Physiological reasons for the absence of menstruation
The first thing a woman does when she is late is buy a pregnancy test. This home procedure shows the presence of an “interesting situation” or its absence. If the answer is no, then among the common reasons for the absence of menstruation are the following:
- Disrupted daily routine;
- Chronic lack of sleep;
- Increased fatigue;
- Increased physical activity on the female body;
- Emotional stress, stress;
- Poor nutrition;
- A sharp change in climatic conditions (while traveling, for example);
- A strict diet or, conversely, sudden weight gain.
These reasons are not considered dangerous for the female body, since in order to normalize the menstrual cycle, you simply need to eliminate them from your daily life without additional medical attention or medication. But in any case, this is an alarming signal for a woman that not everything is in order in the body.
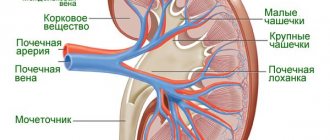
How the kidneys “sick”: pyelonephritis
Urinary tract infections are a fairly well-known and common problem. True, inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) often comes to the fore, while the infection reaches the kidneys in more serious cases.
Why is pyelonephritis dangerous?
The consequences of an untreated kidney infection can include:
- kidney abscess, since the infection is always bacterial;
- renal failure;
- and even sepsis (blood poisoning).
In fairness, it is worth noting that such situations do not develop often, since in modern conditions pyelonephritis is quite “responsive” to treatment.
And the cause of complications, in most cases, is severe immunodeficiency states or excessively late detection. As in the case of bedridden patients who do not feel pain in the lower back, or patients who suppress pain and fever by taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
What will indicate pathology
Most cases of pyelonephritis begin with a lower urinary tract infection and nonspecific inflammatory symptoms.
In this case, weakness, fatigue, frequent urge to go to the toilet (cystitis), and sometimes burning and discomfort when urinating come to the fore. Urine may become cloudy and acquire an unpleasant “fishy” odor. And patients suffering from chronic infections of the bladder or urethra constitute the main risk group.
As the process progresses, periodic aching pain in the lower back, which has no specific features, is added to the symptoms. Such pain can easily be confused with muscle overstrain or “chondrosis,” although there is one “but”: the intensity of the pain increases.
Eventually, the pain reaches such intensity that patients have difficulty changing their position in bed, and with a light tap on the back in the kidney area, the pain increases significantly.
This symptom is known as the “Pasternatsky symptom” and is a classic sign of renal pathology. However, its absence still excludes pyelonephritis.
Another sign of bacterial kidney damage is fever. The temperature reaches 38-39 degrees and, without treatment, only increases. And taking antipyretics often has a very short-term effect.
How to check
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis is based primarily on data from a general urine test and ultrasound of the kidneys.
For pyelonephritis, like other bacterial urinary infections, “says”:
- increase in leukocytes in urine
- detection of bacteria in urine,
- nitrite detection
- increase in the amount of epithelium in the analysis.
Treatment in this case is prescribed immediately and empirically, that is, with one of the broad-spectrum drugs.
It is possible to find out which specific bacteria are “guilty” of the disease and check their sensitivity to antibiotics only with the help of urine culture, based on the results of which the doctor, if necessary, adjusts the treatment.
To assess the body's systemic response to infection, a general blood test is indicated, in which an increase in leukocytes is most often observed with pyelonephritis.
However, it is still not worth relying on blood data when making a diagnosis, since due to the subtleties of the inflammatory response, a leukocyte reaction may not be observed at the stage of analysis.
Forecasts
With timely treatment, the prognosis for treatment of pyelonephritis is positive. Most patients recover completely without any residual effects or consequences.
However, in the case:
- resistance of the bacterial flora to the drug (if the antibiotic is prescribed without taking into account sensitivity),
- violation of the treatment regimen (the patient did not comply with the frequency of taking the drug or finished taking it prematurely)
- or aggravating factors (severe immunodeficiency, removal of one kidney, bedridden patients, and so on),
the disease can become chronic and recur periodically, becoming a source of infection for other organs and increasing the risk of complications.
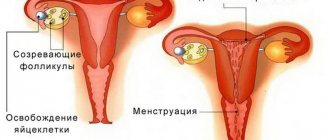
Pathological causes of absence of menstruation
If menstruation does not begin within 10 days, the etiology of the delay may indicate an exacerbation in the female body of a pathological process that is prone to its chronic course. In medical practice, the following diagnoses are known, which are accompanied by a ten-day delay in menstruation:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Endometriosis;
- Medical termination of pregnancy and other types of abortions;
- Mechanical cleaning of the uterus;
- Previous miscarriage;
- Adenomyosis;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Malignant tumors of the cervix or uterus.
It is difficult to determine the disease by its symptoms, so the local gynecologist refers the patient to an ultrasound to accurately identify the etiology of this pathology. Additionally, a number of laboratory tests are required to clarify and confirm the diagnosis.
Risk of kidney damage due to infectious diseases in children
Nephrologist, hospital №6 Bolgarova Olga Gennadievna
With ARVI, influenza and other infectious diseases in children, the urinary system may be damaged. The appearance of viruses in the urine and the accumulation of viruses in the body is observed against the background of an acute period of viral infection on days 2–5 of the disease and can last for 2–3 weeks. It is possible to develop kidney disease after an infection in the long term - within a period of 2 weeks to 1.5 months (with bacterial or recurrent viral infections).
The nature of kidney damage during infections is varied and is determined, first of all, by the properties of the infectious agent and the state of the child’s body.
The following kidney lesions are distinguished:
- Undifferentiated urinary syndrome (or simply put, changes in the general analysis of urine), which in the future may disappear without a trace or cause kidney disease.
- Acute renal failure.
- Kidney diseases (Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, acute glomerulonephritis, acute pyelonephritis)
Such a dangerous condition as acute renal failure often occurs during a viral infection (influenza, adenovirus, etc.), less often against the background of a bacterial infection (meningococcal, purulent meningitis, scarlet fever, deftheria). Severe disease, severe intoxication, reduction or complete absence of urine are alarming signs that require immediate hospitalization.
The most common complication in childhood is interstitial nephritis, which is explained by the affinity of certain viruses (Epstein-Barr, measles, rubella, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis), bacteria (streptococci, pneumococci, Corynebacterium diphtheria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Leptospira, Yersinia and etc.) parasites (Toxoplasma) to the tubulointerstitial tissue of the kidneys. I would like to note that recently cytomegalovirus infection and Epstein Barr infection have become more frequent in children, which can cause mononucleosis.
Another complication of infectious diseases is glomerulonephritis, which develops primarily after streptococcal infections, herpes viruses, hepatitis B and C and can take on a chronic progressive course.
Acute pyelonephritis, or febrile urinary tract infection, is a bacterial inflammation of the renal parenchyma and pelvis. Ascending urinary tract infection and congenital structural features of the kidneys (pyelectasia, megaureter) are of particular importance here.
In addition, kidney pathology as a manifestation of the main infectious disease is represented by quite rare diseases (hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; leptospirosis, etc.)
1. How to prevent kidney damage during infectious diseases? Firstly, carry out prevention of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza, which is most important during the season of rising incidence, including adequate vaccine prevention. Avoid hypothermia. Carry out activities that increase the overall resistance of the body: rational nutrition, hardening, daily routine, psychological comfort in the family and children's team. Secondly, treat infections adequately while observing the drinking regime. Thirdly, in risk groups it is necessary to monitor general blood and urine tests, and, if indicated, conduct other studies.
2.What symptoms should alert parents to kidney damage?
- Dysuric phenomena: changes in the frequency of urination and urine volume, the predominance of nighttime diuresis over daytime.
- Change in urine color, cloudiness and appearance of blood.
- Pain syndrome: pain when urinating, pain in the lower back, in young children pain in the abdomen, in particular in the umbilical region.
- Presence of fever or elevated body temperature in the absence of other symptoms. A repeated wave of fever after improvement against or after (after 1.5-2 weeks) an infectious disease.
- The appearance of swelling on the face, especially in the morning. The appearance of bags under the eyes or more widespread swelling.
- Severe course of the disease with severe intoxication and the child’s refusal to drink
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately contact your pediatrician! Do not treat ARVI without examining a doctor! It must be remembered that improper treatment can cause damage to kidney tissue. Some antibacterial and antiviral drugs contribute to the development of interstitial nephritis. You need to be extremely careful with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs!
The pediatrician, in turn, taking into account risk factors, clinical and laboratory signs of renal disorders, will promptly prescribe the necessary examinations, refer your child for consultation with a nephrologist, urologist, or conduct hospitalization in a timely manner.
I wish everyone good health!
Delayed menstruation during pregnancy
If your period is 10 days late , it is important to take a pregnancy test at home. A negative result does not mean that there is no pregnancy, and it is recommended to repeat the test after a couple of days - that’s when two stripes may appear on its surface.
This is explained simply: the concentration of the hCG hormone in the urine in the early stages is insufficient, and pregnancy is not detected. However, after a few days, a repeated test confirms the birth of a new life.
Causes of delayed menstruation in teenage girls
In the teenage body, physiological changes in hormonal levels are observed, so for this category of “women” a delay of 10 days in menstruation is not a global problem. It takes time for hormonal levels to establish, and by the age of 14–15, a teenage girl has a regular menstrual cycle. Further deviation indicates a problem, and it is important to visit a medical center.
One way or another, a delay in monthly menstruation requires high-quality diagnosis. The fact of pregnancy (during sexual activity) and diseases of the reproductive system should not be ruled out. A genetic predisposition is also relevant, when instability of the menstrual cycle is transmitted from mother to mature daughter. In any case, a visit to the doctor will not be in vain.
Return to list