Briefly about the important, or get acquainted - stroke
During a stroke, the blood supply to an area of the brain is disrupted.
As a result, the blood vessels are affected, and the brain does not receive the necessary oxygen supply, and the nerve cells gradually die. Associated symptoms are:
- disorders of the motor system on one side;
- sensory disorders;
- lesions of central motor neurons;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma.
People of all ages are susceptible to stroke, especially those who suffer from heart disease and high blood pressure. The risk group includes patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus and those who abuse bad habits.
Micro-strokes foreshadow an upcoming brain catastrophe. You should pay close attention to the first symptoms, since even short-term vascular disorders lead to pathological changes in the brain substance.
Doctors can handle stroke treatment. Certain drugs restore damaged areas of nervous tissue and protect nerve cells from destruction.
However, complete recovery depends on the patient himself. Impaired brain circulation signals that you need to change your life, and not feel sorry for yourself.
Briefly about the types of stroke
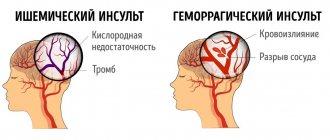
It can be ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Ischemic strokes are much more common and account for about 80% of all acute cerebrovascular accidents. Ischemia is a narrowing and blockage of cerebral vessels. It occurs as a result of blocking of the vascular lumen by a blood clot or foreign body, for example, air bubbles of injection origin that have entered the bloodstream. Due to hypoxia and disturbances in the trophism of nervous tissue, brain cells quickly die. The development of ischemic stroke occurs slowly, but it has several characteristic precursors.
As for hemorrhagic stroke, it is also commonly called subarachnoid hemorrhage with the release of blood from damaged vessels. Vessels may rupture or their walls gradually become thinner. Unlike ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke develops rapidly, with a sharp headache, which patients describe as a “dagger strike.” Loss of consciousness occurs immediately, and sometimes vomiting occurs. A blood clot, or hematoma, appears in the brain tissue, compressing the surrounding space. If the hematoma is large, the patient needs urgent surgical intervention to restore trophism of nerve cells.
Psychosomatic causes of stroke
It's no secret that health depends on a huge number of different factors. One of the causes of circulatory pathology in the brain is sensory perception.
The famous psychologist Louise Hay expressed the idea that the brain is a computer that controls the entire body. Contradictions that cannot be resolved can disrupt its work.
Psychosomatics identifies several main causes affecting the disruption of cerebral blood supply and the development of stroke:
- painful jealousy;
- doubts about fidelity, love;
- feeling of strong enmity and hatred;
- endless tension and the state of “everything needs to be done in time.”
Tormenting jealousy leads to disruptions in the nervous system.
The emotional cause of the disease is that a person has hopelessly lost the desire to do something. He doesn't enjoy anything and doesn't want anything. Life has lost its meaning for him.
Paralysis after a stroke is not uncommon. Suffering from this disorder are mainly those people who defend long-outdated views of the world. They are not flexible and cannot change to suit new circumstances. Accumulated aggression, the inability to perceive someone else’s opinion as correct, and to change one’s principles lead to dire consequences. This is a direct path to self-flagellation, which deprives you of the opportunity to be happy.
Fear is also one of the causes of illness. A person is afraid of losing something, of being left alone. So, for example, on the verge of divorce, having taken all measures to reunite and not finding the desired result, the brain digests the information and responds with hemorrhage.
Stroke, paresis and other neurological disorders according to Sinelnikov and illnesses from the mind according to Louise Hay:
Psychological causes of stroke
Louise Hay explains the occurrence of a stroke by saying that a person gives up or does not want to change: “I would rather die than change.” The reason may also be denial of life.
Psychologist Liz Burbo sees this illness as a manifestation of a problem with one’s own “I”, which contains beliefs, principles, and attitudes. The contradictions associated with them lead to a conflict that destroys the personality, which in physics is signaled by a stroke.
Dr. V. Sinelnikov claims that the basis of a stroke is “paralyzing” jealousy and hatred, and this is especially true for men.
Another psychosomatic reason is resistance to the life process and rejection of one’s life and destiny. As Sinelnikov writes, with such an attitude towards life, man himself “paralyzed” himself and doomed himself to inaction.
The doctor revealed that these people are very inflexible, defending their long-outdated views on the world. They deny themselves change (I would rather die than change my principles).
Another reason for a stroke may be avoiding responsibility, a situation or a person, when you feel unable to change anything.
Often, according to Sinelnikov, the cause of the illness is deeply rooted paralyzing fear and horror.
Sometimes a stroke arises as a subconscious need to unite the family. The doctor explains this by saying that the subconscious is pouring blood onto those brain centers that are responsible for the well-being of the family.
Another famous author on psychosomatics, O. Torsunov, claims that the enemies of the brain are envy, lust, illusion, madness, greed, and anger.
Psychologist E. Guskova revealed that stroke occurs in the recovery phase after strong experiences. So, a person worries that he can’t figure out how to solve some life problem. And his brain literally begins to boil. If this continues for a long time, then resolution of the situation leads to a stroke.
An example of prolonged strong mental stress and relaxation is a classic example: I was preparing a dissertation for a long time and was worried about a stroke when defending my defense.
Ways to Heal
By understanding the emotional causes of illness, you can recover faster and easier. Many people find it more convenient to take a couple of tablets and relieve themselves of pain symptoms. But the main reason remains in the head.
Psychologists say that there are diseases that can be cured only by working on your inner “I”. However, stroke requires a multifaceted approach, as a large number of vital systems in the body are involved.
Therapy consists of simultaneous influence on the physical and mental state. A specialized specialist can correct the consequences after a stroke. But at the same time, a good psychologist can return a person to a full life. It is necessary to identify the psychological cause of the disease. To do this, you need to remember your entire life before the brain stroke. Analyze events, thoughts, feelings and everything that this period was filled with.
The path to healing depends on the cause that provoked the disease. Sources of recovery include:
- forgiveness;
- awareness;
- repentance;
- relaxation.
Music lessons, art therapy, hobbies, walks in nature, and active recreation will help restore inner harmony.
Sometimes, in addition to psychological help, treatment with appropriate psychostimulants, antidepressants, and antipsychotics is required. In this case, the course and dosage are prescribed only by the treating neurologist after a series of diagnostic measures.
Interesting cases
Indifference and stroke ≠ laziness
One patient after a stroke developed an indifferent attitude towards his painful condition. He lay in bed for hours, mindlessly watching all the programs on TV. Those close to the patient believed that laziness was to blame and did not touch him.
But this condition is explained by damage to certain areas of the brain. And here, relatives must patiently encourage the victim to take action, try to induce a desire to move, and engage in self-care. As soon as the relatives gained patience and began to support the patient, he began to recover.
Love conquered the disease
Another interesting case is described by psychologists.
In one family, everything led to a breakdown in relationships. The husband's drunkenness, constant complaints against each other, quarrels, curses forced the wife to take the children and go to her mother.
After some time, she found out that her husband was in the hospital with a stroke and did not want to see anyone but her. His wife went to the hospital to see him, and the result was her husband’s recovery and family reunification.
Stroke in young people
We are all accustomed to thinking that stroke is a disease of older people. Unfortunately, stroke can also develop in young people. Of course, a stroke in youth is not a common occurrence, but it is no less dangerous.
Symptoms and diagnostic difficulties
In fact, the symptoms of stroke in young and old are practically the same. However, in practice, it often happens that a doctor, seeing a young patient with acute weakness in the arm, blurred vision, or an unusual headache, will think of a stroke as the last thing.
Firstly, stroke at a young age is still rare (7 times less common than in people over 45 years of age). Secondly, young people are more likely to have other diseases with similar symptoms (for example, multiple sclerosis, functional disorders or migraine attacks with aura).
Causes of stroke
In young people, both ischemic stroke (due to blockage of a vessel) and hemorrhagic stroke (hemorrhage) occur. Unlike patients in the older group (over 45 years), young people predominantly develop hemorrhagic stroke.
- In a hemorrhagic stroke,
the bleeding usually occurs from a ruptured
aneurysm
(an abnormally dilated artery) resulting from
a vascular malformation
(an abnormal structure). Typically, vascular anomalies, like most congenital anomalies, manifest themselves either in adolescence (for example, epileptic seizures and persistent headaches) or never manifest themselves. Therefore, it is not surprising that most often such a gap occurs at a young age. But at the same time, the abnormal vessel does not necessarily have to rupture. You can live your whole life with a cerebral artery aneurysm without knowing about it, and die in old age from completely different causes.
- The most common mechanism of ischemic stroke
is
vessel thrombosis
(due to
heart disease
or
bleeding disorder
).
Mitral valve prolapse and patent foramen ovale are the most common heart defects
that lead to stroke—impaired blood flow can cause a blood clot to form.
However, owners of these common defects, especially their mild forms, should not worry too much. Typically, stroke in these cases occurs in combination with several other risk factors. As for bleeding disorders
, which can also lead to the development of a blood clot, it is not so easy to identify; a regular biochemical blood test may not show anything. Indirectly, coagulation disorders in women can be indicated by miscarriages and non-developing pregnancies, as well as migraines. In this case, additional thorough examination of the coagulation and immune systems is necessary. A bleeding disorder may not be congenital; it can also be caused by smoking, taking oral contraceptives and other medications (some antibiotics), childbirth and pregnancy, and infectious diseases.
How to protect yourself?
Stroke at a young age can almost always be prevented. The basis of prevention is a healthy lifestyle (no smoking and alcohol abuse, moderate physical activity). Of course, you need to be attentive to your health and well-being and undergo regular medical examinations. This is especially true for people with already established diagnoses - heart defects, migraines with aura, blood clotting disorders.
But in any case, if you suddenly have unusual or new complaints (for example, uncharacteristic headaches, temporary blurred vision, weakness in the arm), be sure to consult a doctor immediately. This will protect you from the very serious consequences of a stroke.
Be healthy!
Maria Meshcherina
Photo istockphoto.com