread and promptly remove the tumor before it damages the lymph nodes and distant tissues of the body.
ICD-10 Category: C43.9
Content
Definition and general information (including epidemiology) [edit]
Melanoma is a malignant tumor that develops from melanocytes. The incidence of melanoma is increasing all the time; In the United States, 32,000 new cases are registered annually, and 6,700 patients die every year. Melanoma occurs in any tissue that contains melanocytes (skin, mucous membranes, eyes, soft membrane of the brain and spinal cord). It can develop on clear skin, from pigmented nevus or lentigo maligna. In people with dark skin, melanoma occurs infrequently, mainly on the palms, nail beds, soles and mucous membranes. The tumor rarely occurs in children; Most often the disease begins at the age of 20-45 years. Risk factors: large congenital pigmented nevus, multiple nevi, dysplastic nevus, history or family history of melanoma. The risk of melanoma in patients with a family history is eight times higher; in those who underwent radical removal of melanoma - nine times (at least 3% of patients develop a second melanoma within 3 years). The tumor sometimes develops asymptomatically, sometimes it quickly increases in size, changes in color, and is accompanied by itching or burning. Metastasis occurs by lymphogenous and hematogenous routes to the bones, brain, skin and regional lymph nodes (deep parotid, cervical, axillary, inguinal, iliac). The risk of metastasis depends on the depth of localization of the primary tumor (see Table 20.1).
Etiology and pathogenesis[edit]
Clinical manifestations[edit]
Clinical classification of melanoma helps make a diagnosis, but it is almost useless for assessing the prognosis and choosing treatment tactics. Lentigo maligna (Dubray's precancerous melanosis) is an in situ melanoma that occurs in older people on the face and other exposed areas of the body. As a rule, this is a spot 2-6 cm in size with irregular outlines and color from light brown to black. Excision of the tumor is indicated. Without surgery, 1/3 of patients develop lentigo-melanoma, that is, tumor cells invade the dermis and one of the tumor areas bulges above the surface of the skin. Another form, superficial spreading melanoma, begins as a dense papule or nodule that gradually increases in size and turns into an irregular plaque with pinkish, white and gray-blue patches. The tumor occurs in adults on the trunk and limbs. Nodular melanoma is a blue-black tumor that clearly protrudes above the surface of the skin (plaque, node, pedunculated polyp), often ulcerates and bleeds; grows quickly and often occurs on clean skin. Acral lentiginous melanoma is a dark brown or black neoplasm localized to the nail bed, nail folds, palms, and soles. This form of melanoma is especially common in people of color; the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. Amelanotic melanoma is a melanoma whose cells do not contain melanin.
Malignant melanoma of the skin, unspecified: Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis is usually made incidentally by taking a biopsy of a growing, red-pink lesion. Since the tumor does not have the characteristic features of melanoma, it is usually not detected in the early stages.
Clinical signs of malignant degeneration of pigmented neoplasms ("IMPACT" scheme): Acceleration of growth, Diameter more than 6 mm, A symmetry, irregular outline, Multi-color, change in color of one of the areas
Diagnosis and staging of the disease
The prognosis and treatment tactics depend on the depth of tumor invasion, which is determined by histological examination of fixed material (and not frozen sections). To make a preliminary diagnosis, a total biopsy is required. Other methods of biopsy and curettage are contraindicated.
The stage of the disease is determined according to the histological criteria of Clark and Breslow:
1. The level of tumor invasion according to Clark corresponds to the histological localization of the tumor:
A. Level I: the tumor is located in the epidermis.
b. Level II: tumor cells penetrate through the basement membrane of the epidermis into the papillary layer of the dermis.
V. Level III: tumor cells fill the papillary dermis and reach the reticular dermis, but do not penetrate it.
d. Level IV: the tumor invades the reticular layer of the dermis.
e. Level V: tumor cells penetrate the subcutaneous tissue.
2. The Breslow technique is based on measuring the thickness of the tumor in millimeters - from the upper border of the granular layer of the epidermis to the deepest point of penetration of tumor cells. The measurement result is used to determine the prognosis and choose treatment tactics (see Table 20.1). The thicker the tumor and the deeper the invasion, the worse the prognosis. Other unfavorable prognostic factors: tumor localization on the scalp or nail bed; advanced age; ulceration. In general, the prognosis for men is less favorable than for women.
3. Stages of the disease. Many methods have been proposed to determine the stage of melanoma. The simplest and most common of them is clinical, according to which three stages of the disease are distinguished.
A. Stage I: the tumor is localized in the primary lesion. The prognosis depends on the thickness of the tumor (see Table 20.1).
b. Stage II: palpable regional lymph nodes (suspected metastases) or histological evidence of metastasis to the lymph nodes. The prognosis is questionable and depends on the degree of lymph node damage.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Although there is little information on the incidence of ocular pigmentation other than physiological melanosis, a study of the histology of pigmented neoplasms reported that 52% were nevi, 21% were primary acquired melanosis, and 25% were melanomas.
- Nevi of the conjunctiva and sclera are the most common cause of eye pigmentation in representatives of fair-skinned races. Pigmentation is usually detected at a young age, more often in Caucasians.
- Physiological (racial) melanosis is observed in 90% of cases in black patients. It can be congenital and often manifests itself in the first years of life.
- Primary acquired melanosis is usually found in middle-aged/elderly people and is also more common in Caucasians. Conjunctival melanoma is rare, with an incidence of 0007% (7 per 1,000,000) in Caucasians; among representatives of other races it is even less common.