Author of the article
Anatoly Shishigin
Reading time: 3 minutes
AA
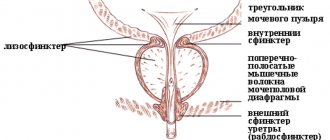
Pain, burning or itching when urinating or ejaculating semen after sexual intercourse are quite unpleasant symptoms, which, moreover, are quite dangerous. Many men ignore these sensations, most often with the hope that they will go away on their own without special treatment. This cannot be allowed, therefore, first of all, you need to figure out why the urethra hurts after ejaculation, a man must find out the source of such discomfort.
Non-pathological itching
This group includes unpleasant sensations due to external causes that have nothing to do with pathologies. Urethral itching in women without discharge is typical for this group of causes.
What can be attributed to them:
- Hypothermia or overheating is accompanied by stagnation of lymph and blood, their outflow slows down. Because of the cold, blood vessels spasm, and local immunity drops noticeably. Swelling occurs, which narrows the walls of the urethra, urine also passes slowly and begins to irritate the mucous membrane. When hypothermia occurs, pain occurs in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and sacrum, pain and burning when urinating. With timely measures, itching can easily be removed without an inflammatory reaction.
- Insufficient drinking regime - urine becomes more concentrated in terms of salts. It does not pass through the urethra without a trace, irritation and burning with salt crystals will certainly occur. The temperature may rise and the woman may feel sick.
- Wearing tight underwear and clothing provokes the above-mentioned blood stagnation and mechanical damage.
- Mechanical friction in the groin – occurs after cycling. This is always fraught with tissue swelling. The answer is itching in the urethra.
- Excessive consumption of salt, fatty, smoked, spicy foods increases the concentration of salts in urine.
- Genital piercings cause seemingly minor mechanical trauma, but they can cause itching. This also includes microtraumas after sex, trauma to the mucous membrane with nails when washing, the hardness of toilet paper, synthetics and uncomfortable style of underwear, and birth injuries to the ureter. If this fact is ignored, infection of the urethra and itching may occur.
- Taking antibiotics disrupts the number of beneficial microflora and changes the composition of urine. Irritation of the walls of the urethra is its consequence.
- Insufficient hygiene can also cause problems, especially during menstrual periods. Frequent douching has a negative effect. Even sufficient hygiene when using aggressive care products can cause severe irritation of the skin and mucous membranes. You can suspect such products by the strong smell of soap, bright color, cheap price, etc.
- Contact with allergens can also occur when using laundry washed in cheap washing powders, inappropriate lubricant on a condom, aromatic additives in pads, tampons, etc.
- Surgery on the urinary tract can provoke itching in the urethra, but in this case it will indicate the healing process. This itching does not require treatment and goes away on its own. At this time, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial suppositories.
Conclusions: a distinctive feature of itching and burning due to the action of natural factors is the absence of discharge; when the irritating factor is eliminated, the symptom immediately disappears.
The main causes of pathology
So why do some representatives of the stronger sex experience pain after ejaculation? This pathology often appears due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and urethritis (inflammation of the urethra).
If a man has a chronic or infectious disease, scar tissue gradually forms in the genital area. It stretches during intimacy. Because of this, a man often develops small cracks, which is why a burning sensation occurs after ejaculation.
Cystitis may also be the cause of this phenomenon. When the bladder becomes inflamed, the patient experiences severe pain in the area of the urethra. People suffering from cystitis also experience a burning sensation when urinating.
If you have any sexually transmitted disease, cutting pains also appear both during intimacy and after completion of sexual intercourse.
The patient's body temperature often rises and he complains of headaches.
Treatment recommendations
Conservative treatment in medical practice involves the use of antimicrobial agents to counteract the burning sensation inside the urethra. Traditional therapy and herbs help remove inflammation and reduce the symptoms of the disease. Traditional medicine is not able to remove the main cause of the burning sensation, since they are weaker than antibiotics, but they will help improve the patient’s well-being:
- It is necessary to mix equally 1 tbsp. l. horsetail, dried lingonberry leaves and chamomile. Next, the mass is poured with 0.3 kg of water and boiled in a water bath for 10 minutes. When the broth is removed from the heat, it is filtered and drunk hot.
- You need to mix oak bark, linden and bearberry in equal quantities in a thermos. Afterwards the mass is poured with boiling water and left for 60 minutes. You need to use the product 1 tbsp. l. three times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Mix dried birch leaves, licorice root, bearberry and corn silk. The ingredients are mixed in equal proportions, and then a glass of boiling water is added to the finished mixture and kept in a water bath for 15 minutes. After the specified period, the medicinal herbs are removed from the water bath and infused in a cool place for approximately 40 minutes. The resulting product must be taken warm three times a day and 30 minutes before meals.
Timely therapy will eliminate the pathological process in the shortest possible time.
In addition to conservative methods of therapy, there are also traditional medicines used at home, but with the permission of the attending physician. Complex treatment with antibiotics and folk remedies gives positive results.
Hormonal changes
The causes of itching in the urethra in women may be due to hormonal imbalance. This manifests itself in painful and frequent urination, burning and itching of the genitals, discharge in the form of leucorrhoea and mucous lumps, discomfort during washing.
Such changes may be associated with thyroid dysfunction and, in physiology, with pregnancy. In its first trimester, a hormonal surge occurs, the mucous membranes swell due to increased levels of prolactin (the pregnancy hormone necessary for its successful course). After 14 weeks, such symptoms disappear on their own, and hormonal levels normalize by this time. You cannot self-medicate in such cases, so as not to provoke a miscarriage.
Pain in the urethra with prostate adenoma
Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not cause pain in the urethra.
The exception is when it reaches large sizes and begins to compress the back of the canal.
A man has difficulty urinating.
Pressure in the urethra increases.
Therefore, urination can be not only difficult, but also painful.
If such symptoms appear, you can get rid of them with the help of medications.
But at a certain stage in the development of the disease, surgery may be required.
Most of the prostate gland is removed, after which urodynamics are restored.
Gonorrhea and other pathologies
Neisseria gonorrhoeae - these gonorrhea pathogens can spread up the urethra even during unprotected sex. The infection is contagious during any type of sex.
Itching in the urethra is the first sign. It intensifies with urination, then the genitals become inflamed and green-white purulent discharge appears.
Chlamydia and herpes simplex are also sexually transmitted and are accompanied by itching in the urethra during urination. The discharge is small in volume and transparent; there is aching pain in the lower abdomen and groin, severe general weakness appears.
Bacterial vaginosis is an imbalance of lactobacilli and an increase in opportunistic microflora, especially gardnerella. Therefore, the second name of the pathology is gardnerellosis. Dryness occurs in the perineum, constant itching in the urethra in women, and frequent urges. The discharge is characterized by its smell of rotten fish. They have a greenish color. The most common cause of burning and itching in the urethra is trichomoniasis. It is the most common. In addition to itching, it is accompanied by discharge from the urethra, hematuria, and pain when urinating.
Signs of the disease appear quickly – 3-5 days after infection. In men, the pathology is often asymptomatic. Self-medication is excluded because, although the symptoms are similar, the causes and treatment are different.
Burning as a sign of prostatitis
Clinical manifestations of prostatitis may differ in different symptoms.
It all depends on the age of the patient, the type of pathogen, and the state of hormonal levels.
The patient rarely pays attention to signs that are of a general nature (decreased performance, increased fatigue, changes in mood, weakness, sleep disturbance).
With further damage to the gland, increased sweating is observed, discomfort appears in the gluteal region and groin.
With pathology of the scrotum, the burning sensation often radiates to the testicles.
With vesiculitis, discomfort is localized in the groin and perineum area.
Symptoms are complemented by attacks of aggression, tearfulness, short temper, etc.
Local signs appear much later and are expressed by the appearance of a burning sensation during urination, impaired urination and erection.
Sometimes there are no symptoms or there are one or two mild signs.
Pain syndrome with prostatitis can be characterized by weak sensations or be so pronounced that to stop the attack the patient will need to take painkillers.
Why does pain occur after ejaculation?
It is useless to hope that these symptoms will go away without treatment, since they indicate diseases in the urinary system. Pain in a man can have different etiologies; it occurs during the ejection of seminal fluid, and after that it becomes aching or very sharp.
The most common clinical picture is the patient interrupting sexual intercourse in order to prevent the woman from becoming fertilized. If used for a long time, then this method of contraception provokes a malfunction of the genitourinary system, and also causes discomfort after intimacy. Usually, after changing the method of ending sexual intercourse, all functions of the organs of the reproductive system return to normal functioning.
The most common reasons for pain after ejaculation are the following:
- diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others;
- inflammation in the genitourinary system - prostatitis, vesiculitis, orchitis;
- inflammation and pathology of the urinary system - urolithiasis, urethritis and cystitis.
It is important to determine the root cause of burning or pain in the urethral canal during urination or ejaculation. Provoking factors can be identified after additional examination and a series of tests in the laboratory of a hospital or clinic. Moreover, each man has concomitant diseases and individual characteristics that need to be considered in more detail.
Painful intercourse syndrome
Unpleasant sensations that arise during intimacy can greatly darken a man’s life. Many representatives of the stronger sex experience the so-called painful sexual intercourse syndrome. It develops after several painful ejaculations.
A man suffering from painful intercourse syndrome tries to convince himself that he will experience unpleasant sensations during ejaculation. As a result, the patient gradually loses interest in intimate life, erection deteriorates, and sexual desire decreases.
Fungal infections
Another common cause of itching and burning in the urethra in women is fungal infections or candidiasis, thrush.
Pathology can be provoked by:
- sweet and flour;
- stress;
- dysbacteriosis;
- decreased immunity, for example, during pregnancy.
In this case, discharge and itching from the urethra in women will accompany you until the fungus is eradicated. Urination becomes more frequent, which becomes painful, and a cheesy discharge with a characteristic sour-milk odor appears.
Burning after ejaculation due to candidiasis
A burning sensation in the urethra after ejaculation also appears with a disease such as candidiasis. Popularly, this disease is usually called thrush. Characteristic symptoms of candidiasis are :
- Pain after ejaculation.
- Itching in the area of the head of the penis.
- Discomfort when urinating.
- The appearance of a white coating on the genitals.
Both partners infected with thrush should visit a doctor. They need to pass the appropriate tests and undergo a medical examination. After completing the treatment course, it is recommended to take the necessary tests again, even if pain after ejaculation no longer bothers the patient.
What tests should I take for pain in the urethra?
It is important to find out the cause of the pain in order to plan the optimal therapeutic strategy.
This requires laboratory and instrumental tests.
The patient is tested for:
- sexually transmitted infections (urethral swab)
- bacteriological culture
- blood for allergies
- general clinical examinations, including general urine analysis
An ultrasound of the kidneys is performed.
During the study, urolithiasis may be detected.
Urethroscopy is performed according to indications.
It is needed primarily for patients with pain of unknown origin, in the absence of signs of inflammation.
If prostate pathology is suspected, a blood test for PSA is performed, a transrectal ultrasound of the prostate is performed, and the secretion is examined.
Treatment for burning in the prostate
Before treating a patient, the doctor must find out why the burning sensation occurs in the prostate.
After a complete examination of the patient, the specialist can prescribe treatment.
If drug therapy does not produce positive results, surgery may be required.
Medication
If the cause of the pathology is infection, then complex therapy is prescribed.
The treatment regimen includes the use of systemic drugs, as well as agents for local use.
The patient is prescribed:
- Antibiotics. If the pathology is provoked by pathogenic bacterial microflora, then macrolides, tetracyclines, and cephalosporins are used. Before a doctor prescribes a drug to a patient, it will be necessary to undergo an antibiotic sensitivity test.
- Antifungal agents. Used if the pathology is caused by fungal microflora.
- Immunomodulators. The action of the drugs is aimed at enhancing immune activity. Thanks to them, the activity of pathogens is reduced and the disease cannot take a chronic course.
- Hepatoprotectors. Prescribed to ensure normal functioning of the liver. Antibiotic therapy often has detrimental effects on the liver.
- Painkillers may be needed if the patient is diagnosed with stones. In this case, analgesics and antispasmodics are used.
- Drugs that break down stones (depending on the type of calcifications), if the cause of pain is urolithiasis.
- Alpha blockers are prescribed for prostatitis and prostate adenoma.
- Vitamin therapy. The administration of vitamins and minerals helps strengthen the body.
- Local anti-inflammatory drugs - rectal suppositories and non-steroidal ointments.
- Microclysters with herbal decoctions. They relieve swelling and reduce inflammation.
If there is congestion in the pelvis, additional physiotherapy is prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic techniques can relieve discomfort and improve blood supply to the prostate gland.
Applicable:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy, phototherapy;
- massage of the gland using a special stimulator.
Kidney diseases
Among them are pyelonephritis and urolithiasis. Their common symptoms:
- frequent urge to urinate and scanty amount of urine;
- itching and burning in the urethra;
- cramps in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lower back and sacrum;
- increased blood pressure - all these symptoms appear gradually and not together.
So, first things first:
- Urolithiasis disease. It can be considered more of a mechanical factor. When stones and sand come out, the walls of the bladder and urethra are damaged. This is what causes pain and burning during urination, itching in the urethra, pain in the lower abdomen, and blood in the urine.
- Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal pelvis. With such inflammation, the composition of urine changes (the appearance of sugar and protein in it), which cannot but be reflected in irritation of the walls of the urethra.
- Cystalgia. It is caused by the high sensitivity of the bladder with normal urine composition, i.e. these disorders are functional. Itching in the urethra in women, burning and pain when urinating, dryness in the perineum occur during menstruation and after intimacy. There are no inflammations or morphological changes in tissues. Cystalgia is typical for young girls. It goes away when menstruation stops or sufficient time has passed since the end of sexual intercourse. If the itching does not stop, you need to look for other causes.
- Foreign bodies - they can get into the urethra through careless removal of a tampon, using various “toys” for sex and masturbation. Suspicions of the presence of a foreign particle arise if, in addition to itching in the urethra, the outflow of urine becomes difficult. The stream becomes thin or does not appear at all. Only a doctor can remove foreign particles.
- Cystitis is the most common cause of itching in the urethra in women with a painful burning sensation. It is then accompanied by frequent imperative urges, scanty urine (false urges), and severe pain in the lower abdomen. When emptying the bladder, the pain intensifies. It is almost constant, it may decrease somewhat, but does not disappear completely. Often cystitis in a woman is a consequence of urethritis. This is the most common cause of itching in women in the urethral area. Pathologies can be provoked by hypothermia, prolonged retention of urination, and ingestion of spicy or spicy foods. Also characteristic of cystitis is a change in the color of urine - white flakes and bloody threads can be seen in it with the naked eye.
Why is there pain in the urethral canal?
What is the cause of pain after sexual intercourse? This syndrome appears during sexual contact due to blood flow to the genital organ, which is directly involved in the process. This all intensifies the symptoms.
More on the topic: Causes of alkaline urine reaction
Inflammation in the male reproductive system is provoked by infections that can be transmitted through sexual intimacy, or by pathogenic bacteria from other organs in the body. Inflammatory processes often cause pain in the groin area after ejaculation. Any diseases of the genitourinary system are fraught with the appearance of pain and burning after any touching of the external genitalia - intimate contact or deurination.
Epididymitis and orchitis
Discomfort after sexual intercourse may occur due to inflammation in the testicles, pain such as orchitis or epididymitis. If the pathology has an acute form, then the man begins to feel severe pain near the sacrum and in the groin. Obvious signs of the disease are swelling in the scrotum or pain in both or one testicle, even with a simple touch. Also, unpleasant symptoms appear when the patient walks or sits for a long time.
Vesiculitis
Painful ejaculation also occurs with vesiculitis, a painful pathology of inflammation in the seminal vesicles. Accompanying symptoms are fever and aching, pulling pain in the groin area. At the same time, there is a decrease in the volume of semen secreted. In order to confirm the diagnosis, you need to conduct a rectal examination, submit secretions from the seminal vesicles for laboratory testing, and do an ultrasound.
Prostate diseases
Most often, pain during ejaculation is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland. The pathology is caused by pathogenic bacteria that penetrate the organ and provoke stagnant processes. Signs of inflammation are an increase in the acidity of the secretion secreted by the prostate, as well as a burning sensation or pain during the eruption of semen.
Prostatitis
If prostatitis takes an acute form, the patient experiences high fever and pain during or after ejaculation. The nature of the pain syndrome itself varies from discomfort to piercing spasms. Spasms are localized in the perineum, lower back or groin, sometimes the pain spreads to the testicles, especially after ejaculation.
Diagnosis of prostatitis should be prescribed by a urologist and include a series of laboratory tests and an ultrasound scan of the prostate gland. The doctor identifies the cause of the disease, assesses the patient’s condition, and prescribes treatment based on it.
More on the topic: In what cases is bladder urography prescribed?
Sexually transmitted diseases
Often discomfort is caused by diseases that are sexually transmitted. The most common is chlamydia. Chlamydia that enters the body may not manifest itself for a long time, but when the infection develops, problems begin with the functioning of the genitourinary system. Usually this phenomenon is accompanied by itching and pain in the urethral canal, discharge, pain in the urinary tract, pain in the scrotum or lower back.
If you start treating the disease in time, improvement will occur within 3 weeks. But self-medication can worsen and complicate the pathology, since chlamydia quickly develops resistance to the active substances in the medicine, after which it is difficult to find an effective medicine.
Equally common is gonorrhea, the bacteria of which multiply in the lower parts of the rectum and in the urinary system. A man first feels pus in the urethral canal after ejaculation or deurination. Further development of the disease causes pain of varying degrees of intensity, which not only intensifies during sexual intercourse and urination, but also causes an involuntary erection. This can be at night and in the morning.
Diseases of the genitourinary system
Pain after ejaculation in a man occurs due to inflammation in the urethral canal and bladder. With urethritis, the patient's frequent companions are discomfort and burning, pain and other unpleasant factors that cause anxiety at the end of sexual intercourse. This is caused by scars on the surface of the urethral canal.
During sexual contact, blood rushes to the genital organ, and the surface of the urethra experiences strong tension, which causes microcracks to appear. Urine during deurination, urine, and during ejaculation, seminal fluid irritate the walls and cause pain and itching. A sign of urethritis is often discharge from the urethra. If they have a greenish tint, an unpleasant odor, and a thickened consistency, this is a sign of a bacterial infection.
If left untreated, the disease can quickly become chronic, with symptoms becoming less severe, which is often mistaken for a symptom of recovery. This feeling is erroneous; in this case, a complex form of the disease in an advanced form becomes especially unpleasant.
More on the topic: What does urine pH mean?
Cystitis
After ejaculation, men often feel a burning sensation or pain due to the development of cystitis. It is very wrong to consider this disease as purely female. Acute forms of the disease are always accompanied by pain syndromes of severe intensity, which occur during the ejection of seminal fluid or during deurination. Pathology can be determined by primary signs, the most striking of which is frequent urges. Between visits to the restroom, a man often feels discomfort in the groin and above the pubis, in the penis.
Factors provoking the occurrence of symptoms
These factors are:
- the need for long-term patience when it is impossible to go to the toilet. As a result, vigorous division of microbes in the bladder occurs, which leads to infection;
- absence of an organ that disinfects the urinary tract (prostate);
- undergoing operations in which a catheter was used;
- diabetes;
- an allergic reaction to medications that the patient is forced to take for a long time;
- openness to bacteria and close proximity to the vagina;
- incontinence in sex.
Symptoms of urethritis in women
In acute urethritis, characteristic symptoms are burning, pain and itching in the urethra in women when urinating. In some cases, there may be purulent discharge from the urethral opening. Subsequently, the pain and swelling decrease, and the discharge stops. Urine is usually clear, sometimes with isolated purulent streaks. In the acute form of urethritis, the urge to urinate is imperative, and pain is more common at the end of urination.
The general condition of urethritis in women is usually not affected. Acute symptoms disappear within 2-2.5 weeks. But this does not mean the cessation of inflammation; you need to be examined by a doctor. With insufficient treatment, acute urethritis becomes chronic. It will become aggravated and will remind itself with hypothermia, sexual arousal and frequent sexual intercourse, and drinking alcohol. Then its symptoms will resemble torpid urethritis.
Symptoms and treatment
This pathology is an inflammatory process in the urethra, which occurs two months after the first symptoms. The most common route of infection is sexual contact with a sick person.
Symptoms of urtritis
During the chronic form, the following symptoms are pronounced:
- burning and unbearable itching in the genital area;
- blue or green discharge accompanied by an unpleasant purulent odor;
- swelling and inflammation of the urethra in men;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- presence of blood in discharge, urine or semen;
- frequent urination;
- adhesion.
If several symptoms appear at once, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. The basis of treatment for this pathology is the use of antibacterial drugs.
Attention! It is important not to delay the course of the disease and begin treatment as early as possible, while keeping in mind that the chronic form lasts from one month to several years and entails serious complications.
Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, but if the form is severe, hospitalization will be required . Here it is important to restore the epithelium and microflora, but do not forget about the immune system, which supports the body and allows it to fight infections.
The presence of a chronic form of the disease is confirmed exclusively by a specialist, as a result of which you cannot self-medicate, even if all the symptoms indicate the presence of this particular pathology.
The most effective medications for topical use are solutions of Garazon and Sofradex , which can reduce the course of treatment by a week.
In addition, they are perfectly absorbed, and the side effects are almost invisible.
But in addition to them, it is important to use antibiotics, combining them with physiotherapy, such as hot baths, ultrasonic frequencies and heating.
As for traditional methods, they are only allowed to be used in conjunction with the main treatment, since otherwise they will not give the desired effect or will worsen the situation.
Surgery
In some cases, doctors may recommend surgery.
There are a number of indications for the operation:
- if drug therapy does not have an effect;
- manifestations of renal failure;
- the presence of constant pain in the gland, if its cause is complications;
- formation of stones in the prostate;
- presence of neoplasms;
- abscess development;
- disturbance of urination (absence or delay);
- presence of blood in the urine;
- the appearance of purulent discharge from the rectum.
When the cause of discomfort in the prostate is an inflammatory process that is difficult to treat, the patient may be offered partial or complete removal of the organ.
For partial removal of prostate adenoma, endoscopy or laser therapy is used.
The use of endoscopic surgery is possible if the size of the adenoma is small.
It is crushed or evaporated.
If a man is diagnosed with prostate cancer, then transurethral resection of the prostate (TUR) is used.
The pathological tissue is removed along with the prostate and lymph nodes that surround the organ.
Before raising the question of surgical intervention, the doctor must take into account the presence of contraindications.
Surgical treatment is contraindicated in the presence of the following conditions:
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- diabetes mellitus;
- age after 70 years;
- acute inflammatory process of the urogenital tract;
- cardiovascular pathology;
- respiratory diseases;
- taking blood thinning medications;
- presence of problems with blood clotting;
- respiratory diseases.
After TUR, catheterization of the bladder is performed.
The catheter is installed for a period of 2-4 to 10 days.
After the patient begins to urinate on his own, a burning sensation may occur.
After some time, the discomfort disappears.
The following complications may develop in the postoperative period:
- heavy bleeding. In this case, a blood transfusion and even repeated surgery may be required;
- there is a high risk of bladder injury. In order to eliminate the complication, an operation is performed;
- exacerbation of the infectious process involving the testicles, prostate, kidneys;
- narrowing of the urethra a couple of months after surgery.
Tumors
Polyps often form in the urethra as tumor precursors. Symptoms at this stage are sparse. The itching increases and becomes burning. Then permanent pain and bloody clots in the urine appear. Without treatment, the general condition worsens. Treatment is only surgical.
Malignant neoplasms are also scanty in manifestations. Over time, the pain increases in the urethra, and blood appears in the urine. In neglected conditions, anemia and general exhaustion develop.
Whatever the cause of burning and itching in the urethra in women, it is imperative to be examined and begin treatment in order to avoid complications and transition to a chronic process, which is much more difficult to treat.
Burning sensation in the prostate with cancer
Pathology most often occurs in men after 50 years of age.
Among the main reasons are heredity and degeneration of a benign tumor.
Symptoms of the pathology boil down to the following complaints:
- urinary disturbance;
- presence of pain syndrome;
- blood in urine (hematuria).
How severe the pain is depends on the stage of the pathology:
- at the beginning of the disease (first stage) - the presence of aching pain in the groin area, which is provoked by compression of the gland and nerve fibers by the growing tumor;
- At the last stage of the cancer process, the pain is very strong and constant. It is associated with the germination of pathological cells into neighboring tissues.
It is possible to reduce the manifestation of pain only with the help of narcotic painkillers.
Gonorrheal urethritis
This pathology is a sexually transmitted disease that is caused by gonococcus, a gram-negative diplococcus of the Neisseriae family.
Based on the severity, gonorrheal urethritis can be of three types:
- Acute, characterized by copious discharge and dysuria.
- Subacute, during which discharge is equally present but there is no dysuria.
- Torpid, in which the discharge may be insignificant and not always detectable.
The first symptoms are discomfort in the urethra with urinary retention and grayish-yellow purulent discharge.
The first portion of urine is cloudy and contains urethral threads that settle at the bottom. When urinating, the patient has pronounced pain and ejaculation.
Drops of blood often appear at the end of urination, and frequent erections also add to the general condition, and there may also be drops of blood in the semen.
Attention! It is very important to start treatment as early as possible, since otherwise the acute form quickly turns into chronic, in which symptoms do not appear, but the inflammatory process remains.
Prostatitis as a possible cause of burning sensation during intimacy
Pain after ejaculation can also be observed with prostatitis. Inflammation of the prostate can be infectious or non-infectious.
Infectious prostatitis is caused by various harmful microorganisms: these include chlamydia and gonococci. First of all, you need to treat the disease that caused prostatitis (for example, gonorrhea). Non-infectious prostatitis occurs due to weakened immunity, hypothermia, an inactive lifestyle, and lack of physical activity.
main symptoms of the disease are distinguished :
- Problems with urination.
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Split stream during urination.
- Pain in the groin area.
- The appearance of discharge from the urethra.
When a man has inflammation of the prostate, his erectile function worsens and the severity of sensations during sexual intercourse decreases. The disease can lead to the development of kidney failure, urolithiasis, and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
With prostatitis, the patient must follow a strict diet. Proper nutrition can reduce pain and normalize the functioning of the male genital organs. Urination usually improves after following a strict diet.
Treatment of urethral itching
During therapy, doctors focus on 3 things:
- normalization of the walls of the urethra;
- normalization of the microflora of the vagina and uterus, by getting rid of pathogens;
- restoration of immunity.
The treatment of itching in women in the urethra should include the following components:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics - cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone), macrolides (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin); fluoroquinolones (“Clinafloxacin”, “Ciprofloxacin”). It is important that for their successful use it is necessary to determine the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to a certain type of antibiotic. Otherwise, the effect may not be seen. For gonorrhea, “Erythromycin”, “Spectinomycin”, “Oletetrin”, “Ceftriaxone”, “Rifampicin”, “Cefacor” are effective. Trichomonas do not like Metronidazole (Trichopol), Imorazole, Ornidazole, Chlorhexidine, or Iodovidone suppositories. For candidiasis - Levorin, Nystatin, Natamycin, Amphoglucamine, Clotrimazole. Chlamydial and mycoplasma urethritis will be well treated with tetracycline antibiotics.
- Local therapy - various sitz baths (a weak mixture of potassium permanganate, furatsilin, herbal decoctions of chamomile and sage, etc.).
- Insertion of special tampons with medicinal ointments into the vagina.
- The use of immunostimulating and immunomodulating drugs. When treating urethritis, the water regime must be strictly observed. It is also important to pay attention to your diet. It is better to exclude provoking foods. For viral urethritis, antiviral drugs are used: Ganciclovir, Acyclovir, Ribavirin, Famciclovir, Penciclovir, etc.
- Physiotherapy in the form of electrophoresis on the pubis and vaginally, diadynamic therapy of the lumbosacral zone, heating applications.
Diagnostic methods
A comprehensive examination when a burning sensation occurs in the urethra and head is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. Research will help determine the degree of development of diseases; the results obtained are also necessary to draw up an effective treatment regimen.
A burning sensation in the urethra and in the head requires the following diagnostic tests:
| Name | Description |
| General urine analysis | The results show the level of red blood cells, white blood cells and protein. |
| General and biochemical blood test | Research allows us to identify the inflammatory process in the patient’s body. |
| Bacterial culture | A diagnostic method by which a specialist determines the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The examination method is used to assess the functioning of the kidneys, bladder, pelvic organs and prostate gland. |
| Cystoscopy | Diagnosis involves examining the mucous membrane in the urinary tract area. The results help identify a tumor, foreign body or stones. During the procedure, the doctor may take materials for laboratory tests (biopsy). |
| Uroflowmetry | A specific examination method during which the doctor examines the upper and lower urinary tract. The purpose of the diagnosis is to evaluate the functioning of the bladder and urinary tract. |
It is important to differentiate the disease, since many pathological processes are accompanied by similar clinical symptoms. It is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis, on which the treatment method depends.
Prevention
Prevention in women:
- hormone replacement therapy for menopause;
- eliminating stress;
- medical examinations with a gynecologist every six months;
- compliance and correct intimate hygiene;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- exclusion of abortion;
Regular sex is also important, but with one partner - the culture of sexual relations. This is not the case when the number of partners turns into quality.
Itching during urination in pregnant women
The fetus puts pressure on the ureter and bladder, so the pregnant woman feels a frequent urge to urinate. Sometimes discomfort appears after an examination by a gynecologist and goes away in one day. This should not cause concern if there are no other symptoms. But if a woman experiences itching and burning after urinating, she must undergo additional examination. This is how infectious and non-infectious diseases and allergies can manifest themselves.
The doctor should choose the course, determining exactly why the genitals and urethra itch.
You cannot take medications or perform procedures at home on your own. They can cause pregnancy pathologies.
How to avoid pain?
The burning sensation after intimacy does not only cause physical discomfort. Lack of treatment can lead to psychological problems, decreased potency and erectile dysfunction. This is due to the fact that a man will try to avoid sex so as not to experience pain.
The following is recommended as a preventive measure:
- Avoid promiscuity;
- Always use a condom during sex;
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations with a urologist;
- Treat any chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- Support immunity with vitamins and a balanced diet.
You should not put off going to a medical specialist if you experience a burning sensation after sexual intercourse. Ignoring a symptom leads to the disease becoming chronic, which is much more difficult to treat and significantly worsens the patient’s quality of life.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of developing diseases that are accompanied by a burning sensation in the penis. But compliance with preventive measures allows you to minimize this likelihood and maintain health.
Diagnostic measures
If a person feels discomfort after intimacy, he is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, and the patient also needs to undergo appropriate tests. In some cases, the secretion of the prostate gland is examined using a microscope.
To identify infections transmitted during sexual intercourse, a smear is taken from the walls of the urethra. After receiving the results of this study, the specialist selects effective medications to eliminate the burning sensation during ejaculation in men.