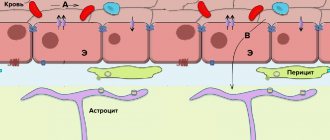
The brain is the most complex and most important organ in our body. It is thanks to him that we are superior to all other species. The brain processes all information and all actions that the body performs.
It controls all cells and is responsible for their adaptation to constantly changing environmental conditions. So, from simple tissue - skin, cells evolved into nerve cells. The former have only mechanical properties: protection, permeability. While the nervous ones in their entirety are capable of learning and allow one to remember information and coordinate thoughts.
However, any physical or chemical process must be provided with energy and nutrients. Therefore, proper nutrition, the absence of negative factors and pathological processes are necessary for long and fruitful brain function.
Different types of brain lesions
Since there are a lot of brain disorders, it was advisable to come up with a classification that would cover all diseases:
- organic brain damage;
- defeat of an infectious nature;
- cerebrovascular diseases;
- tumors (both benign and malignant);
- various congenital pathologies;
- brain diseases that are associated with trauma or abnormal structure;
- ionizing radiation;
- intoxication with various substances;
- negative impact of electromagnetic fields;
- mixed defeat.
Causes
Early, prenatal damage to the central nervous system is always a consequence of pregnancy complications in the expectant mother. Oxygen starvation of the brain negatively affects the intellectual and physical development of the child. Its causes are protracted labor, severe infections suffered by the woman, and premature detachment of the uterine placenta.
Acquired organic brain lesions will have other causes:
- traumatic injuries of the skull, also with penetration into soft tissues, most often transport accidents and domestic injuries;
- infections - bacterial, viral nature, for example, herpetic meningitis, staphylococcal arachnoiditis, less often lesions due to HIV infection;
- various intoxications - abuse of alcohol, tobacco products, damage to the central nervous system due to uncontrolled use of medications, poisoning with mushrooms, metal salts;
- vascular pathologies – up to 2/3 of cases of visits are due to conditions after a stroke of hemorrhagic or severe ischemic origin;
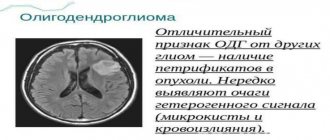
- neoplasms - tumors provoke increased pressure on brain structures, with their deformation and functional impairment;
- demyelinating conditions - the formation of foci without a myelin sheath near the fibers of the central nervous system, often the basis for the development of multiple sclerosis;
- neurodegenerative pathologies - for example, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's syndrome, with a steadily progressing disorder.
Differential diagnosis and identification of causes - infectious lesions have led to organic defects in the central nervous system, or they are the consequences of a penetrating injury to the structures of the skull, the prerogative of the doctor.
Organic brain diseases: their types
Organic brain damage (OMD) is characterized by the presence of pathological changes that can be seen using neuroimaging methods.
Any pathological processes are visualized and correlated: tumors, abscesses, benign cysts, hemorrhages, atherosclerosis, amyloid accumulation.
A feature of organic lesions is that there is a substrate in the brain. For example, epilepsy also has neurological pathological symptoms, but it is impossible to “see” anything. Organic disorders can be either local or diffuse. Symptoms are also different. With local damage, one type of activity (memory, intelligence) is impaired. And with generalized symptoms, general cerebral symptoms appear.
Types of organic brain lesions:
- Brain disorder associated with diseases of the heart, blood vessels and nerves . Most often this is observed in atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. In the first case, a sufficient amount of energy, oxygen, and nutrients do not enter through the narrowed lumen of the vessels. This leads to insufficient trophism of the nervous tissue of the brain and its gradual death. In Alzheimer's disease, plaques form in the brain tissue, the basis of which is the protein amyloid. It is this that leads to degeneration of both the neuron bodies themselves and their processes.
- Brain damage, with diseases of internal organs . Pathological processes occurring in the brain cause functional failure of the liver or kidneys. This is due to the accumulation of a large number of toxins, which negatively affect all body systems, including destroying neural connections. If the organs do not begin to function normally (after transplantation or treatment), then dementia will only progress. Removing toxins is not enough.
- Brain damage associated with intoxication . Excessive amounts of alcohol or its substitutes can cause severe intoxication of the body and lead to damage to neural connections, and subsequently to dementia. The same effect will be observed in case of poisoning with arsenic or nitrogenous products. After the disappearance of the etiological factor and cleansing of the body, the condition may improve. This depends on the duration of exposure and the depth of possible damage. In older people, intoxication can occur due to taking large doses of medications. Additionally, to quickly improve the condition, sedatives and sleeping pills are prescribed to improve the condition of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnostics
Detection of organic brain damage is a complex and difficult process. This means that in order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor will need to carry out a set of diagnostic measures, which include the following types of research:
- Ultrasound of the brain. It is possible to do this only if the fontanelle has not yet closed. That is, such a diagnosis can only be performed on a child under one year old.
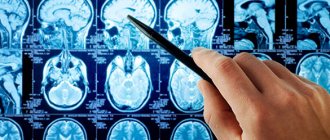
- MRI and CT. Allows you to determine whether there is a change in the brain and which lobes are damaged. A complex procedure that requires complete silence and stillness. For young children, it is usually performed under anesthesia.
- EEG. The study is carried out using special sensors that make it possible to determine how correctly the neural connection is working and whether epileptic activity is present. The study can be carried out from 15 minutes to 2 hours, however, in order to get a more detailed picture of brain function, it is recommended to monitor during sleep. Many clinics currently offer paid services - installing the device overnight.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck. The procedure allows you to determine how correctly the blood supply to the brain is.
On the recommendation of a neurologist or neurosurgeon, a number of additional types of research may be required, such as neurosonography, EchoEg, laboratory tests of blood and urine, as well as ultrasound of internal organs to identify the threshold.
In rare cases, the patient needs to undergo a cerebrospinal fluid puncture. If the diagnosis was carried out correctly, then the doctor will have the opportunity to correctly diagnose and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Residual organic damage: causes and symptoms
Residual organic damage is the consequences that appear after damage to brain structures in the perinatal period (from 22 weeks of pregnancy to 7 days after birth).
Despite the fact that premature pregnancy is not a mandatory indication for organic brain damage, a weakly developed nervous system is very vulnerable to any unfavorable factors, and since the neuromuscular response has not yet been formed, pathological processes may occur.
The causes of residual organic damage are:
- diseases at the chromosome level;
- insufficient consumption or supply of oxygen to the mother’s body and associated hypoxia of the fetal brain;
- radiation;
- ecology;
- use of medications or cleaning products;
- poisoning of the expectant mother with alcohol or drugs;
- poor nutrition, expressed in insufficient consumption of micro or macro substances;
- acute or chronic diseases of women;
- pathology of pregnancy.
Any of these factors can lead to slow growth of the baby, which will provoke organic brain damage in children.
The clinical picture of this lesion appears immediately after birth, which can be determined not only by a neurologist. There is a noticeable violation of muscle tone, trembling of the hands, excitement, and the formation of voluntary movements is delayed. With more serious damage, it is possible to determine which area of the brain is damaged. There is another option when neurological abnormalities can only be detected using hardware methods. This kind of flow is called silent.
Despite the difficulty of diagnosis, this silent pathology does not require treatment. It is important to undergo regular examinations and monitor changes.
How residual organic damage manifests itself:
- Cerebrasthenic syndrome . It is characterized by rapid fatigue, loss of strength, sudden mood swings with a predominance of tearfulness and irritability, and lack of adaptation to any stress.
- Neurosis-like syndrome . It manifests itself as various phobias, urinary incontinence and nervous tics.
- Encephalopathy.
- Psychopathy.
- Organic-psychic infantilism.
- Minimal brain dysfunction . It manifests itself as hyperactivity, which results from a lack of attention.
Early diagnosis helps to begin early treatment that will stop the progression of the pathological process and restore the functioning of the nervous system. If the negative factor continues to act, the condition may worsen or the treatment may become ineffective.
Causes of the disorder
An organic disease that affects the structures of the brain and nervous system can occur for many reasons. These include:
- Disorders associated with pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and nerves. They are more common in atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and parkinsonism. Through the narrowed vascular lumen, a sufficient amount of oxygen does not reach the brain, which leads to the gradual death of nerve cells.
- Disorders caused by diseases of internal organs. Changes may occur due to pathogenic processes in the liver or kidneys (eg, hepatitis, cirrhosis, fibrosis). With the accumulation of toxic substances, a high concentration of which negatively affects the functions of the entire body, neural connections are destroyed. Dementia is treatable if detoxification is started promptly.
- Intoxication of the body (with severe alcoholism, drug addiction).
- Head injuries that appear either immediately or later, and remind you for the rest of your life. Patients suffer from periodic attacks of dizziness and cephalalgia. In severe cases, problems with hearing and vision are observed. Paralysis of the limbs, tics, and episyndrome may develop. Sometimes traumatic brain injuries in newborns occur during childbirth. The consequences of such injuries can be quite severe and threaten not only the health, but also the life of the child.
Infectious diseases (abscess, meningitis, encephalitis), cyst growth, for example, echinococcosis, are provoking factors of the disease.
Infectious lesions
Quite a lot of infections lead to the development of organic brain lesions. This:
- Coxsackie viruses are a common cause of aseptic meningitis.
- Herpes, which attacks the central nervous system, causing meningitis and encephalitis.
- Staphylococcus, which causes staphylococcal meningitis.
- Echoviruses that can infect almost any cell in the body.
In addition, HIV infection in advanced stages affects the central nervous system, manifesting itself as an abscess and leukoencephalopathy. Infectious brain disorders manifest themselves:
- Asthenia.
- Psychotic disorganization.
- Affects.
- Personality disorders.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders.
- Hysteria, neuroses, hypochondria.
Vascular pathologies
Ischemic brain disease, hemorrhagic stroke, DEP (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) are diseases associated with vascular pathologies.
- Ischemia develops due to blockage of the vascular lumen by cholesterol plaques or blood clots.
- In a hemorrhagic stroke, an aneurysm ruptures, causing blood to leak into adjacent areas of the brain.
- DEP provokes a constant lack of oxygen due to diffuse damage to the cerebral vessels. The disorder is characterized by multiple small foci located throughout the surface of the brain.
Signs of brain damage:
- Severe pain in the head.
- Dizziness, the causes of which are initially unclear to the victim.
- Nausea.
- Nervousness.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Fainting.
- Numbness of the limbs.
- Cognitive impairment.
- Affective disorders.
- Parkinsonism.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Voice change.
- Slurred speech.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Violation of stability.
Demyelinating diseases
Among demyelinating brain lesions, a diagnosis such as multiple sclerosis should be noted. This is a chronic autoimmune disease in which foci (scars) of sclerosis are formed throughout the central nervous system with the replacement of healthy tissue with connective tissue. The myelin sheaths of nerve endings gradually disintegrate, which is accompanied by swelling of the nerve fibers, impaired conduction of impulses, and the formation of sclerotic plaques. The disease affects young people and even children. The disease manifests itself:
- Reduced pain threshold.
- Paresis of the limbs on one side of the body.
- Numbness, weakness.
- Gait disturbance.
- Tremors of the hands and neck.
- Low-grade body temperature.
Poisoning
Serious poisoning of the body is caused by alcohol abuse, drug addiction, poisoning with drugs, mushrooms, heavy metals, arsenic, and combustion products of polyvinyl chloride. Each specific case manifests itself with certain symptoms.
For example, intoxication with psychotropic substances is characterized by the appearance of:
- Dizziness.
- Diarrhea.
- Headache.
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Chills.
Chronic intoxication causes nervousness, lethargy, and decreased performance. Cognitive impairments include decreased intelligence, impaired attention and memory.
Brain injuries
These are contact and intracranial injuries of the face, skull bones, membranes and substance of the brain. These include:
- Concussions, brain contusions.
- Fracture of the bones of the skull.
- Diffuse breaks and tears of axons.
- Compression of the brain.
- Intracranial and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
After such injuries, it is necessary to take into account that the brain may be damaged not only at the site of impact. The counter-impact force also plays a significant role, causing hydrodynamic vibrations that negatively affect the meninges.
Perinatal organic damage
Perinatal damage is a condition that occurs when adverse factors influence the still unformed brain of the fetus or newborn:
- complications during pregnancy;
- injuries during childbirth;
- asphyxia;
- diseases of infectious nature;
- blood diseases in newborns.
These reasons will contribute to the appearance of hypoxic-ischemic brain lesions and intracranial hemorrhages. Such complications often lead to residual lesions, which can appear very quickly or, on the contrary, constantly and slowly progress.
Perinatal childhood organic brain lesions have the following symptoms:
- headache;
- irritability;
- dizziness;
- increased excitability;
- insomnia;
- decreased concentration;
- surges in intracranial pressure.
All these symptoms are not constant values and can progress. Deterioration of the condition can lead to diseases such as cerebral palsy, neuropathies of various origins, hydrocephalic syndrome, and epilepsy.
However, it is worth noting that some pathologies can be reversible with the right lifestyle and nutrition. Therefore, it is very important to consult a doctor for help at the initial stages in order to begin treatment as early as possible and in the future forget about any manifestations of organic brain damage.
Clinical picture of acute hypertension
There are practically no specific symptoms that appear with organic brain damage. This is due to the fact that any manifestation depends on the underlying disease, which led to brain damage.
You can identify symptoms that will be characteristic of almost all concomitant pathologies:
- decreased activity;
- apathy, lack of interest in something;
- sloppiness appears.
Memory loss is a rarer symptom, but also occurs. Patients may forget the names of their relatives or friends, or their appearance. There is a violation of counting and people will not be able to list the numbers from 1 to 10 or remember the sequence of days of the week.
Violations of writing and speech are manifested in the rearrangement of syllables and words. In the most severe cases, a person will not be able to speak independently, but will only be able to repeat a small phrase that he hears. Emotionally, there are several possible outcomes.
Or the person becomes kind of unemotional, reacting to everything too calmly, which can’t help but be noticeable. Or, on the contrary, the manifestation of emotions is inadequate and perverted. Hallucinations may occur.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of organic focal diseases of the brain is important both at the earliest stages and at later stages with already prescribed treatment.
Early detection of the disease will allow you to take action and prescribe medications that can stop its progression or even reverse it. The most important diagnostic stages:
- taking anamnesis;
- neurological examination;
- computed tomography of the brain.
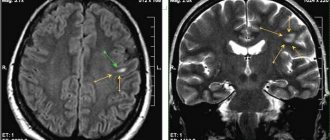
Foci of organic brain damage are shown by arrows
Anamnesis allows you to determine the duration of the disease, its course, and its connection with heredity. A neurological examination is mandatory to identify the causes. Tomography identifies atrophic lesions that cause symptoms.
Treatment tactics
Doctors will, of course, place the main emphasis of therapy for organic brain damage on the pathology that is at the root of the disorder. All large tumors and consequences of brain injuries are subject to surgical correction.
Medications:
- to improve blood flow;
- antioxidants;
- statins;
- antiplatelet agents;
- vitamins;
- sedatives;
- anticonvulsant medications.
Complexes of physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy are relevant, especially with residual damage to the central nervous system, as well as proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. The diet should be dominated by dishes with fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs and healthy microelements.
During the rehabilitation period, psychosocial treatment is important - working with a psychotherapist not only for the patient himself, but also for his family members. In case of severe organic brain damage, the solution seems to be to send the victim to a specialized institution with round-the-clock medical supervision.
Providing medical care
A feature of the nervous system is that restoration of neural connections is impossible. You can only increase the activity of the surviving parts of the brain.
The main groups of drugs prescribed for the treatment of organic brain damage:
- Protecting nerve cells and improving memory, activating brain function (Piracetam, Actovegin). These drugs improve cognitive function and have a positive effect on the central nervous system, both through their effect on nerve impulses and metabolism. Medicines reduce increased platelet aggregation, thereby allowing more red blood cells to enter the microvasculature of the brain. These drugs are prohibited for children, pregnant women and lactation.
- Peptide hydrolysates (Cerebrolysin) are neuroprotectors . Peptides and amino acids for this drug are taken from the brain of pigs. The advantage of this medicine is that the probability of developing anaphylactic shock if taken is 0. With insufficient blood supply to tissues, cells die due to the damaging effects of oxidizing agents. Cerebrolysin reduces their negative effects. It also adapts cells to hypoxia and the influence of other damaging agents.
- Improving blood circulation, thinning the blood (Curantil, Aspirin). There are a large number of drugs in this group, so only a doctor should prescribe them. The most important task of taking these medications is blood thinning (reducing the aggregation of red blood cells and increasing blood volume due to intercellular fluid). This will allow blood cells to pass into the narrow lumens of blood vessels and quickly cleanse the blood of intoxication products. Unfortunately, the drugs have a large number of contraindications.
- Additional medications include anticonvulsants .
In addition to drug therapy, the following general strengthening and therapeutic measures are prescribed:
- massage that improves blood circulation to the brain;
- physiotherapeutic procedures to improve cerebral circulation and relieve spasms;
- individual or group classes with a speech pathologist and psychologist.
Treatment
It is known that neurocells do not recover in any way. Throughout the world, it has not yet been possible to develop a type of treatment that could contribute to the restoration of the affected area of the brain.
However, as a result of research, it was possible to prove that if healthy cells are stimulated, they will take over the work for the inactive area. There are several ways to treat this pathology:
Medications
Medicines that a doctor can prescribe are divided into 3 main groups:
- Neuroleptics and neuroprotectors. Helps improve blood supply to the brain and thin it.
- Anticonvulsants. They are prescribed only if the person has had seizures or epileptic activity has appeared on the EEG.
- Antibiotics and antiseptics. If the cause of organic brain damage is an infectious disease, then for further rehabilitation it is necessary to first eliminate it.
Unfortunately, there are no harmless pills to restore brain activity. They all have certain side effects. In most cases, aggression, restless sleep and irritability appear.
Important!
Before prescribing medications, an EEG procedure must be performed first. If epileptic activity has been detected, then drugs to stimulate brain activity cannot be prescribed. This can trigger severe cramps.
Additional procedures
In addition to medications, it is possible to carry out a number of other modern techniques to eliminate organic damage. These include:
- General body massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy. The procedures are aimed at improving overall blood flow. They also allow you to relieve spasms, get rid of hypotonicity and hypertonicity.
- BAK, Tomatis and microcurrents. The procedures are aimed at external stimulation of the brain.
Procedures are also carried out only in the absence of epileptic activity. Basically, they are carried out in private clinics on a paid basis. Additional types of rehabilitation such as a swimming pool, classes with a speech pathologist and speech therapist, and visits to a psychiatrist may also be available.
Activities for fine motor skills and sensory integration are very important for children, which also helps improve brain function. In rare cases, surgery is required.
Possible outcomes
All possible consequences and outcomes are divided into three points:
- Recovery . This is possible if there are no visible defects and the depth of the lesion is small.
- Disability . The patient is alive, but to a greater or lesser extent loses the ability to work and take care of himself.
- Disability . Without outside help a person cannot survive.
- Death.
Any consequences depend on the massiveness of the lesion, the location of the pathological process, age, etiological factor and correctness of treatment.