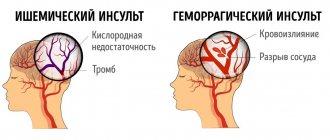
Stroke is a complex disease that disrupts the normal functioning of the brain. Develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, aneurysms. A stroke disrupts brain function and entails changes in the functional characteristics of a number of organs, impaired mobility, and sensitivity.
Stroke ranks first among the causes of disability in middle-aged and elderly people. Moreover, 30% of cases occur in people of working age – up to 65 years.
In case of a stroke, proper first aid plays a significant role. In the process of rehabilitation - competent treatment and care for patients after a stroke. Even after the most severe form of an attack, the victim can regain partial mobility.
Caring for patients after a stroke: what is worth knowing?
While a person who has suffered a stroke is in hospital, he is looked after by qualified medical personnel. But sooner or later the patient is discharged, and then his relatives have to look after him. To help your loved one recover and to maintain the strength to perform the necessary procedures, it is worth learning the basics of correct and high-quality general nursing care.
From a medical point of view, there are two types of paralysis: right-sided and left-sided. The behavior of patients with different types of paralysis differs significantly. This is worth considering when developing an exit strategy. With right-sided paralysis, damage to the left side of the body, the patient’s motor function on the left side of the body is impaired. As a result, he:
- does not feel the left lower and upper limbs;
- does not understand where they are located;
- does not perceive the surrounding space (while walking he bumps into doors, cannot calculate the distance to the nearest object);
- loses place of reading.
Tips that will make life easier for such a patient:
- the bed must be placed so that the patient can see with his right eye the center of the room and whoever enters the room;
- Place household items on the side of your right hand;
- encourage your ward to talk more, as speech helps to quickly restore spatial perception.
With left-sided paralysis, damage to the right side of the body, the patient’s emotional background is disturbed. He is in a lethargic depressed state and does not experience any emotional experiences. Patients with left-sided stroke:
- have problems with speech, it is difficult for them to pronounce words and form sentences;
- have difficulties with perception, do not understand what is being said to them;
- they forget words and names of objects.
Tips on how to make the life of such a patient more comfortable:
- at first, replace words with gestures, facial expressions, and gentle touches;
- speak slowly, clearly, avoid complex sentences;
- try using written language instead of spoken language;
- perform smooth, unhurried movements;
- ask the doctor to develop a speech therapy complex, help the patient perform the developed speech therapy exercises.
Rules for care after a stroke at home
Is it possible to care for a sick person independently? Maybe. But it is difficult not to develop exhaustion of the nervous system from overload, especially if he is in severe paralysis. The best solution is the help of a nurse in this case. If you care about yourself. How to care for a grandparent after a stroke if it is not possible to provide professional care? It is easiest to organize care at home if the patient is in relatively normal condition, without complete paralysis of the body. In this situation, care comes down to monitoring the intake of medications and compliance with procedures prescribed by specialists. And moral support for your loved one, because now it’s even harder for him than usual. If procedures are prescribed, you can go to the hospital. Changing your location and communicating with additional people will always be useful. Especially the elderly. Sharing your experiences with those who are close in spirit is healing for every person.
Preventing swelling of the arms/legs
Poor circulation causes the formation of edema in the upper and/or lower extremities. Factors indicating the appearance of edema are cold, red extremities. Tips on how to prevent the problem:
- Sore limbs should be in a comfortable position. It is important to ensure that they do not hang down.
- Frequently changing the positions of the limbs helps avoid blood stagnation.
- In a sitting position, you can place a soft pillow/cushion under your arm and a strong support (small stool, hard cushion) under your leg. You can place a pad under your calves to improve support.
- In a sitting position, you must ensure that your back fits snugly against the back of the chair or other support.
Repeated stroke
The risk of recurrent stroke after a primary stroke is quite high. In many cases, the second stroke is often more destructive than the first and more brain tissue is damaged, causing more severe neurological deficits. For this reason, it is important to do everything possible to prevent another stroke. This means paying close attention to your loved one's medication, diet, and rehabilitation. Medicines can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of another stroke.
Diet is a very important preventive factor because many foods increase blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Exercise (gymnastics) also helps reduce blood pressure and cholesterol levels. In addition, it is necessary to monitor for signs of recurrent stroke, such as speech or motor impairment or worsening of existing neurological deficits.
Prevention of thrombosis
Almost every stroke patient leads a sedentary lifestyle. This causes the development of physical inactivity—a weakening of muscle tone. As a result, blood clots begin to form in the lower extremities. This process is dangerous due to the occurrence of thrombosis. You can prevent a dangerous condition:
- performing preventive exercises;
- using compression stockings, elastic bandage;
- taking medications to thin the blood (prescribed by your doctor).
Prevention of pneumonia
Prolonged bed rest causes stagnation of blood in the lungs. Against the background of this problem, pneumonia occurs. The danger of the phenomenon is its asymptomatic occurrence. Over time, the bedridden patient experiences weakness, cough, shortness of breath or heart failure, and fever. Pneumonia can occur at an early stage of a stroke (2nd - 3rd day of the disease) or a late stage (2nd - 6th week of the disease). To prevent the occurrence of pneumonia you must:
- perform a drainage massage - lightly tap the back at the level of the lungs (do not touch the spine);
- ventilate, moisten the room - dry air dries out the nasal mucosa, which becomes a breeding ground for infection;
- do passive gymnastics - several times a day the patient should be raised in bed, raise and lower the upper limbs, thus improving breathing;
- perform breathing exercises;
- give expectorants (as prescribed by a doctor).
Restoring motor activity after a stroke.
Exiting bed rest should be done gradually and only in consultation with a doctor.
First, they teach the patient to sit down, then do exercises for the legs, then stand up, and only then walk.
If the person in your care cannot sit up independently:
- First, help him sit up.
- Then he needs to learn to sit in bed.
- Provide the bed with special devices so that the patient can sit up without your help.
- Teach the patient to lower his legs from the bed and move to a nearby chair or wheelchair.
- Gradually teach the patient:
- stand;
- transfer the weight of the body from one side of the body to the other;
- take steps on the spot;
- To learn to walk, purchase a walker.
When teaching walking, stay close to the patient on the affected side.
Preventing constipation
People after a stroke often have problems with bowel movements. Drinking plenty of fluids, abdominal massage, medicinal and natural laxatives (beets, dried apricots, prunes, bran, bananas, and other foods) help combat constipation. Abdominal massage is performed with light circular movements. The intestinal area can be massaged with gentle pressing touches.
You can help improve the bowel movement process by developing a bowel movement routine: daily enemas/suppositories should be done until the natural process is restored. Developing a reflex to have a bowel movement at the same time helps avoid constipation.
You can improve natural intestinal motility with proper nutrition. The patient's diet should include vegetables and fruits, cereals, and dairy products. You should not eat spicy or fatty foods, baked goods, alcohol, or sugar. It is better to steam or bake food.
Care after a stroke with the help of a caregiver
The task of a professional nurse is to provide all possible assistance for the recovery of patients after a stroke. Our Patronage Agency has qualified nurses with medical education. We have medical personnel who carry out any prescriptions of specialized doctors. They will be happy to provide assistance for any patient’s condition, from mild to complete paralysis with loss of speech skills: • Sanitary care; • Medical service; • Rehabilitation procedures; • Leisure activities, • Walks.
Preventing the formation of bedsores
Bedsores are formed under the influence of a number of factors:
- body overheating;
- unsuitable underwear and bed linen - injure the skin;
- illiterate care can provoke the appearance of long-term non-healing wounds;
- untimely treatment of abrasions, cuts, and other damage to the epidermis.
A bedsore is a source of infection entering the blood, which causes complications in the course of the disease. Bedsores appear in places where the skin is in constant contact with a hard surface. This is easy to avoid - you need to periodically change the position of your body. Do all manipulations of turning over and changing body position slowly and carefully. The client must be left in the selected position for 2 – 3 hours. Make sure that no folds form under the body and that the laundry does not bunch up.
Air baths are a good prevention of skin necrosis. Light massage of areas prone to bedsores (shoulder blades, hips, sacral area, heels, other areas) helps avoid damage to the epidermis. Before massage, it is best to lubricate the skin with camphor oil. The massage is done until the surface of the epidermis becomes slightly red, which indicates restoration of blood circulation.
Prevention of bedsores in stroke patients
A person who has suffered a stroke remains in one position all the time, often horizontally. This can lead to the appearance of bedsores - necrosis of areas of the epidermis. The occurrence of bedsores can be observed on the shoulder blades, elbows, tailbone, heels, and in the pelvic area. Due to increased pressure on these areas of the skin, blood circulation is impaired or completely stopped. The result is the death of soft tissue.
Necrosis can occur after several hours of lying in one position. Depending on the time of continuous pressure, it can be mild or severe. The danger of bedsores is that through them an infection can enter the patient’s body, which can cause sepsis or death. Therefore, it is important to carry out preventive measures that can prevent the occurrence of skin necrosis.
The following actions will help avoid the occurrence of bedsores:
- changing the patient's position every two hours;
- thorough daily inspection of the integument under pressure to identify the initial stage of necrosis;
- performing daily skin hygiene;
- treatment of areas of the epidermis with antiseptic (alcohol) solutions;
- frequent change of bed linen;
- When making the bed, you need to make sure that no folds form on the surface of the sleeping place, that there are no unnecessary objects, crumbs, or anything that can create additional pressure on the body;
- use of special mattresses or beds;
- performing light massage, therapeutic exercises;
- placing rubber circles under areas of the body that experience maximum stress.
If necrosis cannot be avoided, treatment should be started immediately. This will prevent infection from entering the body.
Prevention of contractures
A side effect of a stroke is loss of mobility. Against the background of this functional disorder, contractures occur—limited mobility of the upper and lower extremities. Limitation of mobility leads to the fact that the patient cannot move, work with his arms and legs. This joint disease is easier to prevent than to treat later. Preventive measures:
- Correct body position - in bed, the patient should lie in a position close to normal physiological. To reduce muscle tone, you need to use rollers, pillows, and other means. Orthoses help keep your limbs in the correct position. To prevent your hand from clenching into a fist, it is convenient to use a massage ball, dumbbell, etc.
- Therapeutic gymnastics - exercises should affect all joints. Start gymnastics by warming up the muscles. For maximum effect, you can use a special gel. Therapeutic gymnastics lasts 20–30 minutes, includes 5–10 repetitions. A set of exercises must be practiced from the first days of the disease. This will avoid joint contracture and guarantee a better result.
Caring for a patient who has suffered a stroke requires great patience and perseverance from the caregiver.
Remember, high-quality home care, compliance with doctor’s orders, and emotional support are the conditions for the patient’s rapid recovery. In contact with
Concomitant somatic diseases
Often strokes occur against the background of various somatic diseases. For example, many strokes occur as a result of diabetes, so controlling blood sugar levels after a stroke may help prevent another stroke. In addition, diabetes can lead to other health problems, such as vision impairment (including blindness) and kidney disease, which can make caring for a stroke patient much more difficult. If diabetes is compensated, then it is necessary to control sugar levels and adhere to a diet.
Cardiovascular diseases are most often present in patients who have suffered a stroke. If high cholesterol levels lead to the formation of plaque in a blood vessel in the brain and the development of a stroke, then similar problems can occur in the heart muscle. For this reason, it is important to monitor the condition of the cardiovascular system after a stroke.
It is necessary to be prepared for the fact that after a stroke a patient may develop a heart attack due to vascular thrombosis, since after a stroke there may be a disturbance in blood rheology and regulation of vascular tone, including blood pressure. Blood clots can also form in the vessels of the lower extremities and travel through the bloodstream to the heart or vessels of the lungs. Therefore, control of the vessels of the lower extremities is also necessary, especially if the patient has varicose veins.